Abstract
Infertility, affecting 15 to 25% of couples in the most developed countries, is recognized by the World Health Organization as a public health issue at a global level. Different causes are acknowledged to reduce fertility in both sexes. In particular, about 40–50% of cases recognize a male factor. Dietary habits and lifestyle are acknowledged to influence sperm quality and are therefore important modifiable factors in male reproductive health. Conditions such as overweight/obesity, impaired glucose metabolism and determinants of metabolic syndrome, together with unhealthy lifestyle behavior, i.e., smoking cigarettes and physical inactivity, are suggested to have a negative impact on male fertility. While individual elements and characteristics of the Western diet and habits are considered risk factors for male infertility, the Mediterranean diet (MD) seems to promote reproductive potential for improving sperm quality. It is also interesting to note that previous observational studies reported a positive correlation between the consumption of the single food classes of the MD pattern (i.e., vegetables and fruits, poultry, fish and seafood, whole grains, low-fat dairy products) and the quality of several sperm parameters. To evaluate the relationship between sperm parameters and MD adherence, we performed a cross-sectional study on the seminal data of 300 males (mean age 34.6 ± 9.1 years) who spontaneously referred to our center of reproductive medicine. The evaluation of adherence to MD was performed with a validated 14-point Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS) questionnaire. Our findings showed that sperm parameters such as sperm count, motility, viability and normal morphology are significantly and positively correlated with MEDAS, independently of BMI and age. In addition, the application of an ROC curve on MEDAS value vs. seminal alterations identified 6.25 as the score threshold value below which altered sperm parameters were more likely to occur [AUC = 0.096 (CI: 0.059–0.133; p < 0.00)]. Therefore, adhering to the MD with at least a MEDAS score of 6.26 increases the probability of normozoospermia. Moreover, subjects who had a MEDAS value lower than 6.25 had an Odds Ratio of 6.28 (CI = 3.967–9.945) for having at least one altered sperm parameter compared to those who were more adherent to the MD. In conclusion, our findings show that a higher adherence to the MD is associated with better semen parameters, in particular in relation to sperm count, sperm concentration, typical sperm morphology, and sperm progressive motility.
Keywords:
Mediterranean diet; fertility; nutrition; sperm parameters; diet; infertility; foods; ultra-processed food 1. Introduction
Nowadays, infertility affects 15 to 25% of couples in Western countries. Reduced fertility can have different causes and affects both sexes [1]. In particular, about 40–50% of cases are ascribable to male factors. In addition to congenital problems, certain conditions such as overweight/obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, atherosclerosis, and hypertension, together with unhealthy lifestyle behavior such as cigarette smoking, alcohol abuse, and physical inactivity, have been suggest to have a negative impact on male fertility [2,3]. Moreover, there is growing awareness of the relationship between unhealthy diet and male infertility [4].
Currently, there is a large body of research supporting the hypothesis that some foods may have beneficial effects on semen quality (fish, seafood, poultry, whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and low-fat dairy products) or, on the contrary, may be harmful (i.e., preserved and processed meat, foods high in saturated fatty acids, alcohol, and sugary beverages and sweets) [5]. In relation to individual nutrients, a low consumption of saturated fatty acids and trans fatty acids and an adequate intake of some nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidant molecules, and vitamins are associated with greater reproductive health [6,7,8]. In fact, it has been shown that a higher dietary intake of vitamins, various polyphenols, and carotenoids was positively correlated with better sperm quality [9]. On the other hand, dietary patterns are clearly associated with sperm quality, suggesting that nutritional interventions could play a key role in male fertility preservation, as opposed to the inadequate eating habits of the Western diet [10]. The Western diet is characterized by a high consumption of ultra-processed foods with a high intake of sugars and fats, inducing a nutritional imbalance due to the introduction of excessive calories. Hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia, which are the hallmarks of insulin resistance and typical of obesity, have been reported to be responsible for sperm’s altered glucose metabolism, thus playing a role in impaired glycolysis and consequently in increased oxidative stress [11]. In addition to hyperinsulinemia, obesity is characterized by hyperleptinemia. High levels of these hormones have been shown in the seminal plasma of dysmetabolic subjects and associated with an impairment of sperm quality and reproductive function [12].
