Potential Dietary and Therapeutic Strategies Involving Indole-3-Carbinole in Preclinical Models of Intestinal Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vivo Studies
2.2. Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) Treatment
2.3. Diet Studies
2.4. In Vitro Experiments
2.5. Cell Treatments
2.6. Histology
2.7. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Assay
2.8. Measuring Intestinal Permeability
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Microbiota and Bioinformatics
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
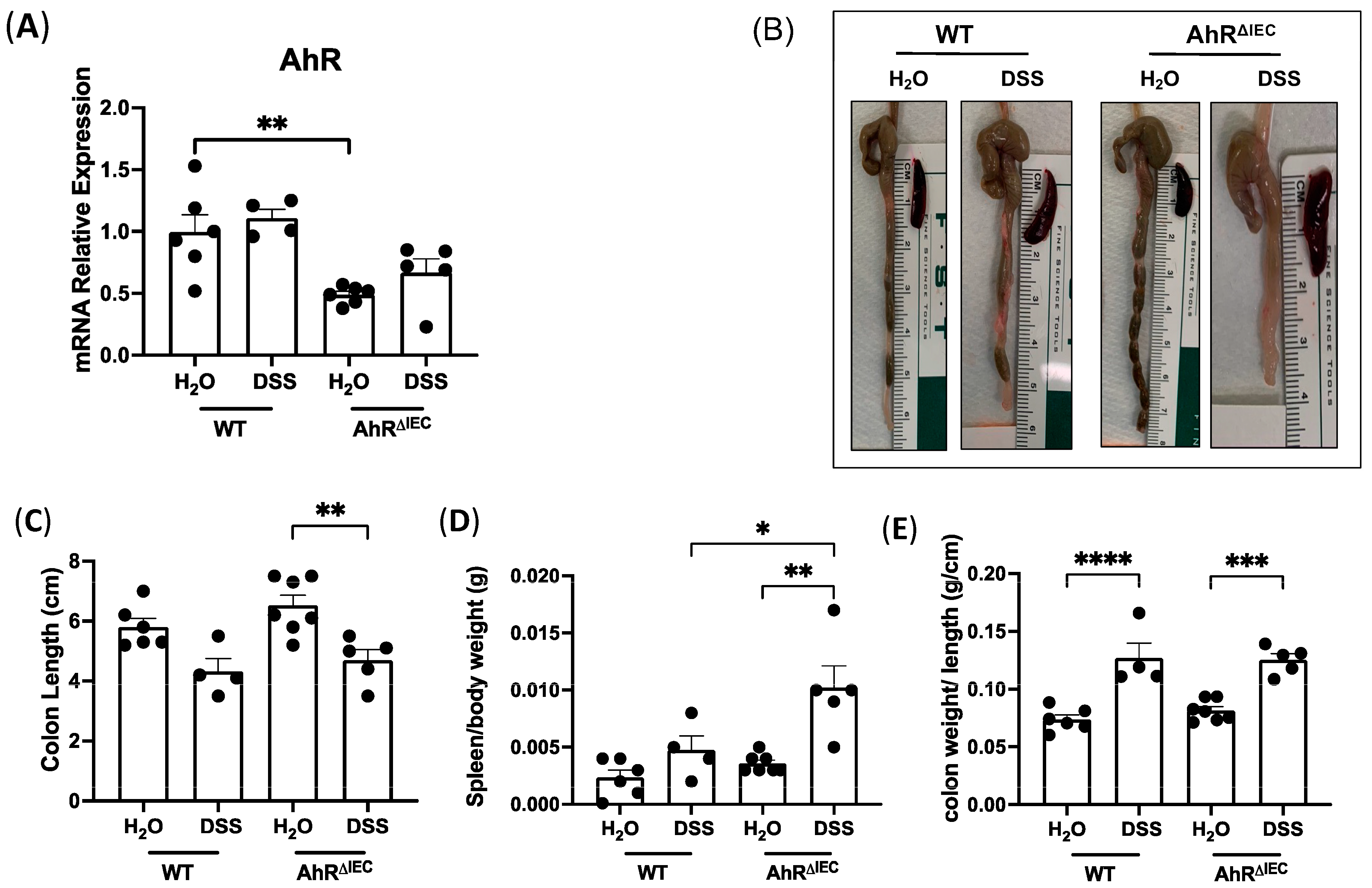
3.1. Deletion of AhR Specifically in IECs in Mice Induced with Chronic Colitis Results in Worsened Inflammatory Phenotype
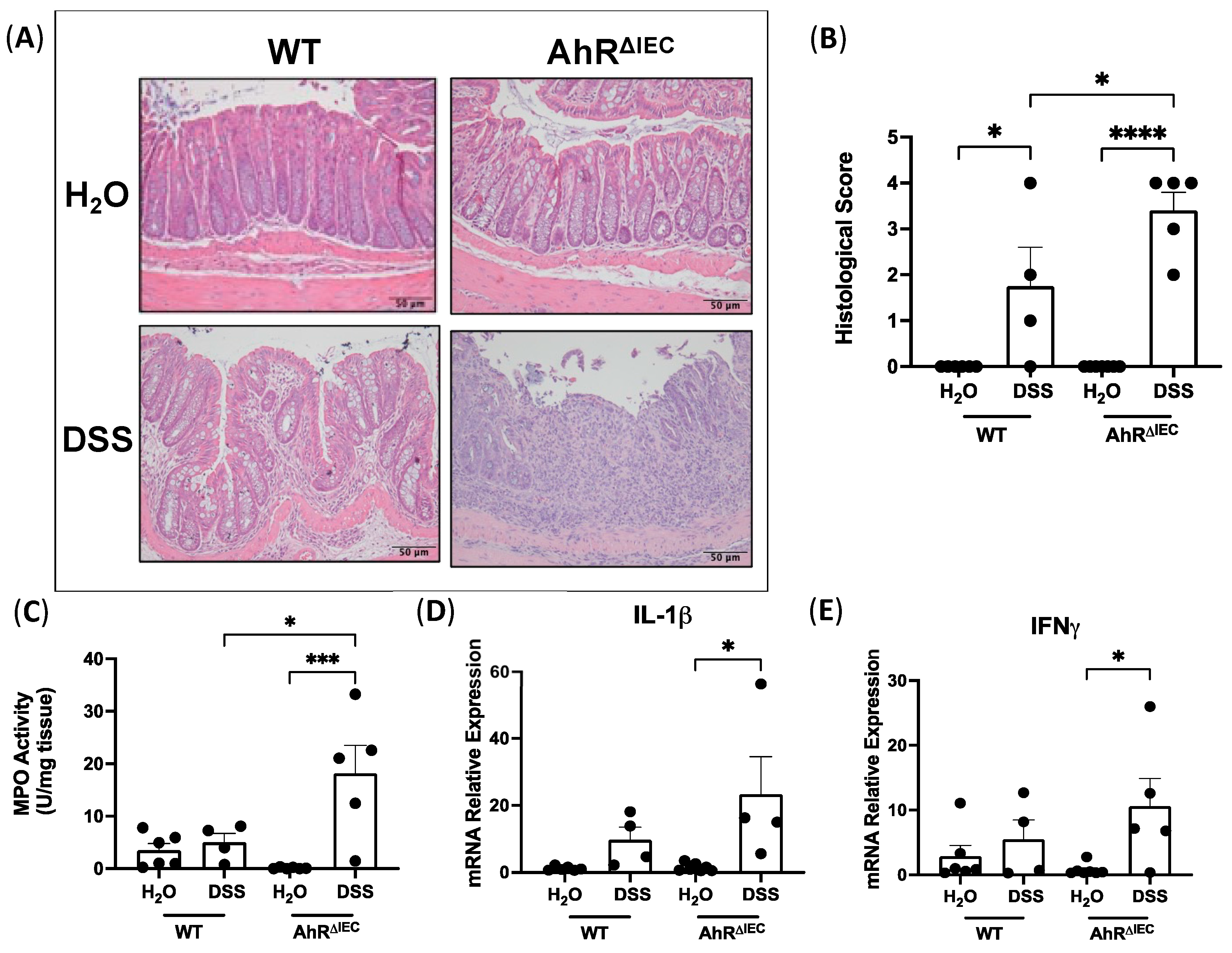
3.2. Evaluation of Histological Scoring and Inflammatory Markers in AhRΔIEC Mice with Chronic DSS Treatment
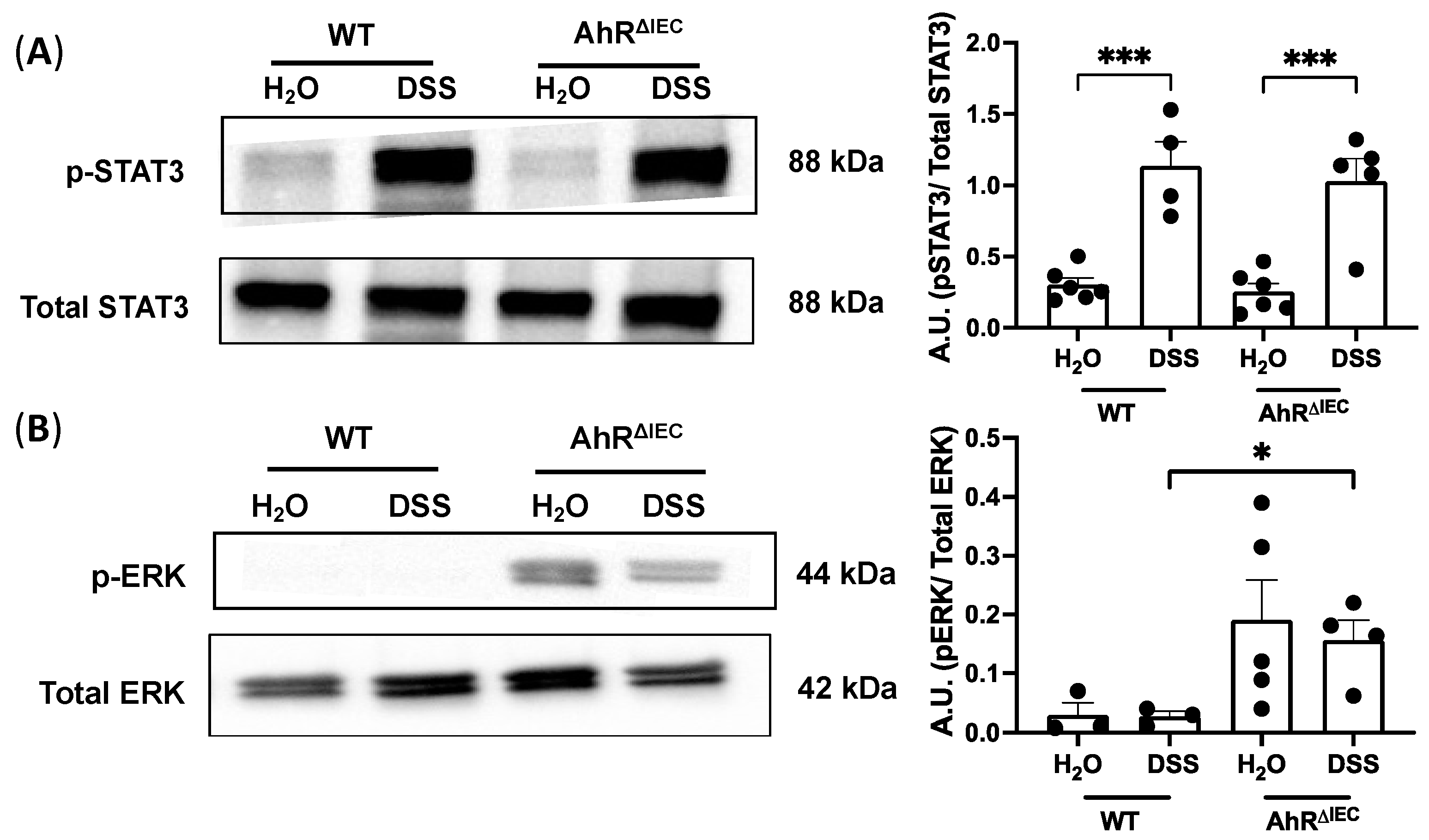
3.3. Phosphorylation of ERK Is Upregulated in AhRΔIEC Mice Treated with Chronic DSS Treatment
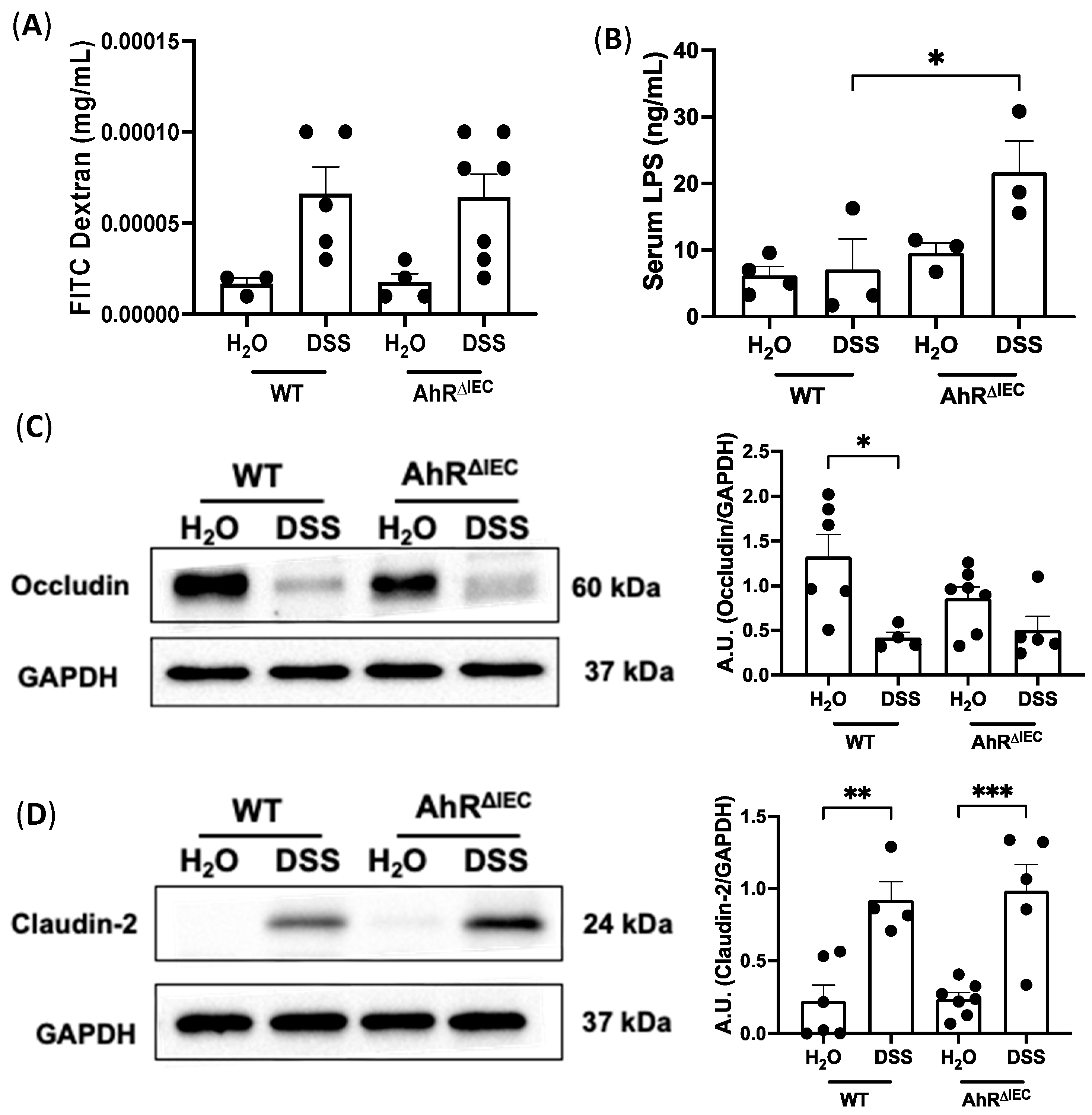
3.4. Intestinal Permeability in AhRΔIEC Mice with and without Chronic Colitis
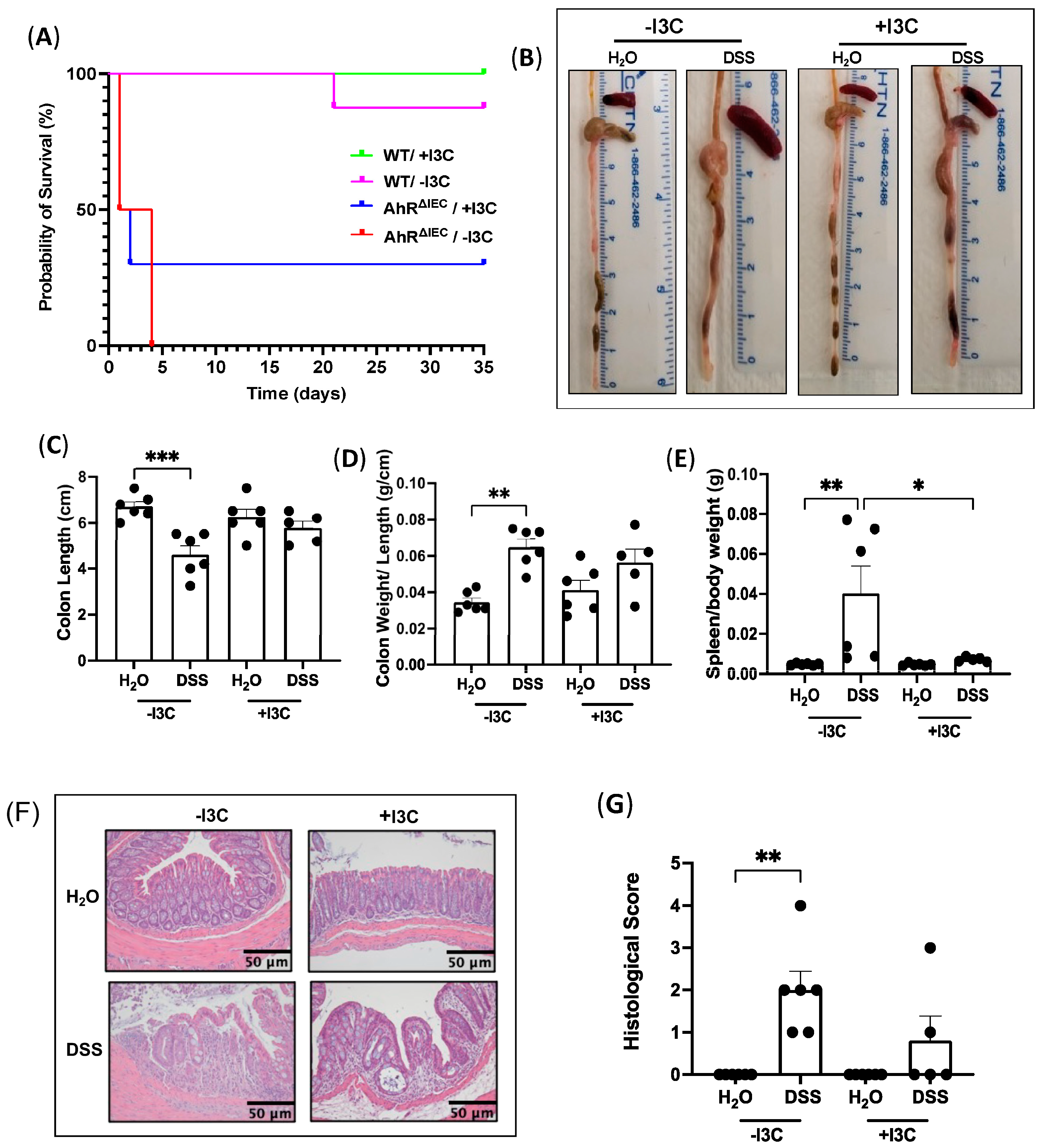
3.5. Depletion of Dietary I3C Is Fatal in AhRΔIEC Mice and Worsens Chronic Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice
3.6. Supplementation of I3C Attenuates Chronic Colitis in WT Mice
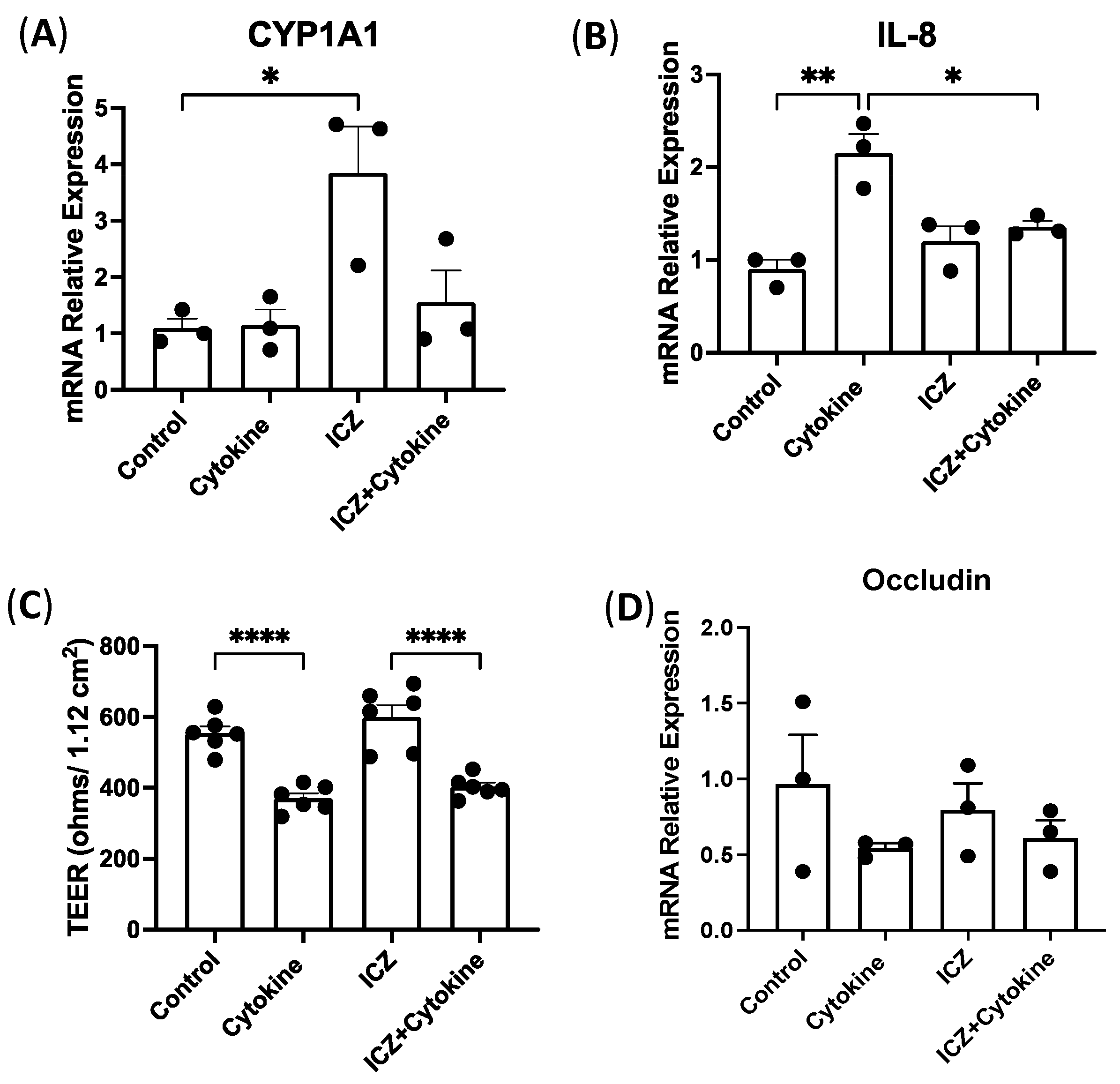
3.7. Permeability in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Treated with Cytokines and ICZ
3.8. Microbiota Analysis of C57BL/6 Mice Fed −/+I3C Diets Induced with Chronic Colitis
3.9. Supplementation of I3C Improves Paneth Cell Function in Mouse Model of Crohn’s Ileitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Q. A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7247238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, L.P.; Cross, R.K. Adverse events in IBD: To stop or continue immune suppressant and biologic treatment. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 8, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Van Sommeren, S.; Huang, H.; Ng, S.C.; Alberts, R.; Takahashi, A.; Ripke, S.; Lee, J.C.; Jostins, L.; Shah, T.; et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, I.A.; Perdew, G.H. Ligand activation of the Ah receptor contributes to gastrointestinal homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzella, C.; Singhal, M.; Alrefai, W.A.; Saksena, S.; Dudeja, P.K.; Gill, R.K. Serotonin is an endogenous regulator of intestinal CYP1A1 via AhR. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, Y.; Sujino, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Harada, Y.; Tanemoto, S.; Ono, K.; Umeda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Teratani, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signals in epithelial cells govern the recruitment and location of Helios+ Tregs in the gut. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maradana, M.R.; Delàs, M.J.; Metidji, A.; Graelmann, F.; Llorian, M.; Chakravarty, P.; Li, Y.; Tolaini, M.; Shapiro, M.; et al. Cell-intrinsic Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor signalling is required for the resolution of injury-induced colonic stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metidji, A.; Omenetti, S.; Crotta, S.; Li, Y.; Nye, E.; Ross, E.; Li, V.; Maradana, M.R.; Schiering, C.; Stockinger, B. The Environmental Sensor AHR Protects from Inflammatory Damage by Maintaining Intestinal Stem Cell Homeostasis and Barrier Integrity. Immunity 2018, 49, 353–362.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Singh, U.P.; Singh, B.; Price, R.L.