Poor Nutritional Status during Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients without an Early Nutritional Intervention Predicts a Poor Prognosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Primary Endpoint
2.3. Evaluations of Nutrition Indices
2.4. Nutritional Intervention
2.5. Statistical Analysis
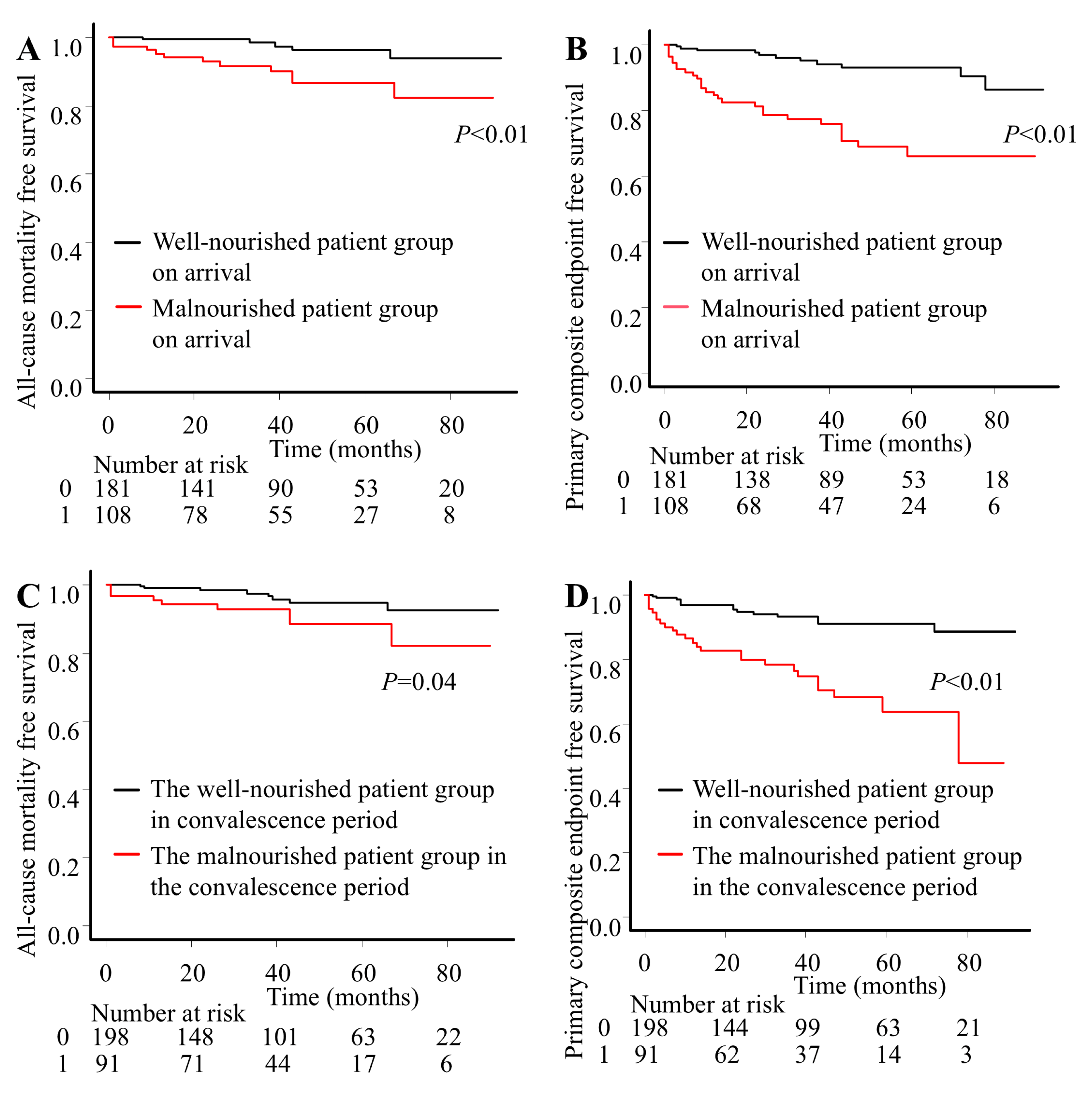
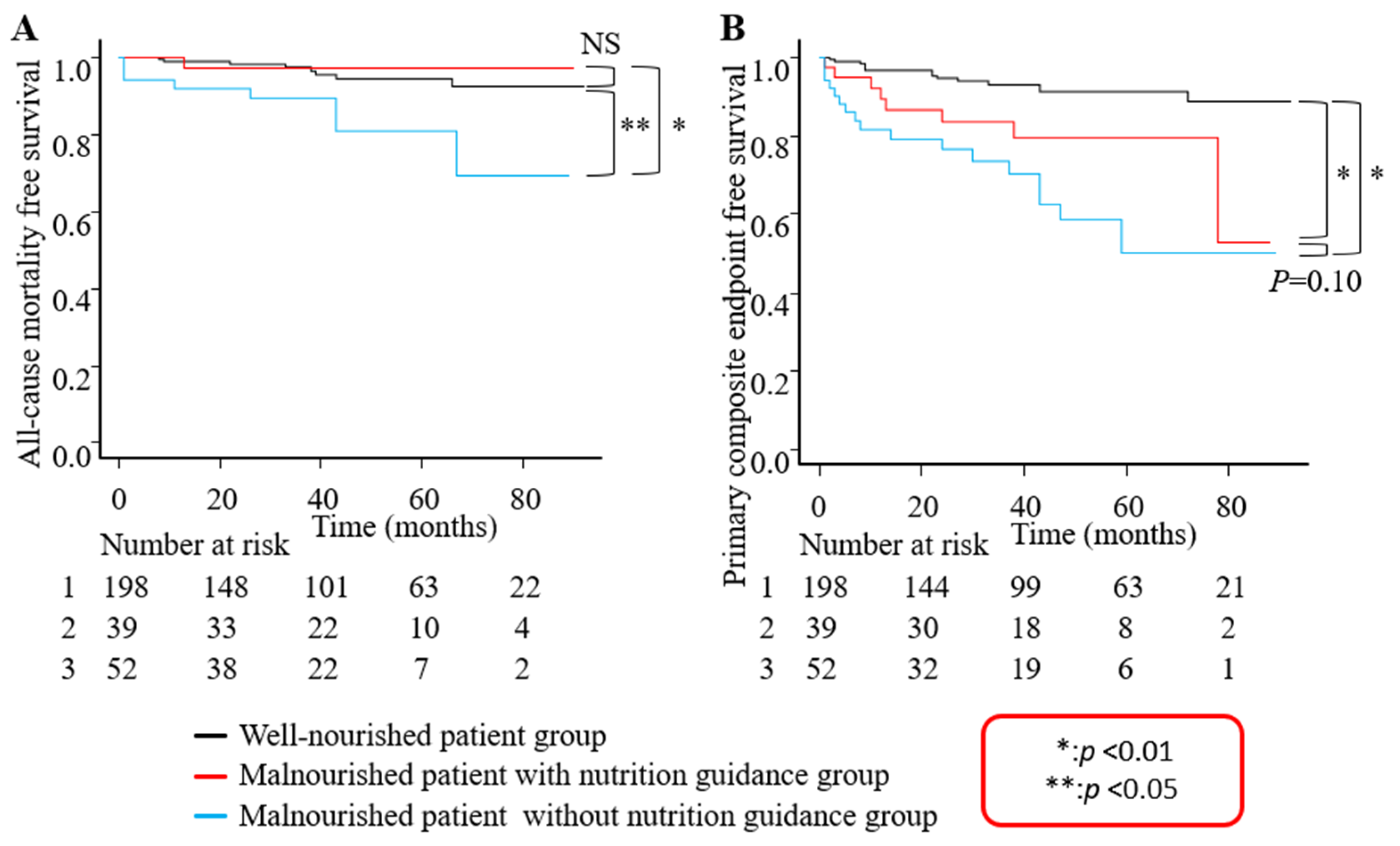
3. Results
3.1. Baseline and Procedural Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implication
4.2. Malnutrition on Convalescence Period in AMI Patients
4.3. Enteral Nutrition
4.4. Nutritional Guidance
4.5. New Directions for Future Research
4.6. Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; Task Force Members; ECG Group; Imaging Group; Intervention Group; et al. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation 2007, 116, 2634–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Choo, E.H.; Choi, I.J.; Hwang, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, S.N.; Hwang, B.H.; Kim, C.J.; Park, M.W.; Lee, J.M.; et al. Impact of the risk of malnutrition on bleeding, mortality, and ischemic events in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Haraguchi, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Ishida, T.; Momomura, S.I. Prognostic impact of malnutrition in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 2022, 37, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, K.; Koh, J.S.; Park, J.R.; Hwang, S.J.; Jeong, Y.