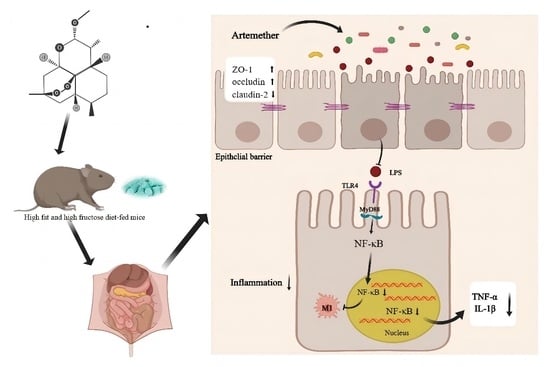
Artemether Attenuates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Intestinal Flora Imbalance in High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
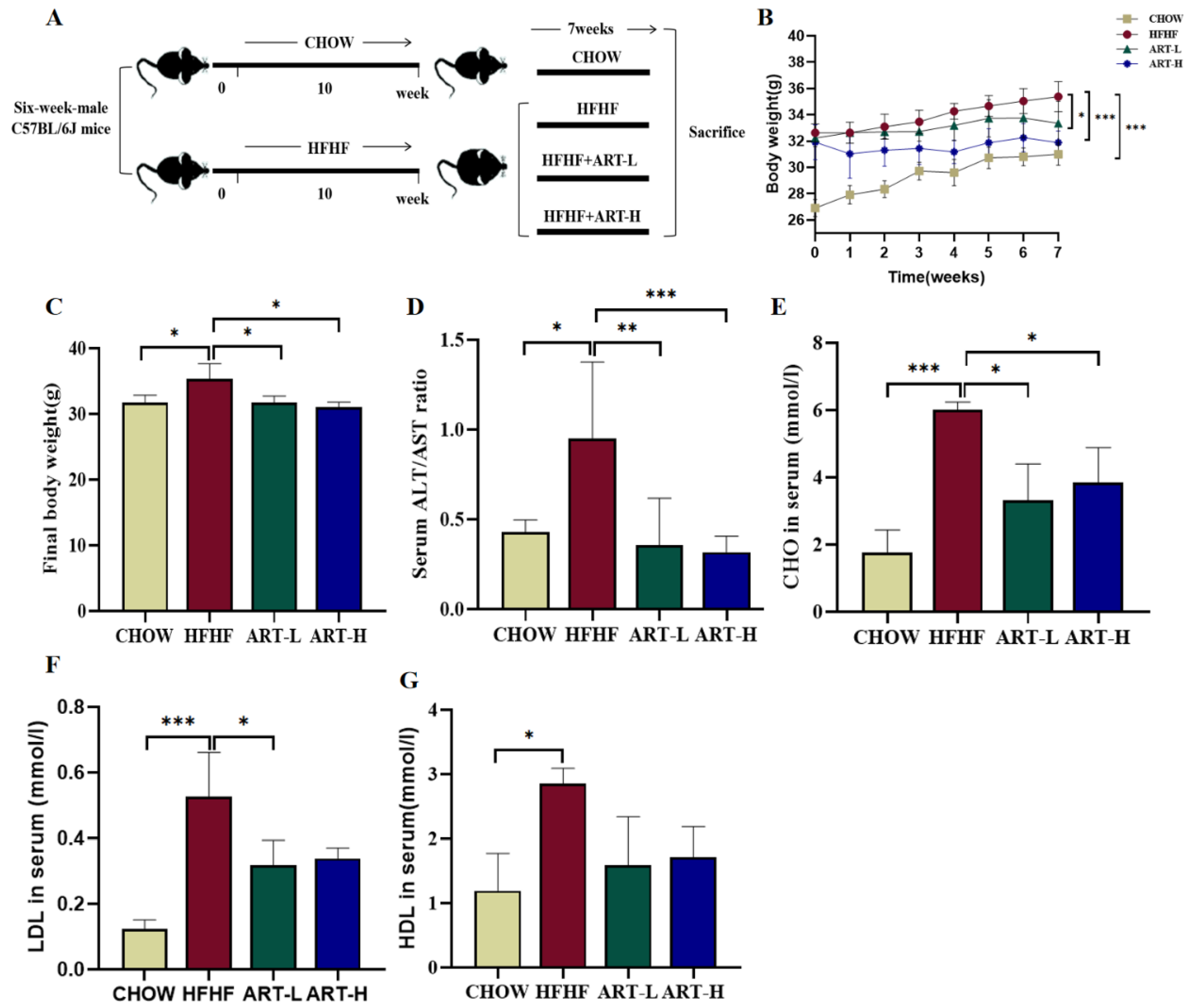
2.2. Animal Models
2.3. Determination of Serum Parameters
2.4. Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.5. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.7. Western Blotting
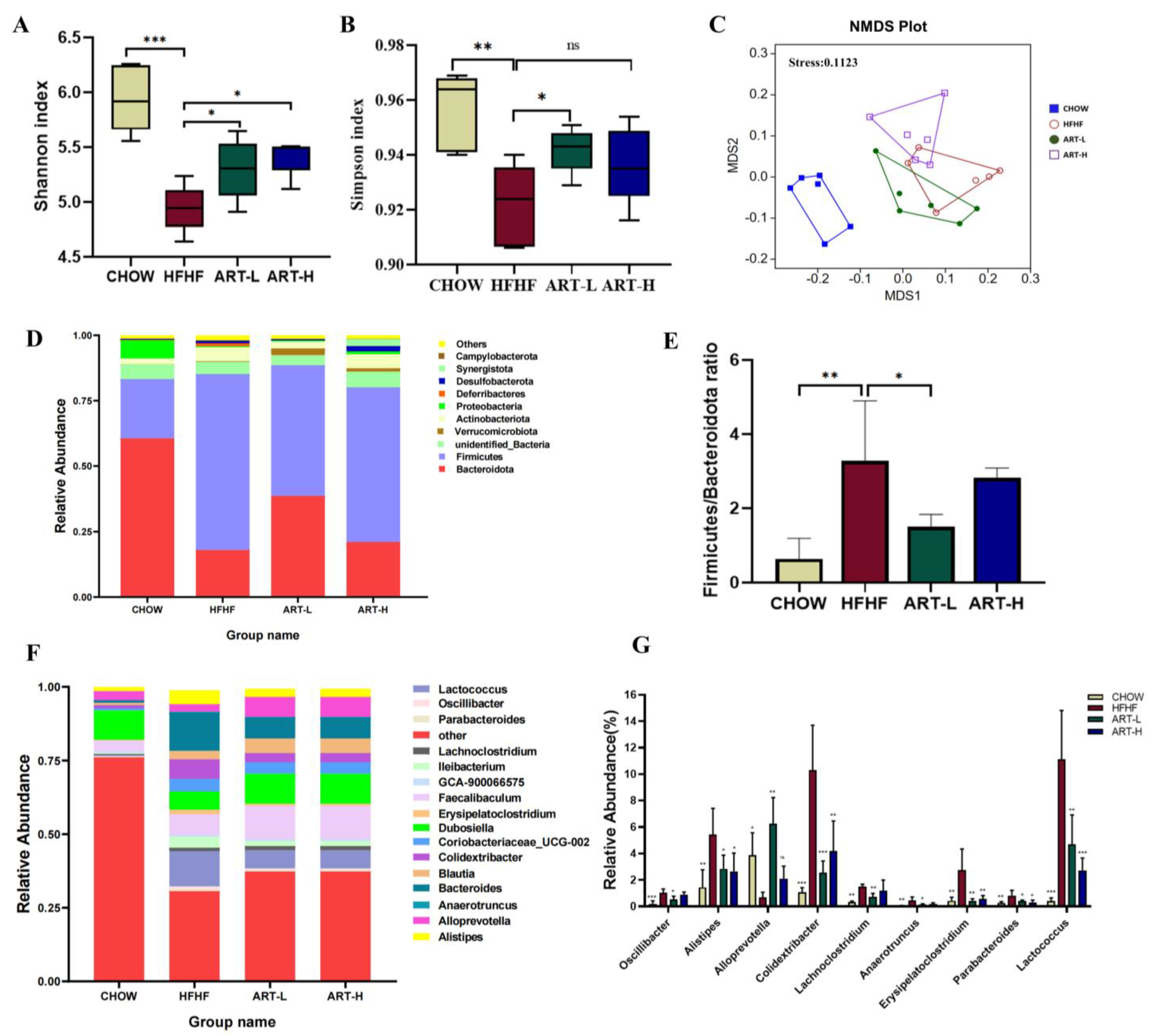
2.8. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Artemether Suppresses METABOLIC Disorders in HFHF Diet-Fed Mice
3.2. Artemether Regulates the Flora Diversity of HFHF Fed Mice
3.3. Artemether Regulates the Microbiota Composition of the HFHF Fed Mice
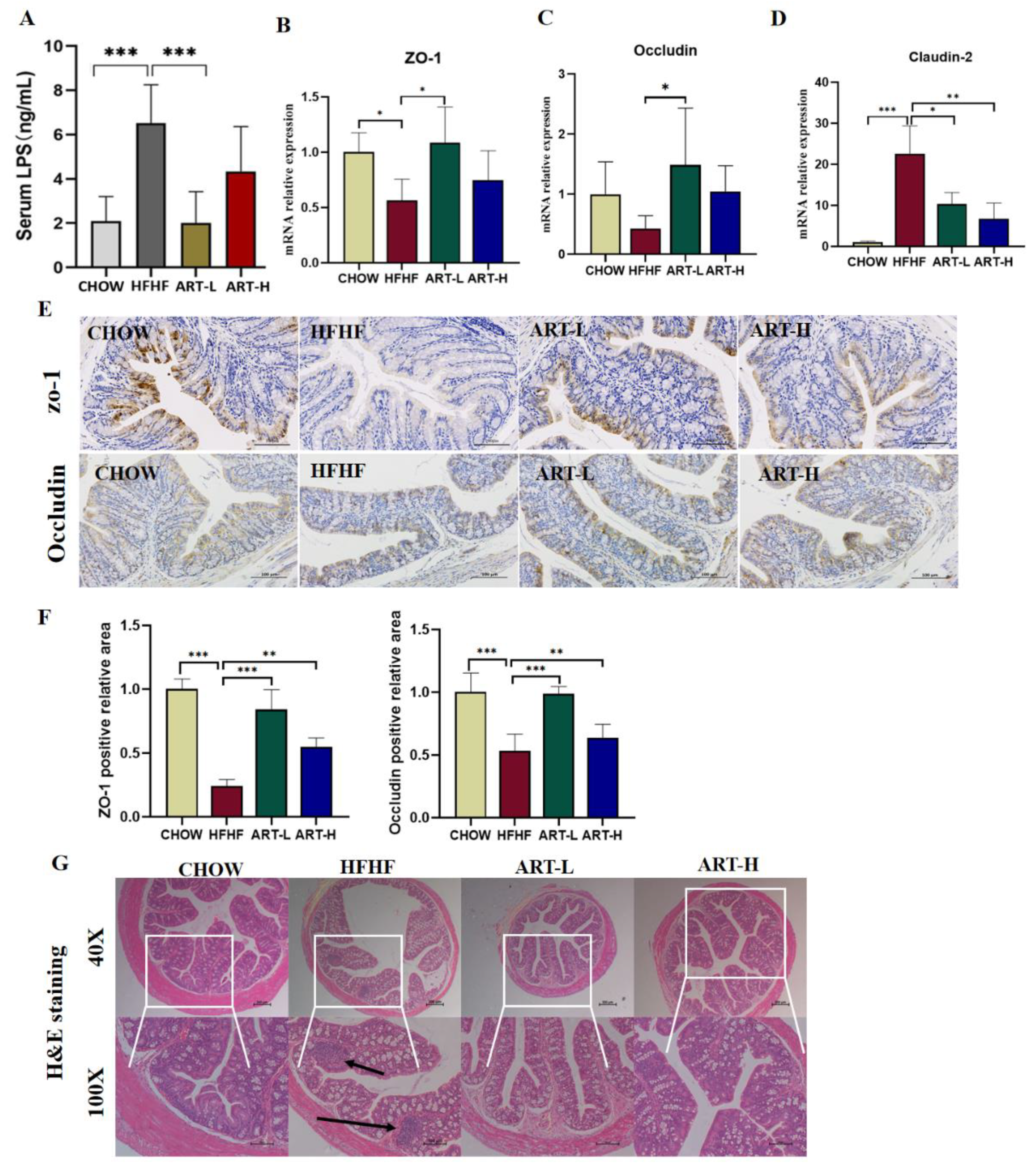
3.4. Artemether Improves Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction on HFHF-Fed Mice
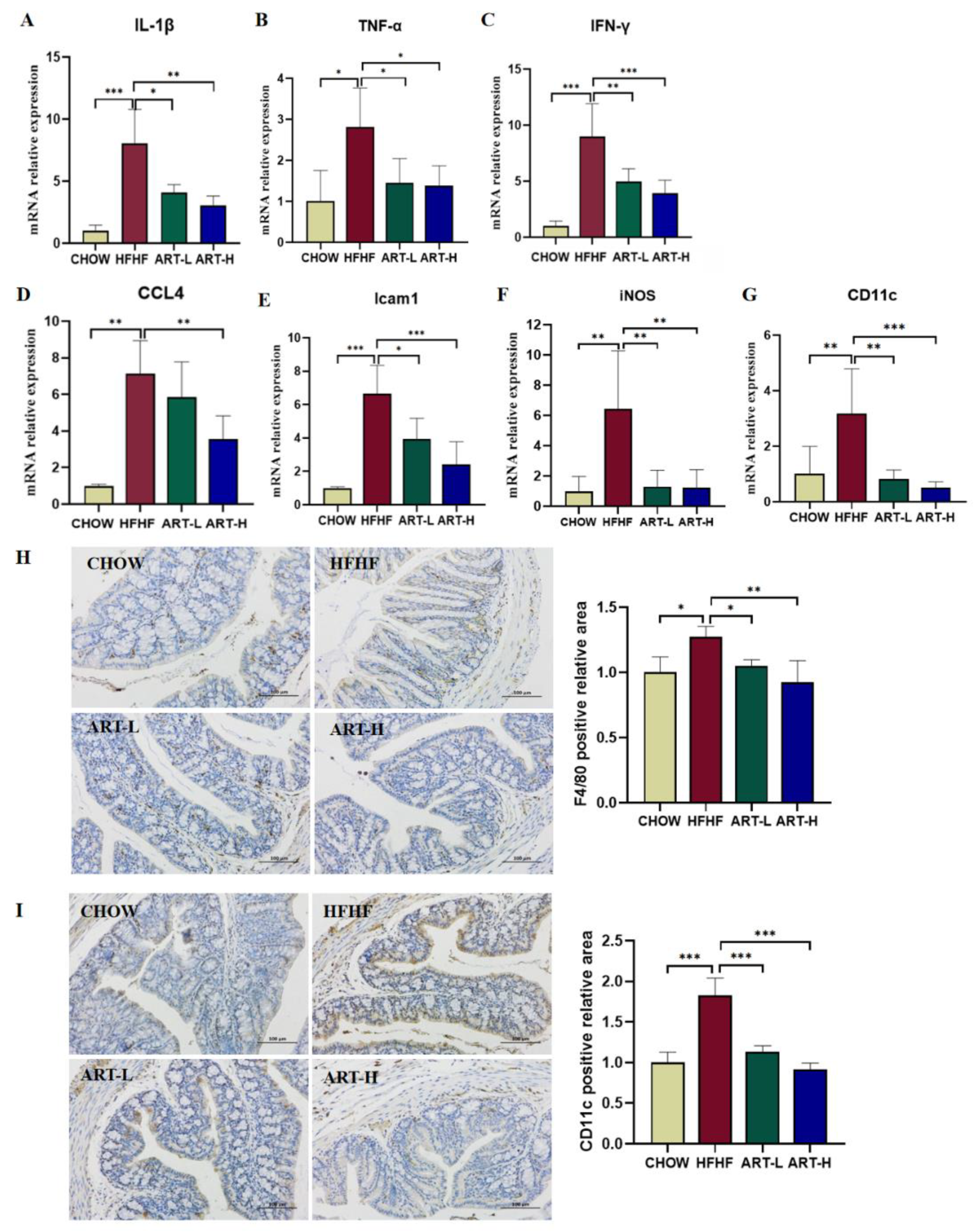
3.5. Artemether Regulates the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Factors
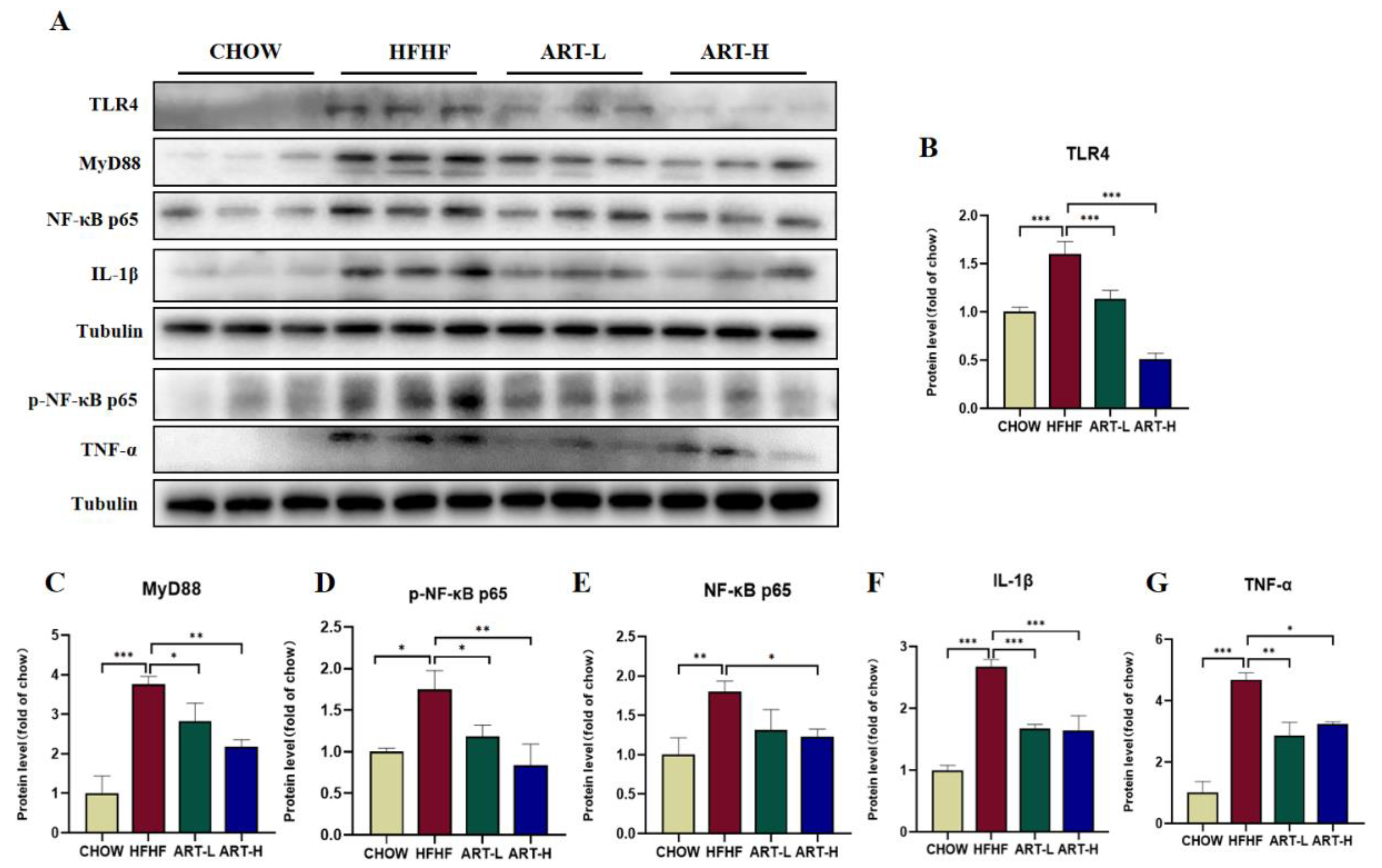
3.6. Artemether Inhibits LPS/TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Activation
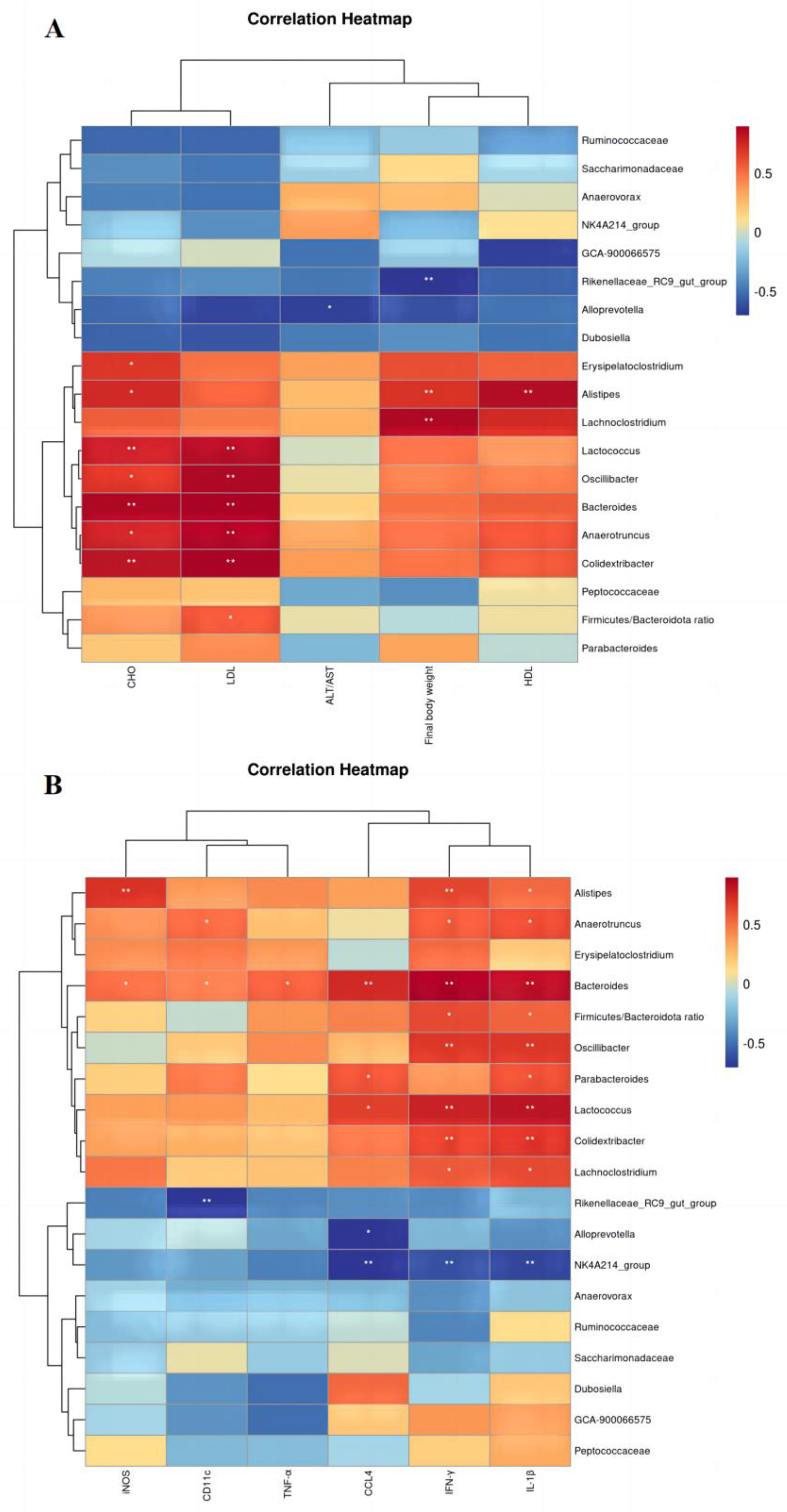
3.7. Correlation Analysis of Physical and Chemical Indicators with Intestinal Flora
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gao, X.Y.; Chang, S.L.; Liu, S.F.; Peng, L.; Xie, J.; Dong, W.M.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Correlations between alpha-Linolenic Acid-Improved Multitissue Homeostasis and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. mSystems 2020, 5, e00391-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.Y.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Twins Discordant for Obesity Modulate Metabolism in Mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, J.T.; Su, C.