Sexual Dimorphism in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experiments
2.4. Gas Chromatography (GC) Assay for Fat Absorption
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Fast-Performance Liquid Chromatography (FPLC) for Lipoprotein Fractions
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Fecal DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.9. Sequence Curation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reduced Weight Gain in Female Mice
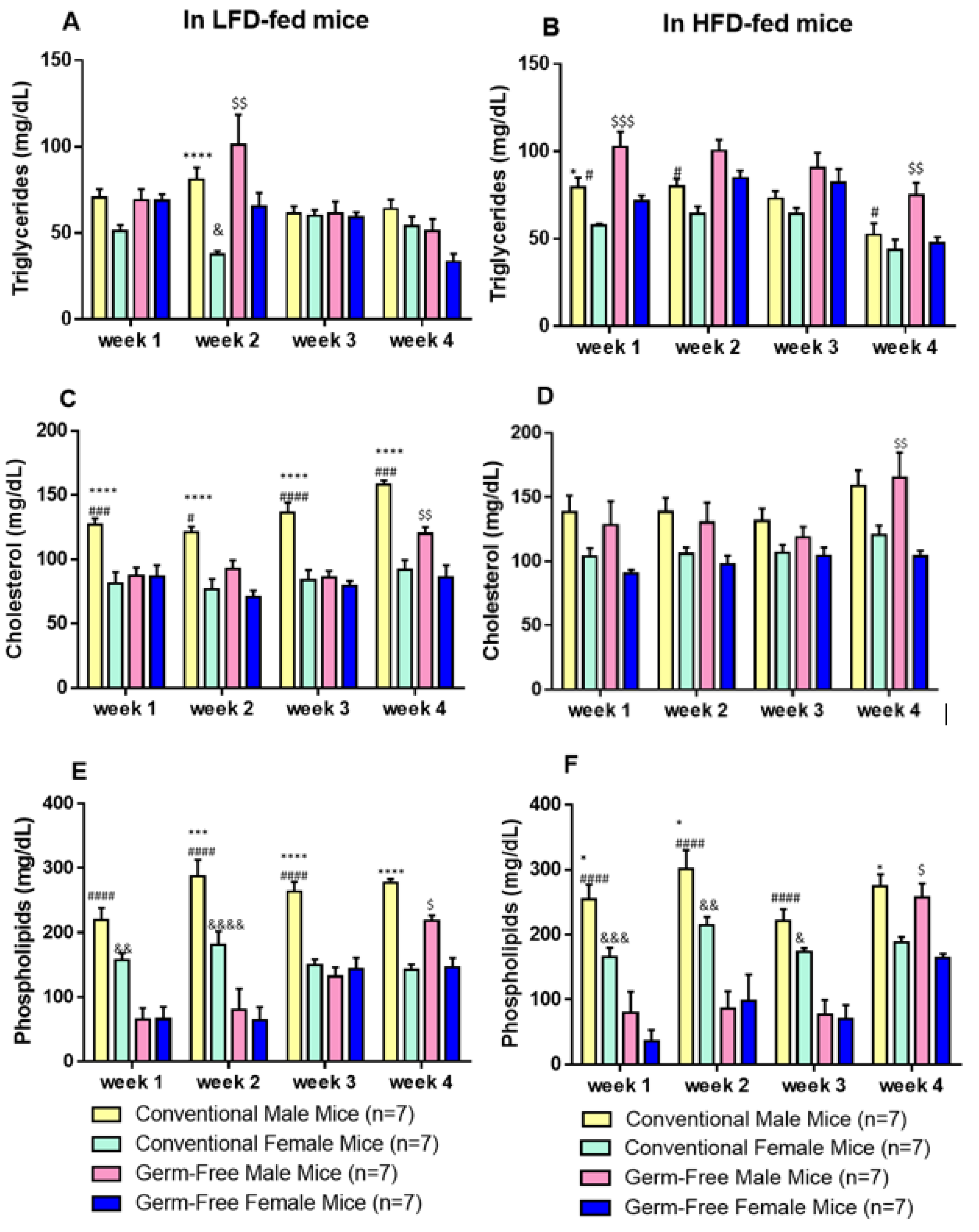
3.2. Ameliorated Lipid Profile in Female Mice
3.3. Lipid Absorption
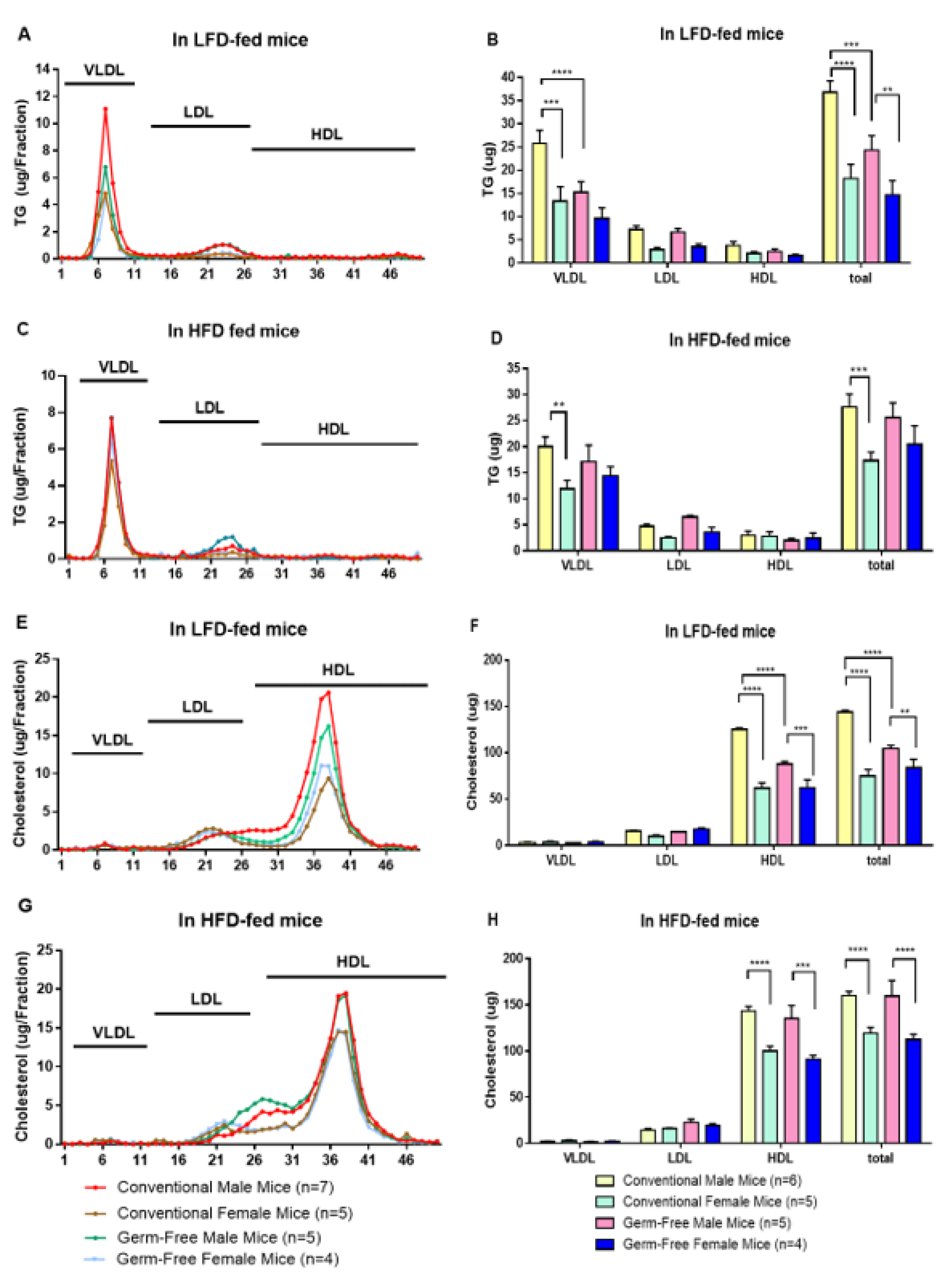
3.4. Lipoprotein Distribution in Plasma
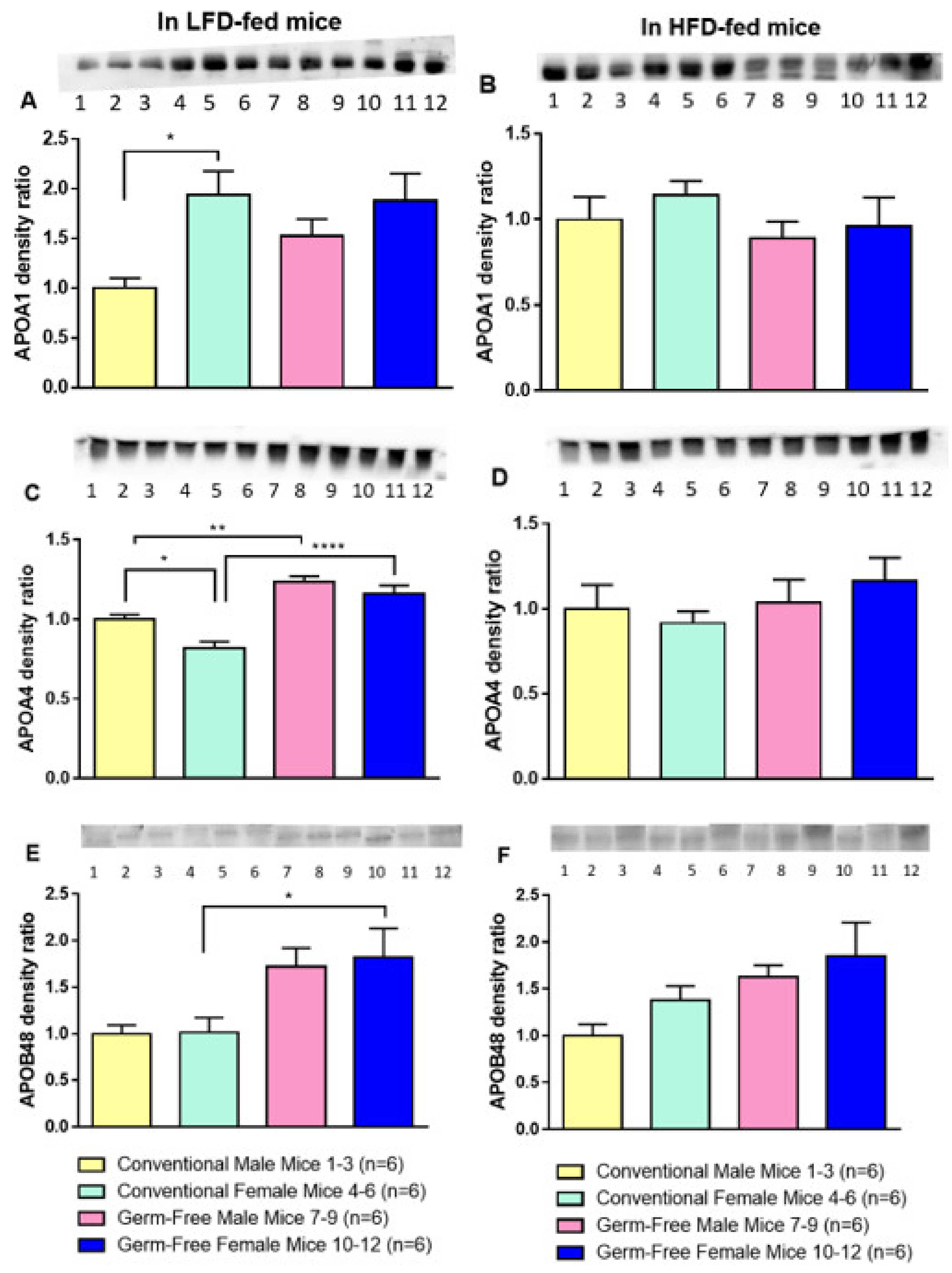
3.5. Apolipoprotein Levels
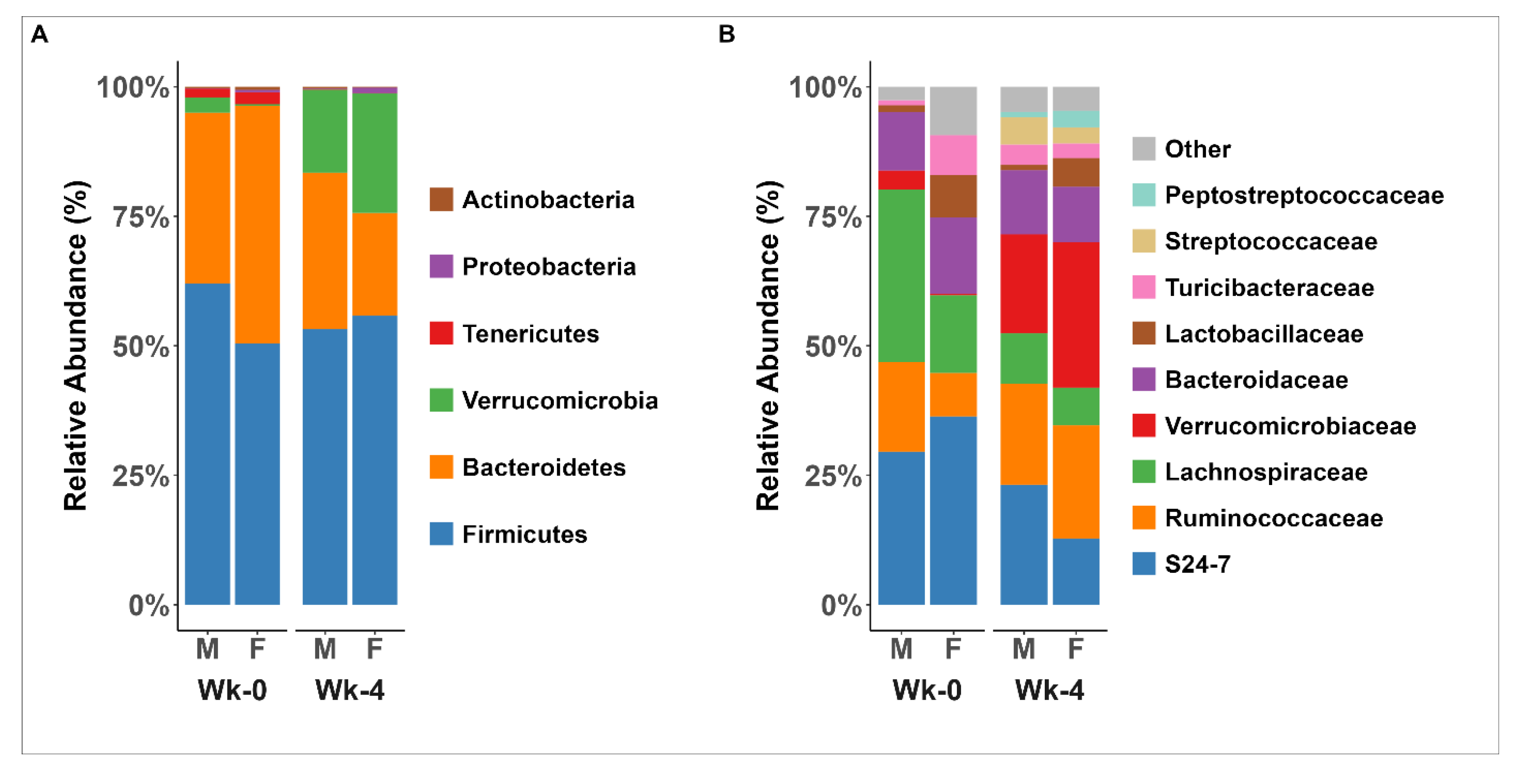
3.6. The Microbial Response to HFD was Dependent on Sex
3.7. Select Bacterial Species Correlated to Metabolic and Lipid Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TG | triglyceride |
| CHOL | cholesterol |
| PL | phospholipid |
| NEFA | non-esterified fatty acid |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| LFD | low-fat diet |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| lfcSE | log2 fold-change standard error |
| padj | FDR corrected p-value |
| df | degrees of freedom |
References
- Jia, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, S. Impact of Gut Microbiota and Microbiota-Related Metabolites on Hyperlipidemia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Zhang, L.S.; Martinez, K.; Chang, E.B.; Yang, Q.; Wang, F.; Howles, P.N.; Hokari, R.; Miura, S.; Tso, P. Antibiotics Suppress Activation of Intestinal Mucosal Mast Cells and Reduce Dietary Lipid Absorption in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wan, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; He, Y.; Wan, H.; Li, C. Naoxintong Capsule Alternates Gut Microbiota and Prevents Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat-Diet Fed Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 843409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Org, E.; Mehrabian, M.; Parks, B.W.; Shipkova, P.; Liu, X.; Drake, T.A.; Lusis, A.J. Sex differences and hormonal effects on gut microbiota composition in mice. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliannan, K.; Robertson, R.C.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Kang, C.; Wang, B.; Hao, L.; Bhan, A.K.; Kang, J.X. Estrogen-mediated gut microbiome alterations influence sexual dimorphism in metabolic syndrome in mice. Microbiome 2018, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; He, C. Sex-specific association between the gut microbiome and high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Su, J.; Liu, R.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Li, D.; Shi, J.; Gu, B.; Zhang, J.; et al. Sexual dimorphism in glucose metabolism is shaped by androgen-driven gut microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandacek, R.J.; Heubi, J.E.; Tso, P. A novel, noninvasive method for the measurement of intestinal fat absorption. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. C. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: Final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J.; Rushing, P.A.; D’Alessio, D.; Tso, P. A controlled high-fat diet induces an obese syndrome in rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, L.; Yang, Q.; Nauli, A.M.; Bingamon, M.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Tso, P. Sexual dimorphism in intestinal absorption and lymphatic transport of dietary lipids. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 5015–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tso, P.; Wang, D.Q.; Woods, S.C.; Davidson, W.S.; Sakai, R.; Liu, M. Up-regulation of apolipoprotein E by leptin in the hypothalamus of mice and rats. Physiol Behav. 2009, 98, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Winker, K.; Kado, D.M.; Orwoll, E.; Manary, M.; et al. Phylogenetic Placement of Exact Amplicon Sequences Improves Associations with Clinical Information. mSystems 2018, 3, e00021-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan Community Ecology Package Version 2.5-7; R Project for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; He, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. LinDA: Linear models for differential abundance analysis of microbiome compositional data. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessau, R.B.; Pipper, C.B. R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Ugeskr. Laeger 2008, 170, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Tso, P.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Davidson, W.S.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Silencing steroid receptor coactivator-1 in the nucleus of the solitary tract reduces estrogenic effects on feeding and apolipoprotein A-IV expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamov, O.; Bethea, C.L.; Roberts, C.T. Sex-specific differences in lipid and glucose metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Lo, C.M.; Tso, P.; Davidson, W.S.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Estradiol increases the anorectic effect of central apolipoprotein A-IV. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3163–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryzgalova, G.; Lundholm, L.; Portwood, N.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Khan, A.; Efendic, S.; Dahlman-Wright, K. Mechanisms of antidiabetogenic and body weight-lowering effects of estrogen in high-fat diet-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E904–E912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.Q.H.; Tso, P.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Estradiol stimulates apolipoprotein A-IV gene expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract through estrogen receptor-α. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bless, E.P.; Reddy, T.; Acharya, K.D.; Beltz, B.S.; Tetel, M.J. Oestradiol and diet modulate energy homeostasis and hypothalamic neurogenesis in the adult female mouse. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 26, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kanda, S.; Guigni, B.A.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Carvalho, C.R.O.; Petersen, K.F.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Cellular Mechanism by Which Estradiol Protects Female Ovariectomized Mice From High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic and Muscle Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, S.; Membrez, M.; Bruneau, A.; Gérard, P.; Harach, T.; Moser, M.; Raymond, F.; Mansourian, R.; Chou, C.J. Germ-free C57BL/6J mice are resistant to high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance and have altered cholesterol metabolism. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, D.H.; Lancaster, N.; Schonfeld, G. The effects of fat feeding on apolipoprotein AI secretion from rat small intestinal epithelium. Metabolism 1982, 31, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, M.J.; Hawken, S.; Wang, X.; Ounpuu, S.; Sniderman, A.; Probstfield, J.; Steyn, K.; Sanderson, J.E.; Hasani, M.; Volkova, E.; et al. Lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins as risk markers of myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): A case-control study. Lancet 2008, 372, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, A.B.; Wang, F.; Lo, C.-M.; Liu, M.; Tso, P. ApoA-IV: Current and emerging roles in intestinal lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and satiety. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G472–G481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.M.; Nordskog, B.K.; Nauli, A.M.; Zheng, S.; Vonlehmden, S.B.; Yang, Q.; Lee, D.; Swift, L.L.; Davidson, N.O.; Tso, P. Why does the gut choose apolipoprotein B48 but not B100 for chylomicron formation? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G344–G352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L.; Pullinger, C.; Kroes, I.; Kroes, J.; Hardman, D.A.; Chen, G.; Curtiss, L.K.; Gutierrez, M.M.; Kane, J.P.; Schumaker, V.N. A single copy of apolipoprotein B-48 is present on the human chylomicron remnant. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Cardelli, J.A.; Nutting, D.F.; Bergstedt, S.; Tso, P. Fat feeding increases size, but not number, of chylomicrons produced by small intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, G709–G719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velazquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of high-fat diet on gut microbiota: A driving force for chronic disease risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtman, T.A.; Eckermann, H.A.; Smidt, H.; de Weerth, C. Gut microbiota and BMI throughout childhood: The role of firmicutes, bacteroidetes, and short-chain fatty acid producers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Collado, M.C.; Ben-Amor, K.; Salminen, S.; De Vos, W.M. The mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila is an abundant resident of the human intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Wang, G. Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce the damage of gluco/lipotoxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation, and normalize intestine microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.; Yuan, G. Gut microbiota mediates positive effects of liraglutide on dyslipidemia in mice fed a high-fat diet. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1048693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Abbatini, F.; Russo, A.; Quagliariello, A.; Reddel, S.; Capoccia, D.; Caccamo, R.; Corradini, S.G.; Nobili, V.; De Peppo, F.; et al. Gut microbiota markers in obese adolescent and adult patients: Age-dependent differential patterns. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekelja, M.; Berget, I.; Næs, T.; Rudi, K. Unveiling an abundant core microbiota in the human adult colon by a phylogroup-independent searching approach. ISME J. 2011, 5, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, G.; Russo, E.; Niccolai, E.; Dinu, M.; Di Pilato, V.; Magrini, A.; Bartolucci, G.; Baldi, S.; Menicatti, M.; Giusti, B.; et al. Influence of a 3-month low-calorie Mediterranean diet compared to the vegetarian diet on human gut microbiota and SCFA: The CARDIVEG Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2011–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, K.