Metabolic Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity: An Analysis of Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasound Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Assessment
2.3. Ultrasound (US) Assessment
2.4. Assessment of RA Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Group
3.2. Clinical Parameters of RA Activity in RA MetS (+) vs. RA MetS (−) Patients
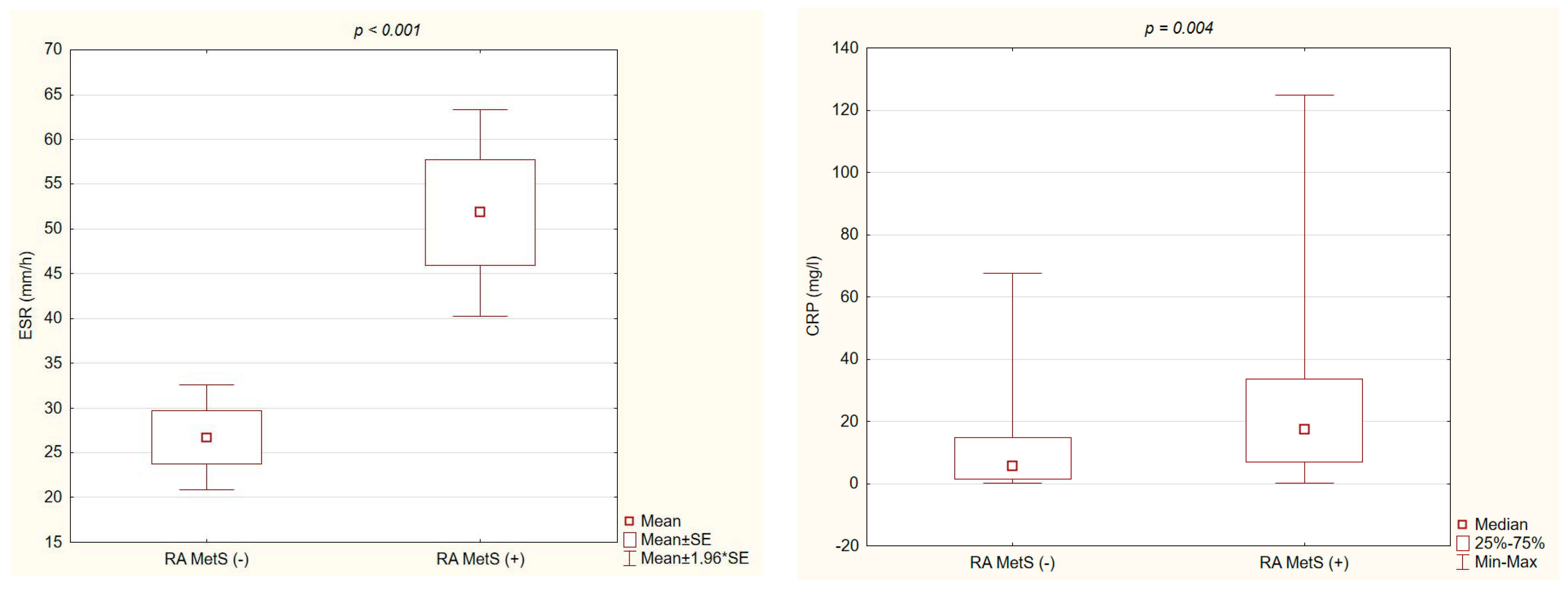
3.3. Laboratory Parameters of RA Activity in RA MetS (+) vs. RA MetS (−) Patients
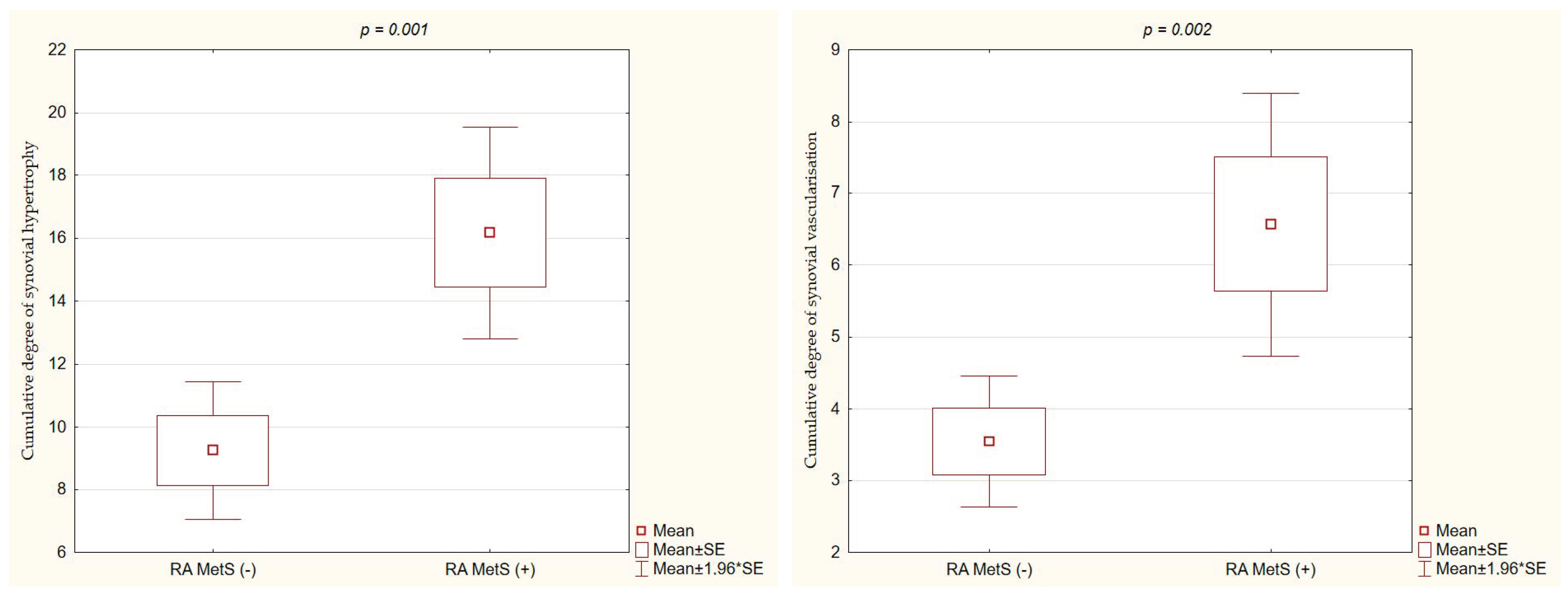
3.4. Ultrasound Parameters of RA Activity in RA MetS (+) vs. RA MetS (−) Patients
3.5. Correlations between Metabolic and RA Activity Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz-Amaro, I.; González-Juanatey, C.; López-Mejias, R.; Riancho-Zarrabeitia, L.; González-Gay, M.A. Metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 710928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, I.; Sehgal, A.; Zengin, G.; Brisc, C.; Brisc, M.C.; Munteanu, M.A.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.C.; Bungau, S. The Lipid Paradox as a Metabolic Checkpoint and Its Therapeutic Significance in Ameliorating the Associated Cardiovascular Risks in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kerekes, G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; González-Gay, M.A.; Seres, I.; Paragh, G.; Kardos, Z.; Baráth, Z.; Tamási, L.; Soltész, P.; Szekanecz, Z. Rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, M.; Cojocaru, I.; Silosi, I.; Vrabie, C.D. Metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis. Maedica 2012, 7, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hallajzadeh, J.; Safiri, S.; Mansournia, M.; Khoramdad, M.; Izadi, N.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Pakzad, R.; Ayubi, E.; Sullman, M.J.; Karamzad, N. Metabolic syndrome and its components among rheumatoid arthritis patients: A comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góralska, M.; Majewska-Szczepanik, M.; Szczepanik, M. Immunological mechanisms involved in obesity and their role in metabolic syndrome. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 1384–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Metsios, G.S.; Koutedakis, Y.; Kitas, G.D. Obesity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, R.; Fernandes, K.; Lora, P.S.; Filippin, L.I.; Xavier, R.M. Prevalence of rheumatoid cachexia in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-García, L.; Redondo-Rodríguez, R.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Domínguez-Quesada, C.; Crisóstomo Vacas, J.; Armenteros-Ortiz, P.; Ruiz-Vilchez, D.; Martín-Martín, J.M.; García-Studer, A.; Ortiz-Márquez, F.; et al. Prevalence of Malnutrition Factors in Older Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeka, S.; Dura, M.; Zuchowski, P.; Zwierko, B.; Waszczak-Jeka, M. The role of ultrasonography in the diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis and monitoring its therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.; Hock, E.; Stevenson, M.; Wong, R.; Dracup, N.; Wailoo, A.; Conaghan, P.; Estrach, C.; Edwards, C.; Wakefield, R. What is the added value of ultrasound joint examination for monitoring synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis and can it be used to guide treatment decisions? A systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2018, 22, 1–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, M.A.; Terslev, L.; Aegerter, P.; Backhaus, M.; Balint, P.; Bruyn, G.A.