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Leads to Reciprocal Epigenetic Regulation of FoxP3 and IL-17 Expression and Amelioration of Experimental Colitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Ma, J.; Tang, N.; Zhang, H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation ameliorates experimental colitis by modulating the tolerogenic dendritic and regulatory T cell formation. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettel, J.A.; Gandhi, R.; Kenison, J.E.; Yeste, A.; Murugaiyan, G.; Sambanthamoorthy, S.; Griffith, A.E.; Patel, B.; Shouval, D.S.; Weiner, H.L.; et al. AHR Activation Is Protective against Colitis Driven by T Cells in Humanized Mice. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, K.; Han, B.; Sheng, B.; Yin, J.; Pu, A.; Li, L.; Sun, L.; Yu, M.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibits inflammation in DSS-induced colitis via the MK2/p-MK2/TTP pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 41, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E. Indoles Derived From Glucobrassicin: Cancer Chemoprevention by Indole-3-Carbinol and 3,3′-Diindolylmethane. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 734334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busbee, P.B.; Menzel, L.; Alrafas, H.R.; Dopkins, N.; Becker, W.; Miranda, K.; Tang, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Singh, U.P.; Nagarkatti, M.; et al. Indole-3-carbinol prevents colitis and associated microbial dysbiosis in an IL-22–dependent manner. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, 127551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Ardiansyah; Hirahara, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Tomita, S.; Aso, H.; Komai, M.; et al. Dietary tryptophan alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 42, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Perdew, G.H. β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.N.; Panopoulos, M.; Neumann, W.L.; Turner, K.; Cantarel, B.L.; Thompson-Snipes, L.; Dassopoulos, T.; Feagins, L.A.; Souza, R.F.; Mills, J.C.