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Bearman, G.M.L.; Edmond, M.B. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in adult patients with nosocomial bloodstream infections due to enterococci. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zheng, C.; Song, B.; Li, F.; Kong, X.; Xu, K. Inflammatory Links Between High Fat Diets and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozeš, Š.; Bujňáková, D.; Šefčíková, Z.; Kmeť, V. Intestinal microflora and obesity in rats. Folia Microbiol. 2008, 53, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Maurya, A.K.; Parker, K.D.; Kant, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Kabir, M.I.; Kumar, D.; Weber, A.M.; Agarwal, R.; Kuhn, K.A.; et al. Gender-based effect of absence of gut microbiota on the protective efficacy of Bifidobacterium longum-fermented rice bran diet against inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2022, 61, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, A.; Oosting, A.; Lohuis, M.; Koehorst, M.; El Aidy, S.; Hugenholtz, F.; Smidt, H.; Mischke, M.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Verkade, H.J.; et al. Sex differences in lipid metabolism are affected by presence of the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalla, J.; García de Lomas, J.M.; Chueca, N.; Pérez-Stachowski, X.; De Salazar, A.; Del Arco, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; De la Torre, J.; Prada, J.L.; García-Alegría, J.; et al. Effect of daily consumption of extra virgin olive oil on the lipid profile and microbiota of HIV-infected patients over 50 years of age. Medicine 2019, 98, e17528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conterno, L.; Martinelli, F.; Tamburini, M.; Fava, F.; Mancini, A.; Sordo, M.; Pindo, M.; Martens, S.; Masuero, D.; Vrhovsek, U.; et al. Measuring the impact of olive pomace enriched biscuits on the gut