Association between Diet Quality and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: Findings from the CORDIOPREV Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Dietary Intake Assessment
2.3. Nutrient-Rich Food Index 9.3 Calculation
2.4. Alternative Healthy Eating Index-2010 Calculation
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements and Laboratory Tests
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
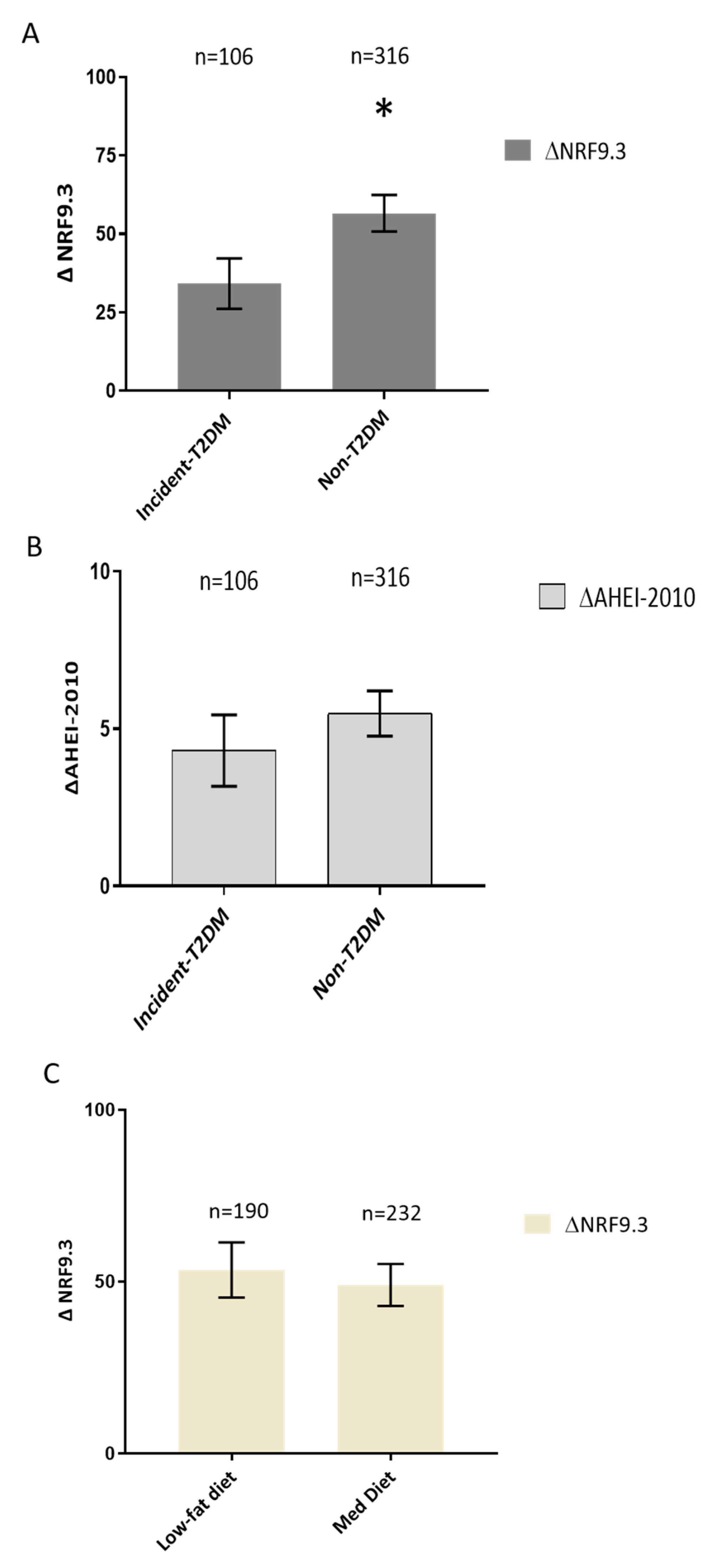
3.2. Effect of the Dietary Intervention on NRF9.3 Scores
3.3. Effect of the Dietary Intervention on AHEI-2010 Scores
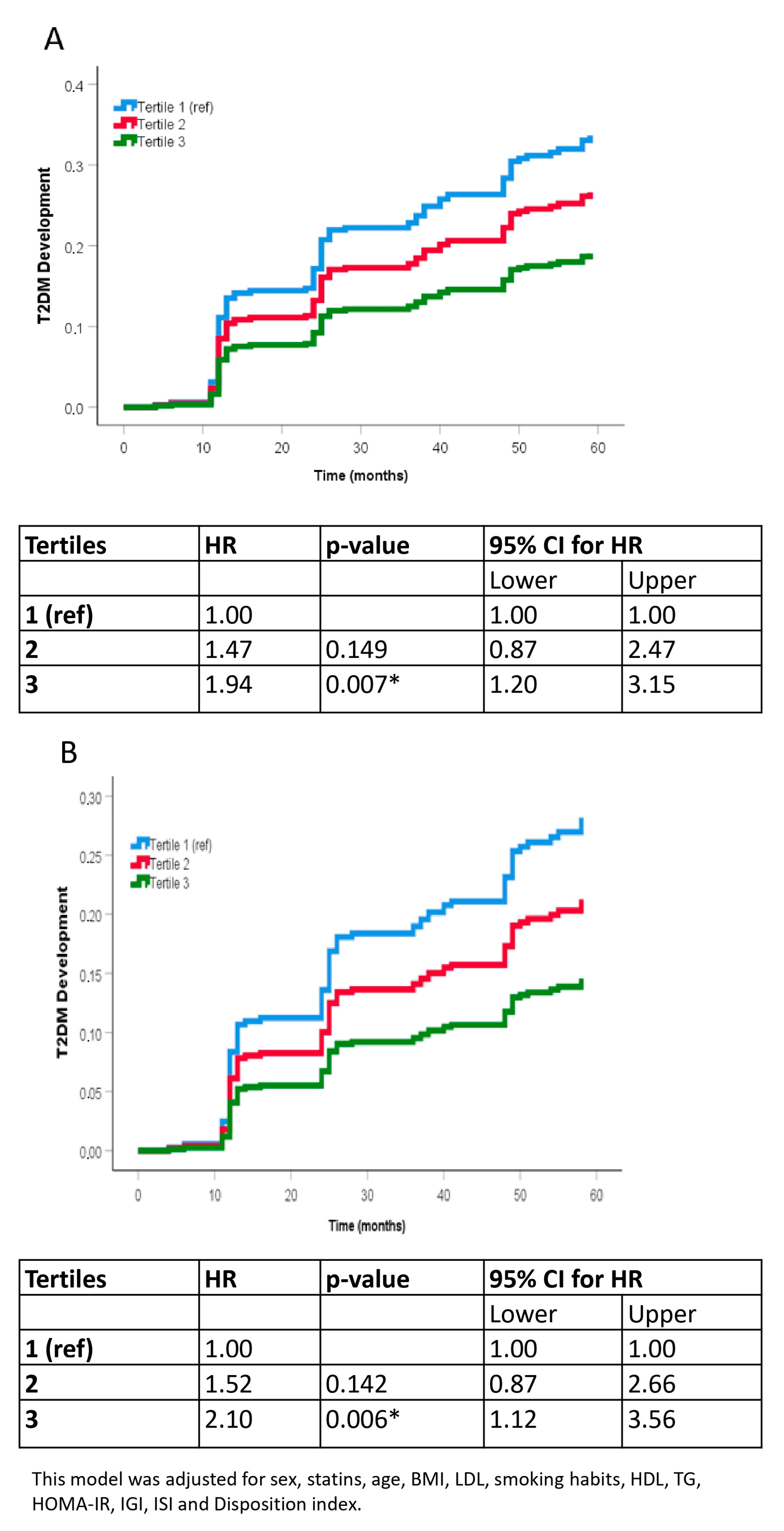
3.4. Analysis of the Probability of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Incidence
3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Willigendael, E.M.; Singhal, R.; Kooreman, Z.E.; Ramnarain, D.; Mahawar, K.; et al. The Many Faces of Diabetes. Is There a Need for Re-Classification? A Narrative Review. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigrezaei, S.; Ghiasvand, R.; Feizi, A.; Iraj, B. Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, B.T.; Tjaden, A.H.; Venditti, E.M.; Apolzan, J.W.; Dabelea, D.; Delahanty, L.M.; Edelstein, S.L.; Hoskin, M.A.; Temple, K.A.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; et al. Diet Quality, Weight Loss, and Diabetes Incidence in the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). BMC Nutr. 2020, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraattalab-Motlagh, S.; Jayedi, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Sulu, C.; Katsiki, N.; Hassapidou, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cucalón, G.; Pazderska, A.; Yumuk, V.D.; Colao, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-Related Disorders: What Is the Evidence? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cabrera, J.L.; García-Ríos, A.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.F.; Martín-Piedra, L.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Luque, R.M.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean Lifestyle Improves Metabolic Status in Coronary Heart Disease Patients: A Prospective Analysis from the CORDIOPREV Study. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Martínez, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Athyros, V.G.; Bullo, M.; Couture, P.; Covas, M.I.; de Koning, L.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Lifestyle Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Syndrome: An International Panel Recommendation. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiki, N.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M. Dietary Patterns in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Stay on the Straight and Narrow Path! Clin. Investig. Arterioscler. 2022, 34 (Suppl. S1), S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morze, J.; Danielewicz, A.; Hoffmann, G.; Schwingshackl, L. Diet Quality as Assessed by the Healthy Eating Index, Alternate Healthy Eating Index, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Score, and Health Outcomes: A Second Update of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 1998–2031.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Liu, G.; Hu, F.B.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Sun, Q. Association Between Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Ros, E. Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Insights From the PREDIMED Study. Progress. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, T.A.; Drewnowski, A.; O’Neil, C.E. The Nutrient Density Approach to Healthy Eating: Challenges and Opportunities. Public. Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Ibáñez, N.