Urolithin A Modulates PER2 Degradation via SIRT1 and Enhances the Amplitude of Circadian Clocks in Human Senescent Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Lentivirus Production, Infection to TIG-3 Cells, and Real-Time Luciferase Monitoring Assay
2.4. Analyses of the Circadian Period and Amplitude
2.5. RNA Extraction and qPCR
2.6. Quantification of Intracellular NAD+
2.7. Protein Half-Life Assay
2.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
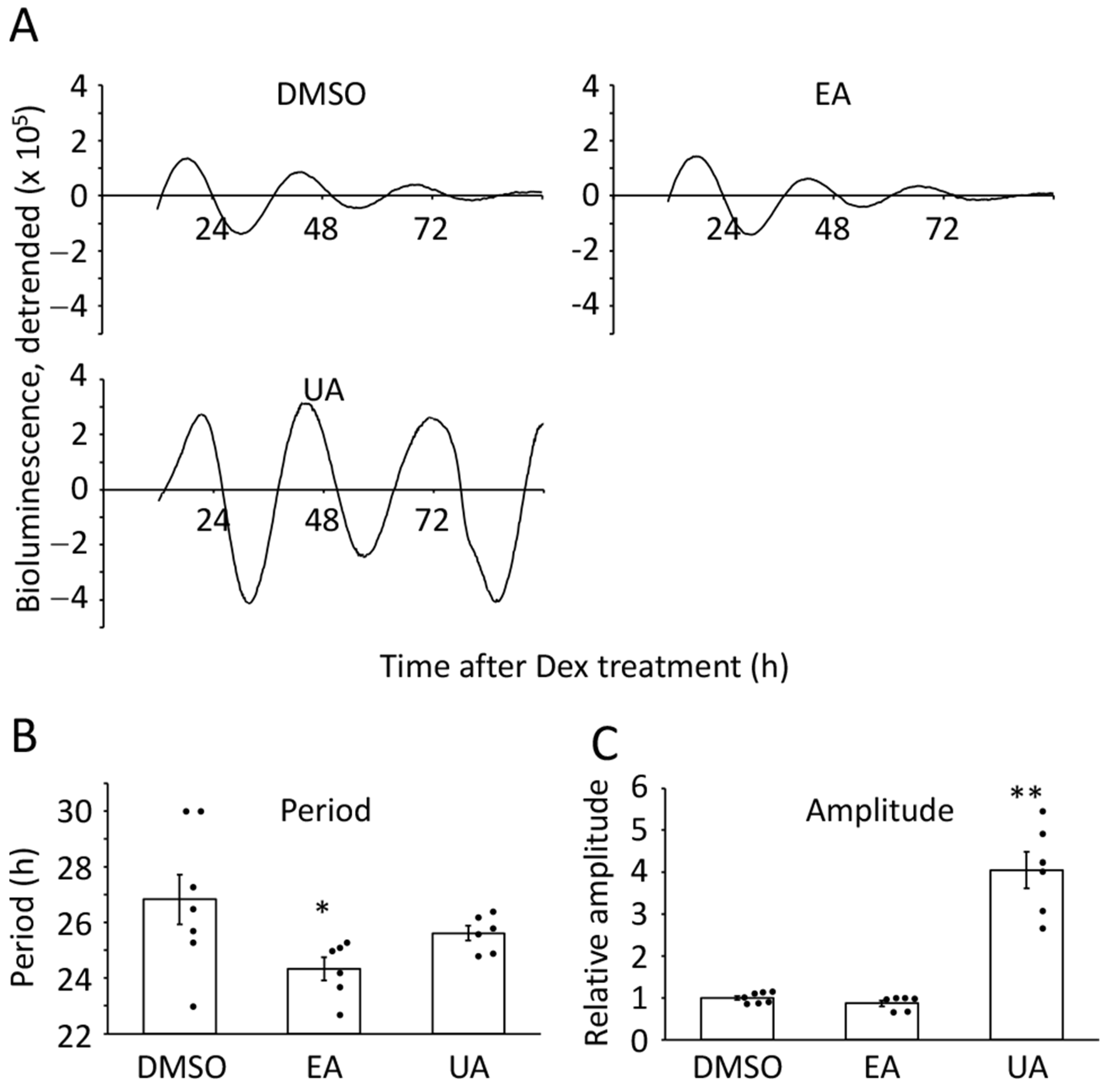
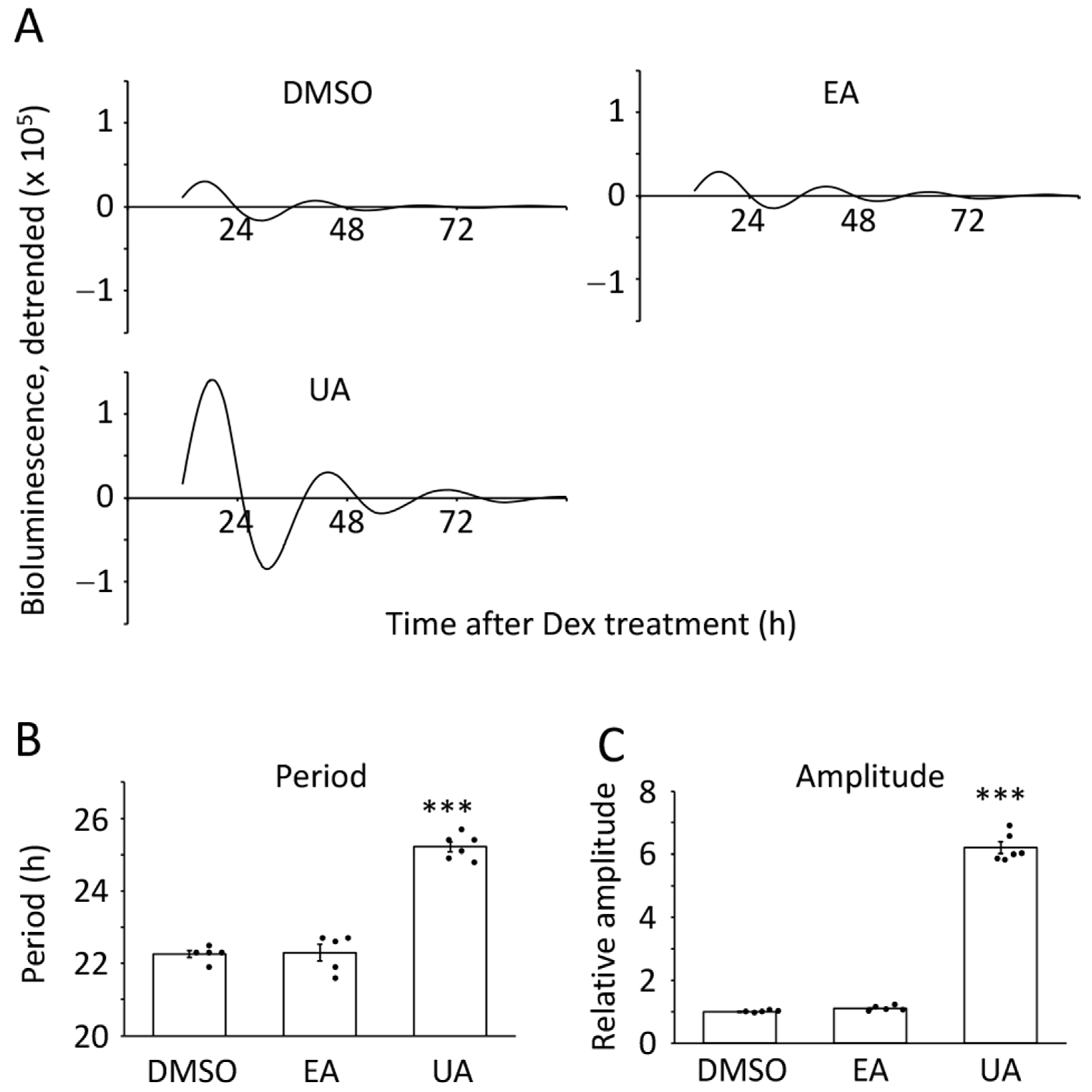
3.1. Urolithin A Boosted the Amplitude of Bmal1 Promoter-Driven Luciferase Oscillation
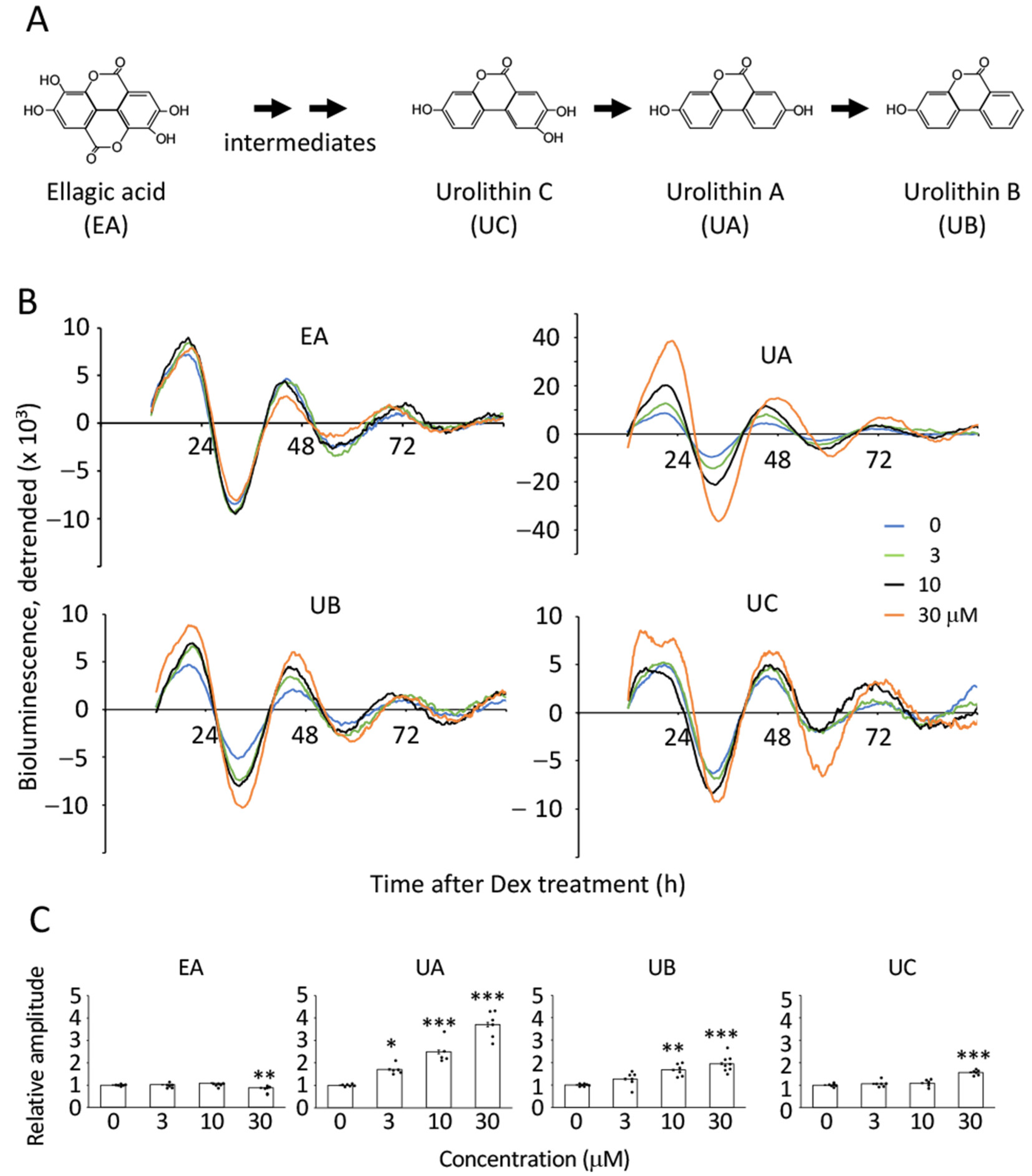
3.2. Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites Boosted the Amplitude of Bmal1 Promoter-Driven Luciferase Oscillation in Senescent Cells
3.3. UA Treatment Unstabilized Per2-luc Fusion Protein
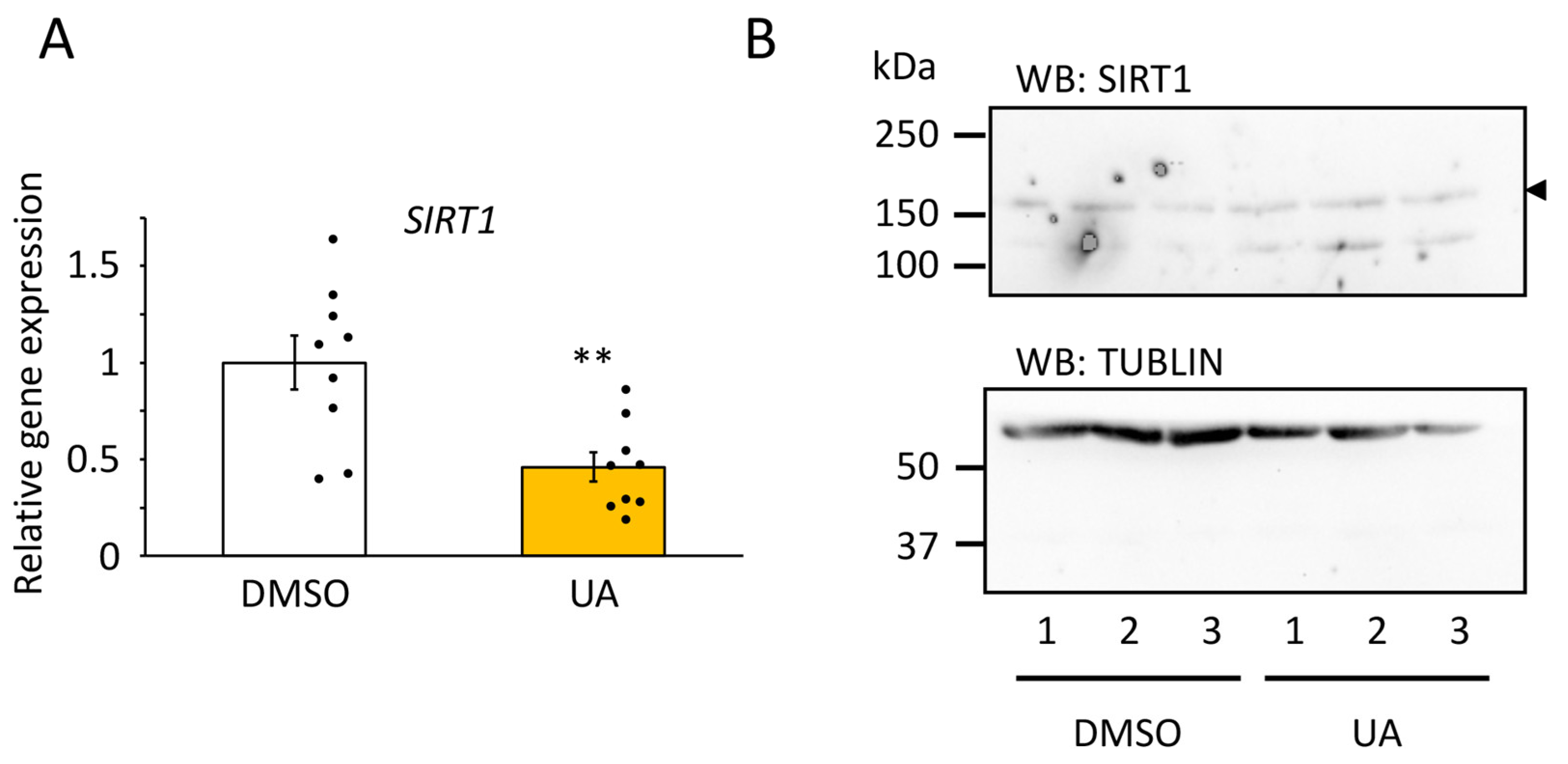
3.4. SIRT1 Was Upregulated in UA-Treated Senescent Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asher, G.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Time for food: The intimate interplay between nutrition, metabolism, and the circadian clock. Cell 2015, 161, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Personalized medicine and circadian rhythms: Opportunities for modern society. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, S. The mammalian circadian system: A hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J. Physiol. Sci. JPS 2018, 68, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L. Circadian Control of Global Transcription. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 187809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Becquet, D.; Franc, J.L.; Francois-Bellan, A.M. Circadian processes in the RNA life cycle. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M. Rheumatoid arthritis: Circadian and circannual rhythms in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, M.; Villaggio, B.; Otsa, K.; Aakre, O.; Sulli, A.; Seriolo, B. Altered circadian rhythms in rheumatoid arthritis patients play a role in the disease’s symptoms. Autoimmun. Rev. 2005, 4, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattis, J.; Sehgal, A. Circadian Rhythms, Sleep, and Disorders of Aging. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.J.; Nakamura, W.; Tokuda, I.T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kudo, T.; Colwell, C.S.; Block, G.D. Age-Related Changes in the Circadian System Unmasked by Constant Conditions. eNeuro 2015, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittendrigh, C.S.; Daan, S. Circadian oscillations in rodents: A systematic increase of their frequency with age. Science 1974, 186, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellix, M.T.; Evans, J.A.; Leise, T.L.; Castanon-Cervantes, O.; Hill, D.D.; DeLisser, P.; Block, G.D.; Menaker, M.; Davidson, A.J. Aging differentially affects the re-entrainment response of central and peripheral circadian oscillators. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16193–16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentinuzzi, V.S.; Scarbrough, K.; Takahashi, J.S.; Turek, F.W. Effects of aging on the circadian rhythm of wheel-running activity in C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, R1957–R1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.J.; Takasu, N.N.; Nakamura, W. The suprachiasmatic nucleus: Age-related decline in biological rhythms. J. Physiol. Sci. JPS 2016, 66, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, S.; Amir, S. The aging clock: Circadian rhythms and later life. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Ashimori, A.; Iwamoto, S.; Matsui, T.; Nakahata, Y.; Bessho, Y. Replicative senescent human cells possess altered circadian clocks with a prolonged period and delayed peak-time. Aging 2019, 11, 950–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Nakahata, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Bessho, Y. Cellular Senescence Triggers Altered Circadian Clocks With a Prolonged Period and Delayed Phases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 638122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahata, Y. Impact of Cellular Senescence on Cellular Clocks. In Sleep and Clocks in Aging and Longevity, Jagota, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakura, Y.; Okada, M.; Tsuji, S.; Tonogai, Y. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination with photodiode array detection of ellagic acid in fresh and processed fruits. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 896, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracassetti, D.; Costa, C.; Moulay, L.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Ellagic acid derivatives, ellagitannins, proanthocyanidins and other phenolics, vitamin C and antioxidant capacity of two powder products from camu-camu fruit (Myrciaria dubia). Food Chem. 2013, 139, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Lozoya, J.E.; Lombardini, L.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L. Electron-beam irradiation effects on phytochemical constituents and antioxidant capacity of pecan kernels [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch] during storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10732–10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kumar, M.N. Analytical methods for assay of ellagic acid and its solubility studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loren, D.J.; Seeram, N.P.; Schulman, R.N.; Holtzman, D.M. Maternal dietary supplementation with pomegranate juice is neuroprotective in an animal model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Stoner, G.D. Inhibition of N-nitrosobenzylmethylamine-induced esophageal tumorigenesis in rats by ellagic acid. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Khopde, S.M.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohan, H. Free radical studies of ellagic acid, a natural phenolic antioxidant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo, M.A.; Sanchez-Hidalgo, M.; Cardeno, A.; de la Lastra, C.A. Protective effect of ellagic acid, a natural polyphenolic compound, in a murine model of Crohn’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Nunez-Sanchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Espin, J.C. Urolithins, the rescue of “old” metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Liang, M.; Qin, R.; Qin, F.; Wang, X. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates Renal Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury Through NOX4/JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2020, 43, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosillo, M.A.