Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds
2.2. Cells and Viral Infection
2.3. Assay of the CDN-Mediated Reduction in Virus-Induced Cytopathic Effects
2.4. MTS Assay
2.5. HCoV-OC43 RNA Copy Number Quantification
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining Analysis
2.8. Real-Time PCR for mRNA Quantitation
2.9. Cytometric Bead Array Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
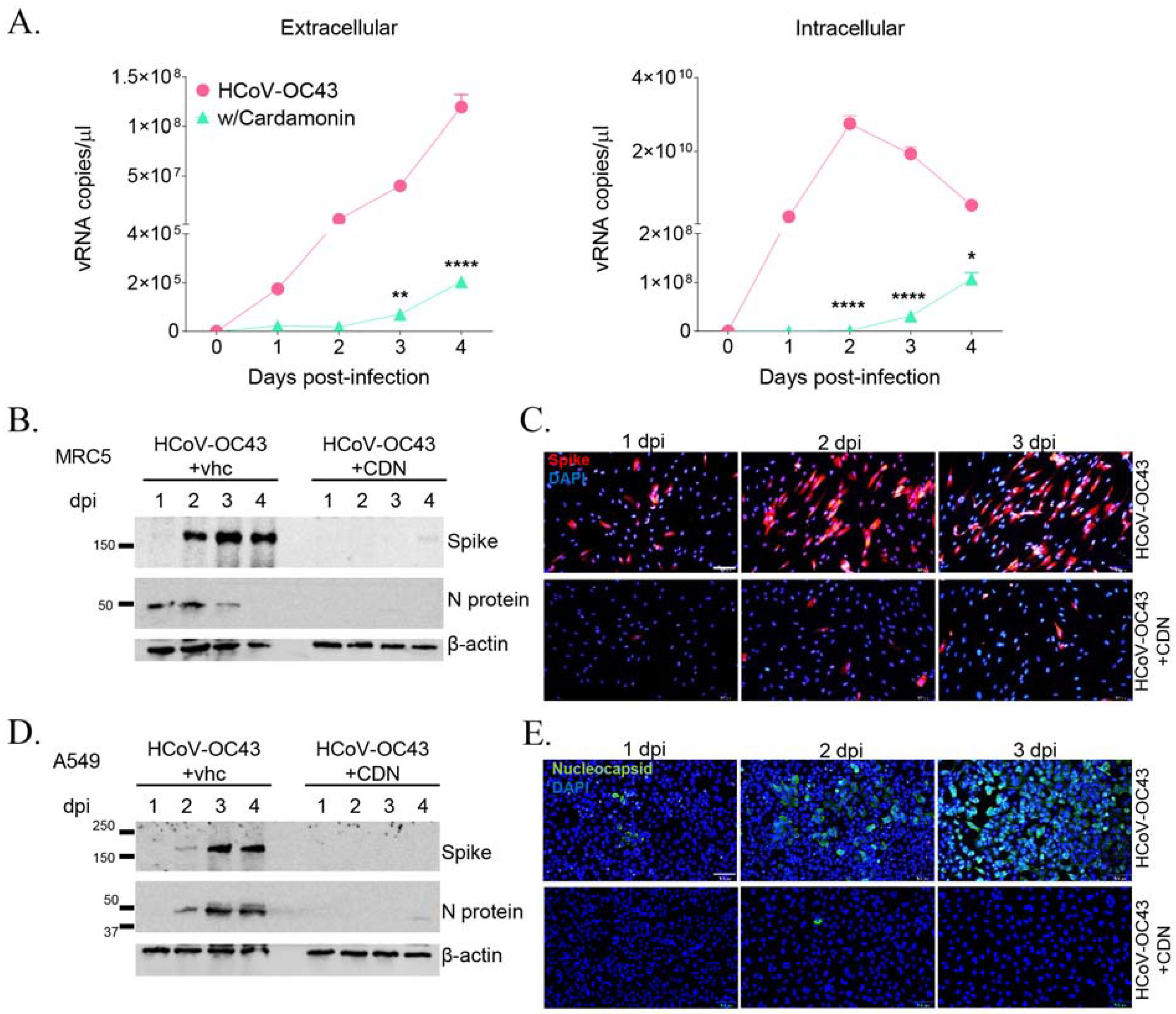
3.1. CDN Protected Cells from HCoV-OC43-Induced Cytopathic Effects
3.2. CDN Inhibited HCoV-OC43 Replication and Viral Protein Expression in Human Lung Cells
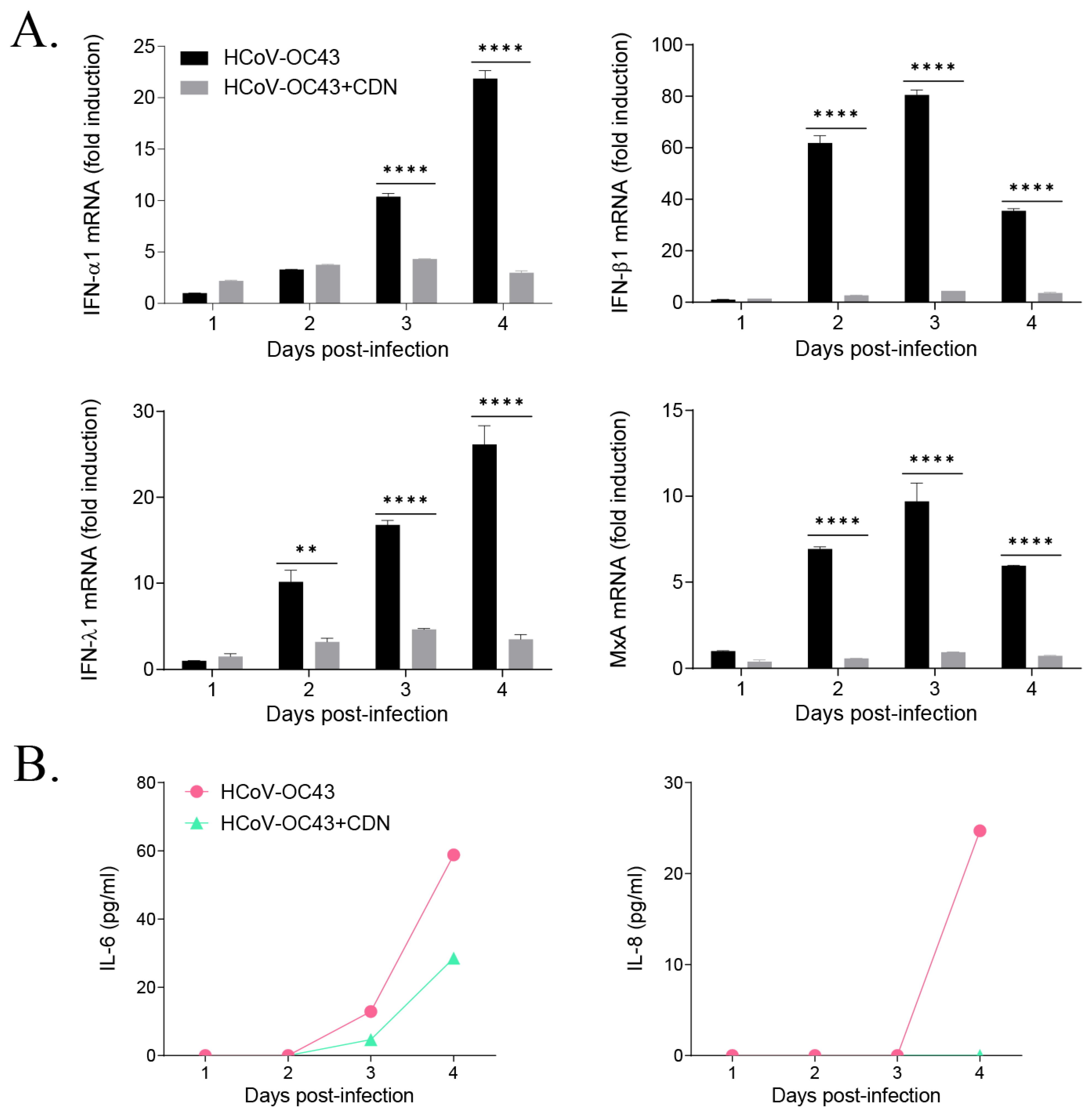
3.3. CDN Did Not Induce a Host IFN-Related Antiviral Response during HCoV-OC43 Infection
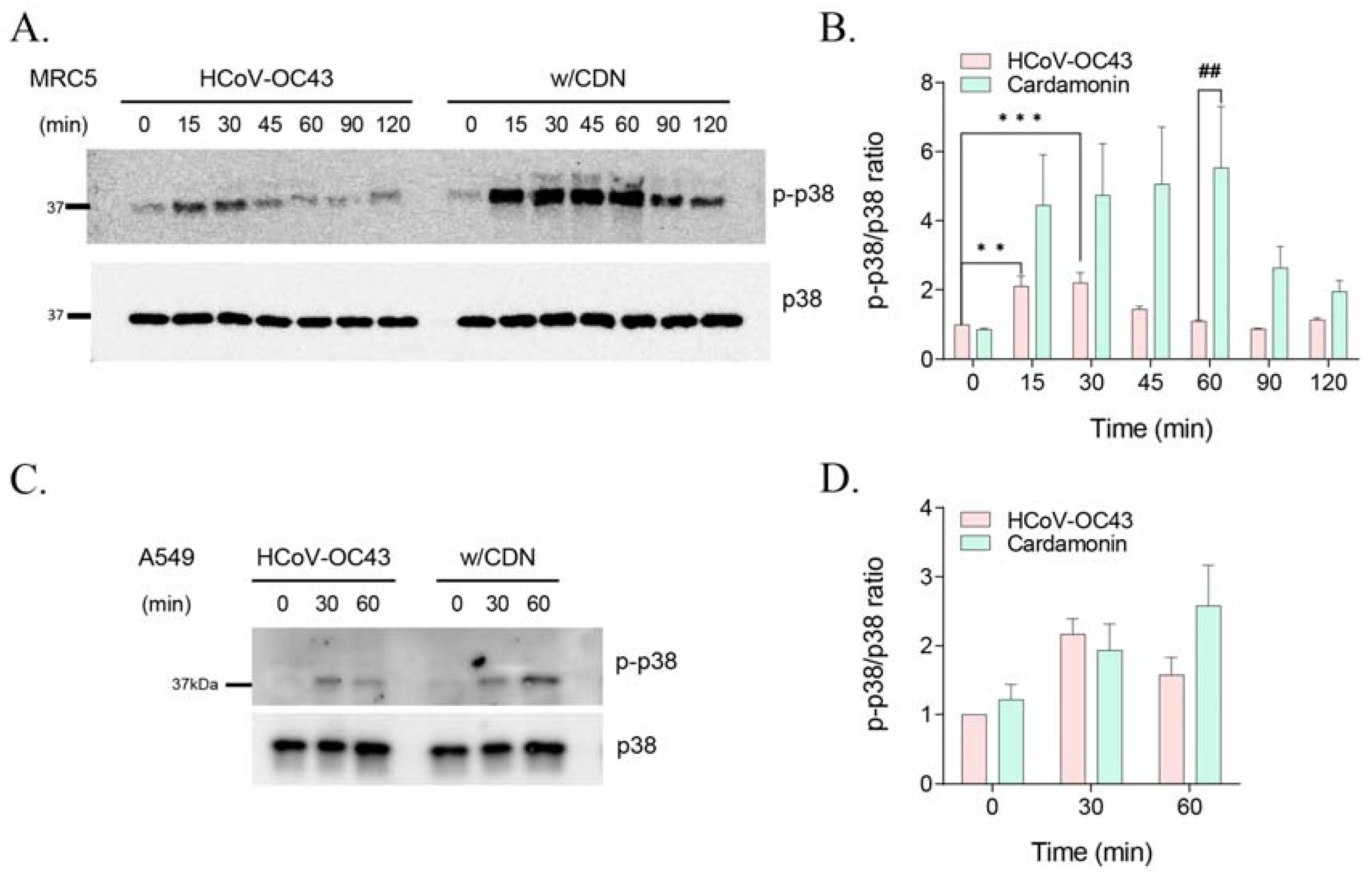
3.4. CDN Amplified and Extended HCoV-OC43-Induced p38 Phosphorylation
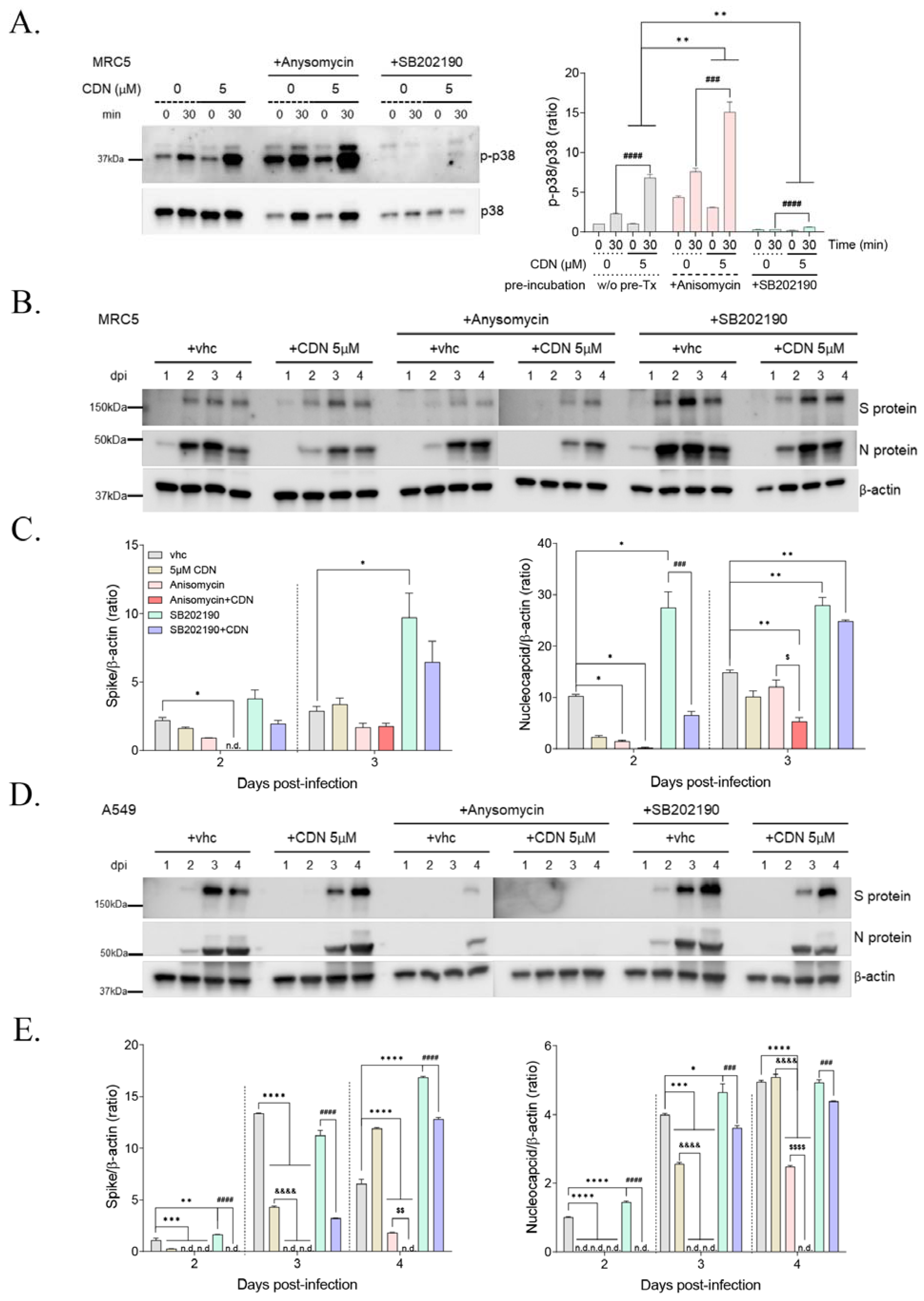
3.5. p38 MAPK Activation by CDN and/or Anisomycin Suppressed HCoV-OC43 Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Renia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S. Medical reviews. Coronaviruses. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1974, 47, 234–251. [Google Scholar]
- Baggen, J.; Vanstreels, E.; Jansen, S.; Daelemans, D. Cellular host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.X.; Ng, Y.L.; Tam, J.P.; Liu, D.X. Human Coronaviruses: A Review of Virus-Host Interactions. Diseases 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.S.; Kim, D.E.; Jin, Y.H.; Kwon, S. Kurarinone Inhibits HCoV-OC43 Infection by