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Park, Y.; Bae, J.S.; et al. Comparative analysis of three nutrition scores in predicting mortality after acute myocardial infarction. Nutrition 2021, 90, 111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kook, H.Y.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, Y.; Jeong, M.H. Influence of undernutrition at admission on clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.; Kang, Y.; Xiu, J.; Tu, J.; Pan, Y.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic impact of malnutrition in critical patients with acute myocardial infarction: Results from Chinese CIN cohort and American MIMIC-III database. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 890199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yuan, L.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Tao, J.; Li, W.; Zheng, R. Correlations and prognostic roles of the nutritional status and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing primary coronary intervention. Int. Heart J. 2020, 61, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Karataş, M.B.; Çanga, Y.; Durmuş, G.; Güzelburç, Ö.; Durak, F.; Emre, A. Prognostic performance of Controlling Nutritional Status score in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2022, 26, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, S.; Shen, S.; Deng, L.; Shen, L.; Qian, J.; Ge, J. Association of controlling nutritional status score with 2-year clinical outcomes in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.J.; Qu, H.J.; Li, D.Z.; Li, X.M.; Zhu, J.J.; Xiang, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.T.; Yang, Y.N. Prognostic nutritional index predicts clinical outcome in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Hayıroğlu, M.I.; Keskin, T.; Kaya, A.; Tatlısu, M.A.; Altay, S.; Uzun, A.O.; Börklü, E.B.; Güvenç, T.S.; Avcı, I.I.; et al. A novel and useful predictive indicator of prognosis in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the prognostic nutritional index. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, G.; Chatzianagnostou, K.; Paradossi, U.; Botto, N.; Del Turco, S.; Taddei, A.; Berti, S.; Mazzone, A. The prognostic impact of objective nutritional indices in elderly patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary coronary intervention. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2231–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, T.; Sasaki, J.; Ishibashi, S.; Birou, S.; Daida, H.; Dohi, S.; Egusa, G.; Hiro, T.; Hirobe, K.; Iida, M.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2013, 20, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- America Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2010. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (Suppl. 1), S11–S61.
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A.; et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.; Sucher, K.; Hollenbeck, C.B. Comparison of ideal body weight equations and published height-weight tables with body mass index tables for healthy adults in the United States. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2006, 21, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Dietary Reference Intakes for Japanese 2020; Daiichi Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 2020.
