Aerobic Exercise Prevents High-Fat-Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Male Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Exercise Protocol
2.3. Glucose Tolerance Test
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Histomorphology Staining
2.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analyses
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorated HFD-Induced Adiposity
3.2. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorates HFD-Induced IR
3.3. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Vascular Density and VSMC Phenotype Switching of Adipose
3.4. Correlation between IR and VSMC Phenotype Switching
3.5. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorated VAT Inflammation in HFD Mice
3.6. Correlation between Inflammation and VSMC Phenotype in HFD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a Link between Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Kong, W. Cross Talk between Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 9821506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Olefsky, J.M. The Origins and Drivers of Insulin Resistance. Cell 2013, 152, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orliaguet, L.; Ejlalmanesh, T.; Alzaid, F. Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigny, P.; Boucher, J.; Arner, P.; Langin, D. Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in White Adipocytes: Pathways, Dysfunction and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Fujisaka, S.; Cai, W.; Winnay, J.N.; Konishi, M.; O’Neill, B.T.; Li, M.; García-Martín, R.; Takahashi, H.; Hu, J.; et al. Adipocyte Dynamics and Reversible Metabolic Syndrome in Mice with an Inducible Adipocyte-Specific Deletion of the Insulin Receptor. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, L.; Gu, S.; Qin, L.; Pang, B.; Yan, F.; Yang, W. Contribution of Epicardial and Abdominopelvic Visceral Adipose Tissues in Chinese Adults with Impaired Glucose Regulation and Diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummen, M.; Dorenbos, E.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E.; Raben, A.; Fogelholm, M.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Adam, T.C. Long-Term Effects of Increased Protein Intake after Weight Loss on Intrahepatic Lipid Content and Implications for Insulin Sensitivity: A PREVIEW Study. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E885–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.; Lamendola, C.; Liu, A.; Abbasi, F. Preferential Fat Deposition in Subcutaneous versus Visceral Depots Is Associated with Insulin Sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1756–E1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte Dysfunctions Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Delp, J.M.; Hotta, K.; Chen, B.; Behnke, B.J.; Maraj, J.J.; Delp, M.D.; Lucero, T.R.; Bramy, J.A.; Alarcon, D.B.; Morgan, H.E.; et al. Effects of Age and Exercise Training on Coronary Microvascular Smooth Muscle Phenotype and Function. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Shi, L. Role of the Balance of Akt and MAPK Pathways in the Exercise-Regulated Phenotype Switching in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Li, D.; Tang, B.; Yang, Y. Oleic Acid Induces Smooth Muscle Foam Cell Formation and Enhances Atherosclerotic Lesion Development via CD36. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xie, Y.; Salvador, A.M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, G.; Xiao, J. Exosomes: Multifaceted Messengers in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Ma, Y.; Christophi, C.A.; Florez, H.; Golden, S.H.; Hazuda, H.; Crandall, J.; Venditti, E.; Watson, K.; Jeffries, S.; et al. Metformin, Lifestyle Intervention, and Cognition in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztalryd, C.; Brasaemle, D.L. The Perilipin Family of Lipid Droplet Proteins: Gatekeepers of Intracellular Lipolysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.Y.; Siu, K.L.; Lob, H.E.; Itani, H.; Harrison, D.G.; Cai, H. Role of Vascular Oxidative Stress in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.Y.; Learnard, H.; Kant, S.; Gealikman, O.; Rojas-Rodriguez, R.; DeSouza, T.; Desai, A.; Keaney, J.F.; Corvera, S.; Craige, S.M. Exercise Rescues Gene Pathways Involved in Vascular Expansion and Promotes Functional Angiogenesis in Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawans, P.; Behl, T.; Bhardwaj, S. Angiogenesis in Obesity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, I.; Franckhauser, S.; Ferré, T.; Vilà, L.; Tafuro, S.; Muñoz, S.; Roca, C.; Ramos, D.; Pujol, A.; Riu, E.; et al. Adipose Tissue Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects Against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolterman, O.G.; Gray, R.S.; Griffin, J.; Burstein, P.; Insel, J.; Scarlett, J.A.; Olefsky, J.M. Receptor