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Camargo, A.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Perez-Corral, I.; Arenas-de Larriva, A.P.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Perez-Martinez, P.; et al. Long-Term Effect of a Dietary Intervention with Two-Healthy Dietary Approaches on Food Intake and Nutrient Density in Coronary Patients: Results from the CORDIOPREV Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3019–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; de Victoria, E.M.; Olza, J. Indicadores de evaluación de la calidad de la dieta. Rev. Española Nutr. Comunitaria 2015, 21 (Suppl. S1), 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Haines, P.S.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Popkin, B.M. The Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I) Provides an Effective Tool for Cross-National Comparison of Diet Quality as Illustrated by China and the United States. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiuve, S.E.; Fung, T.T.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; McCullough, M.L.; Wang, M.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Alternative Dietary Indices Both Strongly Predict Risk of Chronic Disease. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannasch, F.; Kröger, J.; Schulze, M.B. Dietary Patterns and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onvani, S.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Surkan, P.J.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. Adherence to the Healthy Eating Index and Alternative Healthy Eating Index Dietary Patterns and Mortality from All Causes, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 30, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Van Zyl, T.; Hanekom, S.M.; Baumgartner, J.; Van der Hoeven, M.; Taljaard-Krugell, C.; Smuts, C.M.; Faber, M. Nutrient Density, but Not Cost of Diet, Is Associated with Anemia and Iron Deficiency in School-Age Children in South Africa. Nutrition 2021, 84, 111096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streppel, M.T.; Sluik, D.; van Yperen, J.F.; Geelen, A.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Feskens, E.J.M. Nutrient-Rich Foods, Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: The Rotterdam Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgoni, V.L.; Keast, D.R.; Drewnowski, A. Development and Validation of the Nutrient-Rich Foods Index: A Tool to Measure Nutritional Quality of Foods. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, C.; Moreno, L.; Lopez-Chaves, C.; Nebot, E.; Pietschmann, P.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Galvez, J.; Montes-Bayon, M.; Sanz-Medel, A.; Llopis, J. Effect of Vanadium on Calcium Homeostasis, Osteopontin mRNA Expression, and Bone Microarchitecture in Diabetic Rats. Metallomics 2017, 9, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán, R.; Llopis, J.; Portolés, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Coltell, O.; Rivas-García, L.; Asensio, E.M.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Corella, D.; Sánchez-González, C. Influence of Demographic and Lifestyle Variables on Plasma Magnesium Concentrations and Their Associations with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Mediterranean Population. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Stevens, J.F. Vitamins C and E: Beneficial Effects from a Mechanistic Perspective. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khillan, J. Vitamin A/Retinol and Maintenance of Pluripotency of Stem Cells. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Entezari, M.H.; Mohammadi, H.; Jayedi, A.; Lazaridi, A.