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76 (Suppl. 1), S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Greenland, P. Effects of Exercise, Dietary Cholesterol, and Dietary Fat on Blood Lipids. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Kimura, T.; Ishihara, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nakao, K.; Miyauchi, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Tsujita, K.; Hagiwara, N.; Miyazaki, S.; et al. JCS 2018 Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1085–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Shimada, K.; Shimizu, M.; Kunimoto, M.; Ouchi, S.; Aikawa, T.; Kadoguchi, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Shiozawa, T.; et al. Correlation of nutritional indices on admission to the coronary Intensive Care Unit with the development of delirium. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwata, S.; Yatsu, S.; Kasai, T.; Sato, A.; Matsumoto, H.; Shitara, J.; Shimizu, M.; Murata, A.; Kato, T.; Suda, S.; et al. Prognostic effect of a novel simply calculated nutritional index in acute decompensated heart failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Shimada, K.; Sugita, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Murata, A.; Kato, T.; Aikawa, T.; Suda, S.; Shiozawa, T.; et al. Low docosahexaenoic acid, dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid levels associated with long-term mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in different nutritional statuses. Nutrients 2017, 9, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furui, K.; Morishima, I.; Morita, Y.; Kanzaki, Y.; Takagi, K.; Nagai, H.; Watanabe, N.; Yoshioka, N.; Yamauchi, R.; Miyazawa, H.; et al. Impact of preoperative nutritional status on the outcome of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circ. J. 2022, 86, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, T.; Yasumoto, K.; Ohashi, M.; Momoki, C.; Habu, D. Association between early enteral nutrition and clinical outcome in patients with severe acute heart failure who require invasive mechanical ventilation. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottillo, S.; Filion, K.B.; Genest, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Rinfret, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersberger, L.; Dietz, A.; Bürgler, H.; Bargetzi, A.; Bargetzi, L.; Kägi-Braun, N.; Tribolet, P.; Gomes, F.; Hoess, C.; Pavlicek, V.; et al. Individualized nutritional support for hospitalized patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Well-Nourished Patient | Malnutrition Patient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 289 | 198 | 91 | |
| Age | 61.50 [52.00, 72.00] | 73.00 [64.50, 80.00] | <0.001 |
| Male (n, %) | 164 (82.8) | 55 (60.4) | <0.001 |
| BMI | 24.71 [22.83, 26.98] | 22.86 [20.63, 25.57] | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 130 (65.7) | 68 (74.7) | 0.135 |
| Dyslipidemia (n, %) | 166 (83.8) | 60 (65.9) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 75 (37.9) | 41 (45.1) | 0.301 |
| Family history of CVD (n, %) | 41 (20.7) | 14 (15.4) | 0.335 |
| Smoking (n, %) | 138 (69.7) | 51 (56.0) | 0.033 |
| CKD (n, %) | 36 (18.2) | 35 (38.5) | <0.001 |
| History of HF (n, %) | 2 (1.0) | 3 (3.3) | 0.182 |
| Atrial fibrillation (n, %) | 3 (1.5) | 5 (5.5) | 0.114 |
| Old myocardial infarction (n, %) | 17 (8.6) | 4 (4.4) | 0.233 |
| Old cerebral infarction (n, %) | 10 (5.1) | 7 (7.7) | 0.422 |
| ST-elevated myocardial infarction (n, %) | 181 (91.4) | 78 (85.7) | 0.150 |
| Hospitalization day (day) | 12.00 [9.00, 16.00] | 20.00 [14.00, 31.50] | <0.001 |
| LVEF on arrival (%) | 50.00 [40.00, 55.00] | 45.00 [40.00, 55.00] | 0.192 |
| Nutrition guidance (n, %) | 123 (62.1) | 39 (42.9) | 0.003 |
| Start of enteral nutrition (day) | 1.74 [1.00, 2.00] | 2.53 [2.00, 3.00] | <0.001 |
| Laboratory data on arrival | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.80 [13.83, 15.78] | 13.50 [11.70, 15.05] | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.10 [3.80, 4.40] | 3.60 [3.30, 3.90] | <0.001 |