and Postreceptor Defects Contribute to the Insulin Resistance in Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, C.C.; Scott, C.L.; Uronen-Hansson, H.; Gudjonsson, S.; Jansson, O.; Grip, O.; Guilliams, M.; Malissen, B.; Agace, W.W.; Mowat, A.M. Resident and Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages in the Colon Represent Alternative Context-Dependent Fates of the Same Ly6Chi Monocyte Precursors. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høydal, M.A.; Wisløff, U.; Kemi, O.J.; Ellingsen, O. Running Speed and Maximal Oxygen Uptake in Rats and Mice: Practical Implications for Exercise Training. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Cardiol. Work. Groups Epidemiol. Prev. Card. Rehabil. Exerc. Physiol. 2007, 14, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, M.; Unal, R.; Zhu, B.; Rasouli, N.; McGehee, R.E.; Peterson, C.A.; Kern, P.A. Adipose Tissue Extracellular Matrix and Vascular Abnormalities in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1990–E1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvera, S.; Gealekman, O. Adipose Tissue Angiogenesis: Impact on Obesity and Type-2 Diabetes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gealekman, O.; Guseva, N.; Hartigan, C.; Apotheker, S.; Gorgoglione, M.; Gurav, K.; Tran, K.V.; Straubhaar, J.; Nicoloro, S.; Czech, M.P.; et al. Depot-Specific Differences and Insufficient Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Angiogenesis in Human Obesity. Circulation 2011, 123, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieß, A.M.; Thiel, A. Physical Activity and Sports in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetol. Stoffwechs. 2017, 12, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, D.W.; Guth, L.M.; Horowitz, J.F. Aerobic Exercise Elevates Markers of Angiogenesis and Macrophage IL-6 Gene Expression in the Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue of Overweight-to-Obese Adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985 2017, 123, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ai, L.; Zhang, Y. Modulation of TRIB3 and Macrophage Phenotype to Attenuate Insulin Resistance After Downhill Running in Mice. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 637432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolahdouzi, S.; Talebi-Garakani, E.; Hamidian, G.; Safarzade, A. Exercise Training Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Remodeling by Promoting Capillary Density and Macrophage Polarization. Life Sci. 2019, 220, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onogi, Y.; Wada, T.; Kamiya, C.; Inata, K.; Matsuzawa, T.; Inaba, Y.; Kimura, K.; Inoue, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishii, Y.; et al. PDGFRβ Regulates Adipose Tissue Expansion and Glucose Metabolism via Vascular Remodeling in Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, J.A.; Jiang, B.H.; Iyer, N.V.; Agani, F.; Leung, S.W.; Koos, R.D.; Semenza, G.L. Activation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Transcription by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, N.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L. Exercise Intensity-Dependent Reverse and Adverse Remodeling of Voltage-Gated Ca(2+) Channels in Mesenteric Arteries from Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkaily, G.; Abdallah, N.A.; Simon, Y.; Jazzar, A.; Jacques, D. Vascular Smooth Muscle Remodeling in Health and Disease. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.-S.; Lee, M.-G. Rescue Effect of Exercise on Impaired Arteriolar Myogenic Response with Advancing Age. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 26, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, P.L. Hot-Tub Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Ping, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Zhao, W.; Guo, M.; Shen, F.; et al. Local Hyperthermia Therapy Induces Browning of White Fat and Treats Obesity. Cell 2022, 185, 949–966.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for Insulin Resistance: Common Threads and Missing Links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benador, I.Y.; Veliova, M.; Mahdaviani, K.; Petcherski, A.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Assali, E.A.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Shum, M.; Oliveira, M.F.; Cinti, S.; et al. Mitochondria Bound to Lipid Droplets Have Unique Bioenergetics, Composition, and Dynamics That Support Lipid Droplet Expansion. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 869–885.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, N.; Crozet, L.; Holtman, I.R.; Loyher, P.L.; Lazarov, T.; White, J.B.; Mass, E.; Stanley, E.R.; Elemento, O.