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.F.; Liu, S.X. Phenolics from noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit alleviate obesity in high fat diet-fed mice via modulating the gut microbiota and mitigating intestinal damage. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Blagih, J.; Zani, F.; Rees, A.; Hill, D.G.; Jenkins, B.J.; Bull, C.J.; Moreira, D.; Bantan, A.I.M.; Cronin, J.G.; et al. Fructose reprogrammes glutamine-dependent oxidative metabolism to support LPS-induced inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Waliullah, S.; Godfrey, V.; Khan, M.A.W.; Ramachandran, R.A.; Cantarel, B.L.; Behrendt, C.; Peng, L.; Hooper, L.V.; Zaki, H. Dietary simple sugars alter microbial ecology in the gut and promote colitis in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffin, M.; Fedorak, R.; Zalasky, A.; Park, H.; Gill, A.; Agrawal, A.; Keshteli, A.; Hotte, N.; Madsen, K.L. A high-sugar diet rapidly enhances susceptibility to colitis via depletion of luminal short-chain fatty acids in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajstova, A.; Galanova, N.; Coufal, S.; Malkova, J.; Kostovcik, M.; Cermakova, M.; Pelantova, H.; Kuzma, M.; Sediva, B.; Hudcovic, T.; et al. Diet Rich in Simple Sugars Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Response via Gut Microbiota Alteration and TLR4 Signaling. Cells 2020, 9, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.B.; Liu, H.X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, X.M.; Xia, X.D. Polysaccharides from the seeds of Gleditsia sinensis Lam. attenuate DSS-induced colitis in mice via improving gut barrier homeostasis and alleviating gut microbiota dybiosis. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; Yao, L.L.; Meng, T.Y.; Li, C.F.; Wang, L. Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Ait.) Hassk fruit phenolic-rich extract mitigates intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation in mice. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zeng, Y.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lepp, D.; Tsao, R.; Sadakiyo, T.; Zhang, H.; Mine, Y. Regulatory Effect of Isomaltodextrin on a High-Fat Diet Mouse Model with LPS-Induced Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11258–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.E.; Kim, D.K.; Seo, W.; Gao, B.; Yoo, S.H.; Song, B.J. Fructose Promotes Leaky Gut, Endotoxemia, and Liver Fibrosis Through Ethanol-Inducible Cytochrome P450–2E1-Mediated Oxidative and Nitrative Stress. Hepatology 2021, 73, 2180–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Xu, X.Y.; Tang, G.Y.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Dietary plants, gut microbiota, and obesity: Effects and mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.A.; Hennet, T. Mechanisms and consequences of intestinal dysbiosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2959–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, H.-M.; Jiang, W.-D.; Feng, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.-Q. Dietary nucleotides in the diets of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) suppress Aeromonas hydrophila induced intestinal inflammation and enhance intestinal disease-resistance via NF-κB and TOR signaling. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, H.S.; Dong, Y.J.; Zhou, F.C.; Cheng, B.B.; Li, L.Z.; Xu, W.F.; Su, J.; et al. Ganluyin ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the enteric-origin LPS/TLR4/NF-cB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 289, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Del Bo, C.; Marino, M.; Gargari, G.; Cherubini, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Hidalgo-Liberona, N.; Peron, G.