Does NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 Influence Eating Behaviors in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder? Toward a Neurobiological Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 3T3-L1 Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.2. Adipose Tissue Biopsies from Human Subjects
2.3. Western Blot Analyses
2.4. Patient Enrollment and Clinical Characterization
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements
2.6. Psychopathological Features
- -
- The 21-item self-report Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) [49] to evaluate depressive symptoms. Scores of 0–9, 10–16, 17–29, and ≥30 indicate minimum, mild, moderate, and severe depression, respectively. Cronbach’s alpha in the present research was 0.917. BDI-II score was used as a covariate in the statistical analysis.
- -
- The Binge Eating Scale (BES) [50] is useful to evaluate binge-eating severity. Total BES scores <17, 17–27, and >27, respectively, indicate unlikely, possible, and probable risk of BED.
- -
- The State-Trait Anxiety Disorder (STAI) [51]. This 40-items tool measures state (STAI-St) and trait (STAI-Tr) anxiety. Cronbach’s alpha for the data in this study was 0.845.
2.7. Determination of Patients’ Plasma Levels of Nesfatin-1
2.8. Patient Genotyping
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Nesfatin-1 Protein Secretion in Hypoxic 3T3-L1 Cells
3.2. Nesfatin-1 Protein Secretion in Human Adipose Tissue
3.3. Demographic, Anthropometric, and Psychopathological Characteristics of Patients
3.4. Circulating Nesfatin-1 Levels in Human Plasma
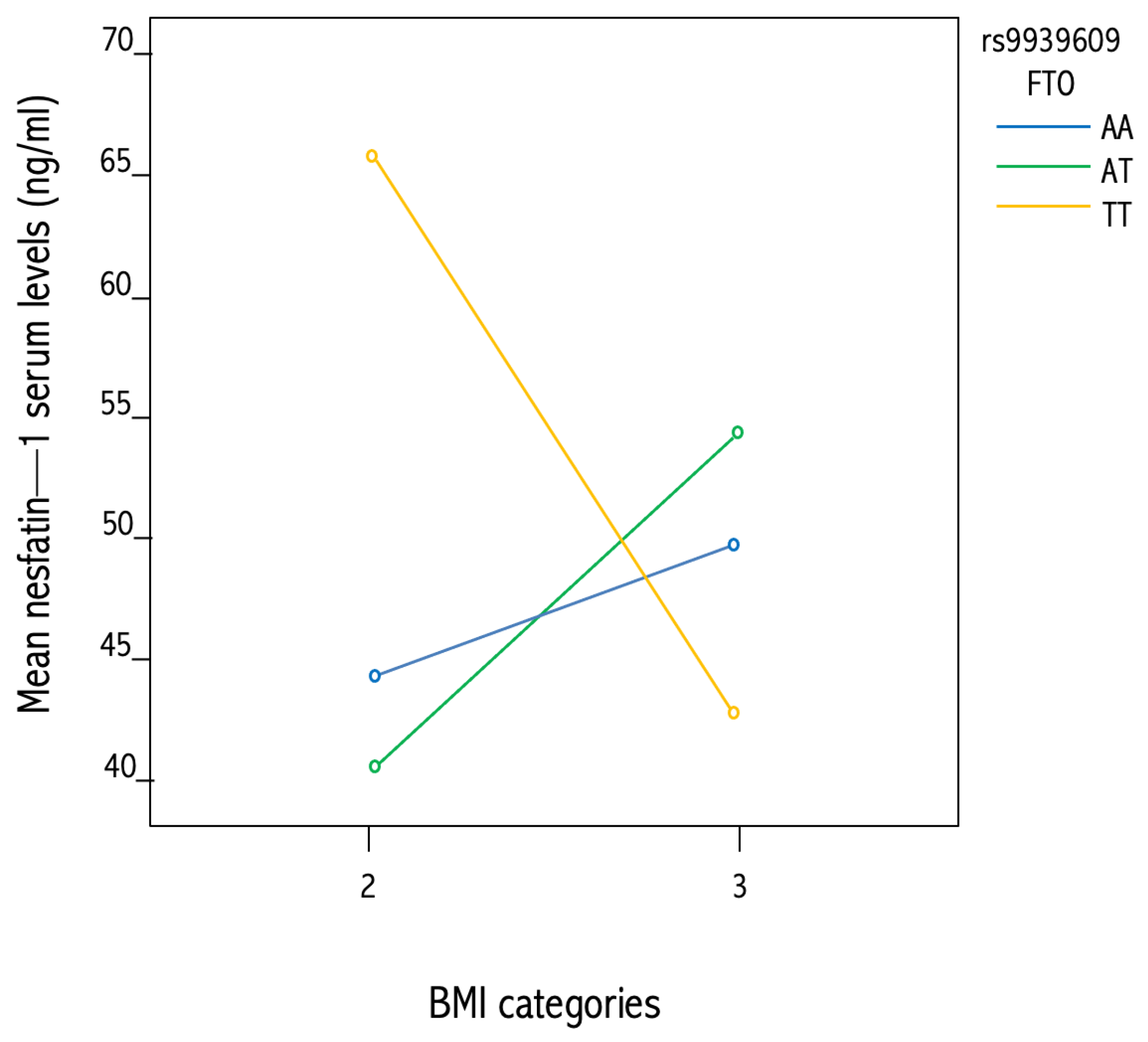
3.5. Association between NUCB2 rs757081 and FTOrs9939609 Genetic Polymorphisms and Circulating Nesfatin-1
4. Discussion
Limits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, G.A.; Frühbeck, G.; Ryan, D.H.; Wilding, J.P.H. Management of obesity. Lancet 2016, 387, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.T. Obesity: The worldwide epidemic. Clin. Dermatol. 2004, 22, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddon, H.; Guéant, J.L.; Meyre, D. The importance of gene-environment interactions in human obesity. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1571–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrell, S.; Murray, S.B. Eating Disorders in Males. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 28, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mond, J.M.; Arrighi, A. Gender differences in perceptions of the severity and prevalence of eating disorders. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2011, 5, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.; Dalton, B.; Kekic, M.; Bartholdy, S.; Campbell, I.C.; Schmidt, U. A systematic review of temporal discounting in eating disorders and obesity: Behavioural and neuroimaging findings. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 506–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroleo, M.; Primerano, A.; Rania, M.; Aloi, M.; Pugliese, V.; Magliocco, F.; Fazia, G.; Filippo, A.; Sinopoli, F.; Ricchio, M.; et al. A real world study on the genetic, cognitive and psychopathological differences of obese patients clustered according to eating behaviours. Eur. Psychiatry 2018, 48, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, G.K.W.; Shott, M.E.; DeGuzman, M.C. The Neurobiology of Eating Disorders. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 28, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, T.; Mercer, J.G. Hunger and Satiety Mechanisms and Their Potential Exploitation in the Regulation of Food Intake. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, L.K.; Lam, D.D. An appetite for life: Brain regulation of hunger and satiety. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 37, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, B.J.; Hill, J.O.; Gunn, A.J. Obesity: Scope, Lifestyle Interventions, and Medical Management. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 23, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.; Elbelt, U.; Ahnis, A.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Stengel, A. Sex-specific regulation of NUCB2/nesfatin-1: Differential implication in anxiety in obese men and women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 60, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Aguilar, I.; Ibarra-Reynoso, L.D.R.; Malacara, J.M. Association of Nesfatin-1, Acylated Ghrelin and Cortisol with Scores of Compulsion, Food Addiction, and Binge Eating in Adults with Normal Weight and with Obesity. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 73, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegers, D.; Beckers, S.; de Freitas, F.; Jennes, K.; van Camp, J.K.; Mertens, I.L.; van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Rooman, R.P.; Desager, K.N.; Massa, G.; et al. Identification of mutations in the NUCB2/nesfatin gene in children with severe obesity. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-I, S.; Shimizu, H.; Satoh, T.; Okada, S.; Adachi, S.; Inoue, K.; Eguchi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Imaki, T.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 2006, 443, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Taché, Y. Nesfatin-1—Role as possible new potent regulator of food intake. Regul. Pept. 2010, 163, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Rodríguez-Penas, D.; García-Rúa, V.; Mosquera-Leal, A.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Lago, F. Nesfatin-1: A new energy-regulating peptide with pleiotropic functions. Implications at cardiovascular level. Endocrine 2016, 52, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegers, D.; Beckers, S.; Mertens, I.L.; van Gaal, L.F.; van Hul, W. Association between polymorphisms of the Nesfatin gene, NUCB2, and obesity in men. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 103, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, R.; Levata, L.; Lehnert, H.; Schulz, C. Nesfatin-1: Functions and physiology of a novel regulatory peptide. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R45–R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, P.; Goebel-Stengel, M.; Teuffel, P.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Stengel, A. Peripheral and central localization of the nesfatin-1 receptor using autoradiography in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałasz, A.; Janas-Kozik, M.; Borrow, A.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Worthington, J.J. The potential role of the novel hypothalamic neuropeptides nesfatin-1, phoenixin, spexin and kisspeptin in the pathogenesis of anxiety and anorexia nervosa. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 113, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, A. Nesfatin-1—More than a food intake regulatory peptide. Peptides 2015, 72, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kras, K.; Muszyński, S.; Tomaszewska, E.; Arciszewski, M. Minireview: Peripheral Nesfatin-1 in Regulation of the Gut Activity-15 Years since the Discovery. Animals 2022, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Wan, X. Association of the polymorphism in nucleobindin 2 gene and the risk of metabolic syndrome. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2016, 20, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Hsuchou, H.; Kastin, A.J. Nesfatin-1 crosses the blood-brain barrier without saturation. Peptides 2007, 28, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Mori, M. The brain-adipose axis: A review of involvement of molecules. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.O.; Samson, W.K.; Niehoff, M.L.; Banks, W.A. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to a novel satiety molecule nesfatin-1. Peptides 2007, 28, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanjaneya, M.; Chen, J.; Brown, J.E.; Tripathi, G.; Hallschmid, M.; Patel, S.; Kern, W.; Hillhouse, E.W.; Lehnert, H.; Tan, B.K.; et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 in human and murine adipose tissue: A novel depot-specific adipokine with increased levels in obesity. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3169–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, J.F.; Carrero, J.J.; Lobo, J.C.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Leal, V.O.; Calixto, A.; Geloneze, B.; Mafra, D. The newly identified anorexigenic adipokine nesfatin-1 in hemodialysis patients: Are there associations with food intake, body composition and inflammation? Regul. Pept. 2012, 173, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Hallschmid, M.; Kern, W.; Lehnert, H.; Randeva, H.S. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid/plasma ratio of the novel satiety molecule, nesfatin-1/NUCB-2, in obese humans: Evidence of nesfatin-1/NUCB-2 resistance and implications for obesity treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, G.M.; Yamamah, G.; Ibrahim, A.; El-lebedy, D.; Farid, T.M.; Mahmoud, R. Regulatory Peptides Nesfatin-1 in childhood and adolescent obesity and its association with food intake, body composition and insulin resistance. Regul. Pept. 2014, 188, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Shimizu, H.; Yamada, M.; Osaki, A.; Oh-I, S.; Ariyama, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Okada, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Satoh, T.; et al. Fasting concentrations of nesfatin-1 are negatively correlated with body mass index in non-obese males. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 73, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaci, A.; Catli, G.; Anik, A.; Kume, T.; Bober, E. The relation of serum nesfatin-1 level with metabolic and clinical parameters in obese and healthy children. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T.; Stengel, A.; Ahnis, A.; Buße, P.; Elbelt, U.; Klapp, B.F. NUCB2/nesfatin-1 is associated with elevated scores of anxiety in female obese patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, K.; Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Keshavarz, S.A.; Koohdani, F.; Saboor-Yaraghi, A.A.; Hosseini, S.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Djalali, M. Crosstalk between circulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, adipokines and metabolic syndrome in obese subjects. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ari, M.; Ozturk, O.H.; Bez, Y.; Oktar, S.; Erduran, D. High plasma nesfatin-1 level in patients with major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T.; Weibert, E.; Ahnis, A.; Obbarius, A.; Elbelt, U.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Stengel, A. Alterations of circulating NUCB2/nesfatin-1 during short term therapeutic improvement of anxiety in obese inpatients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 79, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.; Ahnis, A.; Elbelt, U.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Stengel, A. NUCB2/nesfatin-1 is associated with elevated levels of anxiety in anorexia nervosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałasz, A.; Rojczyk, E.; Siwiec, A.; Janas-Kozik, M. Nesfatin-1 in the neurochemistry of eating disorders. Psychiatr. Pol. 2020, 54, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paonessa, F.; Foti, D.; Costa, V.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, G.; Leone, F.; Luciano, F.; Wu, F.; Lee, A.S.; Gulletta, E.; et al. Activator protein-2 overexpression accounts for increased insulin receptor expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5085–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.A.; Labadorf, A.; Kennedy, N.J.; Han, M.S.; Yap, Y.S.; Matthews, B.; Xin, X.; Sun, L.; Davis, R.J.; Lodish, H.F.; et al. Analysis of In Vitro Insulin-Resistance Models and Their Physiological Relevance to InVivo Diet-Induced Adipose Insulin Resistance. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Danielson, K.M.; Benton, M.C.; Ziegler, O.; Shah, R.; Stubbs, R.S.; Das, S.; Macartney-Coxson, D. miRNA Signatures of Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Obesity 2017, 25, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corigliano, D.M.; Syed, R.; Messineo, S.; Lupia, A.; Patel, R.; Reddy, C.V.R.; Dubey, P.K.; Colica, C.; Amato, R.; De Sarro, G.; et al. Indole and 2,4-Thiazolidinedione conjugates as potential anticancer modulators. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Currò, G.; Navarra, G.; Brunetti, F.S.; Mirabelli, M.; Corigliano, D.M.; Kintscher, U.; Britti, D.; et al. Obesity-related hypoxia via miR-128 decreases insulin-receptor expression in human and mouse adipose tissue promoting systemic insulin resistance. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO World Health Organization. Obesity Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Rep. WHO Consult. 2000, 894, 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.W.; Karg, R.S.; Spitzer, R.L. SCID-5-CV. Intervista Clinica Strutturata per i Disturbi del DSM-5; Raffaello Cortina Editore: Milano, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Calugi, S.; Milanese, C.; Sartirana, M.; El Ghoch, M.; Sartori, F.; Geccherle, E.; Coppini, A.; Franchini, C.; Dalle Grave, R. The Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire: Reliability and validity of the Italian version. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroleo, M.; Carbone, E.A.; Greco, M.; Corigliano, D.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Fazia, G.; Rania, M.; Aloi, M.; Gallelli, L.; Segura-Garcia, C.; et al. Brain-Behavior-Immune Interaction: Serum Cytokines and Growth Factors in Patients with Eating Disorders at Extremes of the Body Mass Index (BMI) Spectrum. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, R.A.; Ranieri, W.F.; Kumar, G.; Beck, A.T. Beck Depression Inventory-II items associated with self-reported symptoms of ADHD in adult psychiatric outpatients. J. Pers. Assess. 2003, 80, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, R.J.; Tarescavage, A.M.; Ben-Porath, Y.S.; Ashton, K.; Heinberg, L.J. Replication and evaluation of a proposed two-factor Binge Eating Scale (BES) structure in a sample of bariatric surgery candidates. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvaal, K.; Ulstein, I.; Nordhus, I.H.; Engedal, K. The Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI): The state scale in detecting mental disorders in geriatric patients. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 20, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messineo, S.; Laria, A.E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Huertas, R.M.L.; Foti, D.P.; Brunetti, A. Cooperation between HMGA1 and HIF-1 contributes to hypoxia-induced VEGF and Visfatin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 27, 7–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Xiao, T.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Complex Relationship between Obesity and the Fat Mass and Obesity Locus. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaya, Y.; Miura, A.; Okada, S.; Ohshima, K.; Mori, M. Nucleobindin-2 is a positive modulator of EGF-dependent signals leading to enhancement of cell growth and suppression of adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3308–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Oh-I, S.; Okada, S.; Mori, M. Nesfatin-1: An overview and future clinical application. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laria, A.E.; Messineo, S.; Arcidiacono, B.; Varano, M.; Chiefari, E.; Semple, R.K.; Rocha, N.; Russo, D.; Cuda, G.; Gaspari, M.; et al. Secretome analysis of hypoxia-induced 3T3-L1 adipocytes uncovers novel proteins potentially involved in obesity. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1700260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, L.K.; Hofer, M.; Pramsohler, S.; Kaser, S.; Ebenbichler, C.; Haacke, S.; Gatterer, H.; Netzer, N.C. Adiponectin, leptin and visfatin in hypoxia and its effect for weight loss in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, A.; Shimizu, H.; Ishizuka, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Mori, M.; Inoue, S. Enhanced expression of nesfatin/nucleobindin-2 in white adipose tissue of ventromedial hypothalamus-lesioned rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Goebel, M.; Yakubov, I.; Wang, L.; Witcher, D.; Coskun, T.; Taché, Y.; Sachs, G.; Lambrecht, N.W.G. Identification and characterization of nesfatin-1 immunoreactivity in endocrine cell types of the rat gastric oxyntic mucosa. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 25, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wang, B.; Wood, I.S. Hypoxia in adipose tissue: A basis for the dysregulation of tissue function in obesity? Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chan, R.M.E.; Tan, K.M.L.; Poh, L.K.S.; Loke, K.Y.; Wang, J.P.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Lee, K.O.; et al. The association of a nucleobindin 2 gene (NUCB2) variant with childhood adiposity. Gene 2013, 516, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamalizadeh, M.; Mirzaei Dahka, S.; Vahid, F.; Bourbour, F.; Badeli, M.; JavadiKooshesh, S.; Mosavi Jarrahi, S.A.; Akbari, M.E.; Azizi Tabesh, G.; Montazeri, F.; et al. Does the rs9939609 FTO gene polymorphism affect fat percentage? A meta-analysis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuteri, A.; Sanna, S.; Chen, W.M.; Uda, M.; Albai, G.; Strait, J.; Najjar, S.; Nagaraja, R.; Orrú, M.; Usala, G.; et al. Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, R.; Hägglund, M.; Olszewski, P.K.; Stephansson, O.; Jacobsson, J.A.; Olszewska, A.M.; Levine, A.S.; Lindblom, J.; Schiöth, H.B. The obesity gene, FTO, is of ancient origin, up-regulated during food deprivation and expressed in neurons of feeding-related nuclei of the brain. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, K.M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Lara, J.; Ashor, A.W.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Saris, W.H.; Gibney, M.; Manios, Y.; Traczyk, I.; et al. Associations between FTO genotype and total energy and macronutrient intake in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, P.; Yeo, G.S.H. The biology of FTO: From nucleic acid demethylase to amino acid sensor. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.L.; Xie, H.J.; Xie, H.Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, J.; Hu, J.S.; Peng, C.Y. Association between fat mass and obesity associated (FTO) gene rs9939609 A/T polymorphism and polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Guan, H.Z.; Jiang, Z.Y. Fasting plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and the nutrient-related fluctuation of nesfatin-1 level in normal humans. Regul. Pept. 2010, 159, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, K.; Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Keshavarz, S.A.; Koohdani, F.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Saboor-Yaraghi, A.A.; Hosseini, S.; Chamari, M.; Zareei, M.; Djalali, M. Association of nesfatin-1 level with body composition, dietary intake and resting metabolic rate in obese and morbid obese subjects. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2015, 9, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Escoté, X.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Peral, B.; Cardona, F.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. FABP4 Dynamics in Obesity: Discrepancies in Adipose Tissue and Liver Expression Regarding Circulating Plasma Levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anik, A.; Çatli, G.; Abaci, A.; Küme, T.; Bober, E. Fasting and postprandial levels of a novel anorexigenic peptide nesfatin in childhood obesity. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogiso, K.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; Nakahara, T.; Ushikai, M.; Haruta, I.; Koyama, K.I.; Amitani, M.; Harada, T.; Yasuhara, D.; et al. Plasma nesfatin-1 concentrations in restricting-type anorexia nervosa. Peptides 2011, 32, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, J.I.; Blanco, A.M.; Canosa, L.F.; Unniappan, S. Glucose, amino acids and fatty acids directly regulate ghrelin and NUCB2/nesfatin-1 in the intestine and hepatopancreas of goldfish (Carassius auratus) in vitro. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 206, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, A.M.; Bertucci, J.I.; Delgado, M.J.; Valenciano, A.I.; Unniappan, S. Tissue-specific expression of ghrelinergic and NUCB2/nesfatin-1 systems in goldfish (Carassius auratus) is modulated by macronutrient composition of diets. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 195, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çatli, G.; Abaci, A.; Anik, A.; Böber, E. Low serum nesfatin-1 levels may be a contributing factor for monogenic obesity due to prohormone convertase 1 deficiency. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shu, X.; Cong, Z.K.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, H. Nesfatin-1 acts on the dopaminergic reward pathway to inhibit food intake. Neuropeptides 2015, 53, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, U.; Bulbuller, N.; Cakir, T.; Habibi, M.; Mayir, B.; Koc, U.; Aslaner, A.; Ellidag, H.Y.; Gomceli, I. Nesfatin-1 hormone levels in morbidly obese patients after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ser, K.-H.; Chong, K.; Chen, S.-C.; Lee, P.-C.; Liao, Y.-D.; Lee, S.-D. Differential Influences of Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy on Plasma Nesfatin-1 and Obestatin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5830–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, P.K.; Klump, K.L.; Miller, K.B.; McGue, M.; Iacono, W.G. Shared transmission of eating disorders and anxiety disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2005, 38, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.; Xu, L.; Morava, É.; Faludi, G.; Palkovits, M.; Roubos, E.W.; Kozicz, T. Neuropharmacology Sex-specific differences in the dynamics of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript and nesfatin-1 expressions in the midbrain of depressed suicide victims vs. controls. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunay, H.; Tutuncu, R.; Aydin, S.; Dag, E.; Abasli, D. Decreased plasma nesfatin-1 levels in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 36.4 | 12.7 | |
