Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Histology
2.4. IHC Assay
2.5. Plasma and Liver Chemistry
2.6. Real-Time PCR
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analyses
2.8. Elisa
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
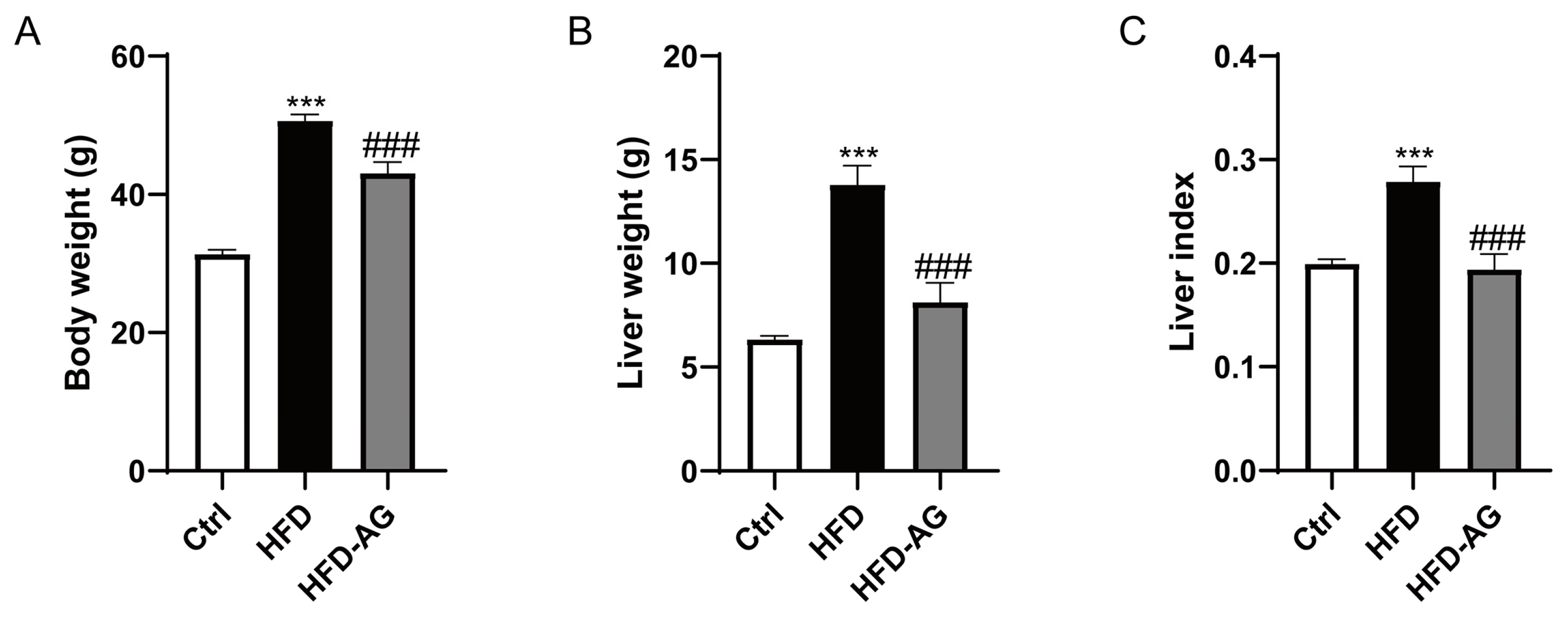
3.1. Effect of AG Administration on Body Weight, Liver Mass, and Liver Index in HFD-Induced Mice
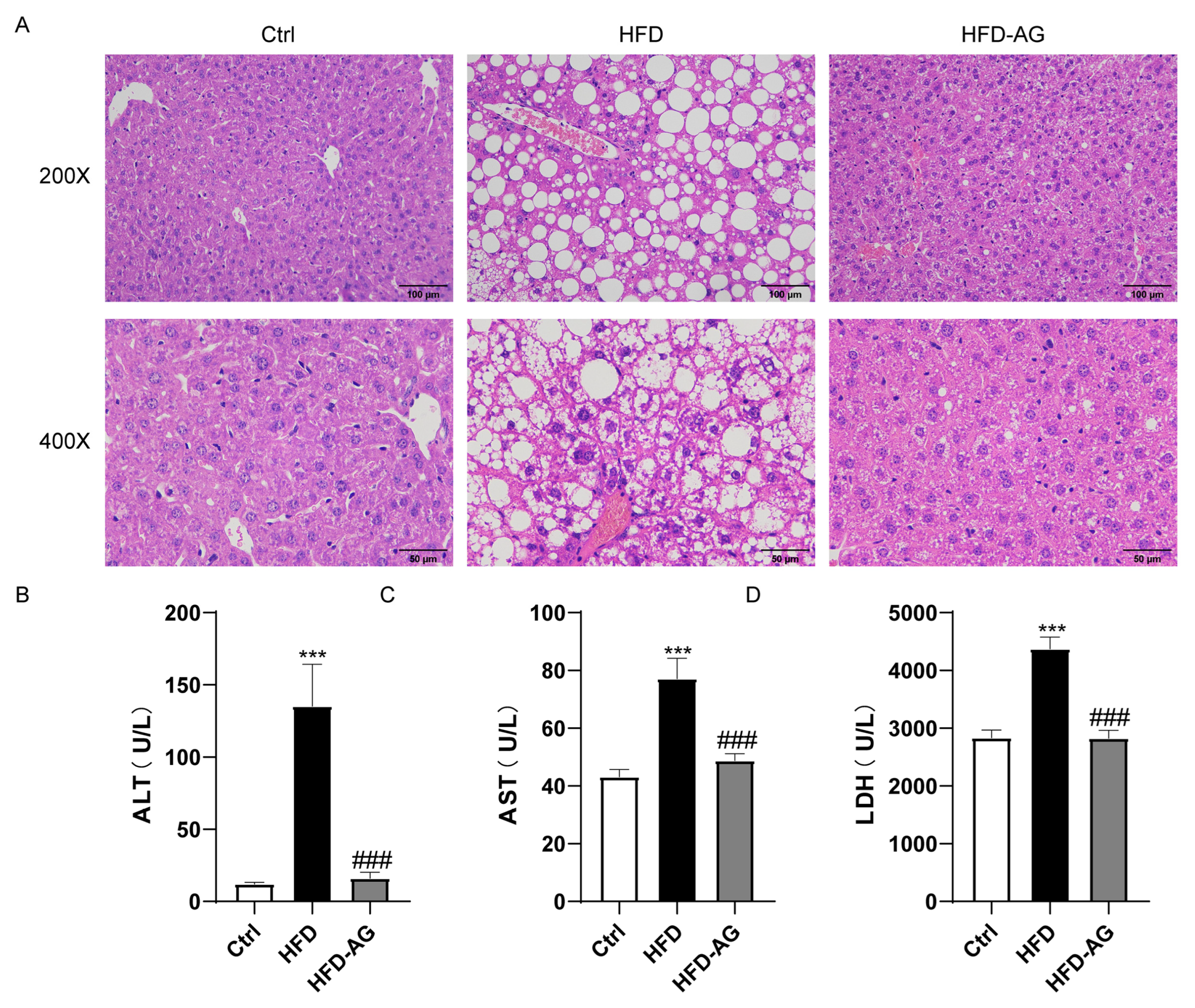
3.2. Effects of AG Treatment on HFD-Induced Liver Damage in Mice
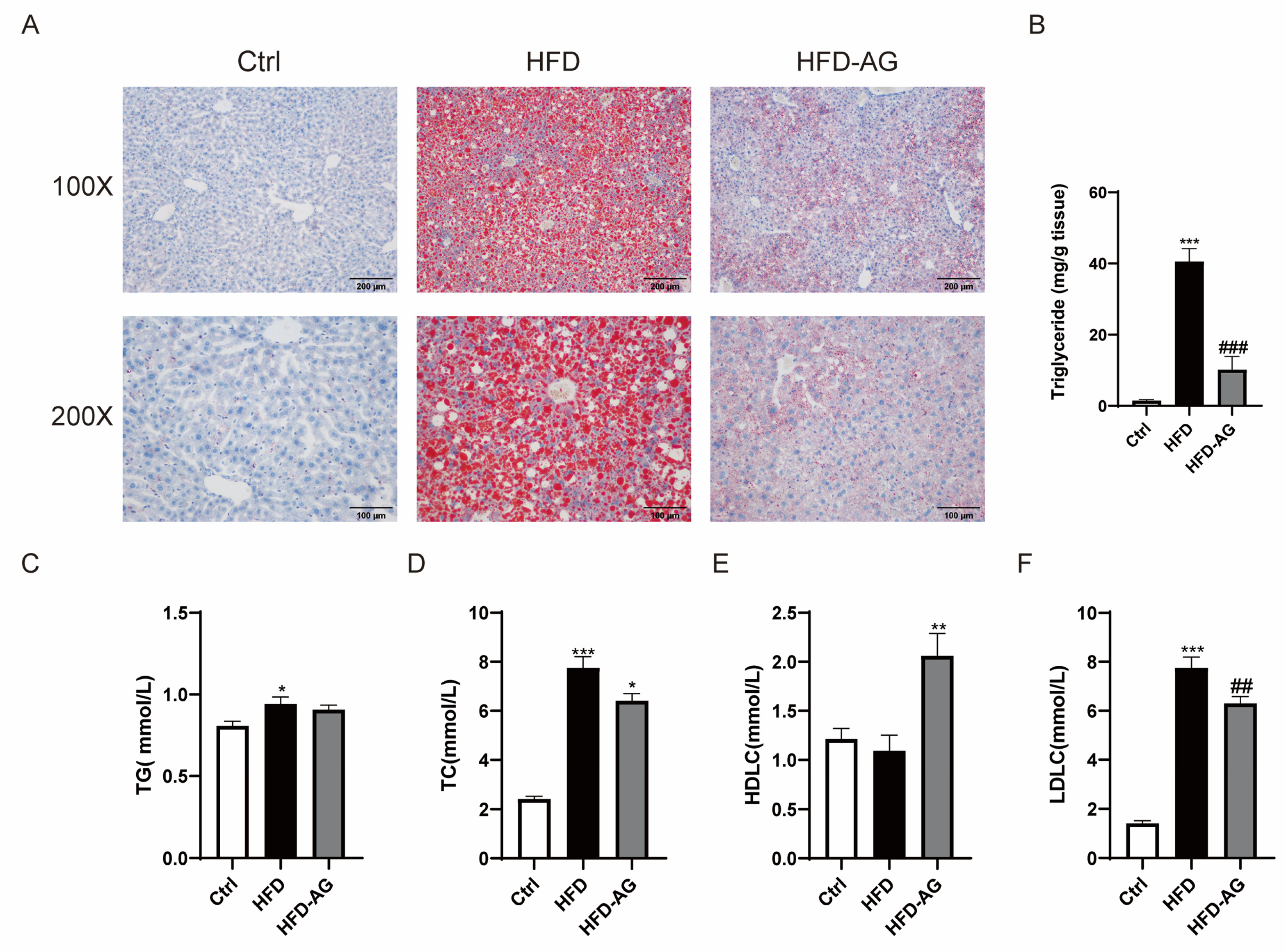
3.3. Attenuation of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation via AG Supplementation in HFD-Induced Mice
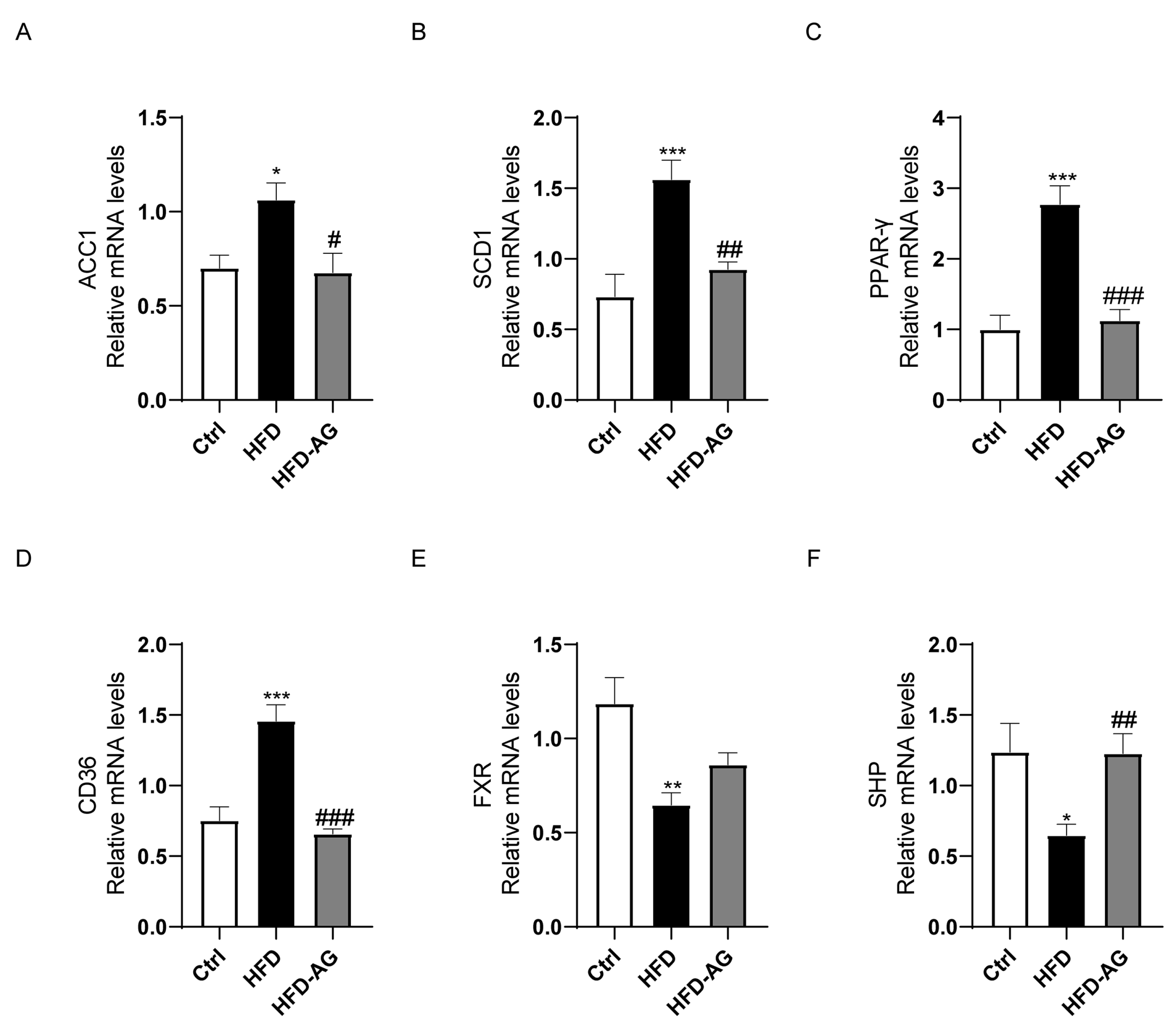
3.4. Impact of AG on Fatty-Acid-Metabolism-Related Genes in NAFLD Mice
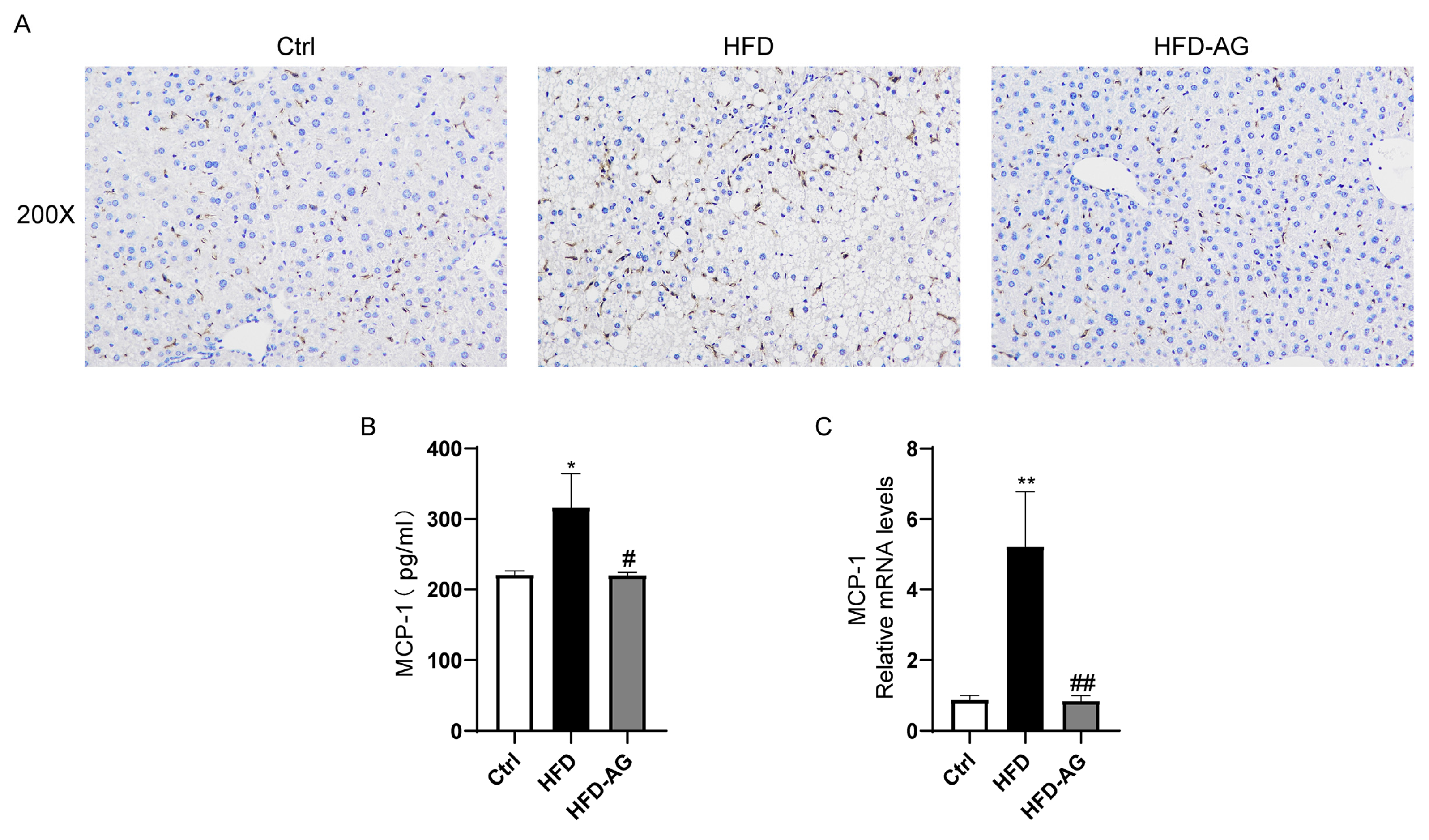
3.5. Mitigation of Macrophage Accumulation by AG in HFD-Treated Mice
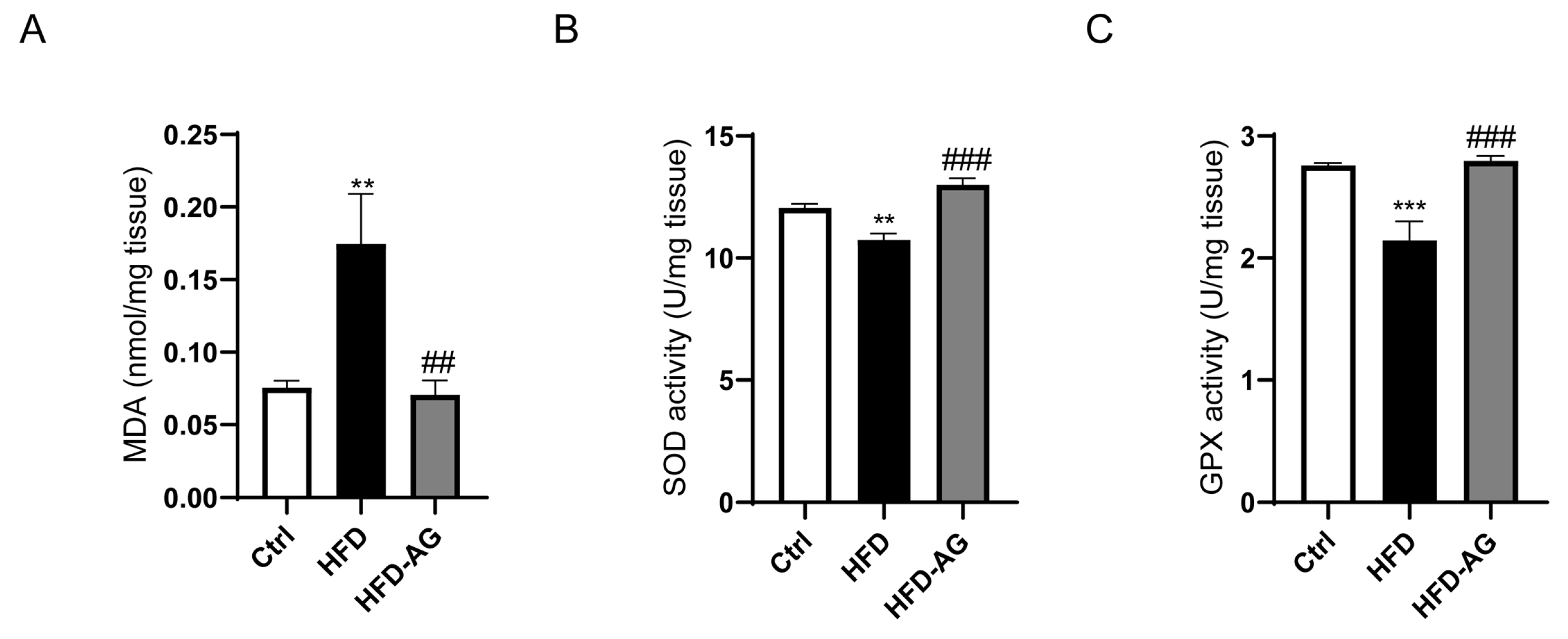
3.6. Hepatic Oxidative Stress Mitigation by AG in HFD-Induced Mice
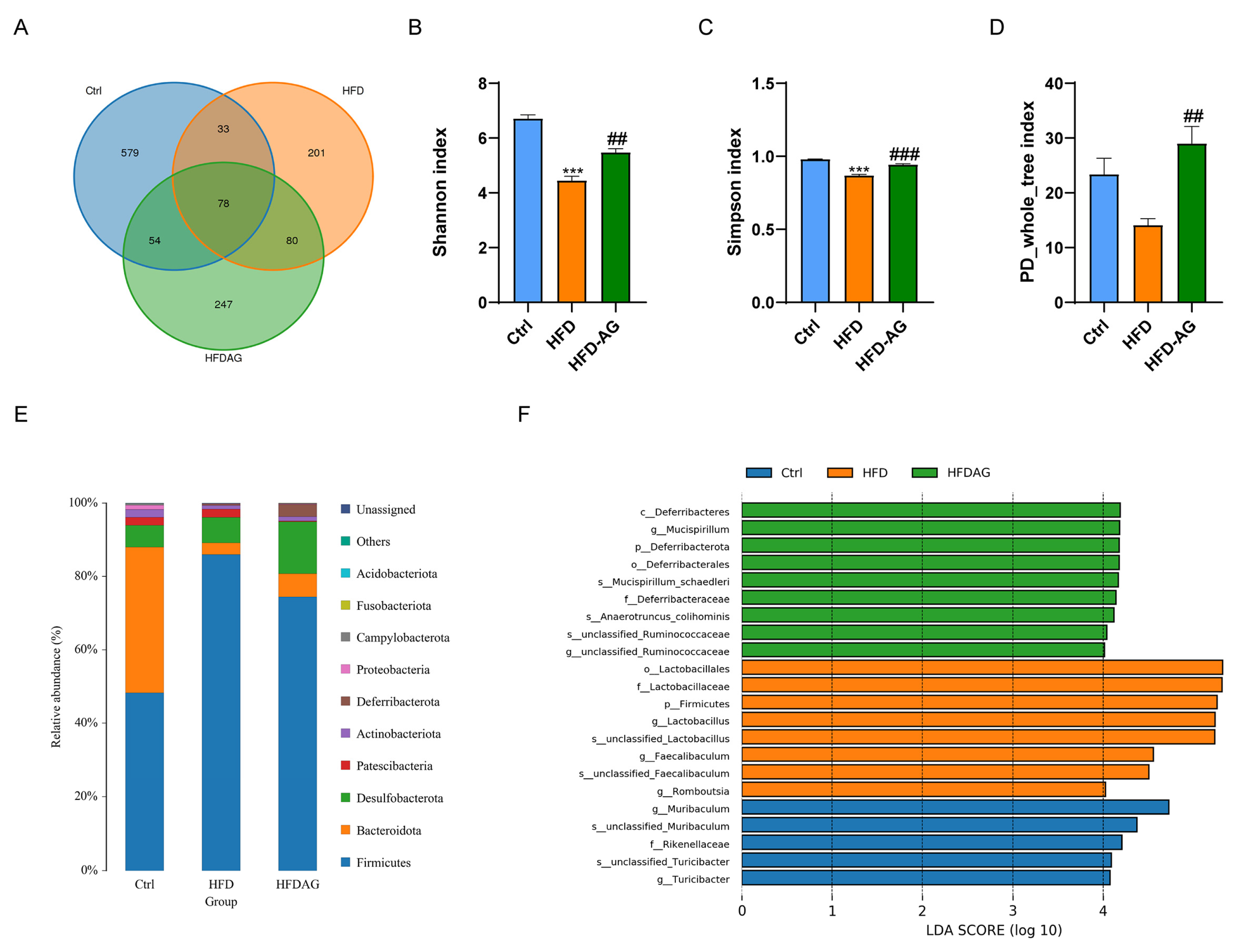