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W.; Iagnocco, A.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; et al. Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: A EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 1: Definition and development of a standardised, consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, M.; Burmester, G.; Gerber, T.; Grassi, W.; Machold, K.P.; Swen, W.A.; Wakefield, R.J.; Manger, B. Working Group for Musculoskeletal Utrasound in the EULAR Standing Committee on International Clinical Studies including Therapeutic Trials. Guidelines for musculoskeletal ultrasound in rheumatology. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, T.; Sokka, T.; Kautiainen, H. Further development of a physical function scale on a MDHAQ [corrected] for standard care of pjidyszatients with rheumatic diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Prevoo, M.L.; van’t Hof, M.A.; Kuper, H.H.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; van de Putte, L.B.; van Riel, P.L. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Nell, V.P.; Stamm, T.; Uffmann, M.; Pflugbeil, S.; Machold, K.; Smolen, J.S. Acute phase reactants add little to disease activity indices for rheumatoid of a clinical activity score. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Breedveld, F.C.; Schiff, M.H.; Kalden, J.R.; Emery, P.; Eberl, G.; van Riel, P.L.; Tugwell, P. A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Tang, X.; Pang, M. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med. 2022, 9, 855141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Chagollán, M.; Hernández-Martínez, S.; Rojas-Romero, A.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Sigala-Arellano, R.; Cerpa-Cruz, S.; Morales-Núñez, J.J.; Lomelí-Nieto, J.A.; Macedo Ojeda, G.; Hernández-Bello, J. Metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Relationship among its clinical components. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, A.; Aly, M.; Amer, A. Metabolic syndrome, hematological markers of inflammation and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 16, 052–058. [Google Scholar]
- Orange, D.E.; Blachere, N.E.; DiCarlo, E.F.; Mirza, S.; Pannellini, T.; Jiang, C.S.; Frank, M.O.; Parveen, S.; Figgie, M.P.; Gravallese, E.M.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Morning Stiffness Is Associated with Synovial Fibrin and Neutrophils. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.K.; Swami, A.; Biswas, T.K.; Thakuria, R. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Treatment Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis and Correlation with Disease Parameters. Arch. Rheumatol. 