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Diet-Regulated Production of PDGFcc by Macrophages Controls Energy Storage. Science 2021, 373, eabe9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Liu, Z.X.; Wang, A.; Beddow, S.A.; Geisler, J.G.; Kahn, M.; Zhang, X.M.; Monia, B.P.; Bhanot, S.; Shulman, G.I. Inhibition of Protein Kinase Cepsilon Prevents Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herpen, N.A.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; Schaart, G.; Mensink, R.P.; Schrauwen, P. Three Weeks on a High-Fat Diet Increases Intrahepatic Lipid Accumulation and Decreases Metabolic Flexibility in Healthy Overweight Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E691–E695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundsgaard, A.-M.; Holm, J.B.; Sjøberg, K.A.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Myrmel, L.S.; Fjære, E.; Jensen, B.A.H.; Nicolaisen, T.S.; Hingst, J.R.; Hansen, S.L.; et al. Mechanisms Preserving Insulin Action during High Dietary Fat Intake. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 50–63.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
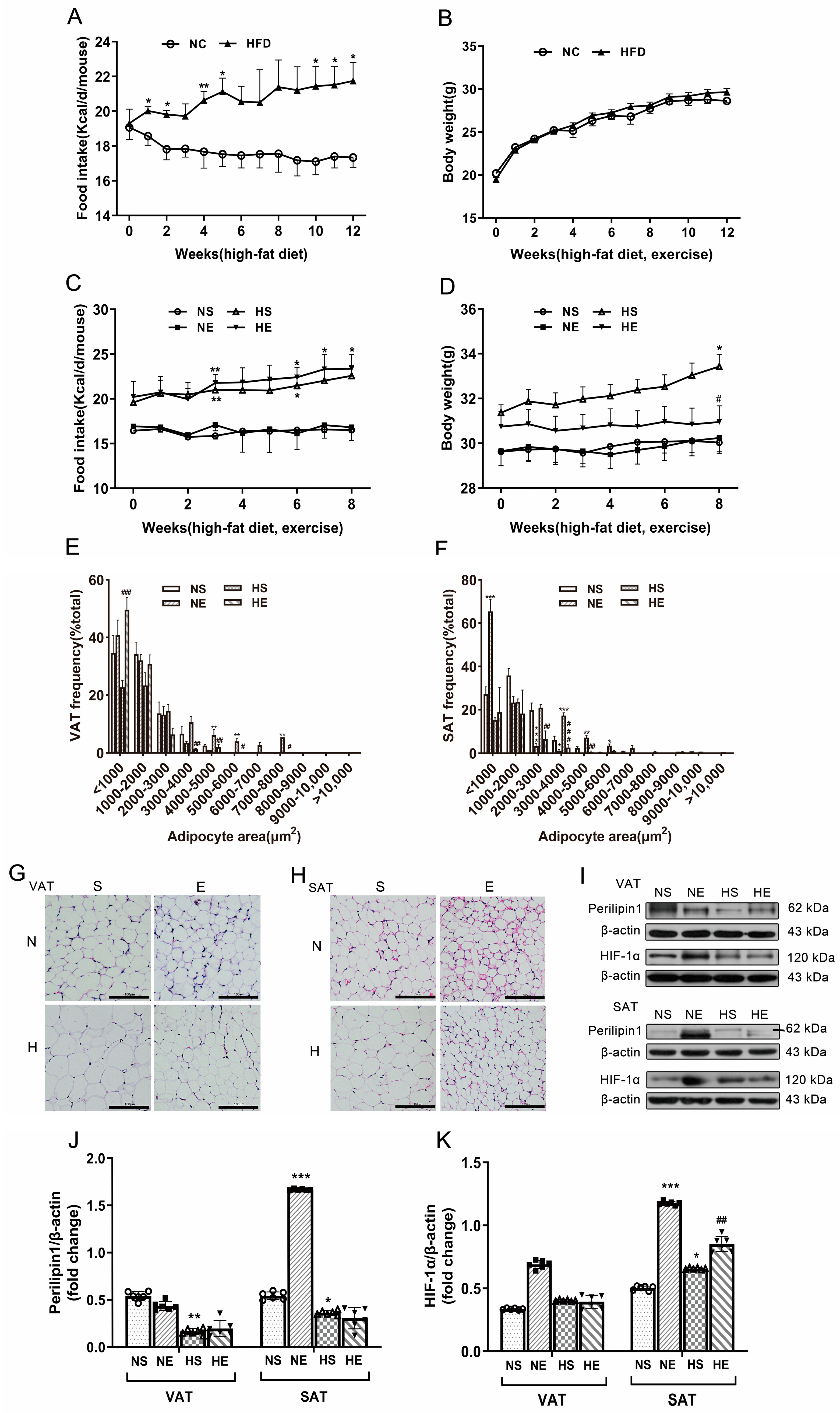
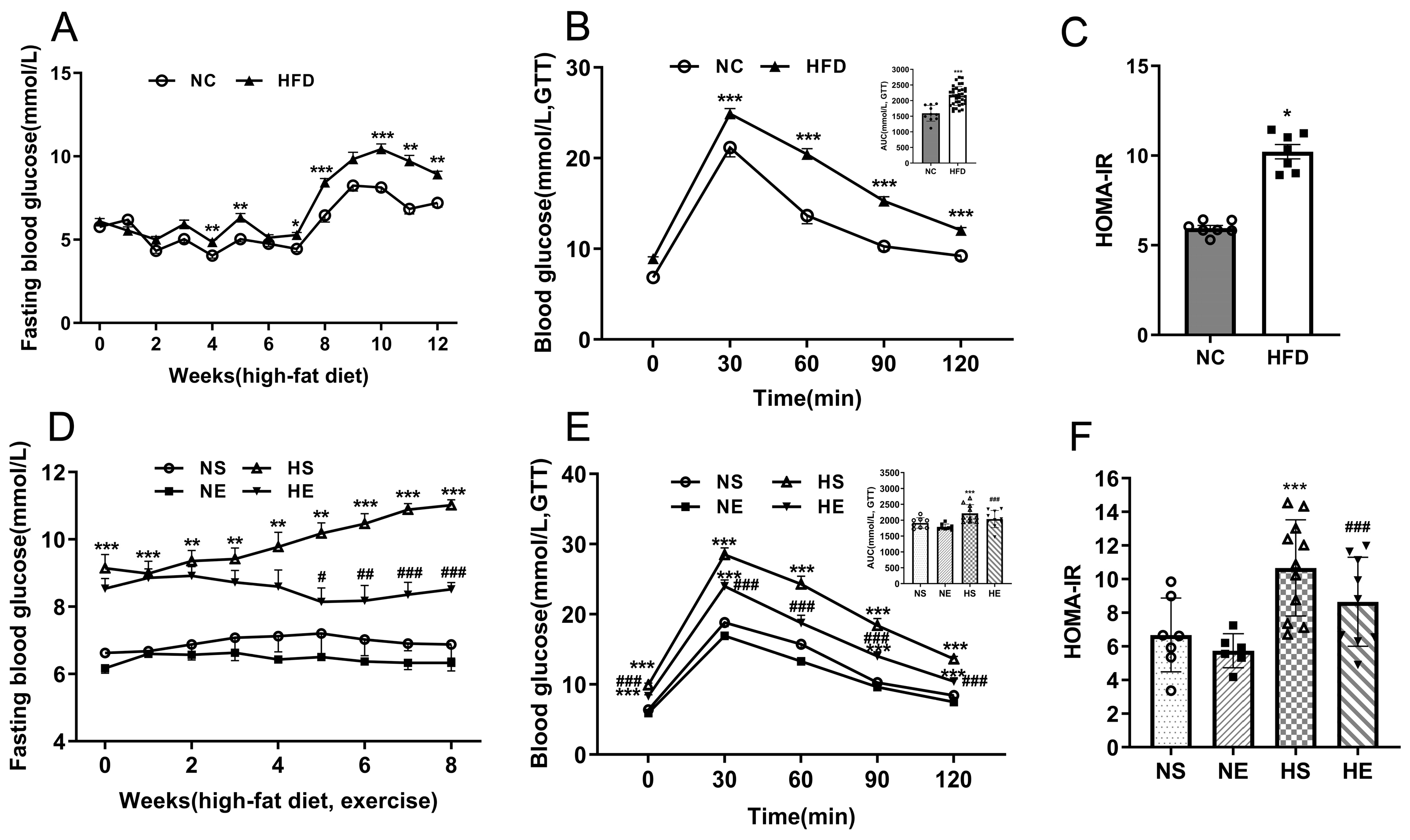
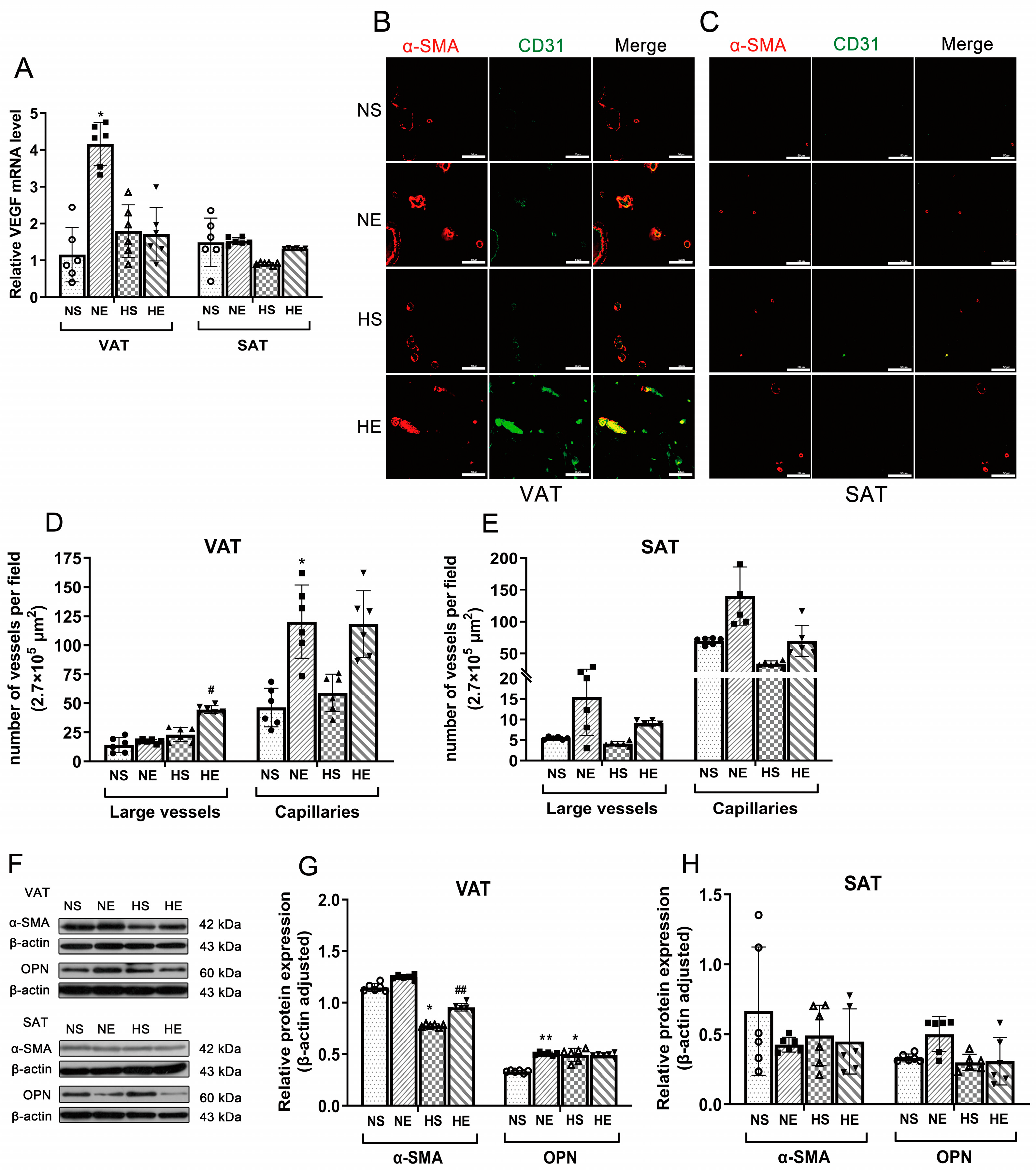
| Fat Weight (g) | NS | NE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAT Mass | 0.277 ± 0.078 | 0.203 ± 0.086 | 0.538 ± 0.138 *** | 0.395 ± 0.175 # |
| SAT Mass | 0.187 ± 0.051 | 0.166 ± 0.179 | 0.356 ± 0.077 *** | 0.236 ± 0.103 ## |
| Serum Lipid Profile (mmol/L) | NS | NE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 2.735 ± 0.445 | 3.152 ± 0.558 | 4.157 ± 1.100 ** | 4.920 ± 0.216 # |
| TG | 0.681 ± 0.135 | 0.601 ± 0.089 | 0.652 ± 0.213 | 0.599 ± 0.066 |
| LDL/HDL | 0.044 ± 0.018 | 0.034 ± 0.018 | 0.099 ± 0.037 *** | 0.622 ± 0.034 ## |
| FBG | AUCGTT | HOMA-IR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAT | Large vessel density | 0.223 | 0.657 * | 0.346 |
| Capillary density | −0.382 | −0.125 | −0.368 | |
| α−SMA | −0.967 ** | −0.830 *** | −0.916 *** | |
| OPN | 0.276 | 0.324 | 0.330 | |
| SAT | Large vessel density | −0.452 | −0.125 | −0.413 |
| Capillary density | −0.677 * | −0.697 * | −0.663 * | |
| α−SMA | −0.848 ** | −0.729 ** | −0.896 *** | |
| OPN | −0.195 | 0.259 | −0.023 |
| Inflammatory Cytokines (pg/mL) | NC | HFD |
|---|---|---|
| Serum TNF-α | 80.125 ± 4.115 | 84.288 ± 8.309 |
| Serum IL-1β | 28.913 ± 0.072 | 29.029 ± 0.184 |