| Fr | % | ||
| Sex | F | 45 | 63.4 |
| M | 26 | 36.6 | |
| BMI | Underweight | 14 | 19.7 |
| Normal weight | 16 | 22.5 | |
| Obese 1 | 14 | 19.7 | |
| Obese 2 | 27 | 38.0 | |
| Diagnosis | Healthy control | 20 | 28.2 |
| Anorexia nervosa | 10 | 14.1 | |
| Binge eating disorder | 17 | 23.9 | |
| Obese | 24 | 33.8 | |
| BDI-II | 16.1 | 12.3 | |
| STAI | State | 43.3 | 13.3 |
| Trait | 45.4 | 13.0 | |
| BES | 12.4 | 11.7 |
| Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | Underweight | 57.54 | 34.582 |
| Normal weight | 59.28 | 25.448 | |
| Obese 1 | 59.05 | 32.268 | |
| Obese 2 | 48.70 | 12.894 | |
| Diagnosis | Healthy control | 56.93 | 23.847 |
| Anorexia nervosa | 61.54 | 39.913 | |
| Binge eating disorder | 50.60 | 20.013 | |
| Obese | 53.58 | 23.355 | |
| Sex | F | 53.31 | 24.843 |
| M | 57.88 | 26.678 |
| Nesfatin-1 (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hyperphagia | r | 0.119 |
| p | 0.478 | |
| Binge | r | −0.033 |
| p | 0.844 | |
| Grazing | r | −0.123 |
| p | 0.462 | |
| Emotional eating | r | 0.031 |
| p | 0.852 | |
| Post-dinner eating | r | −0.218 |
| p | 0.188 | |
| Night-eating | r | −0.015 |
| p | 0.928 | |
| Sweet eating | r | −0.050 |
| p | 0.767 | |
| Social eating | r | 0.180 |
| p | 0.279 | |
| Craving for carbohydrates | r | −0.073 |
| p | 0.663 |
| Variable | Non-Standardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SD Error | β | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 1.765 | 0.140 | 12.603 | 0.000 | |
| Child obesity | 0.599 | 0.283 | 0.307 | 2.115 | 0.040 | |
| 2 | (Constant) | 2.096 | 0.166 | 12.590 | 0.000 | |
| Child obesity | 0.852 | 0.271 | 0.437 | 3.144 | 0.003 | |
| BES | −0.030 | 0.010 | −0.431 | −3.103 | 0.003 | |
| rs757081 | Mean | N | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 49.01 | 12 | 13.468 |
| CG | 52.90 | 11 | 12.494 |
| GG | 40.10 | 3 | 5.157 |
| Total | 49.63 | 26 | 12.655 |
| rs9939609 | Mean | N | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| AA | 47.52 | 5 | 4.619 |
| AT | 50.51 | 14 | 12.569 |
| TT | 49.37 | 7 | 17.470 |
| Total | 54.99 | 26 | 25.432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caroleo, M.; Carbone, E.A.; Arcidiacono, B.; Greco, M.; Primerano, A.; Mirabelli, M.; Fazia, G.; Rania, M.; Hribal, M.L.; Gallelli, L.; et al. Does NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 Influence Eating Behaviors in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder? Toward a Neurobiological Pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020348
Caroleo M, Carbone EA, Arcidiacono B, Greco M, Primerano A, Mirabelli M, Fazia G, Rania M, Hribal ML, Gallelli L, et al. Does NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 Influence Eating Behaviors in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder? Toward a Neurobiological Pathway. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020348
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaroleo, Mariarita, Elvira Anna Carbone, Biagio Arcidiacono, Marta Greco, Amedeo Primerano, Maria Mirabelli, Gilda Fazia, Marianna Rania, Marta Letizia Hribal, Luca Gallelli, and et al. 2023. "Does NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 Influence Eating Behaviors in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder? Toward a Neurobiological Pathway" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020348
APA StyleCaroleo, M., Carbone, E. A., Arcidiacono, B., Greco, M., Primerano, A., Mirabelli, M., Fazia, G., Rania, M., Hribal, M. L., Gallelli, L., Foti, D. P., De Fazio, P., Segura-Garcia, C., & Brunetti, A. (2023). Does NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 Influence Eating Behaviors in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder? Toward a Neurobiological Pathway. Nutrients, 15(2), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020348