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction during loss of prohibitin 1 triggers Paneth cell defects and ileitis. Gut 2020, 69, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western blot: Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela, S.M.A.; Kraïem, H.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; Bideaux, C.; Lara, C.A.A.; Fillaudeau, L. A protocol for recombinant protein quantification by densitometry. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavati, L.; Rastogi, R.; Du, W.; Hüttemann, M.; Fite, A.; Franchi, L. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.-M.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, X.-D.; Du, S.-Y. CTGF-mediated ERK signaling pathway influences the inflammatory factors and intestinal flora in ulcerative colitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, T.T.; Pastorelli, L.; Bamias, G.; Garg, R.R.; Reuter, B.K.; Mercado, J.R.; Chieppa, M.; Arseneau, K.O.; Ley, K.; Cominelli, F. SAMP1/YitFc mouse strain: A spontaneous model of Crohn’s disease-like ileitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 2566–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyhlidal, C.A.; Chapron, B.D.; Ahmed, A.; Singh, V.; Casini, R.; Shakhnovich, V. Effect of Crohn’s Disease on Villous Length and CYP3A4 Expression in the Pediatric Small Intestine. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 14, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaian, M.T.; Page, K.M.; Fish, S.; Brennan, A.; Cook, T.A.; Moreira, K.; Zhang, M.; Jesson, M.; Marquette, K.; Agostinelli, R.; et al. Therapeutic activity of an interleukin-4/interleukin-13 dual antagonist on oxazolone-induced colitis in mice. Immunology 2014, 143, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campmans-Kuijpers, M.J.E.; Dijkstra, G. Food and Food Groups in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): The Design of the Groningen Anti-Inflammatory Diet (GrAID). Nutrients 2021, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manresa, M.C.