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Kroon, P.; et al. Polyphenols and Intestinal Permeability: Rationale and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Bai, A.P. Advances in treatment of ulcerative colitis with herbs: From bench to bedside. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14099–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klayman, D.L. Qinghaosu (Artemisinin)—An Antimalarial Drug from China. Science 1985, 228, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, X.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Zhang, F.; Ren, X.X.; Asakiya, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.L. Artemether Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Repressing Lipogenesis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 851342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, T.H.; DiBaise, J.K.; McClain, C.J. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, obesity-induced inflammation, and liver injury. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 14S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegatheesan, P.; Beutheu, S.; Freese, K.; Waligora-Dupriet, A.J.; Nubret, E.; Butel, M.J.; Bergheim, I.; De Bandt, J.P. Preventive effects of citrulline on Western diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Huangfu, B.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, R.; Huang, K.; He, X. Sulforaphane Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet via LPS/TLR4 in the Gut-Liver Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.N.; Wakita, D.; Franklin, M.K.; Carvalho, T.T.; Abolhesn, A.; Gomez, A.C.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chen, S.; Lehman, T.J.; Sato, K.; et al. Intestinal Permeability and IgA Provoke Immune Vasculitis Linked to Cardiovascular Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 508–521.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Chen, J. A polysaccharide from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation in mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.M.; Geng, Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Cai, M.; Neng, J.; Hu, J.N.; Xia, D.Z.; Cao, W.L.; Yang, K.; Sun, P.L. Ferulic acid improves intestinal barrier function through altering gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet-induced mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3767–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Zmora, N.; Adolph, T.E.; Elinav, E. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Huan, T.; Rahman, G.; Zhi, H.; Xu, Z.; Oh, T.G.; Guo, J.; Coulter, S.; Tripathi, A.; Martino, C.; et al. Paired microbiome and metabolome analyses associate bile acid changes with colorectal cancer progression. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Dopico, T.; Fleming, A.; Dennison, T.W.; Ferdinand, J.R.; Harcourt, K.; Stewart, B.J.; Cader, Z.; Tuong, Z.K.; Jing, C.Z.; Lok, L.S.C.; et al. GM-CSF Calibrates Macrophage Defense and Wound Healing Programs during Intestinal Infection and Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Xu, X.; Liang, L. Inhibitory effect of artemether on intestinal fibrosis in mice with DSS-induced experimental colitis. Mod. Dig. Interv. 2018, 23, 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Duan, C.C.; Yang, G.; Niu, C.H.; Li, S.Y. Lactobacillus plantarum NA136 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota, improving intestinal barrier integrity, and attenuating inflammation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5273–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.X.; Wang, X.N.; Liu, P.; Wei, R.M.; Chen, W.L.; Rajani, C.