2016, 32, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, H.; Do, Q.; Sakamoto, J. Increased frequency of metabolic syndrome among Vietnamese women with early rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimani, S.; Abbas, A.; Ben Ammar, A.; Rahal, F.; Khider, I.; Khelif, K.; Ladjouze-Rezig, A. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Algerian rheumatoid arthritis patients. Correlation with disease activity and functional status. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononoff, A.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Hämäläinen, M.; Kautiainen, H.; Elfving, P.; Savolainen, E.; Arstila, L.; Niinisalo, H.; Rutanen, J.; Marjoniemi, O.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome, Disease Activity, and Adipokines in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Inflammatory Joint Diseases. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, e349–e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šalamon, L.; Morović-Vergles, J.; Marasović-Krstulović, D.; Kehler, T.; Šakić, D.; Badovinac, O.; Vlak, T.; Novak, S.; Štiglić-Rogoznica, N.; Hanih, M.; et al. Differences in the prevalence and characteristics of metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: A multicentric study. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, K.W.P.; Luz, A.J.P.; Felipe, M.R.B.; Beltrão, L.A.; Sampaio, A.X.C.; Rodrigues, C.E.M. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis patients from Northeastern Brazil: Association with disease activity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, J.; Protani, M.; Koh, E.T.; Leong, K.P.; Tan Tock Seng Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Study Group. Metabolic syndrome and its effect on the outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostom, S.; Mengat, M.; Lahlou, R.; Hari, A.; Bahiri, R.; Hajjaj-Hassouni, N. Metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis: Case control study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, A.; ElBakry, S.; Morad, C.; Aly, M.; Abd-El-Samie, A.M. The impact of metabolic syndrome on rheumatoid arthritis in a cohort of Egyptian patients. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2018, 40, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burli, A.P.; Dave, M. Clinical & Demographic Profile and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Correlation with Disease Activity. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, S.; Santos-Faria, D.; Leite Silva, J.; Ramos Rodrigues, J.; Sousa Neves, J.; Peixoto, D.; Tavares-Costa, J.; Alcino, S.; Afonso, C.; Teixeira, F. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and other comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis: Influence on disease activity and quality of life. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2019, 44, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirpourian, M.; Salesi, M.; Abdolahi, H.