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Cárdeno, A.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Villegas, I.; de la Lastra, C.A. Dietary supplementation of an ellagic acid-enriched pomegranate extract attenuates chronic colonic inflammation in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Kajiwara, S.; Orihara, K. Effect of Urolithin A on the Improvement of Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation in Intestinal Barrier Induced by Inflammation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, A.; Du, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Nakamura, T.J.; Shibata, S. Oak extracts modulate circadian rhythms of clock gene expression in vitro and wheel-running activity in mice. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2022, 20, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refinetti, R. Cosinor Software version 3.1. Available online: https://www.circadian.org/softwar.html (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Khaidizar, F.D.; Nakahata, Y.; Kume, A.; Sumizawa, K.; Kohno, K.; Matsui, T.; Bessho, Y. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase delays cellular senescence by upregulating SIRT1 activity and antioxidant gene expression in mouse cells. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell Mech. 2017, 22, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Zuccari, G. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Capabilities, and Bioavailability: Ellagic Acid or Urolithins? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Martin, A.; Selma, M.V.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Espin, J.C. Where to Look into the Puzzle of Polyphenols and Health? The Postbiotics and Gut Microbiota Associated with Human Metabotypes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, G.; Gatfield, D.; Stratmann, M.; Reinke, H.; Dibner, C.; Kreppel, F.