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Harnoss, J.M.; Brown, E.; Cavadas, M.A.; Keogh, C.E.; Cheong, A.; Barrett, K.E.; Cummins, E.P.; et al. Hydroxylase inhibition regulates inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis through the suppression of ERK-mediated TGF-β1 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G1076–G1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfogliarini, C.; Pepe, G.; Dolce, A.; Della Torre, S.; Cesta, M.C.; Allegretti, M.; Locati, M.; Vegeto, E. Tamoxifen Twists Again: On and Off-Targets in Macrophages and Infections. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 879020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdú, E.F.; Deng, Y.; Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M. Modulatory effects of estrogen in two murine models of experimental colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G27–G36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polari, L.; Anttila, S.; Helenius, T.; Wiklund, A.; Linnanen, T.; Toivola, D.M.; Määttä, J. Novel Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator Ameliorates Murine Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Xu, P.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation Modulates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function by Maintaining Tight Junction Integrity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.A.; Fu, J.; Chang, P.V. Microbial tryptophan metabolites regulate gut barrier function via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19376–19387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postal, B.G.; Ghezzal, S.; Aguanno, D.; André, S.; Garbin, K.; Genser, L.; Brot-Laroche, E.; Poitou, C.; Soula, H.; Leturque, A.; et al. AhR activation defends gut barrier integrity against damage occurring in obesity. Mol. Metab. 