Effects of Gestational and Lactational Lead Exposure and High Fat Diet Feeding on Cerebellar Development of Postnatal Rat Offspring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Administration of High Fat Diet and Lead Acetate
2.3. Pb Level Determination in Blood and Measurement of Cerebellar Weight
2.4. Histological Analysis and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
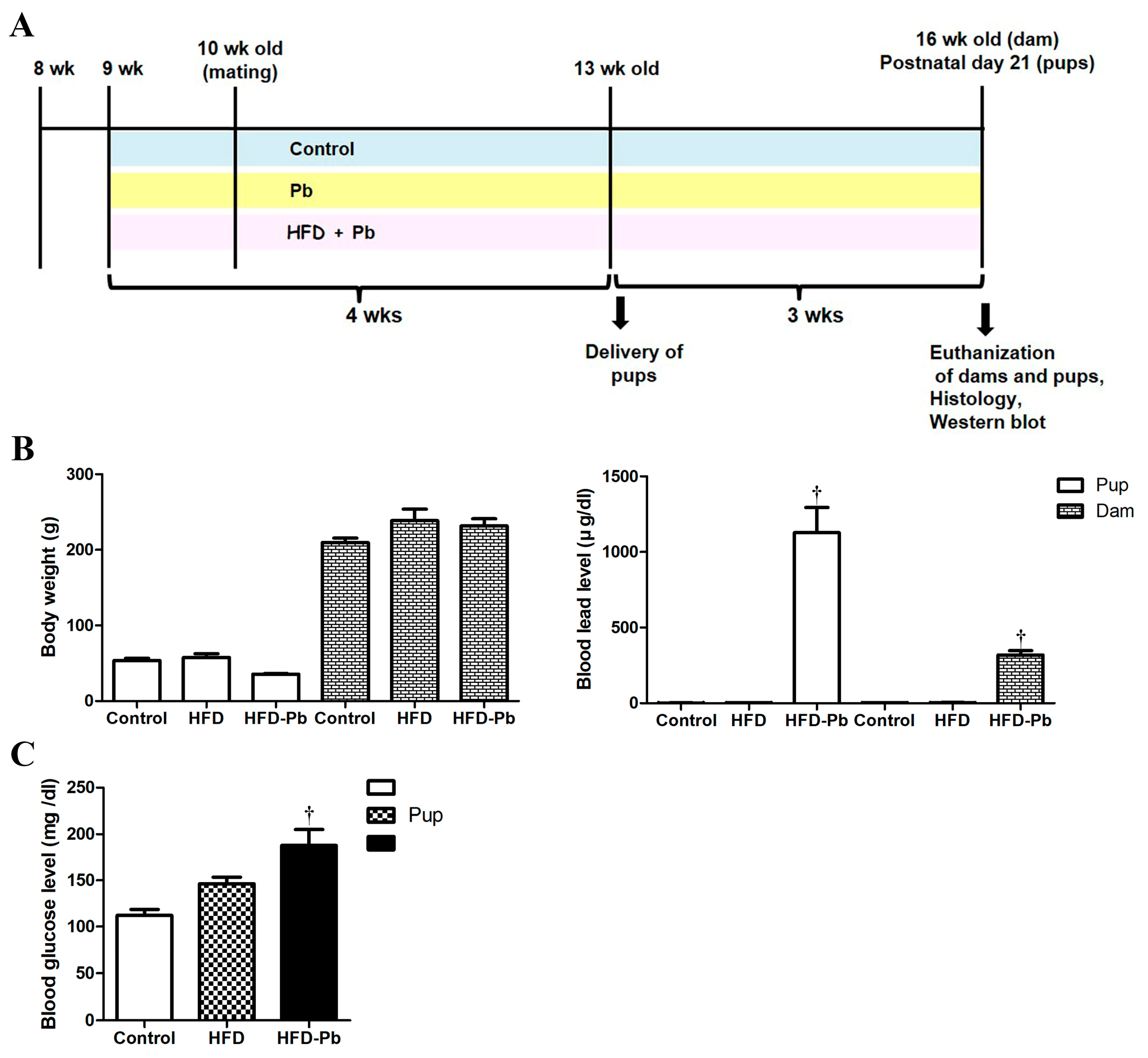
3.1. Physiological Parameters and Blood Pb Levels
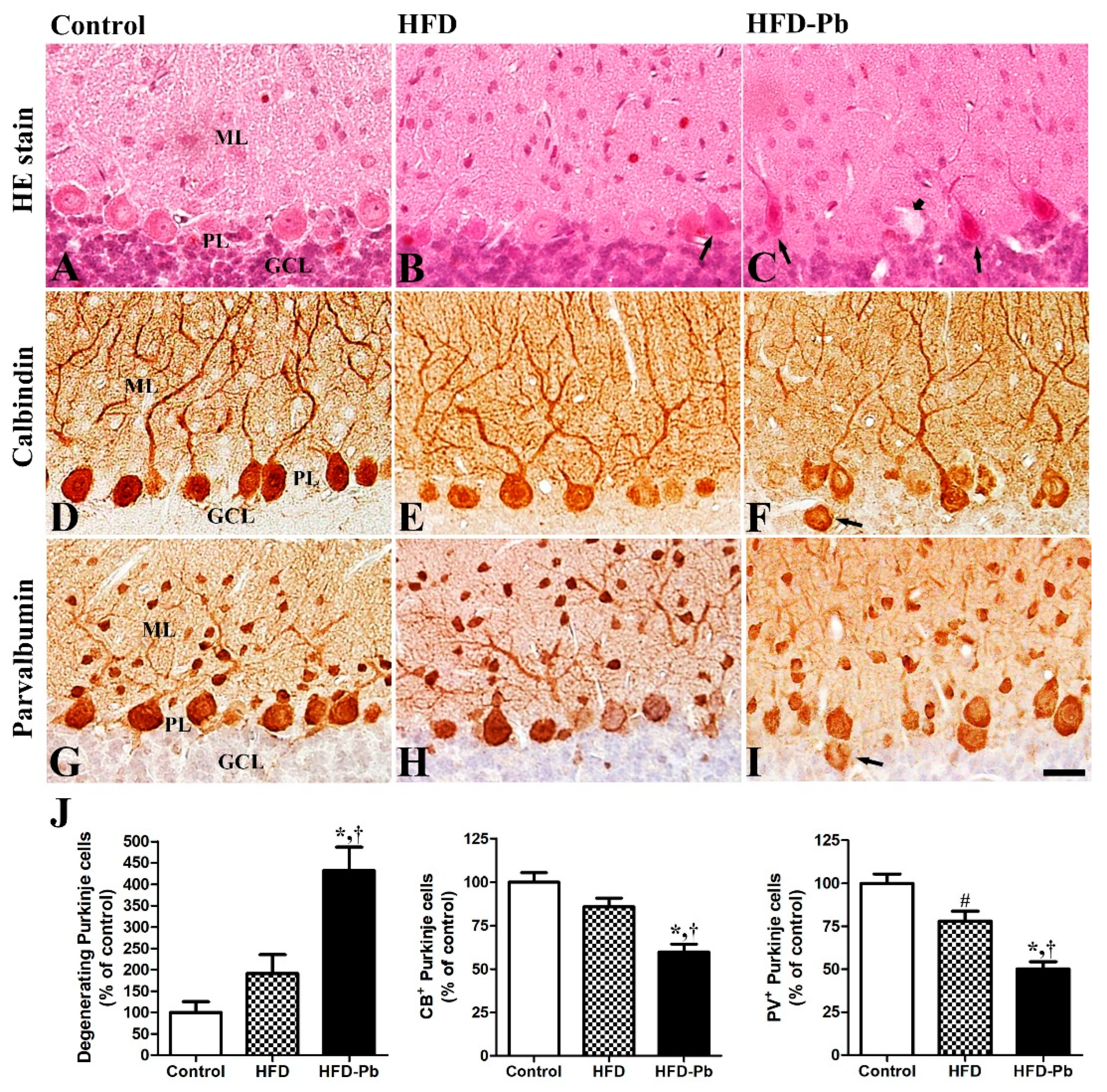
3.2. Effects of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on the Developing Cerebellum (H&E Staining and Calbindin-28 Kd Immunohistochemistry)
3.3. Effects of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on PV Immunoreactivity
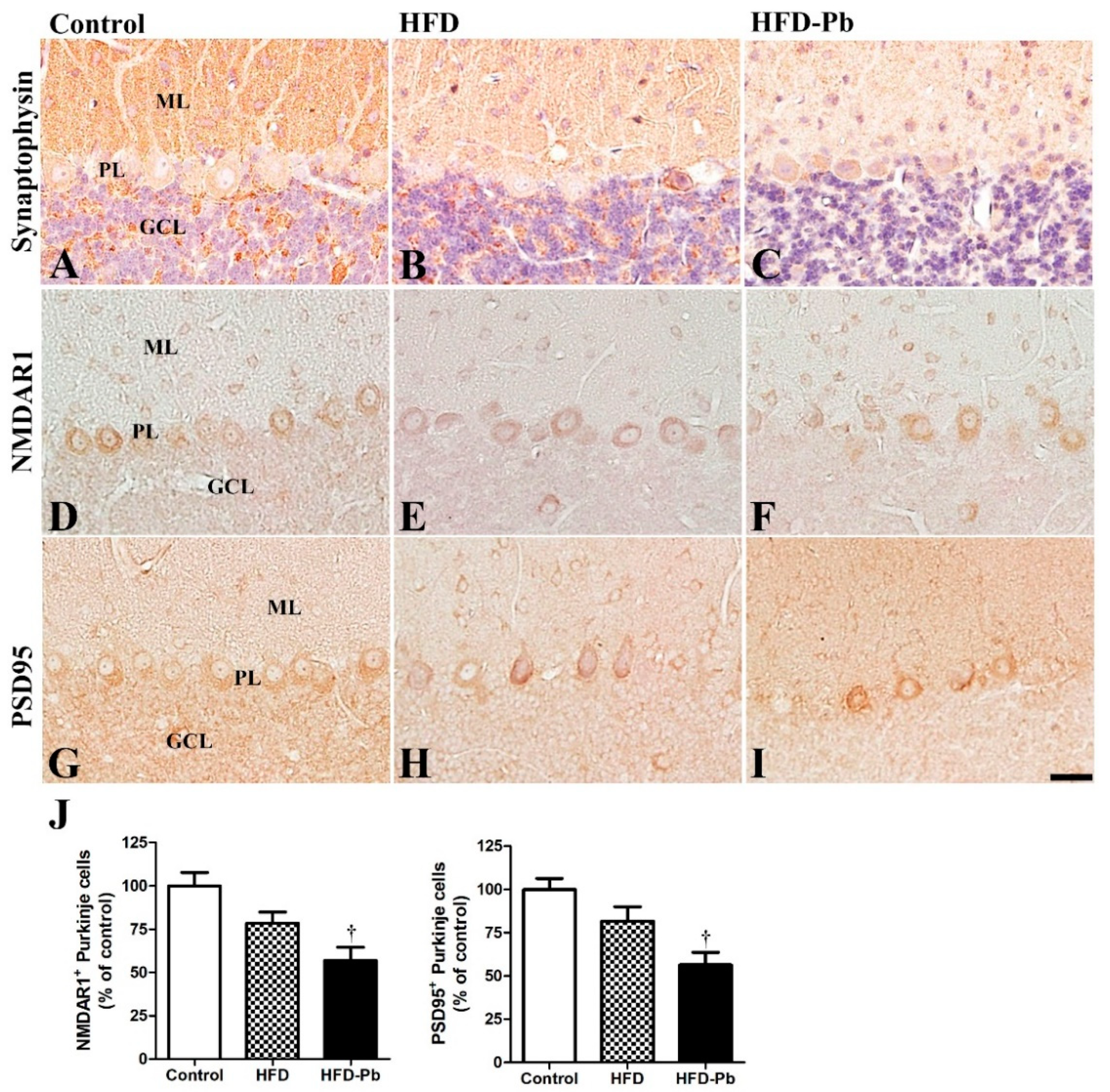
3.4. Effect of Pb and Ascorbic Acid on Presynaptic Synaptophysin
3.5. Effect of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on NMDAR1 and PSD95
3.6. Effect of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on γ-Amino-Butyric Acid (GABA)-Synthesizing Enzyme (GAD67) and GABA Transporter 1 (GABAT1)
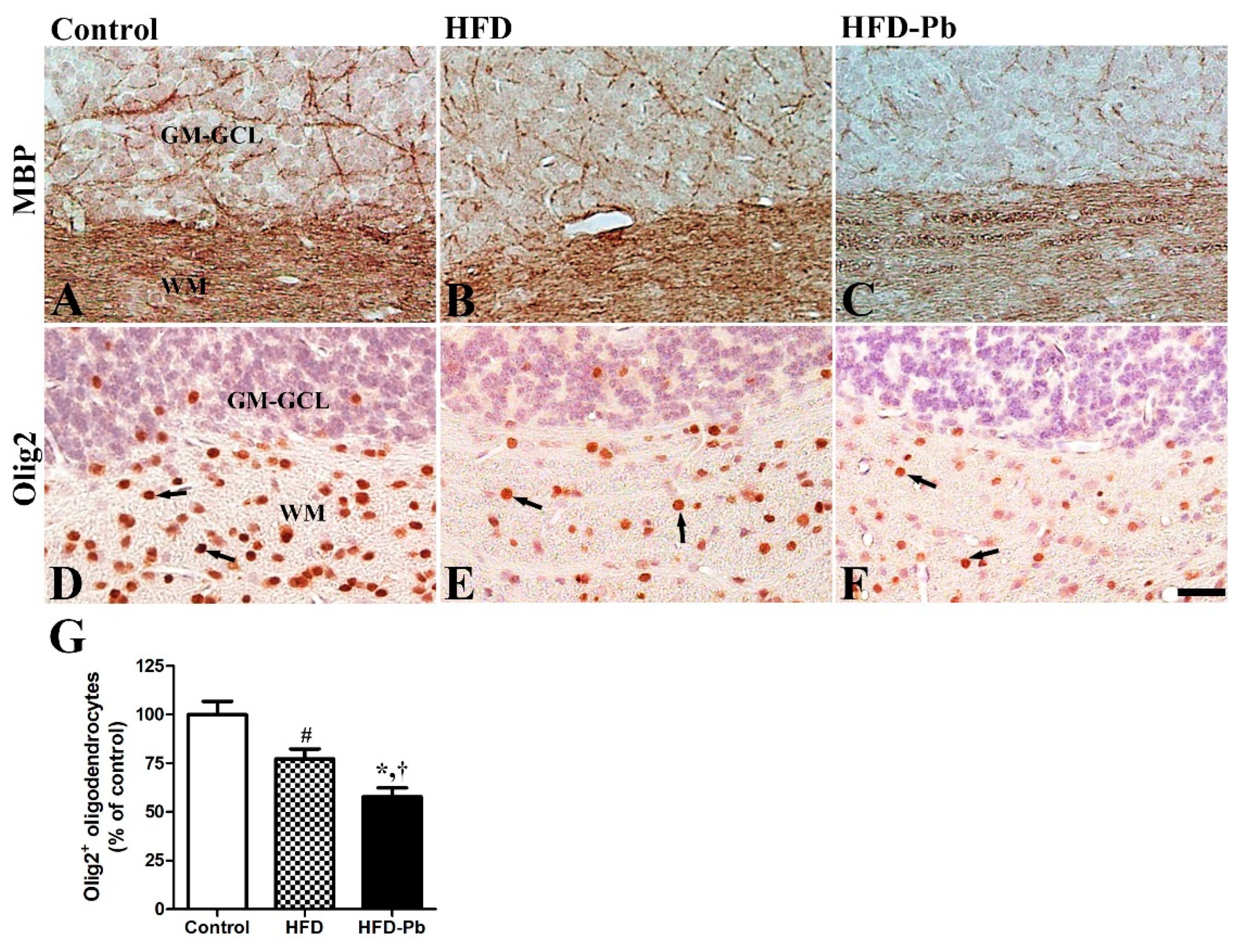
3.7. Effect of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on MBP and Olig2
3.8. Effect of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on Nrf2, HO1, SOD1, SOD2, IL-1β, TNFα, and Iba1
3.9. Effect of HFD Feeding and Pb Exposure on BDNF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeiss, C.J. Comparative Milestones in Rodent and Human Postnatal Central Nervous System Development. Toxicol. Pathol. 2021, 49, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic syndrome pandemic. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glastras, S.J.; Chen, H.; Pollock, C.A.; Saad, S. Maternal obesity increases the risk of metabolic disease and impacts renal health in offspring. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Prescott, S.L.; Nyirenda, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Eriksson, J.G.; Broekman, B.F. Influence of maternal obesity on the long-term health of offspring. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, K.A.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Chow, T.; Alves, J.; Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H. Children exposed to maternal obesity or gestational diabetes mellitus during early fetal development have hypothalamic alterations that predict future weight gain. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, R.; Brown, M.J.; Kashtock, M.E.; Jacobs, D.E.; Whelan, E.A.; Rodman, J.; Schock, M.R.; Padilla, A.; Sinks, T. Lead exposures in US children, 2008: Implications for prevention. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Sharma, B. Biochemical and molecular bases of lead-induced toxicity in mammalian systems and possible mitigations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huo, X.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cong, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels from e-waste exposure are linked to decreased olfactory memory in children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231 Pt 1, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. Substance Priority List. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. 2019. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Hong, S.B.; Im, M.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, E.J.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, B.N.; Yoo, H.J.; Cho, I.H.; Bhang, S.Y.; Hong, Y.C.; et al. Environmental lead exposure and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom domains in a community sample of South Korean school-age children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Lead (Pb) in the tissues of Anatidae, Ardeidae, Sternidae and Laridae of the Northern Hemisphere: A review of environmental studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 12631–12647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, N.; Fuller, R. The Toxic Truth: Children’s Exposure to Lead Pollution Undermines a Generation of Future Potential; UNICEF and Pure Earth: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.unicef.org/reports/toxic-truth-childrens-exposure-to-lead-pollution-2020 (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Roy, S.; Edwards, M.A. Preventing another lead (Pb) in drinking water crisis: Lessons from the Washington DC and Flint MI contamination events. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 7, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowska, K.; Korbecki, J.; Gutowska, I.; Metryka, E.; Tarnowski, M.; Goschorska, M.; Barczak, K.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Pre- and neonatal exposure to lead (Pb) induces neuroinflammation in the forebrain cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of rat pups. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Seo, J.S.; Choi, M.; Nahm, S.S.; Chang, B.J.; Nah, S.Y. Ginseng gintonin attenuates lead-induced rat cerebellar impairments during gestation and lactation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecil, K.M.; Brubaker, C.J.; Adler, C.M.; Dietrich, K.N.; Altaye, M.; Egelhoff, J.C.; Wessel, S.; Elangovan, I.; Hornung, R.; Jarvis, K.; et al. Decreased brain volume in adults with childhood lead exposure. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauptman, M.; Stierman, B.; Woolf, A.D. Children with autism spectrum disorder and lead poisoning: Diagnostic challenges and management complexities. Clin. Pediatr. 2019, 58, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidsky, T.I.; Schneider, J.S. Lead neurotoxicity in children: Basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Brain 2003, 126 Pt 1, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Seo, J.S.; Go, T.H.; Nahm, S.S.; Chang, B.J. Ascorbic acid supplementation prevents the detrimental effects of prenatal and postnatal lead exposure on the Purkinje cell and related proteins in the cerebellum of developing rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.; Mizon, K.; Korsch, M.; Taylor, A. Revisiting mobilisation of skeletal lead during pregnancy based on monthly sampling and cord/maternal blood lead relationships confirm placental transfer of lead. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 90, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Seo, M.; Seo, J.S.; Rhim, H.; Nahm, S.S.; Cho, I.H.; Chang, B.J.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Ascorbic acid mitigates D-galactose-induced brain aging by increasing hippocampal neurogenesis and improving memory function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Skeberdis, V.A.; Francesconi, A.; Bennett, M.V.; Zukin, R.S. Postsynaptic density protein-95 regulates NMDA channel gating and surface expression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10138–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, G.; Prybylowski, K.; Fu, Z.; Luo, J.; Wenthold, R.J.; Vicini, S. PSD-95 regulates NMDA receptors in developing cerebellar granule neurons of the rat. J. Physiol. 2003, 548 Pt 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, A.; Constantine-Paton, M. BDNF induces transport of PSD95 to dendrites through PI3K-AKT signaling after NMDA receptor activation. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, D. GABA receptors in brain development, function, and injury. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, J.C.; St-Pierre, M.K.; Carrier, M.; El Hajj, H.; Novak, S.W.; Sanchez, M.G.; Cicchetti, F.; Tremblay, M.È. Microglial physiological properties and interactions with synapses are altered at presymptomatic stages in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease pathology. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tress, O.; Maglione, M.; May, D.; Pivneva, T.; Richter, N.; Seyfarth, J.; Binder, S.; Zlomuzica, A.; Seifert, G.; Theis, M.; et al. Panglial gap junctional communication is essential for maintenance of myelin in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 7499–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathina, S.; Das, U.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.M.; Cho, I.S.; Seo, J.S.; Go, T.H.; Kim, J.H.; Nahm, S.S.; Chang, B.J.; Lee, J.H. Ascorbic acid attenuates lead-induced alterations in the synapses in the developing rat cerebellum. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 187, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurosy, T.; Jeewon, R. Overweight and obesity epidemic in developing countries: A problem with diet, physical activity, or socioeconomic status? Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 964236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, C.D.; Guilarte, T.R. Lead neurotoxicity: From exposure to molecular effects. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 49, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefa, S.T.; Héroux, P. Both physiology and epidemiology support zero tolerable blood lead levels. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 280, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, T.; Stemmer, P.; Tyrrell, J.; Jog, R. Diabetes and exposure to environmental lead (Pb). Toxics 2018, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Hwang, Y.C.; Woo, J.T.; Sinn, D.H.; Chin, S.O.; Chon, S.; Kim, Y.S. Blood lead is significantly associated with metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: An analysis based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsemans, A.C.; Soule, S.; Weger, M.; Bourdon, E.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Meilhac, O.; Diotel, N. Impaired constitutive and regenerative neurogenesis in adult hyperglycemic zebrafish. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintana, H.; Lietzau, G.; Augestad, I.L.; Chiazza, F.; Nyström, T.; Patrone, C.; Darsalia, V. Obesity-induced type 2 diabetes impairs neurological recovery after stroke in correlation with decreased neurogenesis and persistent atrophy of parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, W.H.; Artlett, C.M.; Zhang, W.; Kreipke, C.W.; Passmore, G.G.; Rafols, J.A.; Sima, A.A.F. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and neuronal deficit in the fatal brain edema of diabetic ketoacidosis. Brain Res. 2008, 1238, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Yao, J.; Fang, C.; Dong, N.; Luscher, B.; Chen, G. Sequential postsynaptic maturation governs the temporal order of GABAergic and glutamatergic synaptogenesis in rat embryonic cultures. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10860–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teune, T.M.; van der Burg, J.; dez Eeuw, C.I.; Voogd, J.; Ruigrok, T.J. Single Purkinje cell can innervate multiple classes of projection neurons in the cerebellar nuclei of the rat: A light microscopic and ultrastructural triple-tracer study in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 392, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkur, R.R.; Bairy, L.K. Histological study on hippocampus, amygdala and cerebellum following low lead exposure during prenatal and postnatal brain development in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwirth, L.S.; Phillips, G.R.; El Idrissi, A. Perinatal Pb2+ exposure alters the expression of genes related to the neurodevelopmental GABA-shift in postnatal rats. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernocchi, G.; Bottone, M.G.; Piccolini, V.M.; Dal Bo, V.; Santin, G.; De Pascali, S.A.; Migoni, D.; Fanizzi, F.P. Developing central nervous system and vulnerability to platinum compounds. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 315418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Salazar, C.; Ramírez-Emiliano, J.; Trejo-Bahena, A.; Oviedo-Solís, C.I.; Solís-Ortiz, M.S. A high-fat diet decreases GABA concentration in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of rats. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serbedzija, P.; Madl, J.E.; Ishii, D.N. Insulin and IGF-I prevent brain atrophy and DNA loss in diabetes. Brain Res. 2009, 1303, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.M.; Seo, J.S.; Nahm, S.S.; Chang, B.J. Effects of ascorbic acid on osteopontin expression and axonal myelination in the developing cerebellum of lead-exposed rat pups. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wu, X.; Cai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, H. Lead poisoning disturbs oligodendrocytes differentiation involved in decreased expression of NCX3 inducing intracellular calcium overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19096–19110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; DU, J.; Wang, Y.T.; Liang, T.T. Effect of oxidative stress on heme oxygenase-1 expression in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Tian, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ming, Q.L.; Ma, J.Q.; Ji, L.P. Effects of gastrodin against lead-induced brain injury in mice associated with the Wnt/Nrf2 pathway. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.L.; Pistell, P.J.; Purpera, M.N.; Gupta, S.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; Hise, T.L.; Keller, J.N.; Ingram, D.K.; Morrison, C.D.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Effects of high fat diet on Morris maze performance, oxidative stress, and inflammation in rats: Contributions of maternal diet. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 35, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of chronic oxidative stress on neuroinflammatory response mediated by CD4+T cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Steliga, A.; Moryś, J. BDNF: A Key Factor with Multipotent Impact on Brain Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodomari, I.; Wada, E.; Nakamura, S.; Wada, K. Maternal supply of BDNF to mouse fetal brain through the placenta. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhnoja, J.; Buch, L.; Pillai, P. Potential role of NGF, BDNF, and their receptors in oligodendrocytes differentiation from neural stem cell: An in vitro study. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozuka, Y.; Kumon, M.; Wada, E.; Onodera, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Wada, K. Maternal obesity impairs hippocampal BDNF production and spatial learning performance in young mouse offspring. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Cejudo, J.