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Alegado, R.; Dong, B.; Li, D.F.; et al. Distinctly altered gut microbiota in the progression of liver disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19355–19366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Yang, H.B.; Zheng, J.P.; Hu, H.M.; Zhu, T.X.; Zou, X.J.; Hu, B.F.; Liu, H.T. Poria cocos oligosaccharides ameliorate dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis mice by regulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. Food Funct. 2022, 14, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Liao, Y.-L.; Yen, G.-C. Ameliorative effect of buckwheat polysaccharides on colitis via regulation of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 227, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Xu, C.; Wu, D.; Yan, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Shao, J. Sodium houttuyfonate derived from Houttuynia cordata Thunb improves intestinal malfunction via maintaining gut microflora stability in Candida albicans overgrowth aggravated ulcerative colitis. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Mao, Y.L.; Gong, L.; Li, X.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, F.; Guo, Q.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, W.F. Dietary Supplementation With Lactobacillus plantarum Ameliorates Compromise of Growth Performance by Modulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Intestinal Dysbiosis in Broilers Under Clostridium perfringens Challenge. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 706148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Fu, X.Y.; Lin, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, N.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhu, P.P.; Guo, F.C.; Huang, F. Conjugated linoleic acid alleviates glycolipid metabolic disorders by modulating intestinal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in obese rats. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xiong, S.B.; Wu, M.C.; Li, B.; Ruan, Z.; Hu, X.B. Dietary l-tryptophan alleviated LPS-induced intestinal barrier injury by regulating tight junctions in a Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R.; Zuo, L. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalinger, M.R.; Sayoc-Becerra, A.; Santos, A.N.; Shawki, A.; Canale, V.; Krishnan, M.; Niechcial, A.; Obialo, N.; Scharl, M.; Li, J.; et al. PTPN2 Regulates Interactions Between Macrophages and Intestinal Epithelial Cells to Promote Intestinal Barrier Function. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1763–1777.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoric, J.; Di Caro, G.; Reibe, S.; Henstridge, D.C.; Green, C.R.; Vrbanac, A.; Ceteci, F.; Conche, C.; McNulty, R.; Shalapour, S.; et al. Fructose stimulated de novo lipogenesis is promoted by inflammation. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Park, H.Y. Polysaccharides: Bowel health and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Tomar, B.; Lahiri, A.; Mulay, S.R. The gut-liver-kidney axis: Novel regulator of fatty liver associated chronic kidney disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Sheng, D.; Shi, J.D.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Z.F.; Yin, Z.Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Chen, S.S.; Li, Y.J.; Gu, Y.; et al. Avicularin alleviates osteoporosis-induced implant loosening by attenuating macrophage M1 polarization via its inhibitory effect on the activation of NF-?B. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, R.B. Mechanisms of disease: Pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 3, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGGCCGGACTCGTCATAC | CCTGGCACCCAG CAC AAT |
