Improvements of Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice by Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889, a Novel Strain with Psychobiotic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of L. helveticus WHH1889
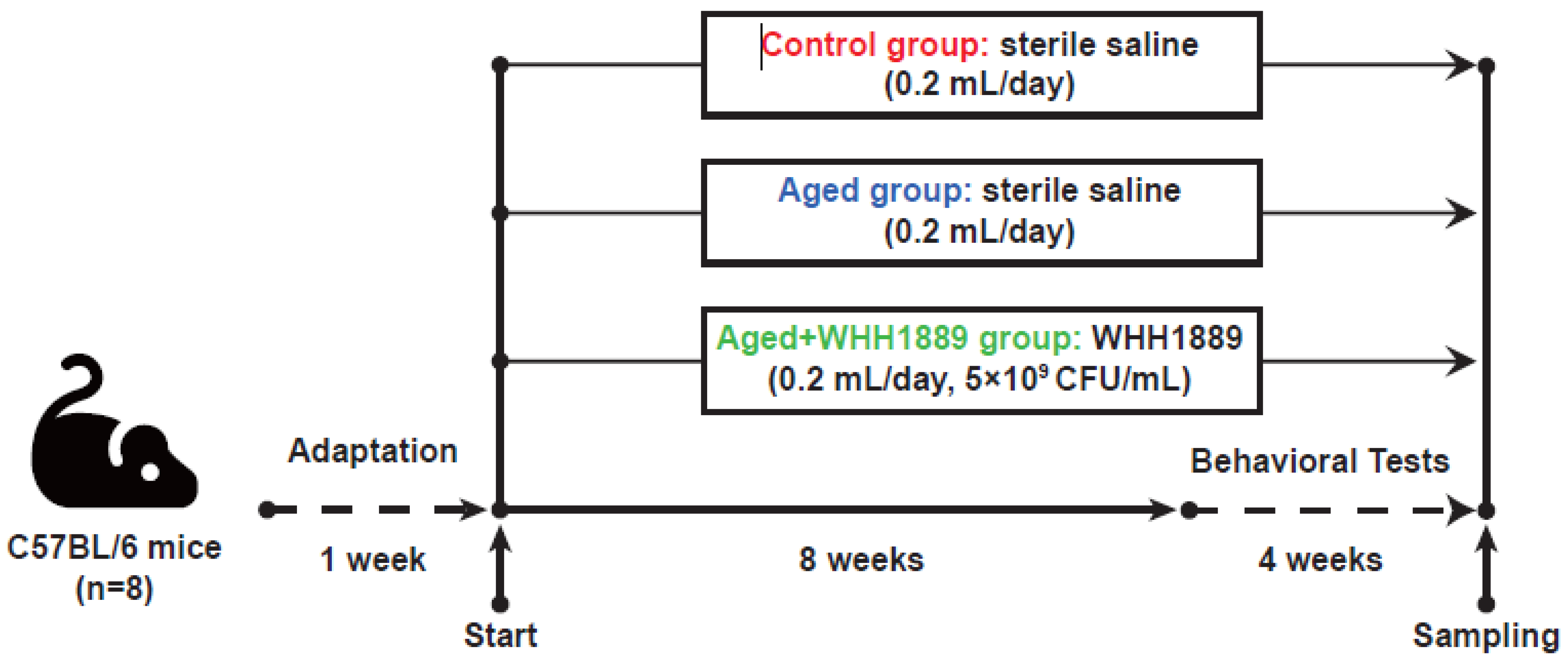
