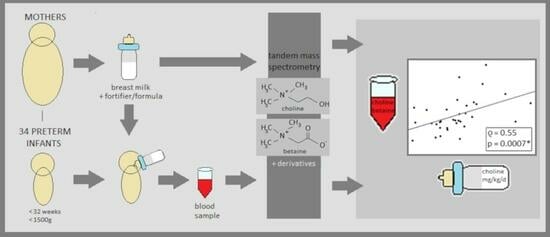
Choline and Betaine Levels in Plasma Mirror Choline Intake in Very Preterm Infants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design (Secondary Analysis)
2.3. Chemical Analysis
- Chemicals:
- Extraction:
2.3.1. Breast Milk Samples
Sample Collection
Sample Extraction
2.3.2. Plasma Samples
Sample Collection
Sample Extraction
2.3.3. Analysis of Breast Milk and Plasma Samples
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Choline Content of the Multicomponent Fortifiers and Preterm Formula and Calculation of Total Enteral Choline Intake
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
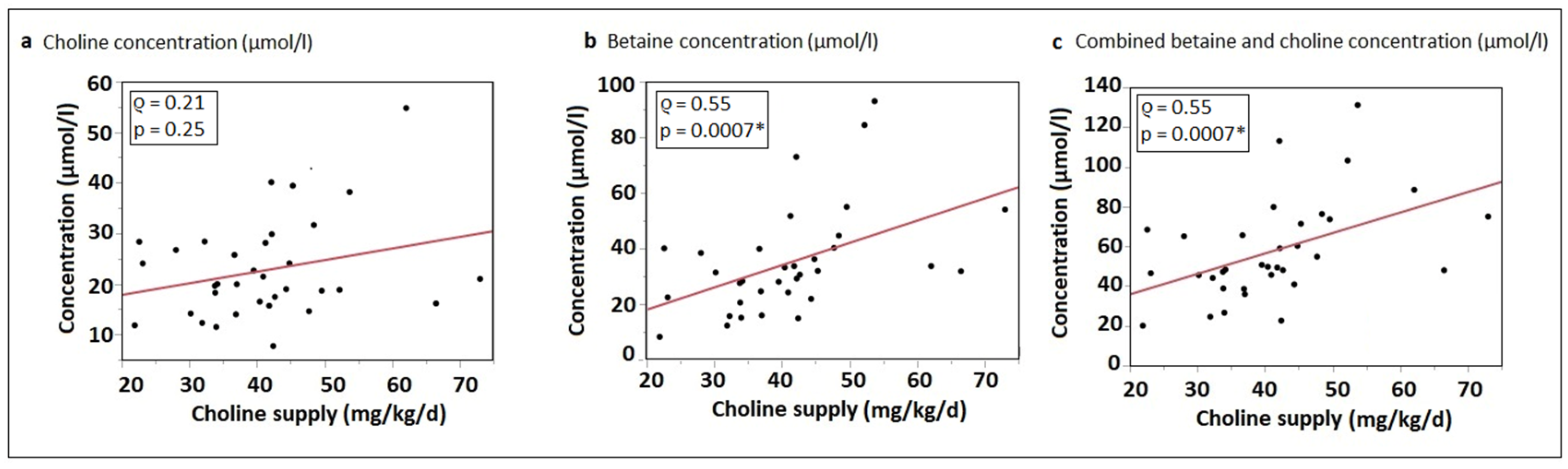
3.2. Choline Supply
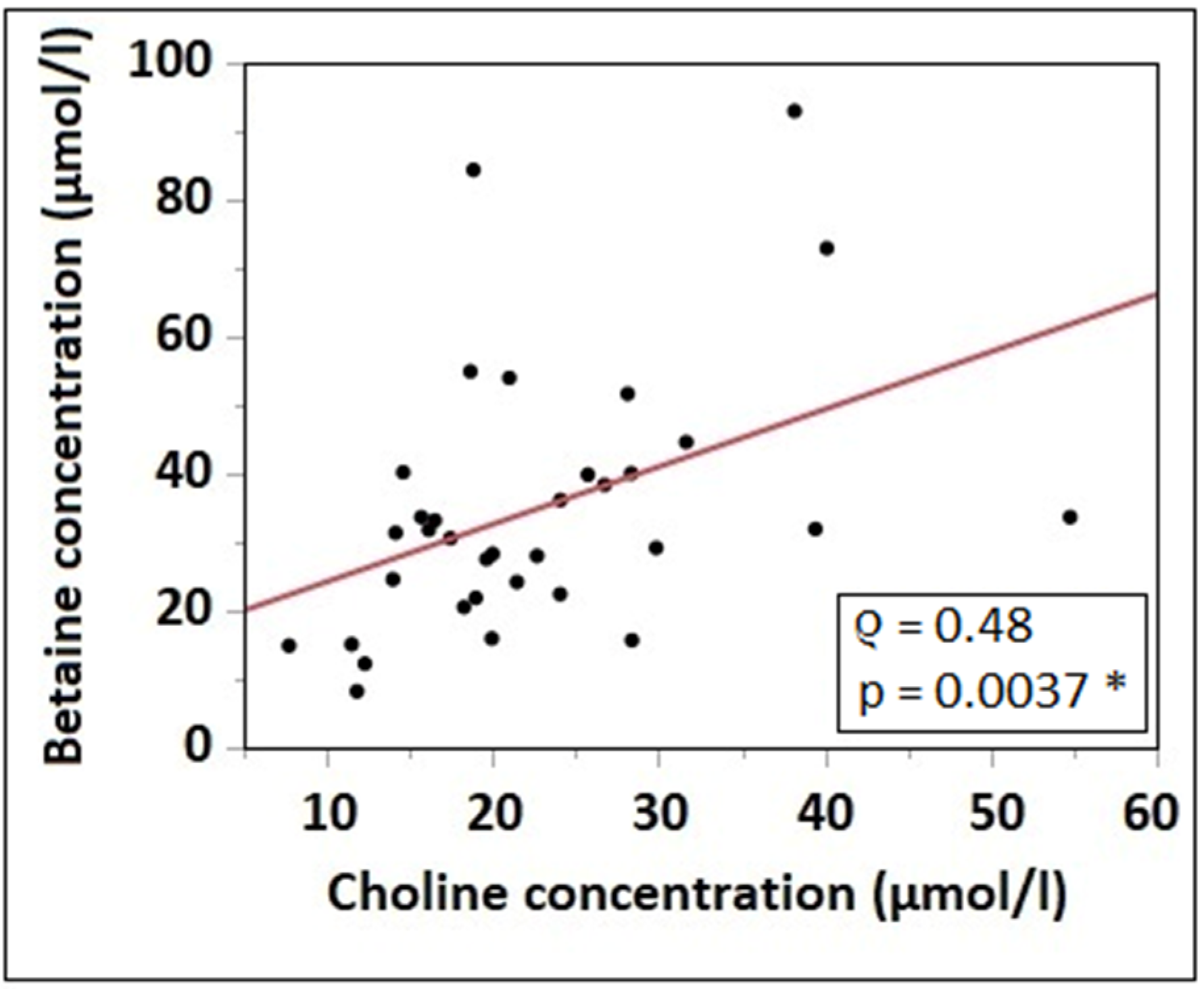
3.3. Plasma Concentrations of Choline, Betaine and Choline Compounds
3.4. Correlation of Choline Intake with Water-Soluble Choline Components and Betaine Plasma Concentrations
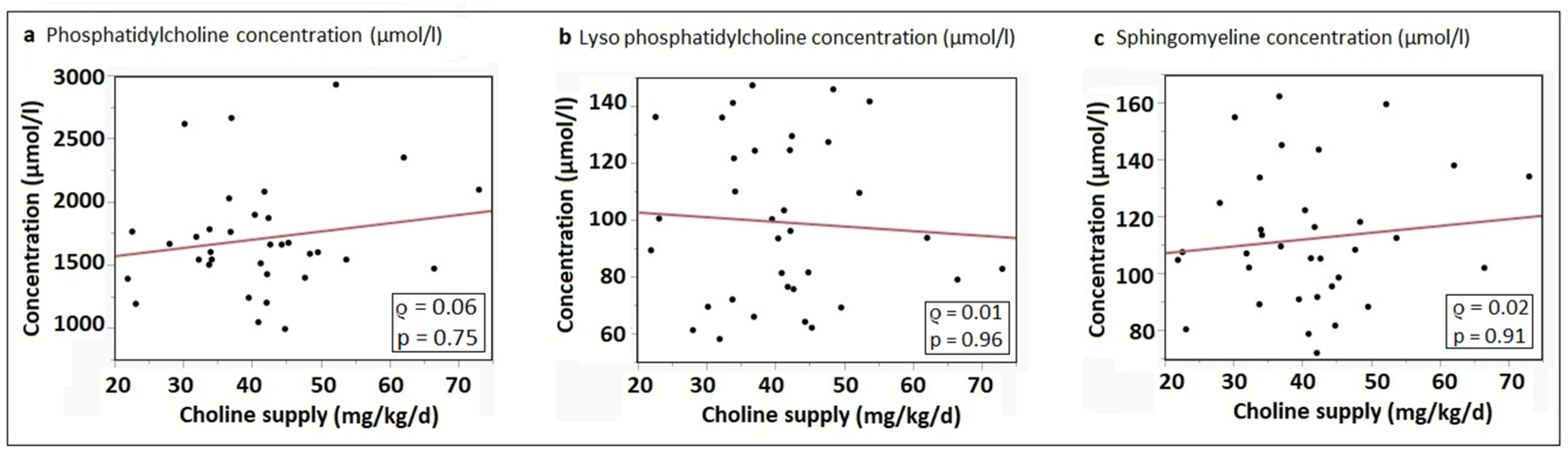
3.5. Correlation of Choline Intake with Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenberger, N.J.; Isselbacher, K.J. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine; Fauci, A., Braunwald, E., Isselbacher, K.J., Wilson, J.D., Martin, J.B., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1725–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline: Critical role during fetal development and dietary requirements in adults. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, J.M.; Schambra, U.B. Morphogenetic roles of acetylcholine. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. 1), 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshida, K.; Shimizu, T.; Takase, M.; Tamura, Y.; Yamashiro, Y. Effects of dietary sphingomyelin on central nervous system myelination in developing rats. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.C.; Zeisel, S.H.; Mar, M.H.; Sadler, T.W. Inhibitors of choline uptake and metabolism cause developmental abnormalities in neurulating mouse embryos. Teratology 2001, 64, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meck, W.H.; Williams, C.L. Characterization of the facilitative effects of perinatal choline supplementation on timing and temporal memory. Neuroreport 1997, 8, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jiang, X.; West, A.A.; Perry, C.A.; Malysheva, O.V.; Devapatla, S.; Pressman, E.; Vermeylen, F.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; et al. Maternal choline intake modulates maternal and fetal biomarkers of choline metabolism in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pynn, C.J.; Henderson, N.G.; Clark, H.; Koster, G.; Bernhard, W.; Postle, A.D. Specificity and rate of human and mouse liver and plasma phosphatidylcholine synthesis analyzed in vivo. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockler, S.; Isbrandt, D.; Hanefeld, F.; Schmidt, B.; von Figura, K. Guanidinoacetate methyltransferase deficiency: The first inborn error of creatine metabolism in man. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 58, 914–922. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, W.; Raith, M.; Kunze, R.; Koch, V.; Heni, M.; Maas, C.; Abele, H.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline concentrations are lower in postnatal plasma of preterm infants than in cord plasma. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, N.a.A.N. Dietary Reference Values for choline. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline and choline-related nutrients in regular and preterm infant growth. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, J.T.; Dehner, L.P.; Husain, A.N. Means and standard deviations of weights and measurements of lifeborn infants by body weight. In Stocker and Dehner’s Pediatric Pathology, 2nd ed.; Stocker, J.T., Dehner, L.P., Eds.; Lippinkott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 1302–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, E.E.; O’Donnell, A.M.; Nelson, S.E.; Fomon, S.J. Body composition of the reference fetus. Growth 1976, 40, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sweiry, J.H.; Yudilevich, D.L. Characterization of choline transport at maternal and fetal interfaces of the perfused guinea-pig placenta. J. Physiol. 1985, 366, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassl, S.M. Choline transport in human placental brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1194, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarda Ilcol, Y.; Uncu, G.; Ulus, I.H. Free and phospholipid-bound choline concentrations in serum during pregnancy, after delivery and in newborns. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 110, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resseguie, M.; Song, J.; Niculescu, M.D.; da Costa, K.A.; Randall, T.A.; Zeisel, S.H. Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT) gene expression is induced by estrogen in human and mouse primary hepatocytes. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, K.E.; Farrell, P.M. Measurement of free choline concentrations in maternal and neonatal blood by micropyrolysis gas chromatography. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1985, 149, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudill, M.A. Pre- and postnatal health: Evidence of increased choline needs. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jiang, X.; West, A.A.; Perry, C.A.; Malysheva, O.V.; Brenna, J.T.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; Gregory, J.F., 3rd; Caudill, M.A. Pregnancy alters choline dynamics: Results of a randomized trial using stable isotope methodology in pregnant and nonpregnant women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.M.; da Costa, K.A.; Galanko, J.; Sha, W.; Stephenson, B.; Vick, J.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline intake and genetic polymorphisms influence choline metabolite concentrations in human breast milk and plasma. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Full, A.; Arand, J.; Maas, C.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline supply of preterm infants: Assessment of dietary intake and pathophysiological considerations. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Koppen, A.; Loffelholz, K. Small rises in plasma choline reverse the negative arteriovenous difference of brain choline. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Raith, M.; Shunova, A.; Lorenz, S.; Bockmann, K.; Minarski, M.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline Kinetics in Neonatal Liver, Brain and Lung-Lessons from a Rodent Model for Neonatal Care. Nutrients 2022, 14, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Vance, D.E. Choline redistribution during adaptation to choline deprivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10283–10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, C.; Franz, A.R.; Shunova, A.; Mathes, M.; Bleeker, C.; Poets, C.F.; Schleicher, E.; Bernhard, W. Choline and polyunsaturated fatty acids in preterm infants’ maternal milk. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, C.; Yan, J.; Taesuwan, S.; Shields, K.; West, A.A.; Jiang, X.; Perry, C.A.; Malysheva, O.V.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; et al. Choline intakes exceeding recommendations during human lactation improve breast milk choline content by increasing PEMT pathway metabolites. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, C.; Mathes, M.; Bleeker, C.; Vek, J.; Bernhard, W.; Wiechers, C.; Peter, A.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Effect of Increased Enteral Protein Intake on Growth in Human Milk-Fed Preterm Infants: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Char, D.; Sheard, N.F. Choline, phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin in human and bovine milk and infant formulas. J. Nutr. 1986, 116, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Raith, M.; Koch, V.; Kunze, R.; Maas, C.; Abele, H.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Plasma phospholipids indicate impaired fatty acid homeostasis in preterm infants. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1533–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shunova, A.; Bockmann, K.A.; Minarski, M.; Franz, A.R.; Wiechers, C.; Poets, C.F.; Bernhard, W. Choline Content of Term and Preterm Infant Formulae Compared to Expressed Breast Milk-How Do We Justify the Discrepancies? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Raith, M.; Koch, V.; Maas, C.; Abele, H.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Developmental changes in polyunsaturated fetal plasma phospholipids and feto-maternal plasma phospholipid ratios and their association with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Bockmann, K.; Maas, C.; Mathes, M.; Hovelmann, J.; Shunova, A.; Hund, V.; Schleicher, E.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Combined choline and DHA supplementation: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Lange, R.; Graepler-Mainka, U.; Engel, C.; Machann, J.; Hund, V.; Shunova, A.; Hector, A.; Riethmuller, J. Choline Supplementation in Cystic Fibrosis-The Metabolic and Clinical Impact. Nutrients 2019, 11, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, R. The metabolic burden of methyl donor deficiency with focus on the betaine homocysteine methyltransferase pathway. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3481–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellott, T.J.; Williams, C.L.; Meck, W.H.; Blusztajn, J.K. Prenatal choline supplementation advances hippocampal development and enhances MAPK and CREB activation. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guo-Ross, S.; Lewis, D.V.; Turner, D.; White, A.M.; Wilson, W.A.; Swartzwelder, H.S. Dietary prenatal choline supplementation alters postnatal hippocampal structure and function. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockmann, K.A.; Bernhard, W.; Minarski, M.; Shunova, A.; Wiechers, C.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline supplementation for preterm infants: Metabolism of four Deuterium-labeled choline compounds. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockmann, K.A.; Franz, A.R.; Minarski, M.; Shunova, A.; Maiwald, C.A.; Schwarz, J.; Gross, M.; Poets, C.F.; Bernhard, W. Differential metabolism of choline supplements in adult volunteers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 61, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W. Choline in cystic fibrosis: Relations to pancreas insufficiency, enterohepatic cycle, PEMT and intestinal microbiota. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1737–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellof, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamatschek, C.; Yousuf, E.I.; Mollers, L.S.; So, H.Y.; Morrison, K.M.; Fusch, C.; Rochow, N. Fat and Fat-Free Mass of Preterm and Term Infants from Birth to Six Months: A Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romberg, J.; Wilke, M.; Allgaier, C.; Nagele, T.; Engel, C.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A. MRI-based brain volumes of preterm infants at term: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Childhood. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022, 107, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechers, C.; Avellina, V.; Luger, B.; Bockmann, K.; Minarski, M.; Maas, C.; Bernhard, W.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Body Composition of Preterm Infants following Rapid Transition to Enteral Feeding. Neonatology 2022, 119, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.T.; Dyer, R.A.; King, D.J.; Richardson, K.J.; Innis, S.M. Early second trimester maternal plasma choline and betaine are related to measures of early cognitive development in term infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Choline Equivalent Content * | Administered Choline at Standard Full Feeds (150 mL/kg/d) | |
|---|---|---|
| FM 85 (before 2017) (standard fortifier) | 1.40 mg/g | 10.5 mg/kg/d |
| 10.01.DE.INF (study fortifier) | 1.54 mg/g | 11.55 mg/kg/d |
| BEBA FN1 (preterm formula <1800 g) | 0.125 mg/mL | 18.75 mg/kg/d |
| Aptamil Eiweiß + (protein supplement) | 0.09 mg/g | - |
| Number of mothers | 33 |
