Multiomics Revealed the Multi-Dimensional Effects of Late Sleep on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Children in Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Study Design
2.2. DNA Preparation and Metagenomics Sequencing
2.3. Taxonomic and Functional Profiling Acquisition
2.4. Alpha- and Beta-Diversity
2.5. Metabolomic Detection and Analysis
Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.6. UPLC Conditions
2.7. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
2.8. KEGG Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Metagenome-Wide Association Study and Metabolomics Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
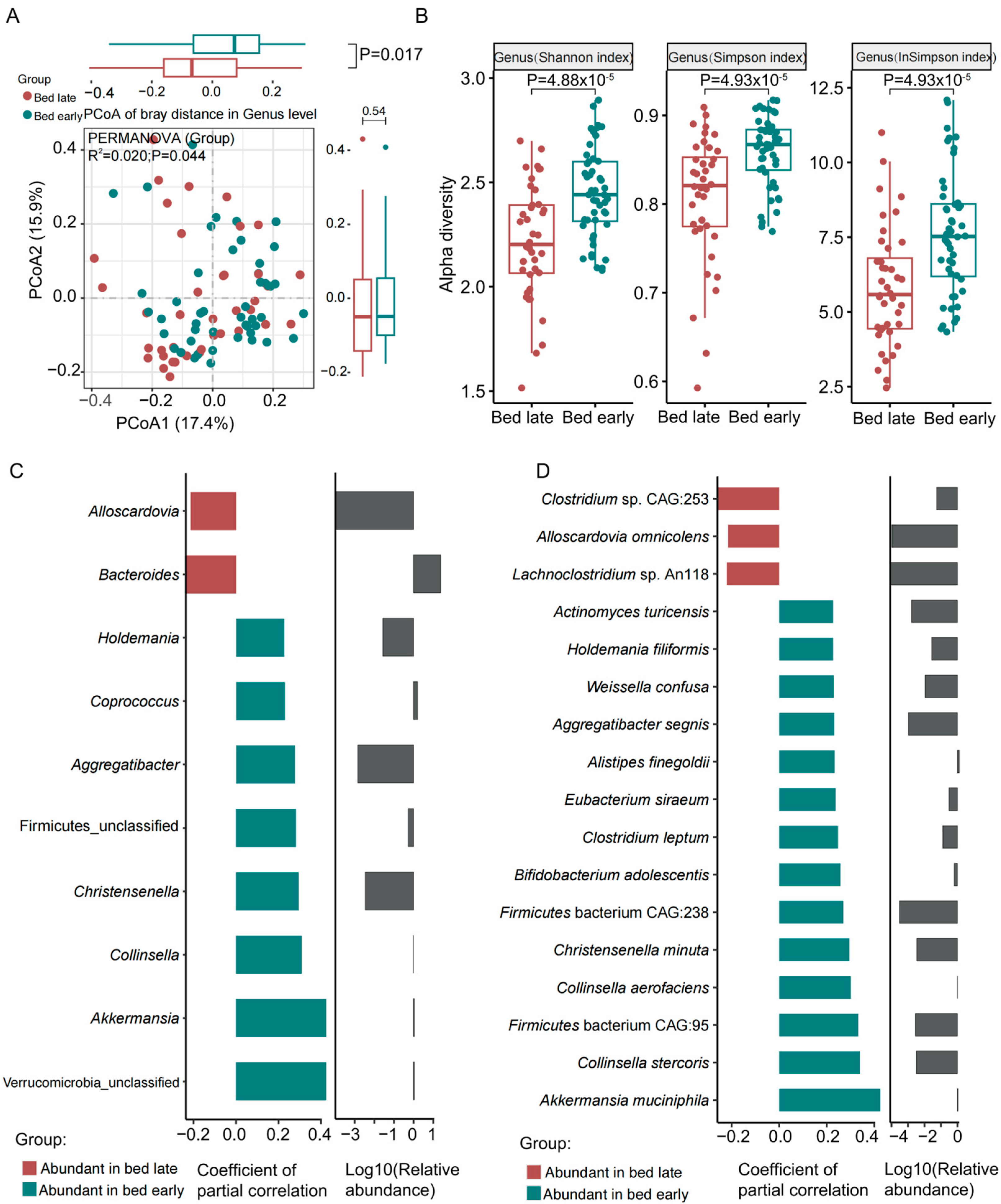
3.1. Gut Microbiota Characterization for Samples
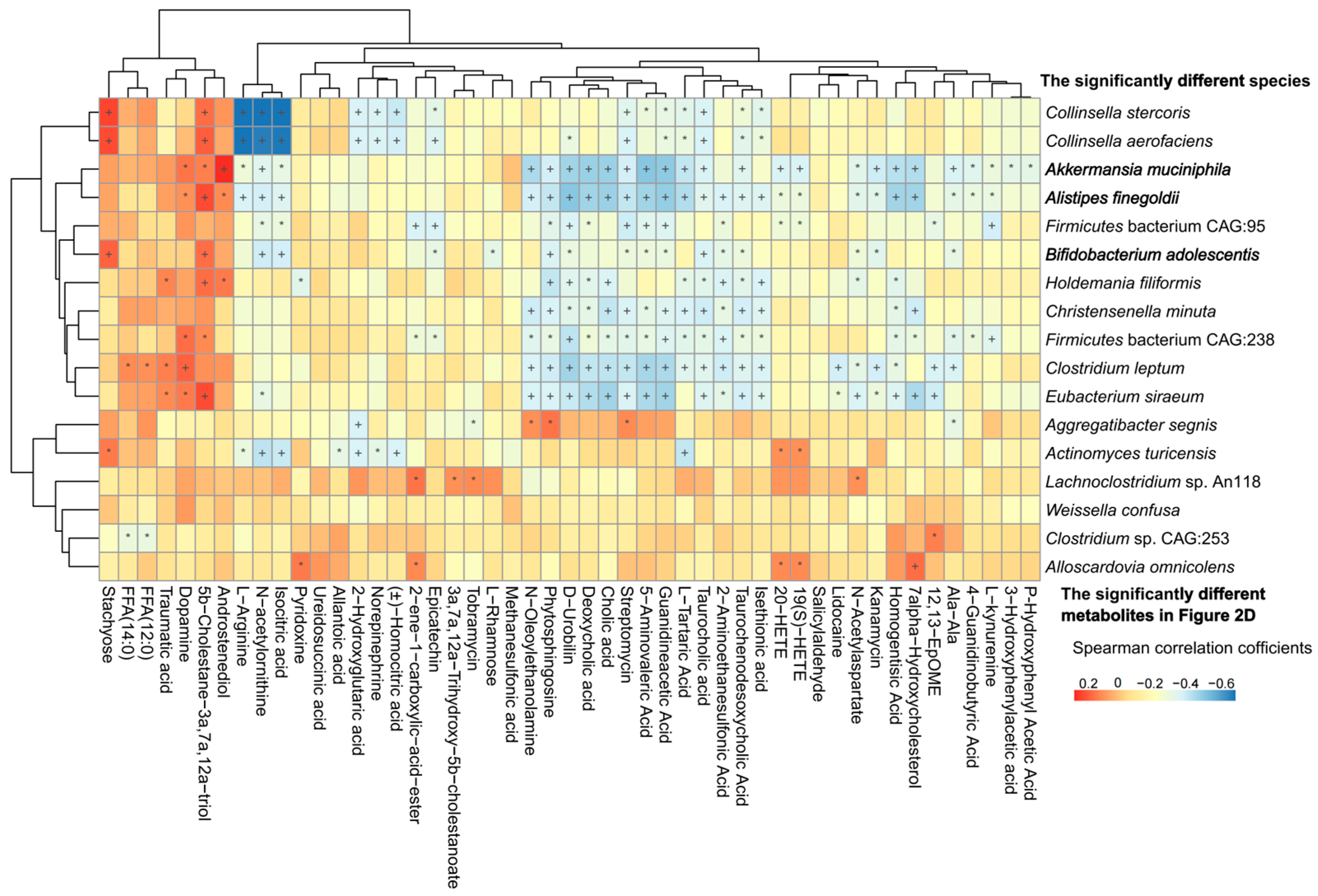
3.2. Differential Analysis of the Gut Microbial Metabolites
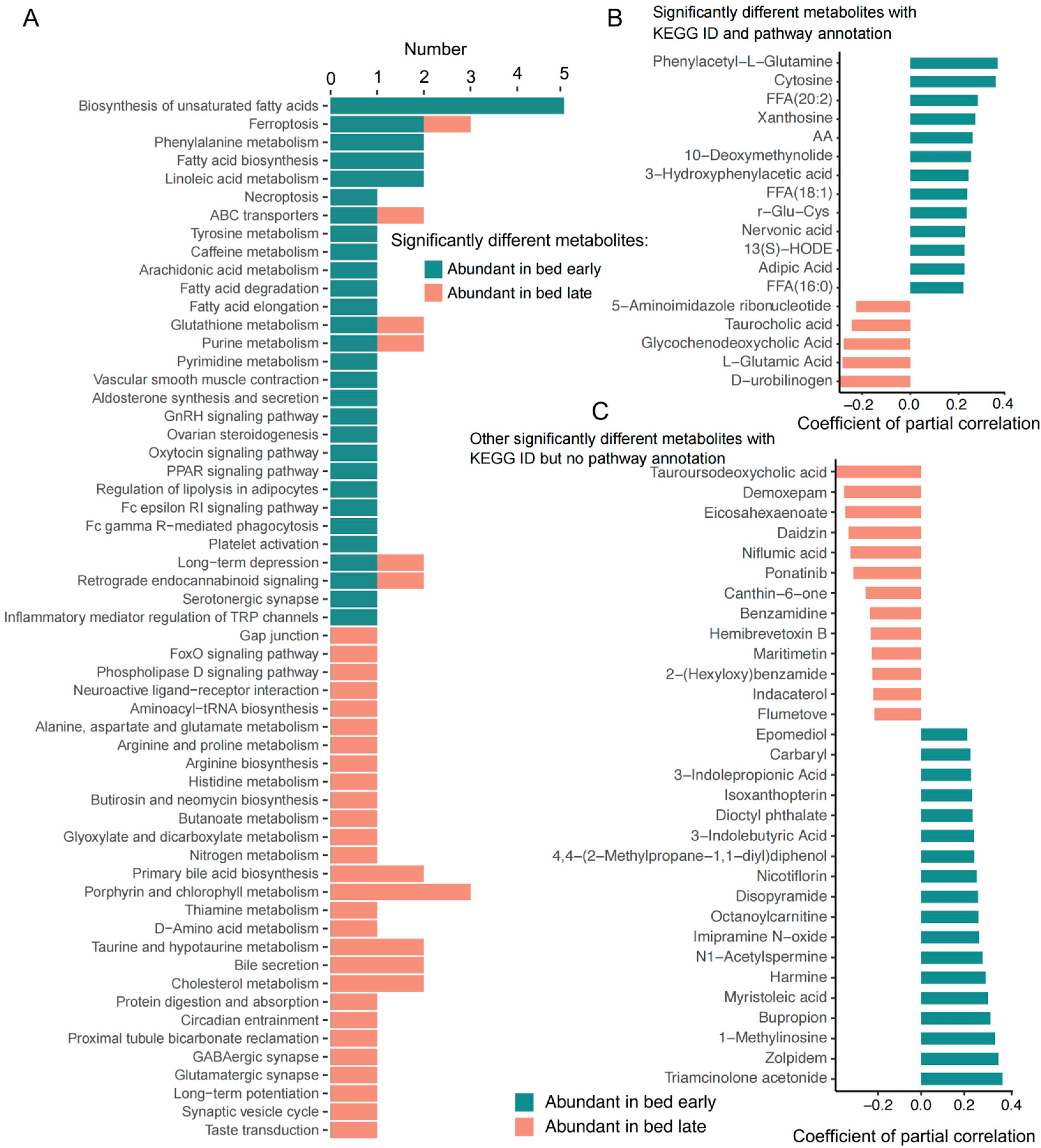
3.3. Difference Study of the Plasma Metabolites
KEGG Pathways Participated by the Significantly Different Metabolites in Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ordway, M.R.; Logan, S.; Sutton, E.H. Sleep Deficiency in Young Children. Clin. Chest Med. 2022, 43, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Rangan, A.; Olsen, N.J.; Heitmann, B.L. Longitudinal association of nighttime sleep duration with emotional and behavioral problems in early childhood: Results from the Danish Healthy Start Study. Sleep 2021, 44, zsaa138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, M.K.; Latreille, V. Sleep Disorders. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matenchuk, B.A.; Mandhane, P.J.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Sleep, circadian rhythm, and gut microbiota. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 53, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J. The interplay between sleep and gut microbiota. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 180, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimov, I.; Magzal, F.; Tamir, S.; Lalzar, M.; Asraf, K.; Milman, U.; Agmon, M.; Shochat, T. Variation in Gut Microbiota Composition is Associated with Sleep Quality and Cognitive Performance in Older Adults with Insomnia. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2022, 14, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddrisu, I.; Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Poveda, C.; Pyle, S.; Shahzad, M.; Andrews, S.; Walton, G.E. Malnutrition and Gut Microbiota in Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, G.A.; Kelley, K.S.; Pate, R.R. Effects of exercise on BMI z-score in overweight and obese children and adolescents: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultima, J.R.; Sunagawa, S.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Mende, D.R.; Arumugam, M.; Pan, Q.; Liu, B.; Qin, J.; et al. MOCAT: A metagenomics assembly and gene prediction toolkit. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Zhong, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, B.; Han, M.; Ren, H.; Lu, H.; Luber, J.M.; Xia, M.; Li, W.; et al. Assessment of the cPAS-based BGISEQ-500 platform for metagenomic sequencing. Gigascience 2018, 7, gix133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Tickle, T.L.; Scholz, M.; Weingart, G.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. Elife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Garcia Yunta, R.; Okuda, S.; Vandeputte, D.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Chaffron, S.; et al. Species-function relationships shape ecological properties of the human gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.; Carey, V.J.; Gentleman, R.; Anders, S.; Carlson, M.; Carvalho, B.S.; Bravo, H.C.; Davis, S.; Gatto, L.; Girke, T.; et al. Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radka, C.D.; Frank, M.W.; Rock, C.O.; Yao, J. Fatty acid activation and utilization by Alistipes finegoldii, a representative Bacteroidetes resident of the human gut microbiome. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, Y.; Doi, S.A.; Mamun, A.A. Longitudinal impact of sleep on overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and bias-adjusted meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Taggart, F.M.; Kandala, N.B.; Currie, A.; Peile, E.; Stranges, S.; Miller, M.A. Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 2008, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriss, M.; Hazleton, K.Z.; Nusbacher, N.M.; Martin, C.G.; Lozupone, C.A. Low diversity gut microbiota dysbiosis: Drivers, functional implications and recovery. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illiano, P.; Brambilla, R.; Parolini, C. The mutual interplay of gut microbiota, diet and human disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.X.; He, Z.M.; Zhu, W.L.; Ji, Y.B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.M.; Yuan, K.; Bao, Y.P.; et al. Gut microbiota modulates the inflammatory response and cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6277–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, M.; Howe, A.C.; Tiedje, J.M. Revealing the bacterial butyrate synthesis pathways by analyzing (meta)genomic data. mBio 2014, 5, e00889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentirmai, E.; Millican, N.S.; Massie, A.R.; Kapas, L. Butyrate, a metabolite of intestinal bacteria, enhances sleep. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, G.M.; Long-Smith, C.M.; Murphy, A.; Dorland, D.; Hojabri, S.F.; Ramirez, L.O.; Marin, D.C.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Cusack, A.M.; Berding, K.; et al. Improvements in sleep indices during exam stress due to consumption of a Bifidobacterium longum. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 10, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, K.; Chang, E.B. Intersection of the Gut Microbiome and Circadian Rhythms in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Kirisako, T.; Kokubo, T.; Miura, Y.; Morishita, K.; Okamura, H.; Tsuda, A. Randomised controlled trial of the effects of L-ornithine on stress markers and sleep quality in healthy workers. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Sakai, N.; Okuro, M.; Karakawa, S.; Tsuneyoshi, Y.; Kawasaki, N.; Takeda, T.; Bannai, M.; Nishino, S. The sleep-promoting and hypothermic effects of glycine are mediated by NMDA receptors in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, A.; Marchesi, N.; Marelli, C.; Coppola, A.; Luzi, L.; Govoni, S.; Giustina, A.; Gazzaruso, C. Microbiota and metabolic