The Mediterranean diet (MD), more correctly known as the Mediterranean food model, is a modern nutritional recommendation inspired by the food traditions of countries of the Mediterranean Sea basin. The importance and effectiveness of MD in the prevention of non-communicable diseases, especially those affecting the cardiovascular system, has been highlighted by many observational and experimental studies [13]. This diet model is characterized by a high consumption of seasonal fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals, nuts, and legumes, a moderate consumption of fish and wine, and a very low consumption of dairy products and meat, where olive oil is the main source of fat. Thus, the Mediterranean diet is rich in fibers, monounsaturated fatty acids, and antioxidants and low in saturated fat [14]. Seasonal fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory molecules, which can act as regulators of the redox status both by acting as a Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) scavenger and as gene modulators [15]. These natural dietary compounds have been suggested to ameliorate sperm parameters and even to improve DNA fragmentation and chromatin integrity [16] and increase sperm concentration, sperm motility, and sperm viability [17], variables that are closely linked to the sperm quality. It is also interesting to highlight that previous observational studies have reported a positive correlation between the consumption of individual classes of healthy foods and the quality of several sperm parameters.
Since MD has been shown to have beneficial effects in several intermediate metabolic outcomes, such as inflammation and oxidative stress, we can hypothesize that a higher MD adherence may have benefits in terms of reproductive health and sperm parameters, as highlighted in other previous papers in both interventional [18] and observational studies [19,20,21,22].
In the present observational study, we investigate the relationship between the level of adherence to the MD model and sperm parameters in a large cohort subject undergoing semen analyses, taking into account many confounding factors which, in our opinion, in previous publications on the same topic, could have been managed better.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Nutritional Habits
This is an observational cross-sectional study aiming to evaluate the relationship between sperm parameters and MD adherence in subjects who consecutively referred to the Andrology and Reproductive Medicine Unit, University Hospital of Padova, for semen analysis. All subjects who voluntary agreed to participate in the study underwent a medical history and an anthropometric evaluation of body weight and height and a lifestyle interview including a dietary questionnaire and smoking habits. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as the ratio between body weight (in kg) and the square of the height (in meters). The MD adherence was assessed through the same validated 14-point a priori Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS), under the supervision of the same dietitian. The MEDAS questionnaire provides three levels of adherence (≤5 low adherence, 6–9 medium adherence, ≥10 high adherence) [23] (see supplementary file). Included subjects also underwent semen collection by masturbation into sterile containers after 2–7 days of sexual abstinence. Samples were allowed to liquefy for 30 min and were examined for semen pH, semen volume (mL), sperm concentration (106 cells/mL), total sperm count (106 cells/ejaculate), sperm viability (%), sperm progressive motility (%), and typical sperm morphology (%) according to the WHO 6th edition manual 2021 [24]. Moreover, semen parameters thresholds, allowing characterization as normozoospermia, oligozoospermia, and asthenozoospermia, were based on the 6th percentiles from WHO criteria.
2.2. Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Hospital of Padova (protocol no. AOP3205, granted on 25 October 2023), and each participant signed informed consent. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All subjects aged 18 to 45 years old who consecutively referred to the Andrology and Reproductive Medicine laboratory between September 2022 and July 2023 were included in the study.
We excluded subjects with a current controlled diet or who had carried one out in the last 3 months, high fever (≥38 °C for at least two days) in the last 3 months, varicocele, metabolic syndrome, malignancies, history of cryptorchidism, history of testicular cancer, endocrinopathies, semen infections, genetic causes of infertility, and the use of medical treatments or dietary supplements in the 3 months preceding the study, and patients that on the day of semen collection did not have the required sexual abstinence. Furthermore, physical activity may affect male fertility, although data from the scientific literature are conflicting [25]. For this reason, we excluded from this study subjects who reported undertaking physical activity for more than 3 h per week.
2.4. Statistics
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (Version 25, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The differences between continuous variables were analyzed with ANOVA. The differences between discrete variables were analyzed with a Chi-square test or Fisher test (if the expected count was <5). The Pearson correlation index or the Spearman correlation index for non-normally distributed variables were used to describe the correlations between variables. On the basis of correlation analyses, we then performed multilinear regression analyses to compare the semen parameters most associated with MEDAS value, after adjusting for the following confounders: age, BMI, and smoking habits.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined for p < 0.05 and p > 0.1, respectively. Ordinal regression analyses were performed to assess the impact of MEDAS value on the increase in the number of semen alterations. The Jonckheere–Terpstra test was performed to calculate the p for the trend in the association between the number of seminal changes and variables of interest.
An ROC curve was calculated by plotting sensitivity values on the y-axis and 1-sensitivity values on the x-axis. The area under the curve (AUC) was determined and evaluated using the Sweets classification and the cutoff values for each considered variable were calculated with Youden’s S statistics.