-V.; ali Kermani, M.H.; Miraghajani, M. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Adult Obesity Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Perez-Caballero, A.I.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Fuentes, F.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; Lopez-Segura, F.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; et al. CORonary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil and Cardiovascular PREVention Study (the CORDIOPREV Study): Rationale, Methods, and Baseline Characteristics. Am. Heart J. 2016, 177, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Fuentes, F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; Gonzalez-Requero, A.I.; Perez-Caballero, A.I.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; et al. Long-Term Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet and a Low-Fat Diet (CORDIOPREV): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-975403-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Moreno, J.M.; Boyle, P.; Gorgojo, L.; Maisonneuve, P.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, J.C.; Salvini, S.; Willett, W.C. Development and Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire in Spain. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1993, 22, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreiras, O.; Carvajal, A.; Cabrera, L.; Cuadrado, C. Tablas de Composición de Alimentos y Guía de Prácticas, 16th ed.; Pirámide (ANAYA Group): Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mataix Verdú, J.; García Diz, L.; Mañas Almendros, M.; Martínez de Victoria, E.; Llopis González, J. Tabla de Composición de Alimentos Españoles. (Spanish Food Composition Tables); Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 2009; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Louie, J.C.Y.; Moshtaghian, H.; Boylan, S.; Flood, V.M.; Rangan, A.M.; Barclay, A.W.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Gill, T.P. A Systematic Methodology to Estimate Added Sugar Content of Foods. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Ávila, J.; Valero, T.; Rodriguez, P.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Breakfast Consumption in Spain: Patterns, Nutrient Intake and Quality. Findings from the ANIBES Study, a Study from the International Breakfast Research Initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and of the Council. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:304:0018:0063:en:PDF (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Dietary Reference Values for Nutrients Summary Report. EFS3 2017, 14, e15121E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guideline: Sugars Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Lucena, R.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.F.; López-Moreno, J.; Roncero-Ramos, I.; Molina-Abril, H.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Caballero-Villarraso, J.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Castaño, J.P.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Development in Coronary Heart Disease Patients from the CORDIOPREV Study. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rojo, R.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Wopereis, S.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Marin, C.; Ordovas, J.M.; van Ommen, B.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Delgado-Lista, J.; et al. The Insulin Resistance Phenotype (Muscle or Liver) Interacts with the Type of Diet to Determine Changes in Disposition Index after 2 Years of Intervention: The CORDIOPREV-DIAB Randomised Clinical Trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; et al. Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Changes in Lifestyle among Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumen, C.; Corpeleijn, E.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Mensink, M.; Saris, W.H.M.; Blaak, E.E. Impact of 3-Year Lifestyle Intervention on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism: The SLIM Study. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncero-Ramos, I.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Jimenez-Lucena, R.; García-Rios, A.; Vals-Delgado, C.; Romero-Baldonado, C.; Luque, R.M.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Prediabetes Diagnosis Criteria, Type 2 Diabetes Risk and Dietary Modulation: The CORDIOPREV Study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-Q.; Ma, Q.-P.; Wei, Y.-F.; Zheng, G.; Zou, B.-J.; Du, Z.-D.; Gao, S.; Yan, S.; Qin, X.; Gong, T.-T.; et al. Nutrients-Rich Food Index Scores and the Overall Survival of Ovarian Cancer Patients: Results from the Ovarian Cancer Follow-Up Study, a Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A.; Fulgoni, V.L. Nutrient Density: Principles and Evaluation Tools. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1223S–1228S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Eguchi, M.; Nanri, A.; Kochi, T.; Kashino, I.; Kuwahara, K.; Hu, H.; Miki, T.; Kabe, I.; Mizoue, T. Association of Dietary and Serum Magnesium with Glucose Metabolism Markers: The Furukawa Nutrition and Health Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 24, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, N.; Jin, M.; Miao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, W. Magnesium Supplementation Enhances Insulin Sensitivity and Decreases Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Rats. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, U.; Abad, K.; Ismail, K. Diabetes Mellitus and Oxidative Stress—A Concise Review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.B. Vitamin E, Its Beneficial Role in Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and Its Complications. JCDR 2012, 6, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbi, M.E.; Tonin, F.S.; Mendes, A.M.; Borba, H.H.; Wiens, A.; Fernandez-Llimos, F.; Pontarolo, R. Antioxidant Effects of Vitamins in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Barquero, S.; Estruch, R. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Disease: The Jury Is Still Out. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Steffen, L.M.; Selvin, E.; Rebholz, C.M. Diet Quality, Change in Diet Quality and Risk of Incident CVD and Diabetes. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.H.; Pan, A.; Li, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B. Changes in Overall Diet Quality and Subsequent Type 2 Diabetes Risk: Three U.S. Prospective Cohorts. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-Ares, S.; Gutiérrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.F.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Podadera-Herreros, A.; Cardelo, M.P.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Arenas-de Larriva, A.P.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; et al. Quality and Quantity of Protein Intake Influence Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Coronary Heart Disease Patients: From the CORDIOPREV Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, M.; Ballon, A.; Weber, K.S.; Norat, T.; Aune, D.; Schwingshackl, L.; Schlesinger, S. Role of Diet in Type 2 Diabetes Incidence: Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Prospective Observational Studies. BMJ 2019, 3, l2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cohrs, C.M.; Stertmann, J.; Bozsak, R.; Speier, S. Human Beta Cell Mass and Function in Diabetes: Recent Advances in Knowledge and Technologies to Understand Disease Pathogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Perez-Corral, I.; Leon-Acuña, A.