| Number of singleton pregnancies | 26 (79%) |
| Number of infants | 34 |
| PMA at birth (weeks) | 30.21 (29.11–31.14) |
| Sex (m/f) | 19/15 |
| Birth weight (kg) | 1.18 (1.04–1.39) |
| Postnatal age at time of blood sampling (days) | 16 (14–19) |
| PMA at time of blood sampling (weeks) | 32.71 (32.04–33.57) |
| Number of infants n (%) with breast milk sample taken relative to blood sample | |
| −5 days | 1 (3%) |
| −4 days | 0 (0%) |
| −3 days | 3 (9%) |
| −2 days | 1 (3%) |
| −1 day | 9 (27%) |
| 0 day | 11 (32%) |
| +1 day | 9 (27%) |
| Compound | Choline Equivalent * (mg/L) Median (p25–p75) | Choline Administered at Full Feeds (150 mL/kg/d) | Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-soluble choline components: | 146.1 (115.1–194.3) | 21.9 mg/kg/d | 84.5 |
| Thereof: | |||
| - Free choline | 17.2 (12.8–24.4) | 2.6 mg/kg/d | |
| - Glycerophosphocholine | 65.4 (44.5–84.8) | 9.8 mg/kg/d | |
| - Phosphocholine | 67.1 (52.4–96.4) | 10.1 mg/kg/d | |
| Betaine | 0.6 (0.3–1.0) | 0.1 mg/kg/d | - |
| Lipid-soluble choline components | |||
| - Phosphatidylcholine | 20.1 (14.3–22.8) | 3.0 mg/kg/d | 11.6 |
| - Lyso-phosphatidylcholine | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 0.3 mg/kg/d | 1.2 |
| - Sphingomyelin | 4.8 (3.9–5.8) | 0.7 mg/kg/d | 2.8 |
| Compound | Plasma Concentrations (µmol/L) Median (p25–p75) | Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Water-soluble choline components: | 20.0 (16.0–28.2) µmol/L | 1.1 |
| Thereof: | ||
| - Free Choline | 18.2 (15.4–25.9) µmol/L | |
| - Glycerophosphocholine | 0.31 (0.12–0.73) µmol/L | |
| - Phosphocholine | 0.40 (0.17–0.85) µmol/L | |
| Betaine | 31.6 (22.3–40.1) µmol/L | - |
| Lipid-soluble choline components | ||
| - Phosphatidylcholine | 1630.7 (1460.2–1876.5) µmol/L | 88.0 |
| - Lyso-phosphatidylcholine | 94.9 (74.7–125.2) µmol/L | 5.1 |
| - Sphingomyelin | 107.8 (94.4–126.9) µmol/L | 5.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minarski, M.; Maas, C.; Heinrich, C.; Böckmann, K.A.; Bernhard, W.; Shunova, A.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Choline and Betaine Levels in Plasma Mirror Choline Intake in Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224758
Minarski M, Maas C, Heinrich C, Böckmann KA, Bernhard W, Shunova A, Poets CF, Franz AR. Choline and Betaine Levels in Plasma Mirror Choline Intake in Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224758
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinarski, Michaela, Christoph Maas, Christine Heinrich, Katrin A. Böckmann, Wolfgang Bernhard, Anna Shunova, Christian F. Poets, and Axel R. Franz. 2023. "Choline and Betaine Levels in Plasma Mirror Choline Intake in Very Preterm Infants" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224758
APA StyleMinarski, M., Maas, C., Heinrich, C., Böckmann, K. A., Bernhard, W., Shunova, A., Poets, C. F., & Franz, A. R. (2023). Choline and Betaine Levels in Plasma Mirror Choline Intake in Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 15(22), 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224758