diseases. Endocrine 2018, 61, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, S.; Garcia-Gavilan, J.; Papandreou, C.; Camacho-Barcia, L.; Arcelin, P.; Palau-Galindo, A.; Rabassa, A.; Bullo, M. Effects of Mediterranean Diet on plasma metabolites and their relationship with insulin resistance and gut microbiota composition in a crossover randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Early Bedtime | Late Bedtime | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 48 | 40 | − |
| Age | 5.5 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 2.3 | 0.685 |
| Sex, % male | 43.8 | 52.5 | 0.399 |
| Current age of father | 37.0 ± 4.5 | 36.3 ± 5.4 | 0.517 |
| Current age of mother | 34.8 ± 4.1 | 34.0 ± 4.6 | 0.393 |
| Height | 113 (106–125) | 110 (100–117) | |
| Weight | 20 (17–30) | 20 (15.5–30) | |
| BMI status | 0.003 | ||
| Thin (n, %) | 4 (8.3) | 1 (2.5) | |
| Normal (n, %) | 38 (79.1) | 21 (52.5) | |
| Overweight (n, %) | 3 (6.3) | 5 (12.5) | |
| Obesity (n, %) | 3 (6.3) | 13 (32.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q. Multiomics Revealed the Multi-Dimensional Effects of Late Sleep on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Children in Northwest China. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204315
Xiang X, Chen J, Zhu M, Gao H, Liu X, Wang Q. Multiomics Revealed the Multi-Dimensional Effects of Late Sleep on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Children in Northwest China. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204315
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Xuesong, Juanjuan Chen, Mingyu Zhu, Huiyu Gao, Xiaobing Liu, and Qi Wang. 2023. "Multiomics Revealed the Multi-Dimensional Effects of Late Sleep on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Children in Northwest China" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204315
APA StyleXiang, X., Chen, J., Zhu, M., Gao, H., Liu, X., & Wang, Q. (2023). Multiomics Revealed the Multi-Dimensional Effects of Late Sleep on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Children in Northwest China. Nutrients, 15(20), 4315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204315