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
In the period 22 September–23 July, 300 consecutive males were enrolled in this study. Their demographic and clinical data are reported in Table 1. The mean age was 34.6 ± 4.1 SD and BMI was 24.3 ± 4.1 SD (a young and normal weight sample). The mean MEDAS value of the whole sample was 7.6, indicating a medium adherence to MD. In particular, 32.3% of subjects had a low MD adherence, 36.7% had a medium MD adherence, and 31.0% had a high MD adherence. Moreover, 213 (71%) subjects were non-smokers and 87 (29%) were smokers. It is also interesting to note that the two groups had a different MD adherence: the mean MEDAS of non-smokers was 7.87 ± 2.98 SD, and the value for smokers was 7.01 ± 2.85 SD. The difference between the two groups was significant (p = 0.022).

Table 1.
Sample characteristics. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
3.2. Correlation Analyses
In order to evaluate the possible role of MD adherence on sperm parameters, a correlation analysis was performed between the MEDAS value and sperm parameters. All sperm parameters, with the exception of pH (p = 0.534), were positively and significantly associated with MEDAS. In particular, sperm concentration, total count, progressive motility, viability, and typical sperm morphology were positively and strongly associated with the MEDAS value. Consequentially, the percentage of not-motile spermatozoa showed a negative correlation (r = −0.498; p < 0.001) with MEDAS. Of note, the strongest level of association observed was between MEDAS and sperm count, then typical sperm morphology, followed by sperm progressive motility. No significant correlation was found between MEDAS and BMI or age (p = 0.093 and p = 0.737, respectively) (Figure 1a–j).
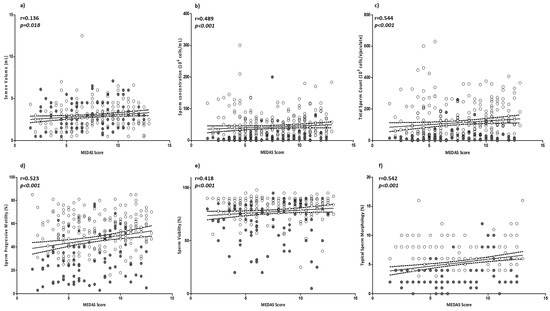
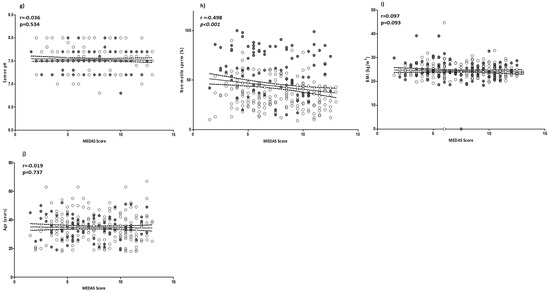
Figure 1.
Correlation analyses between MEDAS and sperm parameters: (a) semen volume; (b) sperm concentration; (c) total sperm count; (d) sperm progressive motility; (e) sperm viability; (f) sperm typical morphology; (g) semen pH; (h) non-motile sperm; (i) BMI; and (j) age. Filled circles = smokers; empty circles = non-smokers. The 95% confidence intervals are represented by dotted lines. Significant p values are highlighted in cursive.
Regarding smoking habit, a correlation analysis was also performed between MEDAS value and sperm parameters, adjusted for age, BMI, and smoking. All sperm parameters, with the exception of pH (p = 0.538), were still positively and significantly associated with MD adherence (see Supplementary Table S1).
After grouping subjects according to MD adherence (low, medium, and high) the multivariate analysis showed a significant difference in sperm parameters in the three groups (Figure 2). The characteristics of sperm concentration, count, semen volume, progressive motility, sperm viability, and morphology were significantly higher in subjects reporting a medium and high adherence to MD. In particular, sperm count and typical morphology were, respectively, 38.67 (106 cells); 3.39 (%) for low, 102.03 (106 cells); 5.12 (%) for medium, and 179.29 (106 cells); 6.98 (%) for high MD adherence.
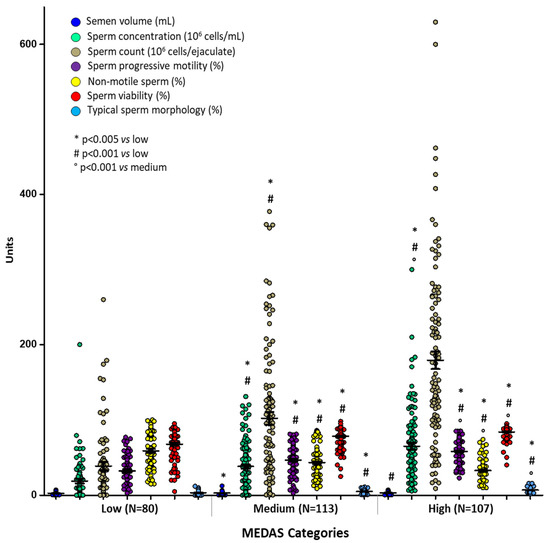
Figure 2.