2.2. Experiment Design and Sampling
2.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.4. Active Shuttle Avoidance Test
2.5. Y-Maze Test
2.6. Passive Avoidance Test
2.7. Levels of Neurochemical Factors and Cytokines Determination
2.8. Levels of 5-HTP Evaluation
2.9. Hippocampal Neuronal Nissl Staining Analysis
2.10. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.11. Serum Tryptophan Metabolism—Targeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.12. Gut Microbiome Composition Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
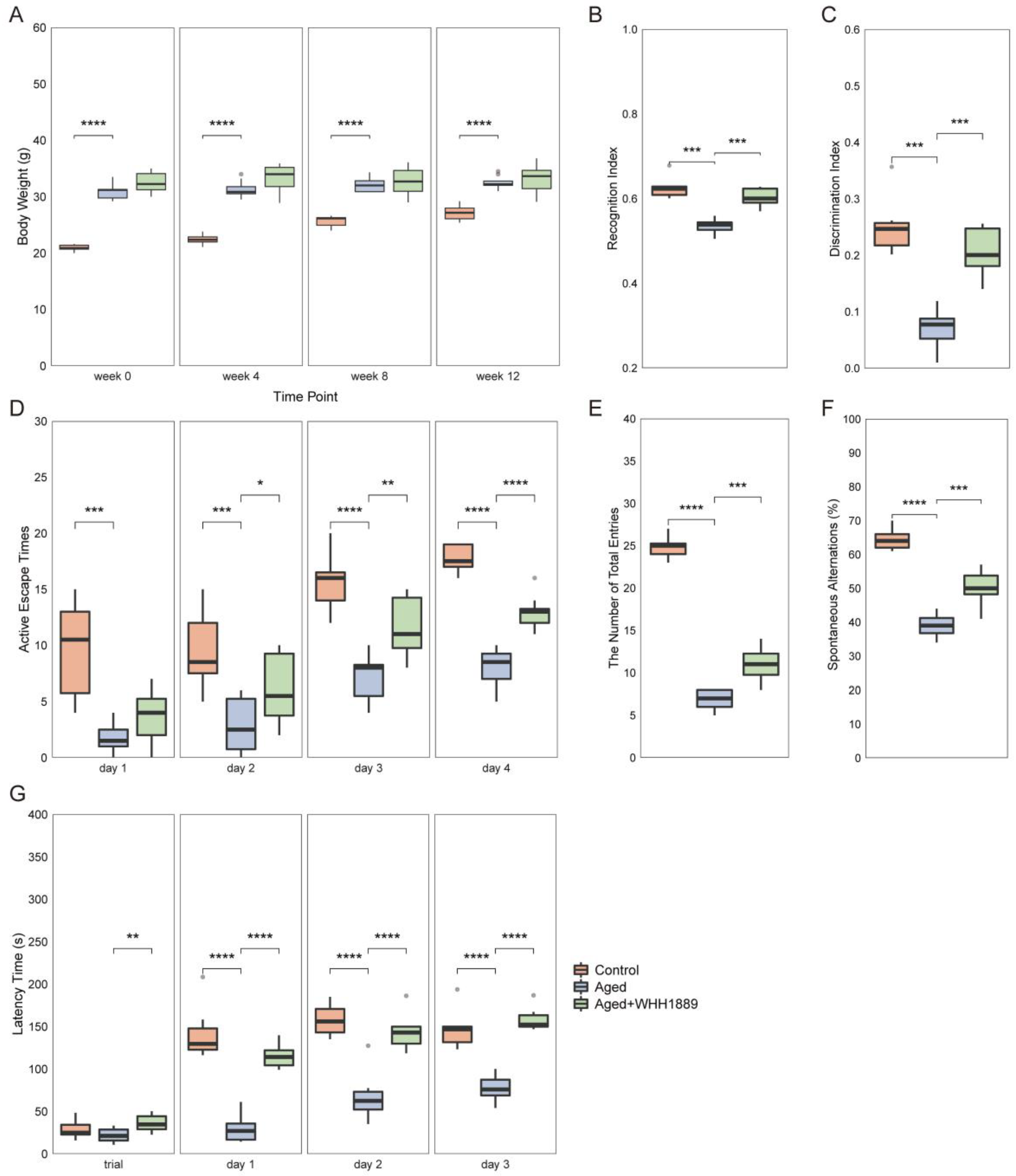