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Alt, F.W.; Schibler, U. SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2 deacetylation. Cell 2008, 134, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Armstrong, C.M.; Kaeberlein, M.; Guarente, L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 2000, 403, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashimori, A.; Nakahata, Y.; Sato, T.; Fukamizu, Y.; Matsui, T.; Yoshitane, H.; Fukada, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Bessho, Y. Attenuated SIRT1 Activity Leads to PER2 Cytoplasmic Localization and Dampens the Amplitude of Bmal1 Promoter-Driven Circadian Oscillation. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 647589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Fouassier, A.M.; Blanco-Bose, W.; Evans, M.; Aebischer, P.; Auwerx, J.; Rinsch, C. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; D’Amico, D.; Shankland, E.; Bhayana, S.; Garcia, J.M.; Aebischer, P.; Rinsch, C.; Singh, A.; Marcinek, D.J. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2144279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Valdes, P.; Singh, A.; Rinsch, C.; Auwerx, J. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Baby, B.V.; Hegde, B.; Kotla, N.G.; Hiwale, A.A.; Saiyed, T.; Patel, P.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; et al. Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Martín, A.; García-Villalba, R.; González-Sarrías, A.; Romo-Vaquero, M.; Loria-Kohen, V.; Ramírez-de-Molina, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C. The gut microbiota urolithin metabotypes revisited: The human metabolism of ellagic acid is mainly determined by aging. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4100–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialonska, D.; Kasimsetty, S.G.; Khan, S.I.; Ferreira, D. Urolithins, intestinal microbial metabolites of Pomegranate ellagitannins, exhibit potent antioxidant activity in a cell-based assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10181–10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasher, G.; Alkahtani, S.; Al-Harbi, L.N. Urolithin A prevents streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by activating SIRT1. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B. Activation of the miR-34a-Mediated SIRT1/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Urolithin A Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging in Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Das, A.; Biswas, N.; Gnyawali, S.; Singh, K.; Gorain, M.; Polcyn, C.; Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Urolithin A augments angiogenic pathways in skeletal muscle by bolstering NAD(+) and SIRT1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Yang, R.; Zhong, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tu, N.; Zhou, H.; et al. Urolithin A attenuates hexavalent chromium-induced small intestinal injury by modulating PP2A/Hippo/YAP1 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A.; Tao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Erb, H.; Guarino, C.; Wu, X. The circadian clock protein Cryptochrome 1 is a direct target and feedback regulator of the Hippo pathway. iScience 2023, 26, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuatov, R.; Takano, J.; Arie, H.; Kominami, M.; Tateishi, N.; Wakabayashi, K.-i.; Takemoto, D.; Izumo, T.; Nakao, Y.; Nakamura, W.; et al. Urolithin A Modulates PER2 Degradation via SIRT1 and Enhances the Amplitude of Circadian Clocks in Human Senescent Cells. Nutrients 2025, 17, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010020
Kuatov R, Takano J, Arie H, Kominami M, Tateishi N, Wakabayashi K-i, Takemoto D, Izumo T, Nakao Y, Nakamura W, et al. Urolithin A Modulates PER2 Degradation via SIRT1 and Enhances the Amplitude of Circadian Clocks in Human Senescent Cells. Nutrients. 2025; 17(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuatov, Rassul, Jiro Takano, Hideyuki Arie, Masaru Kominami, Norifumi Tateishi, Ken-ichi Wakabayashi, Daisuke Takemoto, Takayuki Izumo, Yoshihiro Nakao, Wataru Nakamura, and et al. 2025. "Urolithin A Modulates PER2 Degradation via SIRT1 and Enhances the Amplitude of Circadian Clocks in Human Senescent Cells" Nutrients 17, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010020
APA StyleKuatov, R., Takano, J., Arie, H., Kominami, M., Tateishi, N., Wakabayashi, K.-i., Takemoto, D., Izumo, T., Nakao, Y., Nakamura, W., Shinohara, K., & Nakahata, Y. (2025). Urolithin A Modulates PER2 Degradation via SIRT1 and Enhances the Amplitude of Circadian Clocks in Human Senescent Cells. Nutrients, 17(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010020