Means ± SD of sperm parameters across MEDAS categories. p values were calculated by multivariate analyses corrected for age and BMI. * p < 0.005 vs. low; # p = 0.001 vs. low; ° p = 0.04 vs. medium.
Considering sperm parameters as categorical variables based on the sixth percentiles according to the WHO manual, we performed a logistic regression analysis to evaluate the presence and number of sperm alterations in relation to MEDAS (Figure 3). In particular, altered sperm parameters were considered: semen pH < 7.2, semen volume < 1.4 (mL), sperm concentration < 16 (106 cells/mL), total sperm count < 39 (106 cells/ejaculate), sperm viability < 54 (%), sperm progressive motility < 30 (%), and typical sperm morphology < 4 (%) [26].
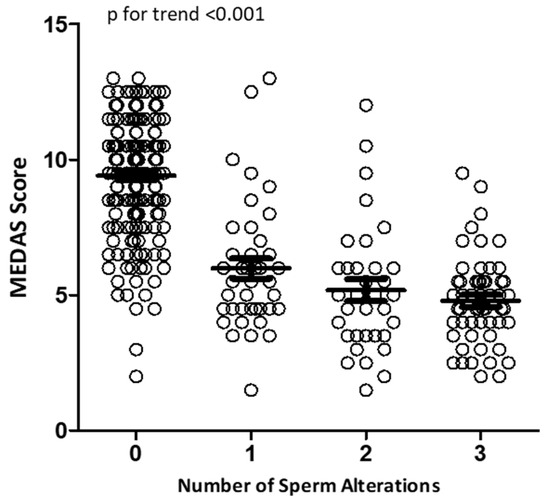
Figure 3.
Logistic regression analysis of MEDAS values in relation to the number of sperm alterations.
Using this analysis, we observed that subjects with normozoospermia had the highest MEDAS values. The cumulative number of sperm alterations was inversely related to the MEDAS value (p for trend < 0.001).
Moreover, the prevalence analyses of at least one semen alteration in any of the considered sperm parameters (under the sixth percentile of WHO criteria) in each MEDAS category showed that 92.5% (99 out of 107) of the subjects with high adherence were normozoospermic (p < 0.001) (Table 2). The prevalence of normozoospermia progressively decreased to 57.5% and 8.80% in, respectively, the medium and low adherence groups. Interestingly, patients in the lower MD adherence group showed at least one sperm alteration in more than 90% of cases.

Table 2.
Chi-square test; MEDAS categories vs. number of sperm alterations.
Finally, an ROC curve was performed in order to identify whether the MEDAS value was able to predict normal sperm parameters (Figure 4). The MEDAS threshold that best identified subjects with at least one altered sperm parameter was 6.25. A MEDAS value of 6.26 predicted normozoospermia, with an AUC = 0.096 (CI: 0.059–0.133; p < 0.00).
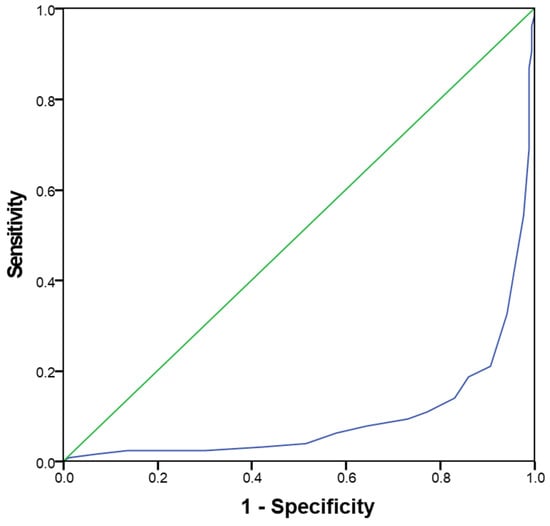
Figure 4.
ROC curve for MEDAS value able to identify subjects with normozoospermia.
Interestingly, using the 6.25 cut-off of the ROC curve, in order to obtain a binary score of MEDAS, the odds ratio of having at least one altered sperm parameter was 6.28 (CI = 3.967–9.945; p < 0.001) for the reduced MEDAS score, compared to being more adherent to the Mediterranean dietary model.
