Alleviating the Effects of Electrolyzed Alkaline Water on Hyperuricemia in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Establishment and Grouping of Hyperuricemia Models
2.4. Measurement of Serum Levels of Uric Acid (UA), Creatinine (CRE), Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Albumin
2.5. Liver and Serum Xanthine Oxidase (XOD) Activity Measurements
2.6. Metabolic Cage Experiments
2.7. Pathological Examination
2.8. mRNA Expression of Genes Related to Uric Acid Metabolism
2.9. Uric Acid Metabolism-Related Protein Expression
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weight Changes
3.2. Urine and Water Intake
3.3. Analysis of Physiological Indexes Related to UA Metabolism in Mice of Each Group
3.4. Histopathologic Findings in the Kidneys
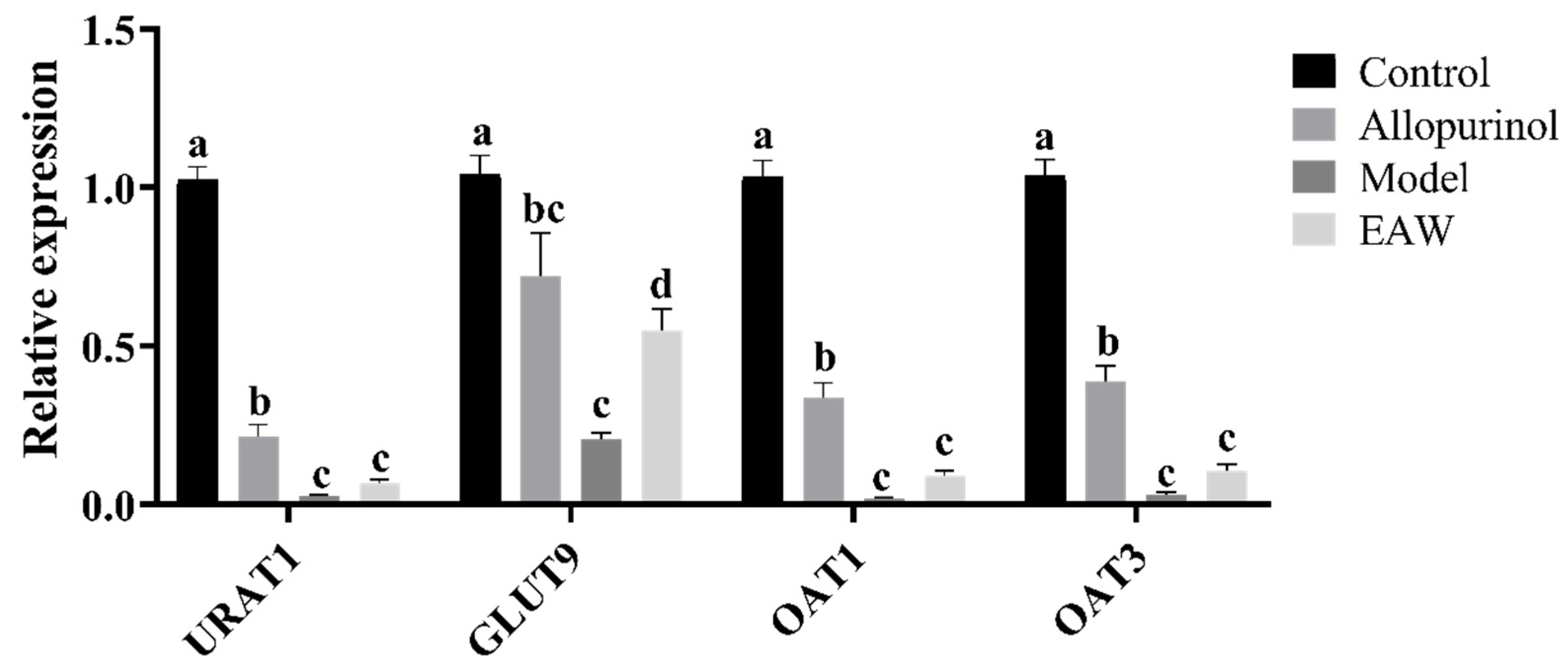
3.5. Renal mRNA Expression of UA Transporter Genes
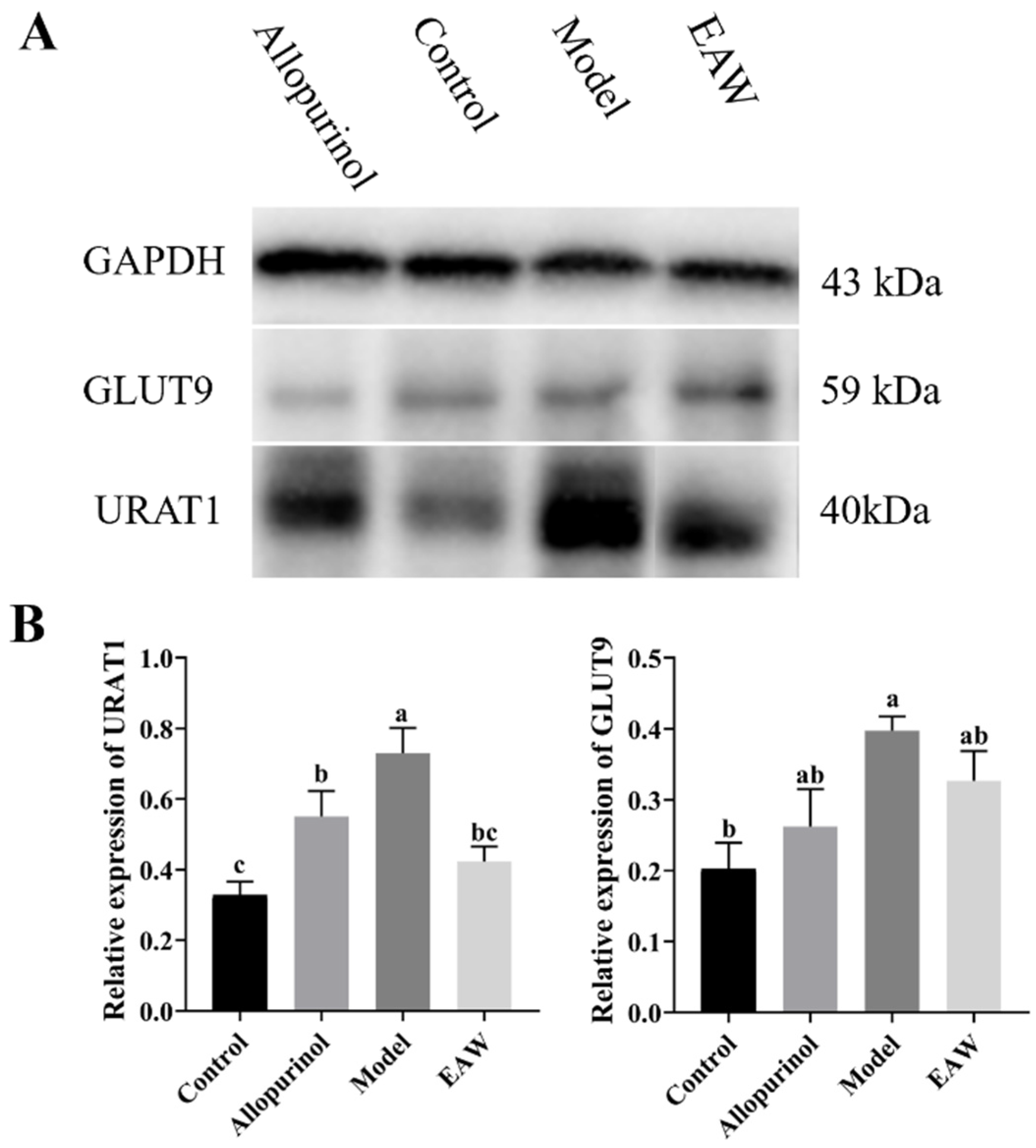
3.6. Renal Uric Acid Transporter Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen-Xu, M.; Yokose, C.; Rai, S.K.; Pillinger, M.H.; Choi, H.K. Contemporary prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the united states and decadal trends: The national health and nutrition examination survey, 2007–2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wei, L.; Wu, X.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Cai, J.; et al. Sonneratia apetala seed oil attenuates potassium oxonate/hypoxanthine-induced hyperuricemia and renal injury in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9416–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Lingala, B.; Mithal, A. Gout and hyperuricaemia in the USA: Prevalence and trends. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2177–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Son, C.N.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, G.H.; Jun, J.B. Distribution of serum uric acid levels and prevalence of hyper-and hypouricemia in a Korean general population of 172,970. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, S264–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Werlinger, P.; Suh, J.W.; Cheng, J. Potential probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MJM60396 prevents hyperuricemia in a multiple way by absorbing purine, suppressing xanthine oxidase and regulating urate excretion in mice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokose, C.; McCormick, N.; Choi, H.K. Dietary and lifestyle-centered approach in gout care and prevention. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Gong, X.; Ji, M.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, J.H.; Li, M.H. Bioactive compounds from plant-based functional foods: A promising choice for the prevention and management of hyperuricemia. Foods 2020, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahata, S.; Kabayama, S.; Nakano, M.; Miura, T.; Kusumoto, K.; Gotoh, M.; Hayashi, H.; Otsubo, K.; Morisawa, S.; Katakura, Y. Electrolyzed–reduced water scavenges active oxygen species and protects DNA from oxidative damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Chambron, J. Physico-chemical, biological and therapeutic characteristics of electrolyzed reduced alkaline water (ERAW). Water 2013, 5, 2094–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufman, A.J.; Johnston, N. Potential benefits of pH 8.8 alkaline drinking water as an adjunct in the treatment of reflux disease. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abol-Enein, H.; Gheith, O.A.; Barakat, N.; Nour, E.; Sharaf, A.E. Ionized alkaline water: New strategy for management of metabolic acidosis in experimental animals. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2009, 13, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.S.; Eltahlawi, R.A.; Jan, A.A.; Alhadramy, O.; Soliman, T.M.; El Sayed, S.M.; Abdallah, H.I.; El-Shazley, M.; Shafik, N.M.; Mariah, R.A.; et al. Zamzam water is pathogen-free, uricosuric, hypolipidemic and exerts tissue-protective effects: Relieving BBC concerns. Am. J. Blood Res. 2020, 10, 386–396. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, A.L. Effect of mineral water containing calcium and magnesium on calcium oxalate urolithiasis risk factors. Urol. Int. 1997, 58, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenov, L.T.; Vasil’ev, M.I. Rehabilitation therapy of convalescents after hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in outpatient clinic. Ter. Arkh. 2004, 76, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Bian, H.G.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.M.; Jin, J. Function of uric acid transporters and their inhibitors in hyperuricaemia. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 667753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yufang, W.; Mingfang, L.; Nan, H.; Tingting, W. Quercetin-targeted AKT1 regulates the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway to protect against doxorubicin-induced nephropathy in mice. Tissue Cell 2023, 85, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chiaramonte, R. In creatinine kinetics, the glomerular filtration rate always moves the serum creatinine in the opposite direction. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Tao, X.; Liang, S.; Pan, Y.; He, L.; Sun, J.; Wenbo, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Protective effect of acidic polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis on acute ethanol-induced liver injury through reducing CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pei, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, K.; Deng, S.; Liang, R.; Xie, Z.; Li, P.; et al. Kidney tea ameliorates hyperuricemia in mice via altering gut microbiota and restoring metabolic profile. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 376, 110449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, S.M.; Song, Y.J.; Islam, M.A.; Rao, P.L.; Zhu, M.J.; Gu, W.Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.X. Red ginseng ameliorates lipotoxicity-induced renal fibrosis in hyperuricemia mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 327, 118014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wen, S.; Shao, Y.; Yao, Z.; He, Y. Huaju xiaoji formula regulates ERS-lncMGC/miRNA to enhance the renal hunction of hypertensive diabetic mice with nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 2024, 6942156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multidisciplinary expert task force on hyperuricemia and related diseases. Chinese multidisciplinary expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of hyperuricemia and related diseases. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.F.; Grainge, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Doherty, M. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Duan, S.; Yuan, X.; Liang, J.; Hou, S. Curcumin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.; Fuchs, T.C.; Henzler, T.; Matheis, K.A.; Herget, T.; Dekant, W.; Hewitt, P.; Mally, A. Evaluation of a urinary kidney biomarker panel in rat models of acute and subchronic nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2010, 277, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.L.; Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhu, Q.F.; Guan, H.Y.; He, X.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.B.; Zou, S.H.; et al. Amelioration effects of α-viniferin on hyperuricemia and hyperuricemia-induced kidney injury in mice. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuqrin, A.; Alshuweishi, Y.A.; Alfaifi, M.; Daghistani, H.; Al-Sheikh, Y.A.; Alfhili, M.A. Prevalence and association of hyperuricemia with liver function in Saudi Arabia: A large cross-sectional study. Ann. Saudi Med. 2024, 44, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Huang, L.; Xu, H.; He, X.; He, X.; Cao, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase downregulation in uric acid-induced hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. MedComm 2023, 4, e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.W.; Yang, G.B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.; Duan, L.X.; Yuan, J.H.; Liao, L.; Zhang, C.F.; Lu, J.R.; Hu, J.; et al. Factors influencing the occurrence of hyperuricemia and poor cardiac and renal outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 342–349. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, T.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D.; Shuai, O.; Chen, S.; Su, J.; Jiao, C.; Feng, D.; Xie, Y. Actions of water extract from Cordyceps militaris in hyperuricemic mice induced by potassium oxonate combined with hypoxanthine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Ro, K.S.; Jiang, C.; Yin, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, D.; Du, L.; Xie, J. The anti-hyperuricemic and gut microbiota regulatory effects of a novel purine assimilatory strain, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum X7022. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 697–711. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Ji, H.; Song, W.; Zhang, D.; Su, W.; Liu, S. Anserine beneficial effects in hyperuricemic rats by inhibiting XOD, regulating uric acid transporter and repairing hepatorenal injury. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9434–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Gong, X.; Gu, H.; Nuermaimaiti, N.; Meng, X.; Liu, D.; Guan, Y. Staufen1 unwinds the secondary structure and facilitates the translation of fatty acid binding protein 4 mRNA during adipogenesis. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Yi, B.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Q. Mettl3/Ythdf2 regulate macrophage inflammation and ROS generation by controlling Pyk2 mRNA stability. Immunol. Lett. 2023, 264, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.P.; Mar, P.K.; McDonald, F.F.; Ramsay, R.L. Involvement of protein kinase C in the regulation of ornithine decarboxylase mRNA by phorbol esters in rat hepatoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1991, 194, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, T.; Ci, X.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, W.; Yi, X.; Liu, C. The effect of polymorphism of uric acid transporters on uric acid transport. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Groups | n | Starting Weight (g) | Terminal Weight (g) | Weight Gain (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 8 | 25.09 ± 0.80 | 26.7 ± 0.72 Δ | 1.8 ± 1.02 Δ |
| Allopurinol group | 8 | 25.40 ± 0.74 | 22.9 ± 0.88 *,Δ | −2.5 ± 1.23 *,Δ |
| Model group | 8 | 25.14 ± 0.43 | 19.14 ± 1.06 * | −6.2 ± 1.31 * |
| EAW group | 8 | 25.61 ± 0.59 | 19.98 ± 0.46 *,Δ | −5.1 ± 0.39 *,Δ |
| Groups | n | The First Week (g) | The Second Week (g) | The Third Week (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 8 | 15.94 ± 2.74 Δ | 17.46 ± 2.95 Δ | 16.58 ± 3.35 Δ |
| Allopurinol group | 8 | 19.45 ± 3.44 * | 23.47 ± 1.48 *,Δ | 21.93 ± 0.66 *,Δ |
| Model group | 8 | 20.15 ± 1.50 * | 29.61 ± 0.15 * | 30.18 ± 2.99 * |
| EAW group | 8 | 20.21 ± 1.54 * | 25.85 ± 1.45 *,Δ | 24.87 ± 0.92 *,Δ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, L.; Zhao, H.; Tian, X.; Qin, Y.; Li, G.; Qin, Z.; Mao, Y.; Ye, X.; Cao, Y.; Tian, S. Alleviating the Effects of Electrolyzed Alkaline Water on Hyperuricemia in Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101673
Mao L, Zhao H, Tian X, Qin Y, Li G, Qin Z, Mao Y, Ye X, Cao Y, Tian S. Alleviating the Effects of Electrolyzed Alkaline Water on Hyperuricemia in Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101673
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Leihong, Haiqin Zhao, Xiaoyan Tian, Yumei Qin, Guohua Li, Zihan Qin, Yuezhong Mao, Xiao Ye, Yanyun Cao, and Shiyi Tian. 2025. "Alleviating the Effects of Electrolyzed Alkaline Water on Hyperuricemia in Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101673
APA StyleMao, L., Zhao, H., Tian, X., Qin, Y., Li, G., Qin, Z., Mao, Y., Ye, X., Cao, Y., & Tian, S. (2025). Alleviating the Effects of Electrolyzed Alkaline Water on Hyperuricemia in Mice. Nutrients, 17(10), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101673