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M.; Otero-Ortega, L.; Rodríguez-Frutos, B.; Fuentes, B.; Vallejo-Cremades, M.T.; Hernanz, T.N.; Cerdán, S.; Díez-Tejedor, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor administration mediated oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelin formation in subcortical ischemic stroke. Stroke 2015, 46, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanessa Fiorentino, T.; Prioletta, A.; Zuo, P.; Folli, F. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5695–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Martín, E.; Mellado-Gil, J.M.; Cobo-Vuilleumier, N.; Martín-Montalvo, A.; Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; Diaz Contreras, I.; Hmadcha, A.; Soria, B.; Martin Bermudo, F.; Reyes, J.C.; et al. Dissecting the brain/islet axis in metabesity. Genes 2019, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q. Control of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes without weight loss by modification of diet composition. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umphonsathien, M.; Rattanasian, P.; Lokattachariya, S.; Suansawang, W.; Boonyasuppayakorn, K.; Khovidhunkit, W. Effects of intermittent very-low calorie diet on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Won, H.-S.; Yang, M.; Nahm, S.-S.; Nam, S.M. Effects of Gestational and Lactational Lead Exposure and High Fat Diet Feeding on Cerebellar Development of Postnatal Rat Offspring. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204325
Seo JS, Lee SH, Won H-S, Yang M, Nahm S-S, Nam SM. Effects of Gestational and Lactational Lead Exposure and High Fat Diet Feeding on Cerebellar Development of Postnatal Rat Offspring. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204325
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jin Seok, Shin Hyo Lee, Hyung-Sun Won, Miyoung Yang, Sang-Seop Nahm, and Sung Min Nam. 2023. "Effects of Gestational and Lactational Lead Exposure and High Fat Diet Feeding on Cerebellar Development of Postnatal Rat Offspring" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204325
APA StyleSeo, J. S., Lee, S. H., Won, H.-S., Yang, M., Nahm, S.-S., & Nam, S. M. (2023). Effects of Gestational and Lactational Lead Exposure and High Fat Diet Feeding on Cerebellar Development of Postnatal Rat Offspring. Nutrients, 15(20), 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204325