4. Discussion
In this study, we provide evidence that the degree of adherence to the Mediterranean diet, evaluated through the MEDAS questionnaire, significantly correlates with sperm parameters and predicts the occurrence of their alteration independently of age and BMI, smoke, and physical activity.
Fertility, and in particular male fertility, is acknowledged to be affected by several environmental factors and lifestyle habits, including smoking, pollution, alcohol consumption, low physical activity and, last but not least, dietary regimen [27,28]. In this regard, a hypercaloric diet and weight gain may exert direct noxious effects on male reproduction by favoring local oxidative stress [29]. It is acknowledged that overweight and obesity negatively interfere with the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis, and the resulting hypogonadism affects both spermatogenesis and energy metabolism in a vicious circle [28,30]. However, aside from this clear two-way negative cross-talk between endocrine alterations and metabolic disorders, there is a considerable “gray zone” in which this association appears much less clear. This is the case for the so-called metabolically unhealthy normal weight phenotype, accounting for up to 30% of normal weight subjects, in which oligozoospermia represents a common feature [31,32]. In this frame, the adherence to a healthy dietary pattern such as MD appears to be a useful intervention to prevent a metabolically unfavorable phenotype in normal-weight men. Recently, Golzarand et al., in a study evaluating 1299 subjects, showed that the adoption of MD or the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension-diet, largely overlapping with MD, was, respectively, associated with a 46% and 47% lower risk of gaining a metabolically unhealthy phenotype, highlighting the driving force of MD as a nutritional approach [33].
The MD model is believed to be positively associated with male fertility status, thanks to its low level of saturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, adequate levels of monounsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids fraction (PUFA), such as omega-3 and omega-6 [34]. Furthermore, this nutritional model provides excellent levels of antioxidant molecules, minerals, and vitamins. By supplying adequate quantities and qualities of fatty acids with the diet, especially in relation to the omega-3/omega-6 ratio, optimal sperm maturation can be achieved. Indeed, dietary fatty acids are constituents of the sperm cell membrane [35]. A diet poor in saturated fatty acids and cholesterol, with a low PUFA ratio, seems to improve semen quality [36,37], ameliorating membrane fluidity [38], reducing oxidative stress, and increasing mitochondrial function [39].
It is also interesting to point out that previous observational studies reported a positive correlation between the consumption of the single food classes of the MD pattern (i.e., vegetables and fruits, poultry, fish and seafood, whole grains, low-fat dairy products) and the quality of several sperm parameters [40,41]. Moreover, a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, evaluating the association between some dietary patterns and semen quality, concluded that a healthy eating pattern could have a positive impact only on semen concentration, but not on other parameters [42]. Is important to underline that the analyzed sample was small and the included studies were very heterogeneous. Instead, Salas-Huetos and colleagues, in a large systematic review on observational studies, found that diets rich in foods classes such as fish, poultry, cereals, vegetables, and fruits, and low in saturated and trans fatty acids, were positively associated with improvements in several sperm parameters [43].
Therefore, nutrition is recognized to affect sperm quality through several mechanisms. As an example, the supply of essential nutrients such as zinc, selenium, essential fatty acids, folic acid, and vitamin B12 is recognized to be important in the maturation of spermatozoa [44]. In addition, weight status, the influence of physiological mechanisms involved in spermatogenesis (hormonal modulation and red-ox balance), and the physiology of the accessory glands, are strongly linked to sperm quality [45,46]. A common denominator of all these aspects is chronic pro-inflammatory conditions, both systemic and testicular, a complex network that could be modulated through nutrition [47,48]. In this context, inflammation may also affect male reproductive potential through anatomical or functional changes in the accessory gland [48]. In fact, it is believed that eating habits are a part of various prostate diseases, from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) to cancer [49]. Diet and certain nutrients can favorably influence prostate health, reducing inflammatory processes and consequently potentially influencing sperm parameters [49]. Evidence shows that prostate concerns are less frequent in men with better adherence to a healthy diet. Moreover, lycopene, zinc, vitamin D, phytosterols, and omega 3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of symptomatic BPH [50].