Impairing the Virus-Induced Autophagic Flux in MRC-5 Human Lung Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Bowman, J.W.; Jung, J.U. Autophagy during viral infection—A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, L.M.; Valente, I.M.; Rodrigues, J.A. An overview on cardamonin. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchandani, S.; Naz, I.; Dhudha, N.; Garg, M. An overview of the potential anticancer properties of cardamonin. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2020, 1, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziieremia, S.; Gray, A.I.; Ferro, V.A.; Paul, A.; Plevin, R. The effects of cardamonin on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory protein production and MAP kinase and NFkappaB signalling pathways in monocytes/macrophages. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Huang, S.S.; Lee, M.M.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, G.J. Anti-inflammatory activities of cardamonin from Alpinia katsumadai through heme oxygenase-1 induction and inhibition of NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathway in the carrageenan-induced paw edema. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doug, H.; Chen, S.X.; Xu, H.X.; Kadota, S.; Namba, T. A new antiplatelet diarylheptanoid from Alpinia blepharocalyx. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Puripattanavong, J.; Panphadung, T. HIV-1 protease inhibitory substances from the rhizomes of Boesenbergia pandurata Holtt. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2003, 25, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Kiat, T.S.; Pippen, R.; Yusof, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Khalid, N.; Rahman, N.A. Inhibitory activity of cyclohexenyl chalcone derivatives and flavonoids of fingerroot, Boesenbergia rotunda (L.), towards dengue-2 virus NS3 protease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Haddad, M.; Alban, J.; Bourdy, G.; Reategui, R.; Castillo, D.; Sauvain, M.; Deharo, E.; Estevez, Y.; Arevalo, J. Activity-guided isolation of antileishmanial compounds from Piper hispidum. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.N.; Furlan, R.L.; Zacchino, S.A. Detection of antifungal compounds in Polygonum ferrugineum Wedd. extracts by bioassay-guided fractionation. Some evidences of their mode of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.E.; Min, J.S.; Jang, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, S.; Jin, Y.H.; Kwon, S. Natural Bis-Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids-Tetrandrine, Fangchinoline, and Cepharanthine, Inhibit Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection of MRC-5 Human Lung Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, P.; Ye, C.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. Cardamonin inhibits the growth of human osteosarcoma cells through activating P38 and JNK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.; Aparna, J.S.; Paul, A.M.; Lankadasari, M.B.; Mohammed, S.; Binu, V.S.; Santhoshkumar, T.R.; Reshmi, G.; Harikumar, K.B. Cardamonin inhibits colonic