2020, 39, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavel, T.; Charrier, C.; Wenning, M.; Haller, D. Parvibacter caecicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium of the family Coriobacteriaceae isolated from the caecum of a mouse. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, E.-J.; Hwang, W.-B.; Kim, D.-J. Indole-3-Carbinol Promotes Goblet-Cell Differentiation Regulating Wnt and Notch Signaling Pathways AhR-Dependently. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Reina-Campos, M.; Nakanishi, N.; Llado, V.; Elmen, L.; Peterson, S.; Campos, A.; De, S.K.; Leitges, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; et al. Control of Paneth Cell Fate, Intestinal Inflammation, and Tumorigenesis by PKCλ/ι. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 3297–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDussen, K.L.; Liu, T.-C.; Li, D.; Towfic, F.; Modiano, N.; Winter, R.; Haritunians, T.; Taylor, K.D.; Dhall, D.; Targan, S.R.; et al. Genetic Variants Synthesize to Produce Paneth Cell Phenotypes That Define Subtypes of Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaloian, S.; Rath, E.; Hammoudi, N.; Gleisinger, E.; Blutke, A.; Giesbertz, P.; Berger, E.; Metwaly, A.; Waldschmitt, N.; Allez, M.; et al. Mitochondrial impairment drives intestinal stem cell transition into dysfunctional Paneth cells predicting Crohn’s disease recurrence. Gut 2020, 69, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Balasubramanian, I.; Laubitz, D.; Tong, K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Lin, X.; Flores, J.; Singh, R.; Liu, Y.; Macazana, C.; et al. Paneth Cell-Derived Lysozyme Defines the Composition of Mucolytic Microbiota and the Inflammatory Tone of the Intestine. Immunity 2020, 53, 398–416.