In the present study, we evaluated semen parameters in 300 non-obese males, in relation to the individual adherence to MD, evaluated through the MEDAS score. Interestingly, all major seminal predictors of fertility potential, including sperm count, sperm motility, typical sperm morphology, and sperm viability, were significantly and positively correlated with the MEDAS score. This evidence suggests the role of the nutritional regimen as a possible marker of sperm abnormalities in those patients who, otherwise, remain defined as idiopathic. Those patients would be susceptible to an in-depth analysis in search of possible dysmetabolism. Our data are consistent with a growing number of reports on this topic. Karayiannis et al. evaluated 225 men from couples attending a fertility clinic [19]. Men in the lowest tertile of MD adherence score showed worse sperm count, total motility, and concentration values, whilst a high-MD adherence score was significantly associated with higher sperm quality. Ricci et al. evaluated the MD adherence in 309 male partners of sub-fertile couples undergoing assisted reproduction techniques [20]. In this study, the MD regimen was positively associated with sperm concentration and count, but not with seminal volume. Importantly, neither of the two previous studies distinguished participants according to congenital fertility problems, thus introducing a bias in the evaluation of the diet role. Salas-Huetos et al. evaluated 106 healthy young participants, concluding that an adherence to MD was positively associated only with sperm motility [21]. Lastly, Cutillas-Tolin et al., in a study on 215 healthy male college students, evidenced that higher MD adherence was positively associated only with sperm count [22].
Compared to previous studies, our data are particularly strengthened by the considerable sample size, the homogeneous evaluation of the dietary regime carried out by a single dietitian, and the exclusion of known andrological, lifestyle, and metabolic causes of infertility such as andrological problems, smoking habits, physical activity, overweight or obesity, and higher age, supporting an independent role of the dietary regimen. Nonetheless, we acknowledge a major limitation of the present study, which is its observational and cross-sectional nature. In fact, a cross-sectional design cannot determine whether MD adherence and semen parameters are causally related. Thus, although we excluded several potential confounding factors, these results should be considered with caution because of the many factors that can affect semen quality, and sperm parameters cannot be directly translated into fertility terms. Further well-designed prospective observational studies and clinical trials on the current topic are therefore recommended.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings confirm a better semen quality in males with higher adherence to the MD. On the contrary, when adherence decreased, the number of sperm alterations increased. In fact, in our sample, subjects who were more adherent to MD (even medium adherence, a MEDAS value > 6.25) had an approximately six times less probability to have sperm alterations compared to those who were poorly adherent. In particular, grouping patients by MEDAS value, we observed that greater adherence to MD was positively correlated with sperm concentration, sperm count, sperm progressive motility, semen volume, sperm viability, and typical sperm morphology independent of age, BMI, and smoking habits.
This dietary food model is rich in compounds that can be useful to sperm composition and function, suggesting a physiological favorable role in male fertility. In contrast, poor diet quality, even when not necessarily characterized by overweight, is more frequently associated with alterations in sperm parameters and male infertility. Therefore, nutritional counseling appears to be a readily implementable, non-invasive clinical practice advisable in all men with signs of alteration in sperm quality.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15234989/s1, Table S1: Correlation analysis between MEDAS Score and semen parameters, in 300 study participants, corrected for subjects age, body mass index and smoking status. Values in bold are significative.
Author Contributions
A.G. and G.C.P. contributed to the conception/design of the research and acquisition/analysis of the literature data; G.C.P., A.G., F.F.-P. and A.F. contributed equally to drafting the manuscript; A.D.N. and L.D.T.: concept and performed data analyses. P.S., A.C., L.D.T., A.M., A.D.N. and G.G. critically revised the paper for important intellectual content. All authors revised and approved the final manuscript, and agree to be fully accountable for ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the work. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and can take responsibility for the integrity of them and the accuracy of the analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Hospital of Padova (protocol no. AOP3205, granted on 25 October 2023) and was conducted in accordance with the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Inhorn, M.C.; Patrizio, P. Infertility around the Globe: New Thinking on Gender, Reproductive Technologies and Global Movements in the 21st Century. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, Y. Home Testing for Male Factor Infertility: A Review of Current Options. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 111, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrilli, D.; Ferlin, A.; Isidori, A.M.; Garolla, A.; Maggi, M.; Pivonello, R.; Santi, D.; Sansone, A.; Balercia, G.; Granata, A.R.M.; et al. Risk Behaviours and Alcohol in Adolescence Are Negatively Associated with Testicular Volume: Results from the Amico-Andrologo Survey. Andrology 2019, 7, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nätt, D.; Kugelberg, U.; Casas, E.; Nedstrand, E.; Zalavary, S.; Henriksson, P.; Nijm, C.; Jäderquist, J.; Sandborg, J.; Flinke, E.; et al. Human Sperm Displays Rapid Responses to Diet. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassan, F.L.; Chavarro, J.E.; Tanrikut, C. Diet and Men’s Fertility: Does Diet Affect Sperm Quality? Fertil. Steril. 2018, 110, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, G.; Amirjannati, N.; Rashidkhani, B.; Sadeghi, M.-R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Intake of Food Groups and Idiopathic Asthenozoospermia: A Case-Control Study. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 3328–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarro, J.E.; Minguez-Alarcon, L.; Mendiola, J.; Cutillas-Tolin, A.; Lopez-Espin, J.J.; Torres-Cantero, A.M. Trans Fatty Acid Intake Is Inversely Related to Total Sperm Count in Young Healthy Men. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareba, P.; Colaci, D.S.; Afeiche, M.; Gaskins, A.J.; Jørgensen, N.; Mendiola, J.; Swan, S.H.; Chavarro, J.E. Semen Quality in Relation to Antioxidant Intake in a Healthy Male Population. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguez-Alarcon, L.; Mendiola, J.; Lopez-Espin, J.J.; Sarabia-Cos, L.; Vivero-Salmeron, G.; Vioque, J.; Navarrete-Munoz, E.M.; Torres-Cantero, A.M. Dietary Intake of Antioxidant Nutrients Is Associated with Semen Quality in Young University Students. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; James, E.R.; Aston, K.I.; Jenkins, T.G.; Carrell, D.T. Diet and Sperm Quality: Nutrients, Foods and Dietary Patterns. Reprod. Biol. 2019, 19, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferramosca, A.; Zara, V. Diet and Male Fertility: The Impact of Nutrients and Antioxidants on Sperm Energetic Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisegang, K.; Bouic, P.J.; Menkveld, R.; Henkel, R.R. Obesity Is Associated with Increased Seminal Insulin and Leptin alongside Reduced Fertility Parameters in a Controlled Male Cohort. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2014, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Di Bella, G.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Longevity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Health Status: Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humaidan, P.; Haahr, T.; Povlsen, B.B.; Kofod, L.; Laursen, R.J.; Alsbjerg, B.; Elbaek, H.O.; Esteves, S.C. The Combined Effect of Lifestyle Intervention and Antioxidant Therapy on Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Seminal Oxidative Stress in IVF Patients: A Pilot Study. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2022, 48, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The Effects of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Foods on Mitochondrial Function: A Focus on Apoptotic Mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesi, S.; Villani, A.; Mantzioris, E.; Takele, W.W.; Cowan, S.; Moran, L.J.; Mousa, A. Anti-Inflammatory Diets in Fertility: An Evidence Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, P.; Caputo, M.; Cirillo, P.; Scappaticcio, L.; Longo, M.; Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Esposito, K. Effects of Mediterranean Diet on Semen Parameters in Healthy Young Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Minerva Endocrinol. 2021, 45, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayiannis, D.; Kontogianni, M.D.; Mendorou, C.; Douka, L.; Mastrominas, M.; Yiannakouris, N. Association between Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Semen Quality Parameters in Male Partners of Couples Attempting Fertility. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 32, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Bravi, F.; Noli, S.; Ferrari, S.; De Cosmi, V.; La Vecchia, I.; Cavadini, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Parazzini, F. Mediterranean Diet and the Risk of Poor Semen Quality: Cross-sectional Analysis of Men Referring to an Italian Fertility Clinic. Andrology 2019, 7, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Babio, N.; Carrell, D.T.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Positively Associated with Sperm Motility: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas-Tolín, A.; Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Mendiola, J.; López-Espín, J.J.; Jørgensen, N.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.M.; Torres-Cantero, A.M.; Chavarro, J.E. Mediterranean and Western Dietary Patterns Are Related to Markers of Testicular Function among Healthy Men. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Conesa, M.-T.; Philippou, E.; Pafilas, C.; Massaro, M.; Quarta, S.; Andrade, V.; Jorge, R.; Chervenkov, M.; Ivanova, T.; Dimitrova, D.; et al. Exploring the Validity of the 14-Item Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS): A Cross-National Study in Seven European Countries around the Mediterranean Region. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (Ed.) WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-0030787. [Google Scholar]