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Karimzadeh, H. The association of body mass index with disease activity and clinical response to combination therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Nemegyei, J.; Pacheco-Pantoja, E.; González-Salazar, M.; López-Villanueva, R.F.; May-Kim, S.; Martínez-Vargas, L.; Quintal-Gutiérrez, D. Association between overweight/obesity and clinical activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol. Clin. 2020, 16, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc, M.; Batmaz, I.; Sariyildiz, M.; Tahtasiz, M.; Cevik, R.; Tekbas, E.; Yildiz, I.; Celepkolu, T. The relationship of metabolic syndrome with disease activity and the functional status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2012, 4, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targońska-Stępniak, B.; Majdan, M. Associations between parameters of nutritional status and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2011, 121, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, W.H. Dyslipoproteinemia in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Effects of disease activity, sex, and menopausal status on lipid profiles. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Kononoff, A.; Elfving, P.; Pussinen, P.; Hörkkö, S.; Kautiainen, H.; Arstila, L.; Laasonen, L.; Savolainen, E.; Niinisalo, H.; Rutanen, J.; et al. Association of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and antibodies to periodontal bacteria with serum lipoprotein profile in drug naive patients. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.G.; Behl, T.; Singh, A.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Vijayabalan, S.; Das, S.; Palanimuthu, V.R. Targeting Probiotics in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Nanomedical approaches in the realm of rheumatoid arthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All RA Patients | RA MetS (+) | RA MetS (−) | p Value MetS (+) vs. MetS (−) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female/Male (n, %) | 57 (87.7) | 18 (78.3) | 39 (92.9) | NS |
| 8 (12.3) | 5 (21.7) | 3 (7.1) | ||
| Age (years) | 50.1 (±16.2) | 53.91 (±15.5) | 48.07 (±16.4) | NS |
| Height (cm) | 165.9 (±8) | 167.22 (±8.1) | 165.11 (±8) | NS |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 88.3 (±11.2) | 95.5 (±7.8) | 84.4 (±10.9) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.8 (±3.8) | 26.8 (±3.5) | 23.7 (±3.6) | 0.001 |
| TC (mg/dl) | 188.9 (±35) | 189.4 (±42.9) | 188.7 (±30.4) | NS |
| HDL-C (mg/dl) | 57.6 (±14.4) | 50.3 (±11.7) | 61.7 (±14.2) | 0.002 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | 109.6 (±29.9) | 113.8 (±34.4) | 107.4 (±27.2) | NS |
| TG (mg/dl) | 106.1 (±44.1) | 121.1 (±53.5) | 98 (±36.1) | 0.042 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 92.5 (±16.9) | 100.8 (±23) | 88.1 (±10.3) | 0.004 |
| Disease duration (months) | 147.2 (±115.8) | 169.17 (±128.9) | 135.19 (±107.7) | NS |
| ACPA (n, %) | 52 (80) | 21 (91.3) | 31 (73.8) | NS |
| RF-IgM (n, %) | 57 (87.7) | 22 (95.7) | 35 (83.3) | NS |
| Current GCS treatment (n, %) | 44 (67.7) | 16 (69.6) | 28 (66.7) | NS |
| Current MTX treatment (n, %) | 43 (66.2) | 16 (69.6) | 27 (64.3) | NS |
| Current SS treatment (n, %) | 4 (6.2) | 1 (4.4) | 3 (7.1) | NS |
| Current LEF treatment (n, %) | 5 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (11.9) | NS |
| Current antimalarial drugs treatment (n, %) | 24 (36.9) | 11 (47.8) | 13 (31) | NS |