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, T.S.; Reuter, B.K.; Scott, K.G.-E.; Morris, M.A.; Wang, X.-M.; Hancock, L.N.; Burcin, T.L.; Cohn, S.M.; Ernst, P.B.; Cominelli, F.; et al. The primary defect in experimental ileitis originates from a nonhematopoietic source. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshii, A.; Yokoi, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Shinozaki, R.; Nakamura, S.; Ohira, S.; Sugimoto, R.; Ayabe, T. Paneth cell α-defensin misfolding correlates with dysbiosis and ileitis in Crohn’s disease model mice. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e201900592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanz, O.; Chijiiwa, R.; Cengiz, S.C.; Majlesain, Y.; Weighardt, H.; Takeyama, H.; Förster, I. Dietary AhR Ligands Regulate AhRR Expression in Intestinal Immune Cells and Intestinal Microbiota Composition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G. Components of the AIN-93 Diets as Improvements in the AIN-76A Diet1,2. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 838S–841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Haub, M.D. Effects of Dietary Fiber and Its Components on Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, L.; Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Bourhis, J.-M.; Béguet-Crespel, F.; Blottière, H.M.; Lapaque, N. Identification of the novel role of butyrate as AhR ligand in human intestinal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, T.; Huang, X.; Bilotta, A.J.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Pan, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linus Pauling Institute. Indole-3-Carbinol. 2014. Available online: https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/indole-3-carbinol (accessed on 24 April 2023).