3.7. Effect of AG on Gut Microbiota Profiles in HFD-Fed Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelmalek, M.F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Another leap forward. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.G.; Kim, S.U.; Wong, V.W. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.E.; Bugianesi, E.; Marchesini, G.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Serfaty, L.; Negro, F.; Caldwell, S.H.; Ratziu, V.; et al. Current and future therapeutic regimens for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternostro, R.; Trauner, M. Current treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhaisi, S.A.M.; Bajaj, J.S. The Influence of the Microbiome on NAFLD and NASH. Clin. Liver. Dis. 2021, 17, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.R.; Yang, W.J.; Tan, Q.H.; Bai, S.; Zhong, H.; Tai, Y.; Tong, H. Gut microbiota therapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from randomized clinical trials. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszak, M.; Szulinska, M.; Walczak-Galezewska, M.; Bogdanski, P. Nutritional Approach Targeting Gut Microbiota in NAFLD-To Date. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ying, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Inflammation, and Regulating Autophagy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Santos, R.; da Silva Cardoso, G.; da Costa Lima, L.; de Sousa Cavalcante, M.L.; Silva, M.S.; Cavalcante, A.K.M.; Severo, J.S.; de Melo Sousa, F.B.; Pacheco, G.; Alves, E.H.P.; et al. L-Glutamine and Physical Exercise Prevent Intestinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Without Improving Gastric Dysmotility in Rats with Ulcerative Colitis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhao, Y. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of the effects of alanyl-glutamine supplementation on C2C12 myoblasts injured by energy deprivation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16114–16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, R.J., Jr.; Silva, R.G., Jr.; Vasconcelos, M.P.; Guimaraes, S.B.; Vasconcelos, P.R.; Garcia, J.H. Preconditioning with L-alanyl-glutamine reduces hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2011, 26 (Suppl. S1), 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.A.; Vasconcelos, P.R.; Souza, C.M.; Andrade, G.M.; Moraes, M.O.; Costa, P.E.; Coelho, G.R.; Garcia, J.H. L-Alanyl-Glutamine Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Liver Transplantation Patients. Transpl. Proc. 2015, 47, 2478–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ying, H.