Effects of Casein-Derived Peptide Met-Lys-Pro on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Research Ethics
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Measurement
2.4. Diary Survey
2.5. Safety Assessment
2.6. Sample Size
2.7. Randomization
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
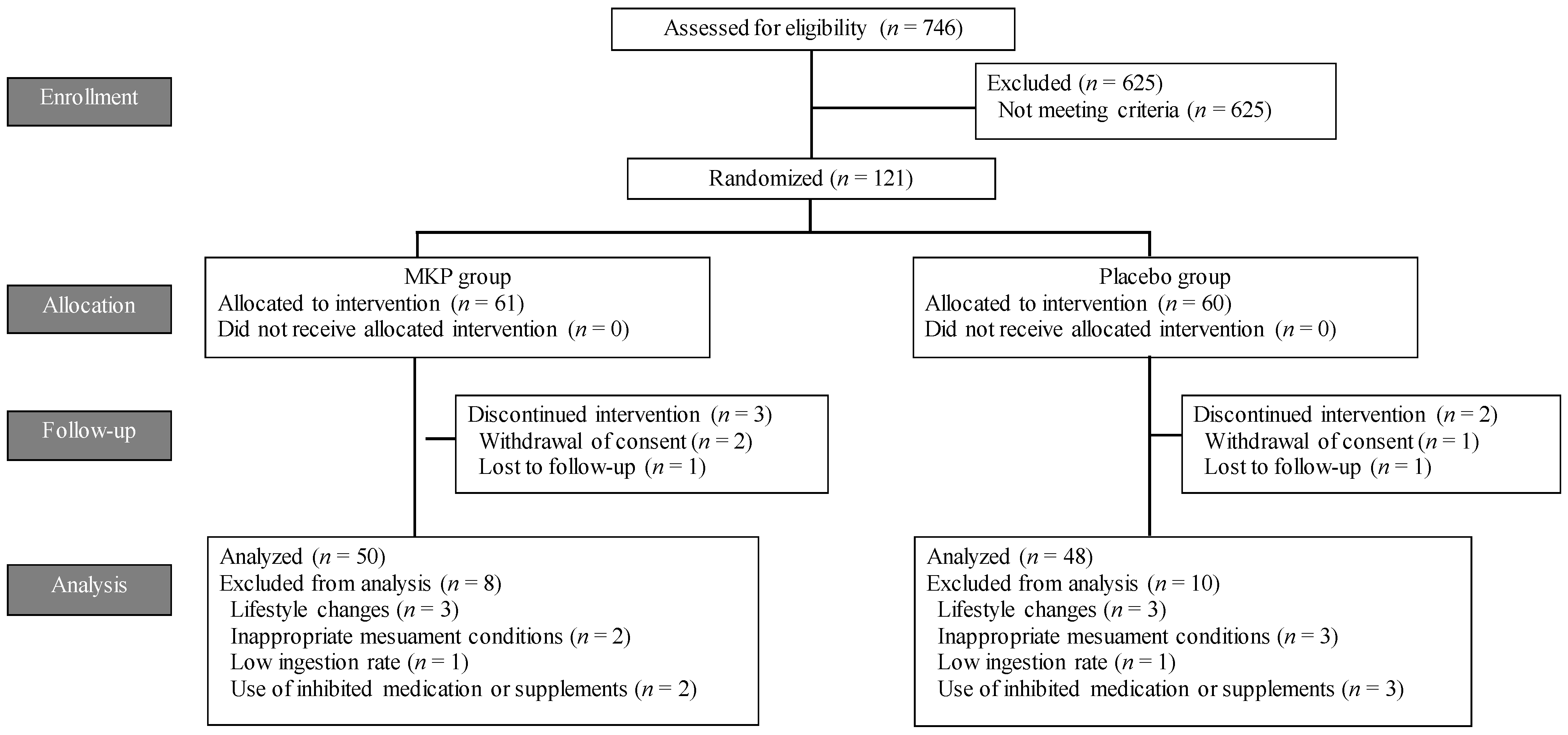
3.1. Participants
3.2. Background
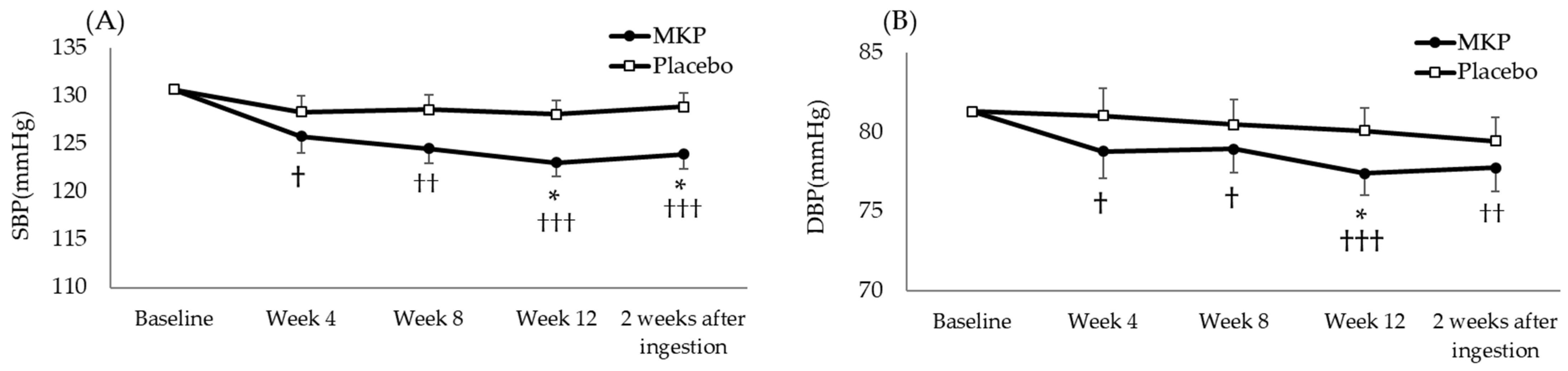
3.3. Effect of MKP Intake on Blood Pressure
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umemura, S.; Arima, H.; Arima, S.; Asayama, K.; Dohi, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Horio, T.; Hoshide, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimitsu, T.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1235–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, N.C.D.R.F. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension in Adults; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573631/ (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niiranen, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; McCabe, E.L.; Xanthakis, V.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S. Prognosis of Prehypertension Without Progression to Hypertension. Circulation 2017, 136, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Roshanravan, N. The role of nutraceuticals in prevention and treatment of hypertension: An updated review of the literature. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y. Milk consumption and multiple health outcomes: Umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in humans. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, S.L.; DellaValle, D.M.; Rodder, S.G.; Prest, M.; Sinley, R.C.; Hoy, M.K.; Papoutsakis, C. 2015 Evidence Analysis Library Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice Guideline for the Management of Hypertension in Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 1445–1458.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, P.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Qin, X. Inverse association between dietary vitamin A intake and new-onset hypertension. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, J.; Amoah, A.N.; Liu, B.; Bo, Y.; Lyu, Q. Folate, vitamin B(6), and vitamin B(12) intakes are negatively associated with the prevalence of hypertension: A national population-based study. Nutr. Res. 2023, 112, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M.; Samtiya, S.; Badgujar, P.C.; Puniya, A.K.; Dhewa, T.; Aluko, R.E. Health-Promoting and Therapeutic Attributes of Milk-Derived Bioactive Peptides. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, P.; Dahal, M.; Rai, S.; Dhakal, M.; Nirmal, N.P.; Maqsood, S.; Al-Asmari, F.; Buranasompob, A. Dairy Milk Protein-Derived Bioactive Peptides: Avengers Against Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, A.; Sakurai, T.; Ochi, D.; Mitsuyama, E.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from bovine casein. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3781–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Sakurai, T.; Ochi, D.; Mitsuyama, E.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F. Antihypertensive effect of the bovine casein-derived peptide Met-Lys-Pro. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoki, Y.; Miyuki, T.; Yamada, A.; Ochi, D.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F.; Sakane, N. Antihypertensive Effect of the Casein—Derived Peptide Met—Lys—Pro in Individuals with High—Normal Blood Pressure or Grade 1 Hypertension―A Randomized, Double—Blind, Placebo—Controlled, Parallel—Group Trial. Jpn. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 46, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Chanson-Rolle, A.; Aubin, F.; Braesco, V.; Hamasaki, T.; Kitakaze, M. Influence of the Lactotripeptides Isoleucine-Proline-Proline and Valine-Proline-Proline on Systolic Blood Pressure in Japanese Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, R.; Peritz, E.; Gabriel, K.R. On Closed Testing Procedures with Special Reference to Ordered Analysis of Variance. Biometrika 1976, 63, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanugula, A.K.; Kaur, J.; Batra, J.; Ankireddypalli, A.R.; Velagapudi, R. Renin-Angiotensin System: Updated Understanding and Role in Physiological and Pathophysiological States. Cureus 2023, 15, e40725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancion, A.; Tridetti, J.; Nguyen Trung, M.L.; Oury, C.; Lancellotti, P. A Review of the Role of Bradykinin and Nitric Oxide in the Cardioprotective Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Focus on Perindopril. Cardiol. Ther. 2019, 8, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heran, B.S.; Wong, M.M.; Heran, I.K.; Wright, J.M. Blood pressure lowering efficacy of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2008, CD003823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.D.; Whelton, P.K. High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2020, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, W.W.; Chadwick, I.G.; Kraskiewicz, M.; Jackson, P.R.; Ramsay, L.E. Resolution of ACE inhibitor cough: Changes in subjective cough and responses to inhaled capsaicin, intradermal bradykinin and substance-P. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuda, N.; Tanaka, M.; Tokushima, M.; Abe, F. Safety evaluation of high-dose intake of casein-derived peptide Met-Lys-Pro in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Participants | ITT Population | PPS Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MKP | Placebo | p-Value | MKP | Placebo | p-Value | ||