| Creatine kinase max (IU/L) | 1712.00 [750.00, 2914.25] | 1406.00 [731.50, 3448.50] | 0.973 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.81 [0.68, 1.00] | 0.91 [0.70, 1.19] | 0.049 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 69.00 [57.00, 85.00] | 58.00 [41.00, 77.00] | <0.001 |
| BNP (pg/mL) | 27.60 [10.30, 100.42] | 63.90 [29.05, 254.60] | <0.001 |
| Na (mEq/dL) | 140.00 [138.00, 141.00] | 140.00 [137.00, 142.00] | 0.834 |
| Cl (mEq/dL) | 101.00 [99.00, 103.00] | 101.00 [99.00, 103.00] | 0.978 |
| K (mEq/dL) | 3.90 [3.60, 4.10] | 4.00 [3.80, 4.40] | 0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.30 [0.10, 0.30] | 0.30 [0.30, 0.80] | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 150.00 [123.75, 194.50] | 161.00 [129.00, 234.50] | 0.035 |
| HbA1c (NGSP) (%) | 6.10 [5.70, 6.70] | 6.00 [5.70, 6.50] | 0.867 |
| T-Cho (mg/dL) | 210.00 [180.50, 242.50] | 192.00 [163.00, 226.75] | 0.002 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 45.50 [39.00, 56.00] | 48.00 [40.00, 59.75] | 0.299 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 129.50 [104.00, 155.75] | 114.00 [87.00, 139.00] | 0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 143.50 [96.25, 211.00] | 114.50 [80.00, 165.25] | 0.002 |
| Medication at discharge | |||
| ASA (n, %) | 193 (97.5) | 81 (89.0) | 0.007 |
| P2Y12 inhibitor (n, %) | 194 (98.0) | 83 (91.2) | 0.011 |
| OAC (n, %) | 21 (10.6) | 19 (20.9) | 0.027 |
| ACE-Inhibitor/ARB (n, %) | 186 (93.9) | 78 (85.7) | 0.025 |
| ARNI (n, %) | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1.1) | 1 |
| MRA (n, %) | 50 (25.3) | 26 (28.6) | 0.567 |
| βblocker (n, %) | 189 (96.4) | 86 (94.5) | 0.528 |
| Statin (n, %) | 194 (98.0) | 88 (96.7) | 0.682 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitor (n, %) | 29 (14.6) | 8 (8.8) | 0.189 |
| Nutrition index | |||
| GNRI on arrival | 102.75 [98.28, 105.73] | 93.82 [89.35, 98.28] | <0.001 |
| GNRI in convalescence period | 104.24 [101.26, 107.22] | 93.76 [89.08, 96.66] | <0.001 |
| HR | 95%CI | p-Value | Adjusted HR | 95%CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | ||||||
| GNRI on arrival | 0.936 | 0.890–0.985 | 0.01 | 0.976 | 0.906–1.053 | 0.53 |
| GNRI in convalescence period | 0.924 | 0.891–0.958 | <0.01 | 0.929 | 0.886–0.974 | <0.01 |
| Primary composite endpoints | ||||||
| GNRI on arrival | 0.931 | 0.902–0.962 | <0.01 | 0.969 | 0.917–1.024 | 0.26 |
| GNRI in convalescence period | 0.931 | 0.908–0.956 | <0.01 | 0.9401 | 0.902–0.979 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Tomaru, M.; Nobushima, Y.; Ajima, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Ishiwata, S.; Kakihara, M.; Maki, M.; Shimai, R.; et al. Poor Nutritional Status during Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients without an Early Nutritional Intervention Predicts a Poor Prognosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224748
Abe H, Miyazaki T, Tomaru M, Nobushima Y, Ajima T, Hirabayashi K, Ishiwata S, Kakihara M, Maki M, Shimai R, et al. Poor Nutritional Status during Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients without an Early Nutritional Intervention Predicts a Poor Prognosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224748
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Hiroshi, Tetsuro Miyazaki, Masato Tomaru, Yuka Nobushima, Tomohi Ajima, Koji Hirabayashi, Sayaki Ishiwata, Midori Kakihara, Masaaki Maki, Ryosuke Shimai, and et al. 2023. "Poor Nutritional Status during Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients without an Early Nutritional Intervention Predicts a Poor Prognosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224748
APA StyleAbe, H., Miyazaki, T., Tomaru, M., Nobushima, Y., Ajima, T., Hirabayashi, K., Ishiwata, S., Kakihara, M., Maki, M., Shimai, R., Aikawa, T., Isogai, H., Ozaki, D., Yasuda, Y., Odagiri, F., Takamura, K., Hiki, M., Iwata, H., Yokoyama, K., ... Minamino, T. (2023). Poor Nutritional Status during Recovery from Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients without an Early Nutritional Intervention Predicts a Poor Prognosis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Nutrients, 15(22), 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224748