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Protects Mice against Methionine- and Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, C.; Wehr, A.; Karlmark, K.R.; Heymann, F.; Vucur, M.; Gassler, N.; Huss, S.; Klussmann, S.; Eulberg, D.; Luedde, T.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut 2012, 61, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Duan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Baicalin Attenuates Oxidative Stress in a Tissue-Engineered Liver Model of NAFLD by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species. Nutrients 2022, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Nakajima, A.; Nogami, A.; Yoneda, M. Current Research on the Pathogenesis of NAFLD/NASH and the Gut-Liver Axis: Gut Microbiota, Dysbiosis, and Leaky-Gut Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recena Aydos, L.; do Amaral, L.A.; de Souza, R.S.; Jacobowski, A.C.; Dos Santos, E.F.; Rodrigues Macedo, M.L. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High-Fat Diet in C57bl/6 Models. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, K.T.; Enos, R.T.; Bader, J.E.; Sougiannis, A.T.; Carson, M.S.; Chatzistamou, I.; Carson, J.A.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Murphy, E.A. Prolonged high-fat-diet feeding promotes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alters gut microbiota in mice. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, S.S.; Sukhdeo, S.V.; Vallikannan, B.; Ponesakki, G. Lutein ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity, fatty liver, and glucose intolerance in C57BL/6J mice. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Wang, H.; Pan, X.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Weng, J. Mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Pathomechanisms and pharmacotherapies. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5681–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Xiaoli, A.M.; Yang, F. Regulation and Metabolic Significance of De Novo Lipogenesis in Adipose Tissues. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liao, S.; Pang, D.; Li, E.; Liu, T.; Liu, F.; Zou, Y. The transported active mulberry leaf phenolics inhibited adipogenesis through PPAR-gamma and Leptin signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, C.J.; Bayliss, J.; Keenan, S.N.; Montgomery, M.K.; Watt, M.J. Investigating dual inhibition of ACC and CD36 for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E187–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, B.L.; Sedgeman, L.R.; Williams, K.J.; Morand, P.; Cheng, A.; Jarrett, K.E.; Chan, A.P.; Brearley-Sholto, M.C.; Wahlstrom, A.; Ashby, J.W.; et al. FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1671–1684.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Liu, S.; Fang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, S.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Xue, S.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Inonotus obliquus and its bioactive compounds alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating FXR/SHP/SREBP-1c axis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 921, 174841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, G.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Meng, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Diosgenin attenuates nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the hepatic FXR-SHP-SREBP1C/PPARalpha/CD36 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 952, 175808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Passarella, S.; Shanmugam, H.; Noviello, M.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Mitochondria as Players and Targets of Therapies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants Balance in Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents in chronic liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.A.; Friedman, S.L. Inflammatory and fibrotic mechanisms in NAFLD-Implications for new treatment strategies. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Metlakunta, A.; Dedousis, N.; Zhang, P.; Sipula, I.; Dube, J.J.; Scott, D.K.; O’Doherty, R.M. Depletion of liver Kupffer cells prevents the development of diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2010, 59, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Hadley, J.T.; Li, Z.; Dong, F.; Xu, H.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Adiponectin Alleviates Diet-Induced Inflammation in the Liver by Suppressing MCP-1 Expression and Macrophage Infiltration. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clement, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhai, Z.; Deng, Z.Y.; De Jonge, H.R.; Wu, X.; Ruan, Z. Uridine attenuates obesity, ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and modifies the gut microbiota composition in mice fed with a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Pan, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H. High-fat-diet-induced gut microbiome changes in mice. Stress. Brain 2022, 2, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Ying, H.; Shi, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183988
Zheng Y, Ying H, Shi J, Li L, Zhao Y. Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183988
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yigang, Hanglu Ying, Jiayi Shi, Long Li, and Yufen Zhao. 2023. "Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183988
APA StyleZheng, Y., Ying, H., Shi, J., Li, L., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Alanyl-Glutamine Dipeptide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. Nutrients, 15(18), 3988. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183988