- Belladelli, F.; Basran, S.; Eisenberg, M.L. Male Fertility and Physical Exercise. World J. Mens Health 2023, 41, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björndahl, L.; Esteves, S.C.; Ferlin, A.; Jørgensen, N.; O’Flaherty, C. Improving Standard Practices in Studies Using Results from Basic Human Semen Examination. Andrology 2023, 11, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łakoma, K.; Kukharuk, O.; Śliż, D. The Influence of Metabolic Factors and Diet on Fertility. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlin, A.; Calogero, A.E.; Krausz, C.; Lombardo, F.; Paoli, D.; Rago, R.; Scarica, C.; Simoni, M.; Foresta, C.; Rochira, V.; et al. Management of Male Factor Infertility: Position Statement from the Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS): Endorsing Organization: Italian Society of Embryology, Reproduction, and Research (SIERR). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 1085–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisegang, K.; Sengupta, P.; Agarwal, A.; Henkel, R. Obesity and Male Infertility: Mechanisms and Management. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Toni, L.; Petre, G.C.; Garolla, A.; De Santis, I.; Valente, U.; Foresta, C.; De Rocco Ponce, M. Prognostic Value of Ultrasound Stratigraphy in Long-Term Weight Loss: Results from a Nutritional Counseling Program. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzaniga, W.; Candela, L.; Boeri, L.; Capogrosso, P.; Pozzi, E.; Belladelli, F.; Baudo, A.; Ventimiglia, E.; Alfano, M.; Abbate, C.; et al. The Impact of Metabolically Healthy Obesity in Primary Infertile Men: Results from a Cross-sectional Study. Andrology 2020, 8, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, R.; Pace, N.P.; Fava, S. Phenotyping Obesity: A Focus on Metabolically Healthy Obesity and Metabolically Unhealthy Normal Weight. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, e3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golzarand, M.; Moslehi, N.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Adherence to the DASH, MeDi, and MIND Diet Scores and the Incidence of Metabolically Unhealthy Phenotypes. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 17, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Moraleda, R.; Giardina, S.; Anton, E.; Blanco, J.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M. Effect of Nut Consumption on Semen Quality and Functionality in Healthy Men Consuming a Western-Style Diet: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza Safarinejad, M.; Safarinejad, S. The Roles of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids in Idiopathic Male Infertility. Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 514–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, A.K.; Simón, L.; Colombo, R.; Avena, M.V.; Monclús, M.; Crescitelli, J.; Cabrillana, M.E.; Conte, M.I.; Cayado, N.; Boarelli, P.; et al. Impact of High Fat Diet on the Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 2 Cholesterol Pathway in the Testicle. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 27, gaab023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahzadeh, S.; Riasi, A.; Tavalaee, M.; Jafarpour, F.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Omega 6/Omega 3 Ratio Is High in Individuals with Increased Sperm DNA Fragmentation. Reprod. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavilani, H.; Doosti, M.; Abdi, K.; Vaisiraygani, A.; Joshaghani, H.R. Decreased Polyunsaturated and Increased Saturated Fatty Acid Concentration in Spermatozoa from Asthenozoospermic Males as Compared with Normozoospermic Males. Andrologia 2006, 38, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferramosca, A.; Moscatelli, N.; Di Giacomo, M.; Zara, V. Dietary Fatty Acids Influence Sperm Quality and Function. Andrology 2017, 5, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskins, A.J.; Colaci, D.S.; Mendiola, J.; Swan, S.H.; Chavarro, J.E. Dietary Patterns and Semen Quality in Young Men. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewicz, A.; Morze, J.; Przybyłowicz, M.; Przybyłowicz, K.E. Association of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, Physical Activity, and Their Combination with Semen Quality: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2019, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, A.; Rafie, N.; Mansourian, M.; Miraghajani, M.; Hajianfar, H. Dietary Patterns and Semen Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Andrology 2018, 6, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Patterns, Foods and Nutrients in Male Fertility Parameters and Fecundability: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garolla, A.; Petre, G.C.; Francini-Pesenti, F.; De Toni, L.; Vitagliano, A.; Di Nisio, A.; Grande, G.; Foresta, C. Systematic Review and Critical Analysis on Dietary Supplements for Male Infertility: From a Blend of Ingredients to a Rationale Strategy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 824078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainez, N.M.; Coss, D. Obesity, Neuroinflammation, and Reproductive Function. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2719–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, R.; Pierantoni, R. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production Alters Sperm Quality. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vignera, S.; Basile, L. Diet and Prostate Health: An Underrated Tool? Aging Male 2022, 25, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Vicari, E.; Tumino, D.; Morgia, G.; Favilla, V.; Cimino, S.; Calogero, A.E. Markers of Semen Inflammation: Supplementary Semen Analysis? J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 100, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagiou, P.; Wuu, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Adami, H.-O.; Trichopoulos, D. Diet and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Study in Greece. Urology 1999, 54, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristal, A.R.; Arnold, K.B.; Schenk, J.M.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Goodman, P.; Penson, D.F.; Thompson, I.M. Dietary Patterns, Supplement Use, and the Risk of Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Results from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).