3.1. Effects of WHH1889 on Cognitive Behaviors in Aged Mice
3.2. Effects of WHH1889 on the Number of Hippocampal Neurons in Aged Mice
3.3. Effects of WHH1889 on Neurochemical Factors, Gene Expressions, and Neuroinflammation in Aged Mice
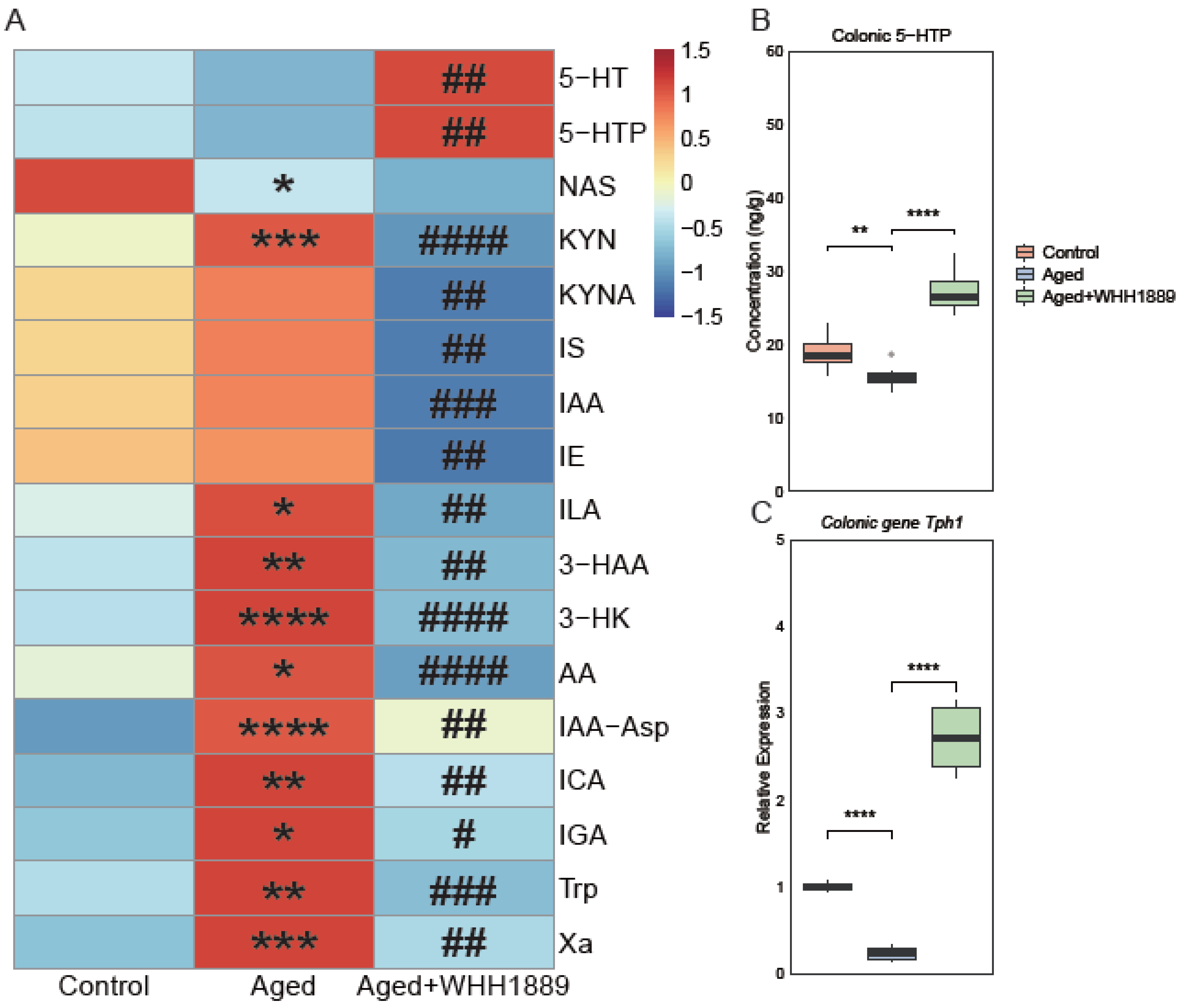