microbiota and its metabolic activity in mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.J.; Hecht, P.M.; Jasarevic, E.; Beversdorf, D.Q.; Will, M.J.; Fritsche, K.; Gillespie, C.H. Sex-specific effects of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on the microbiome and behavior of socially-isolated mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Martínez, I.; Arreaza-Gil, V.; Muguerza, B.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Bravo, F.I.; Torres-Fuentes, C.; Suárez, M. Administration Time Significantly Affects Plasma Bioavailability of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins Extract in Healthy and Obese Fischer 344 Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, U.D.; Zhong, Y.; Lazarenko, O.P.; Chintapalli, S.V.; Piccolo, B.D.; Chen, J.-R.; Shankar, K. Sex-Specific Changes in Gut Microbiome Composition following Blueberry Consumption in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.B.M.S.; Fukiya, S.; Hagio, M.; Fujii, N.; Ishizuka, S.; Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Yokota, A. Bile acid is a host factor that regulates the composition of the cecal microbiota in rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Qi, N.; Shen, L.; Lo, C.C.; Xu, M.; Duan, Q.; Ollberding, N.J.; Wu, Z.; Hui, D.Y.; Tso, P.; et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092175
Zhu Q, Qi N, Shen L, Lo CC, Xu M, Duan Q, Ollberding NJ, Wu Z, Hui DY, Tso P, et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092175
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qi, Nathan Qi, Ling Shen, Chunmin C. Lo, Meifeng Xu, Qing Duan, Nicholas J. Ollberding, Zhe Wu, David Y. Hui, Patrick Tso, and et al. 2023. "Sexual Dimorphism in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092175
APA StyleZhu, Q., Qi, N., Shen, L., Lo, C. C., Xu, M., Duan, Q., Ollberding, N. J., Wu, Z., Hui, D. Y., Tso, P., & Liu, M. (2023). Sexual Dimorphism in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients, 15(9), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092175