| (n = 121) | (n = 61) | (n = 60) | (n = 50) | (n = 48) | |||
| Male/Female | 67/54 | 34/27 | 33/27 | 1.000 | 27/23 | 28/20 | 0.689 |
| Pre-/Post-menopausal | 31/23 | 15/12 | 16/11 | 1.000 | 12/11 | 12/8 | 0.760 |
| Age (years) | 54.1 ± 9.7 | 53.9 ± 9.1 | 54.4 ± 10.4 | 0.751 | 53.7 ± 8.8 | 55.0 ± 10.7 | 0.499 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.3 ± 3.1 | 22.2 ± 3.2 | 22.3 ± 3.2 | 0.912 | 22.0 ± 3.1 | 22.2 ± 2.7 | 0.718 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 130.8 ± 5.6 | 130.7 ± 5.2 | 130.8 ± 6.0 | 0.939 | 130.5 ± 5.4 | 130.8 ± 5.8 | 0.776 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.2 ± 5.3 | 81.4 ± 4.9 | 81.0 ± 5.7 | 0.689 | 81.8 ± 4.6 | 80.7 ± 5.8 | 0.299 |
| Smoker/Non-smoker | 6/115 | 5/56 | 1/59 | 0.207 | 3/47 | 0/48 | 0.243 |
| MKP | Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | Baseline | 1875.2 ± 215.1 | 1917.2 ± 283.9 |
| Week 12 | 1865.6 ± 207.6 | 1887.3 ± 233 | |
| Protein (g) | Baseline | 73.1 ± 6.5 | 75.4 ± 8.9 |
| Week 12 | 73.5 ± 6.8 | 74.5 ± 8.1 | |
| Fat (g) | Baseline | 57.4 ± 4.3 | 59.1 ± 8.2 |
| Week 12 | 58.2 ± 5.7 | 58.2 ± 5.0 | |
| Carbohydrates (g) | Baseline | 265.7 ± 33.0 | 265.8 ± 33.5 |
| Week 12 | 259.5 ± 31.1 | 262.2 ± 30.8 | |
| Fiber (g) | Baseline | 14.6 ± 1.4 | 14.9 ± 1.7 |
| Week 12 | 14.6 ± 1.5 | 14.7 ± 1.5 | |
| Sodium (mg) | Baseline | 3951.6 ± 465.7 | 4000.2 ± 517.7 |
| Week 12 | 3957.8 ± 429.8 | 3944.4 ± 440.3 | |
| Potassium (mg) | Baseline | 2763.7 ± 206.3 | 2849.6 ± 274.9 |
| Week 12 | 2767.6 ± 198.6 | 2794.0 ± 222.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, S.; Ochi, D.; Nabeshima, K.; Sakiyama, R.; Somoto, Y.; Nakano, M.; Tanaka, M.; Nakamura, M. Effects of Casein-Derived Peptide Met-Lys-Pro on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172975
Sato S, Ochi D, Nabeshima K, Sakiyama R, Somoto Y, Nakano M, Tanaka M, Nakamura M. Effects of Casein-Derived Peptide Met-Lys-Pro on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172975
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Soichiro, Daisuke Ochi, Kazumi Nabeshima, Ryo Sakiyama, Yuki Somoto, Manabu Nakano, Miyuki Tanaka, and Masahiko Nakamura. 2024. "Effects of Casein-Derived Peptide Met-Lys-Pro on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172975
APA StyleSato, S., Ochi, D., Nabeshima, K., Sakiyama, R., Somoto, Y., Nakano, M., Tanaka, M., & Nakamura, M. (2024). Effects of Casein-Derived Peptide Met-Lys-Pro on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study. Nutrients, 16(17), 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172975