| ZO-1 | ACCACCAACCCGAGAAGAC | CAGGAGTCATGGACGCACA |
| Occludin | TTGAAAGTCCACCTCCTTACAGA | CCGGATAAAAAGAGTACGCTGG |
| Claudin-2 | CAACTGGTGGGCTACATCCTA | CCCTTGGAAAAGCCAACCG |
| iNOS | GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA | GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC |
| CD11c | CTGGATAGCCTTTCTTCTGCTG | GCACACTGTGTCCGAACTCA |
| IFN-γ | ATGAACGCTACACACTGCATC | CCATCCTTTTGCCAGTTCCTC |
| CCL4 | TTCCTGCTGTTTCTCTTACACCT | CTGTCTGCCTCTTTTGGTCAG |
| Icam1 | GTGATGCTCAGGTATCCATCCA | CACAGTTCTCAAAGCACAGCG |
| IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| TNF-α | GACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG | TTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, K.; He, X. Artemether Attenuates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Intestinal Flora Imbalance in High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234860
Ren X, Xu J, Xu Y, Wang Q, Huang K, He X. Artemether Attenuates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Intestinal Flora Imbalance in High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234860
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xinxin, Jia Xu, Ye Xu, Qin Wang, Kunlun Huang, and Xiaoyun He. 2023. "Artemether Attenuates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Intestinal Flora Imbalance in High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234860
APA StyleRen, X., Xu, J., Xu, Y., Wang, Q., Huang, K., & He, X. (2023). Artemether Attenuates Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Intestinal Flora Imbalance in High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice. Nutrients, 15(23), 4860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234860