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Arenas de Larriva, A.P.; Corina, A.; Camargo, A.; et al. Long-Term Dietary Adherence and Changes in Dietary Intake in Coronary Patients after Intervention with a Mediterranean Diet or a Low-Fat Diet: The CORDIOPREV Randomized Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Incident-T2DM | Non-T2DM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 106 | 316 | |
| Men/Women (n) | 86/20 | 266/50 | 0.466 |
| Age (years) | 58.8 ± 0.9 | 57.2 ± 0.5 | 0.127 |
| Med diet/low-fat diet (n) | 65/41 | 167/149 | 0.892 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.4 ± 0.5 | 29.9 ± 0.2 | 0.001 * |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 105.1 ± 1.1 | 101.4 ± 0.6 | 0.003 * |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 133.1 ± 6.7 | 117.9 ± 3.3 | 0.027 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 165.3 ± 3.4 | 159.3 ± 1.6 | 0.090 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 43.6 ± 1.1 | 44.3 ± 0.6 | 0.560 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 93.5 ± 2.7 | 90.6 ± 1.4 | 0.313 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.0 ± 0.03 | 5.8 ± 0.02 | <0.001 * |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.2 ± 1.1 | 92.3 ± 0.6 | 0.001 * |
| Fasting insulin (mU/L) | 10.4 ± 0.6 | 8.4 ± 0.3 | 0.005 * |
| ISI | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 0.001 * |
| IGI | 0.66 ± 0.30 | 1.15 ± 0.08 | 0.023 * |
| HOMA-IR | 3.36 ± 0.30 | 2.55 ± 0.09 | 0.001 * |
| Disposition index | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | <0.001 * |
| NRF9.3 | 724.6 ± 8.0 | 724.1 ± 5.4 | 0.964 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas-Garcia, L.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Alcala-Díaz, J.F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Arenas-de Larriva, A.P.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; López-Moreno, A.; Malagon, M.M.; Katsiki, N.; Perez-Martinez, P.; et al. Association between Diet Quality and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: Findings from the CORDIOPREV Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081249
Rivas-Garcia L, Quintana-Navarro GM, Alcala-Díaz JF, Torres-Peña JD, Arenas-de Larriva AP, Rangel-Zuñiga OA, López-Moreno A, Malagon MM, Katsiki N, Perez-Martinez P, et al. Association between Diet Quality and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: Findings from the CORDIOPREV Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081249
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas-Garcia, Lorenzo, Gracia M. Quintana-Navarro, Juan F. Alcala-Díaz, Jose D. Torres-Peña, Antonio P. Arenas-de Larriva, Oriol Alberto Rangel-Zuñiga, Alejandro López-Moreno, Maria M. Malagon, Niki Katsiki, Pablo Perez-Martinez, and et al. 2024. "Association between Diet Quality and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: Findings from the CORDIOPREV Study" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081249
APA StyleRivas-Garcia, L., Quintana-Navarro, G. M., Alcala-Díaz, J. F., Torres-Peña, J. D., Arenas-de Larriva, A. P., Rangel-Zuñiga, O. A., López-Moreno, A., Malagon, M. M., Katsiki, N., Perez-Martinez, P., Lopez-Miranda, J., & Delgado-Lista, J. (2024). Association between Diet Quality and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: Findings from the CORDIOPREV Study. Nutrients, 16(8), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081249