| RA MetS (+) (n = 23) | RA MetS (−) (n = 42) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAS28 | 5.62 (±1.2) | 4.53 (±1.4) | 0.002 |
| CDAI | 25.54 (±11.3) | 18.85 (±8.8) | 0.01 |
| SDAI | 28.65 (±12.9) | 20.43 (±9.8) | 0.005 |
| TJC | 9.4 (±5.5) | 5.8 (±3.8) | 0.003 |
| SJC | 6.5 (±3.8) | 4.0 (±2.9) | 0.003 |
| Morning stiffness (minutes) | 80 (30–120) | 50 (15–60) | 0.017 |
| PGA (VAS) (mm) | 50.3 (±24.9) | 51.05 (±2.3) | NS |
| PhGA (VAS) (mm) | 46.0 (±17) | 39.6 (±17.9) | NS |
| M-HAQ | 1.4 (±0.6) | 1.1 (±0.7) | NS |
| BMI | Waist Circumference | TC | HDL-C | LDL-C | TG | Glucose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJC | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | r = 0.33 |
| p = 0.009 | |||||||
| SJC | NS | NS | r = −0.3 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.014 | |||||||
| Morning stiffness | NS | NS | NS | rs = −0.38 | NS | NS | rs = 0.33 |
| p = 0.002 | p = 0.008 | ||||||
| M-HAQ | NS | r = 0.36 | NS | NS | NS | NS | r = 0.35 |
| p = 0.003 | p = 0.005 | ||||||
| DAS28 | NS | r = 0.36 | NS | r = −0.35 | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.004 | p = 0.004 | ||||||
| SDAI | NS | NS | r = −0.33 | r = −0.31 | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.008 | p = 0.012 | ||||||
| CDAI | NS | NS | r = −0.3 | r = −0.28 | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | ||||||
| CRP | NS | r = 0.34 | NS | rs = −0.32 | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.005 | p = 0.01 | ||||||
| ESR | r = 0.3 | r = 0.45 | NS | r = −0.34 | NS | NS | NS |
| p = 0.015 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.006 |
| Waist Circumference | TC | HDL-C | Glucose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning Stiffness | NS | NS | b = −1.14 | NS |
| p = 0.01 | ||||
| M-HAQ | b = 0.02 | NS | NS | b = 0.01 |
| p = 0.02 | p = 0.02 | |||
| DAS28 | b = 0.39 | NS | b = −0.3 | NS |
| p = 0.007 | p = 0.007 | |||
| SDAI | NS | b = −0.08 | NS | NS |
| p = 0.04 | ||||
| ESR | b = 1.56 | NS | b = −0.58 | NS |
| p < 0.001 | p = 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzechnik, K.; Targońska-Stępniak, B. Metabolic Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity: An Analysis of Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasound Parameters. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224756
Grzechnik K, Targońska-Stępniak B. Metabolic Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity: An Analysis of Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasound Parameters. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224756
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzechnik, Krzysztof, and Bożena Targońska-Stępniak. 2023. "Metabolic Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity: An Analysis of Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasound Parameters" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224756
APA StyleGrzechnik, K., & Targońska-Stępniak, B. (2023). Metabolic Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity: An Analysis of Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasound Parameters. Nutrients, 15(22), 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224756