neoplasia through modulation of MicroRNA expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlquist, P.; Noueiry, A.O.; Lee, W.M.; Kushner, D.B.; Dye, B.T. Host factors in positive-strand RNA virus genome replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8181–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Gao, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yi, W.; Huang, Z.; et al. Virus-induced p38 MAPK activation facilitates viral infection. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12223–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgeling, Y.; Schmolke, M.; Viemann, D.; Nordhoff, C.; Roth, J.; Ludwig, S. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase impairs influenza virus-induced primary and secondary host gene responses and protects mice from lethal H5N1 infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Heo, J.; Yi, C.M.; Ban, J.; Lee, N.J.; Lee, N.R.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, N.J.; Inn, K.S. A novel p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) specific inhibitor suppresses respiratory syncytial virus and influenza A virus replication by inhibiting virus-induced p38 MAPK activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, J.R.; Hsu, C.H.; Li, Y.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Chang, Z.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; et al. A zebrafish model of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by dual expression of hepatitis B virus X and hepatitis C virus core protein in liver. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.C.; Martinez, O.; Honko, A.N.; Hensley, L.E.; Olinger, G.G.; Basler, C.F. Pyridinyl imidazole inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase impair viral entry and reduce cytokine induction by Zaire ebolavirus in human dendritic cells. Antivir. Res. 2014, 107, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, Y.; Kumar, R.; Khandelwal, N.; Singh, N.; Shringi, B.N.; Barua, S.; Kumar, N. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in virus replication and potential for developing broad spectrum antiviral drugs. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| N | AGCAACCAGGCTGATGTCAATACC | AGCAGACCTTCCTGAGCCTTCAAT |
| IFN-α1 | GTGCTCAGCTGCAAGTCAAG | TTATCCAGGCTGTGGGTCTC |
| IFN-β1 | ACCAACAAGTGTCTCCTCCA | GTAGTGGAGAAGCACAACAGG |
| IFN-λ1 | GTCACCTTCAACCTCTTCCG | TCAGACACAGGTTCCCATCG |
| MxA | CAACCTGTGCAGCCAGTATG | GTCCTGCTCCACACCTAGAG |
| β-actin | GGAAATCGTGCGTGACATCA | ATCTCCTGCTCGAAGTCCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.-H.; Min, J.S.; Kwon, S. Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061335
Jin Y-H, Min JS, Kwon S. Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061335
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Young-Hee, Jung Sun Min, and Sunoh Kwon. 2023. "Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061335
APA StyleJin, Y.-H., Min, J. S., & Kwon, S. (2023). Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells. Nutrients, 15(6), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061335