| Inflammatory Cytokines (pg/mL) | NS | NE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum TNF-α | 73.886 ± 5.232 | 72.758 ± 3.514 | 74.606 ± 3.618 | 80.013 ± 5.311 |
| Serum IL-1β | 28.520 (28.394, 28.787) | 28.524 (28.516, 28.667) | 28.671 (28.614, 28.714) | 28.660 (28.462, 28.857) |
| VAT IL-1β | 23.505 ± 1.256 | 20.644 ± 0.798 | 49.149 ± 3.799 *** | 35.799 ± 3.120 ### |
| VAT IL-10 | 24.587 ± 8.804 | 39.824 ± 7.359 | 12.908 ± 1.266 * | 23.141 ± 3.536 # |
| SAT IL-1β | 17.973 ± 10.440 | 15.005 ± 7.049 | 19.203 ± 0.801 | 20.842 ± 2.220 |
| SAT IL-10 | 52.773 ± 1.528 | 55.058 ± 1.259 | 49.939 ± 4.252 | 48.022 ± 2.053 |
| Serum TNF-α | Serum IL-1β | Serum IL-10 | AT IL-1β | AT IL-10 | CD11C/CD206 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAT | Large vessel density | −0.171 | 0.012 | 0.156 | 0.392 | −0.350 | 0.302 |
| Capillary density | −0.434 | 0.107 | 0.279 | −0.163 | 0.740 ** | −0.237 | |
| α−SMA | 0.273 | −0.086 | 0.075 | −0.962 *** | 0.807 *** | −0.947 *** | |
| OPN | 0.270 | −0.218 | −0.681 * | 0.384 | 0.122 | 0.541 * | |
| SAT | Large vessel density | −0.153 | 0.288 | 0.242 | −0.456 | 0.526 | 0.385 |
| Capillary density | −0.237 | 0.090 | 0.119 | −0.661 ** | 0.642 * | 0.336 | |
| α−SMA | 0.162 | 0.340 | 0.379 | −0.129 | 0.303 | −0.076 | |
| OPN | 0.209 | −0.326 | 0.035 | 0.687 | −0.494 | −0.410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Li, N.; Shi, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, J.; Zhou, Y. Aerobic Exercise Prevents High-Fat-Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Male Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203451
Guo Q, Li N, Shi H, Gan Y, Wang W, Jia J, Zhou Y. Aerobic Exercise Prevents High-Fat-Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Male Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(20):3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203451
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qiaofeng, Nan Li, Haiyan Shi, Yanming Gan, Weiqing Wang, Jiajie Jia, and Yue Zhou. 2024. "Aerobic Exercise Prevents High-Fat-Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Male Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 20: 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203451
APA StyleGuo, Q., Li, N., Shi, H., Gan, Y., Wang, W., Jia, J., & Zhou, Y. (2024). Aerobic Exercise Prevents High-Fat-Diet-Induced Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Male Mice. Nutrients, 16(20), 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203451