| Primer | Host | Forward Sequence 5′→3′ | Reverse Sequence 5′→3′ | Amplicon Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AhR | Mouse | GGTACAAGTGCACAATGCCTGC | CAGTGGAATAAGGCAAGAGTGA | 44 bp |
| CYP1A1 | Mouse | GGGTTTGACACAGTCACAA | GGGACGAAGGATGAATGCC | 38 bp |
| CYP1A1 | Human | TCGGCCACGGAGTTTCTTC | GGTCAGCATGTGCCCAAT | 37 bp |
| CYP1B1 | Mouse | CACCAGCCTTAGTGCAGACAG | GAGGACCACGGTTTCCGTGG | 41 bp |
| AhRR | Mouse | GTGGGTTACGATGGACTCAAGG | GTCCCCTGAACAGTGAAATGC | 44 bp |
| IL-4 | Mouse | TGATGGGTCTCAGCCCCACCTTGC | CTTTCAGTGTTGTGAGCGTGGACTC | 49 bp |
| IL-8 | Human | ATGACTTCCAAGCTGGCCGTGGCT | TCTCAGCCCTCTTCAAAACTTCTC | 48 bp |
| IL-22 | Mouse | CGATCTCTGATGGCTGTCCT | ACGCAAGCATTTCTCAGAGA | 40 bp |
| IL-1β | Mouse | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAAC | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT | 42 bp |
| TNFα | Mouse | TACTGAACTTCGGGGTGATTGGTCC | CAGCCTTGTCCCTTGAAGAGAACC | 49 bp |
| IFNγ | Mouse | ATGAACGCTACACACTGCATC | CCATCCTTTTGCCACTTCCTC | 42 bp |
| CXCL2 | Mouse | CGCTGTCAATGCCTGAAGAC | ACACTCAAGCTCTGGATGTTCTT | 43 bp |
| CCL20 | Mouse | CGACTGTTGCCTCTCGTCACA | GAGGAGGTTCACAGCCCTTT | 41 bp |
| Occludin | Human | ACTTCAGGCAGCCTCGTTAC | GCCAGTTGTGTAGTCTGTCTCA | 42 bp |
| GAPDH | Mouse | TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCGA | CCTGCTTCACCACCTCTTGAT | 40 bp |
| GAPDH | Human | GAAATCCCATCACCATCTT | AAATGAGCCCCAGCCTTCT | 38 bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qazi, A.; Comiskey, S.; Calzadilla, N.; Amin, F.; Sharma, A.; Khin, E.; Holton, N.; Weber, C.R.; Saksena, S.; Kumar, A.; et al. Potential Dietary and Therapeutic Strategies Involving Indole-3-Carbinole in Preclinical Models of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234980
Qazi A, Comiskey S, Calzadilla N, Amin F, Sharma A, Khin E, Holton N, Weber CR, Saksena S, Kumar A, et al. Potential Dietary and Therapeutic Strategies Involving Indole-3-Carbinole in Preclinical Models of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234980
Chicago/Turabian StyleQazi, Aisha, Shane Comiskey, Nathan Calzadilla, Fatimah Amin, Anchal Sharma, Ei Khin, Nathaniel Holton, Christopher R. Weber, Seema Saksena, Anoop Kumar, and et al. 2023. "Potential Dietary and Therapeutic Strategies Involving Indole-3-Carbinole in Preclinical Models of Intestinal Inflammation" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234980
APA StyleQazi, A., Comiskey, S., Calzadilla, N., Amin, F., Sharma, A., Khin, E., Holton, N., Weber, C. R., Saksena, S., Kumar, A., Alrefai, W. A., & Gill, R. K. (2023). Potential Dietary and Therapeutic Strategies Involving Indole-3-Carbinole in Preclinical Models of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients, 15(23), 4980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234980