3.4. Effects of WHH1889 on Serum Tryptophan Metabolism in Aged Mice
3.5. Effects of WHH1889 on the Level of 5-HTP and Gene Expression of Tph1 in the Colon of Aged Mice
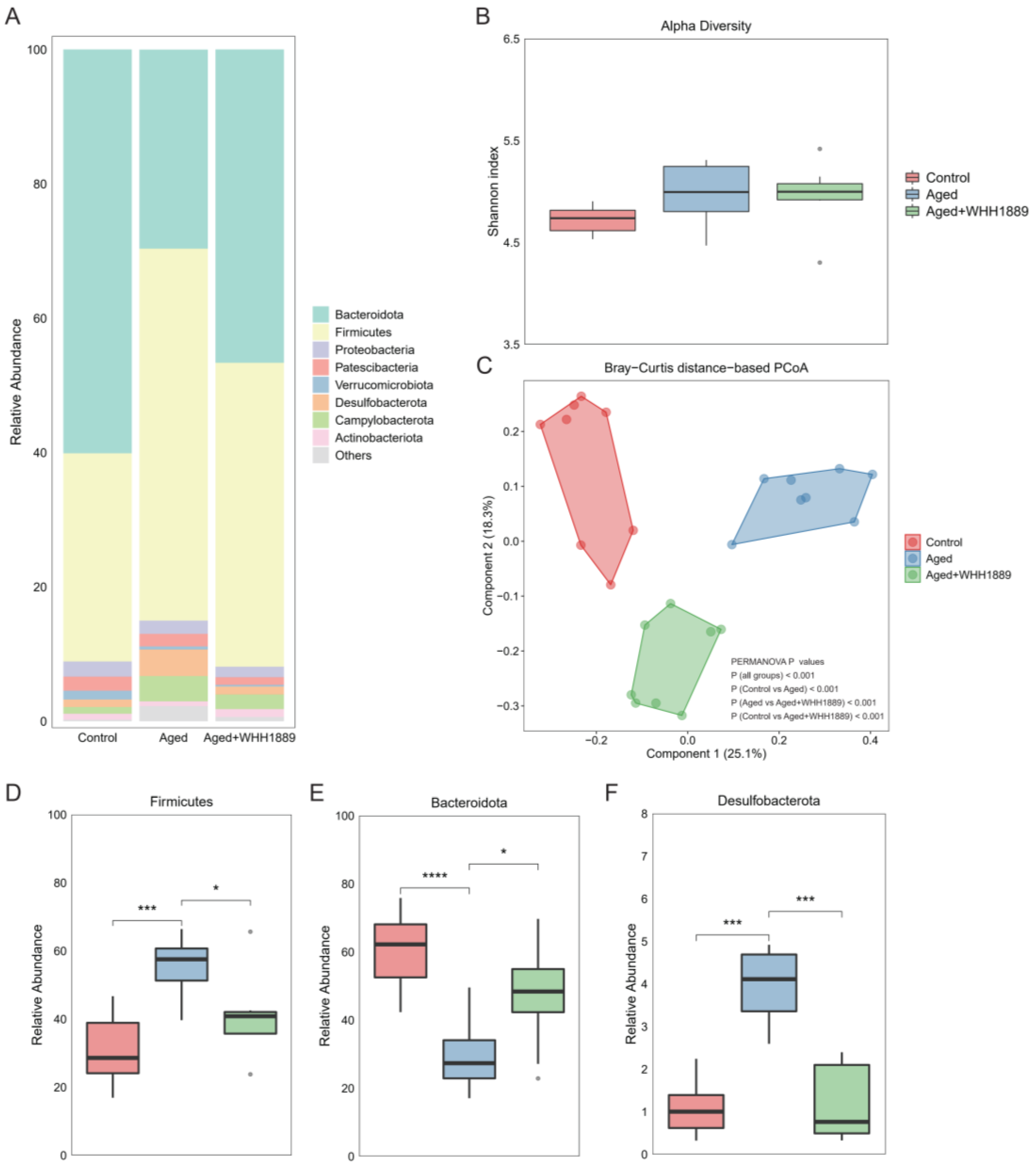
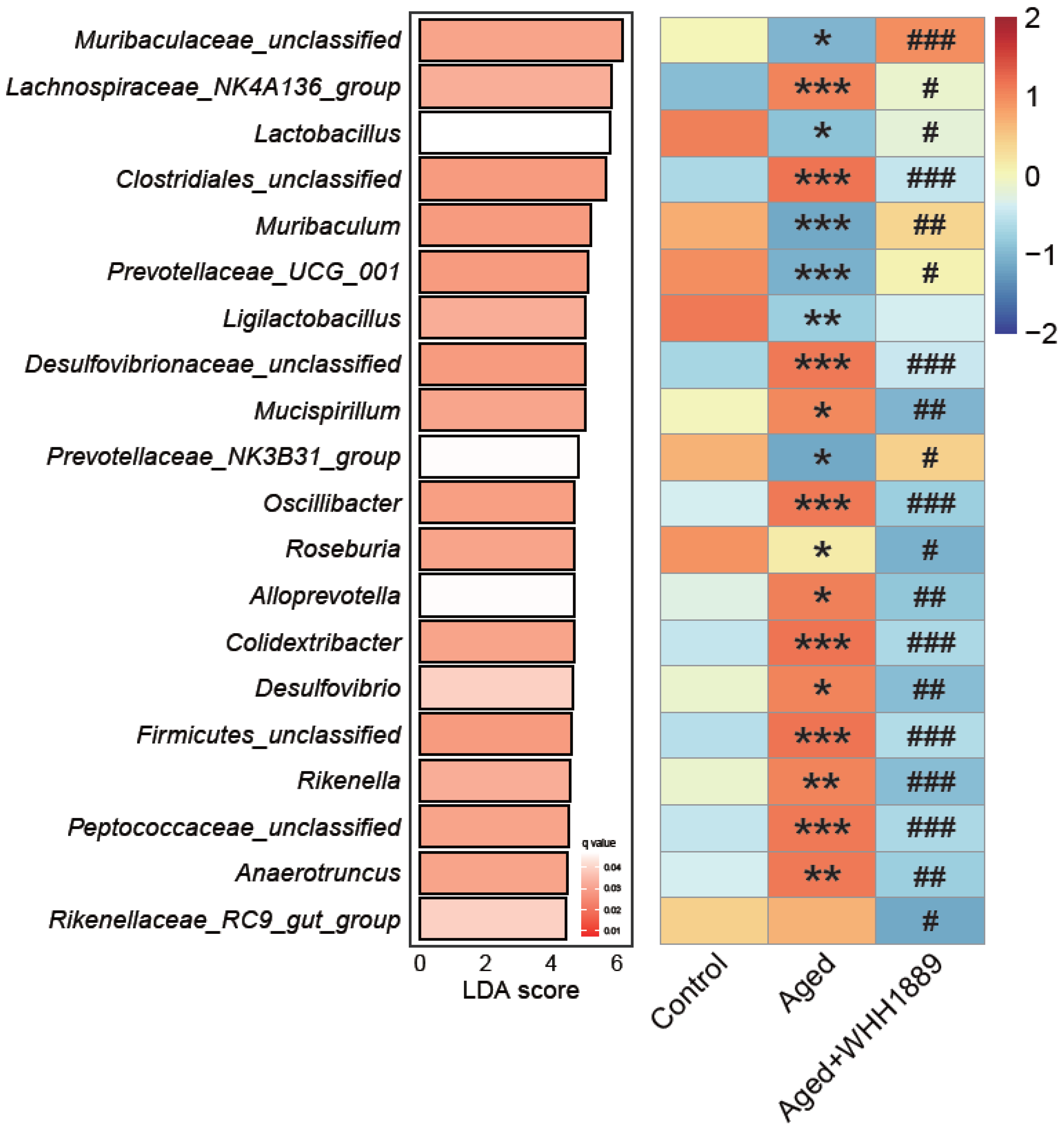
3.6. Impacts of WHH1889 on the Gut Microbial Community in Aged Mice
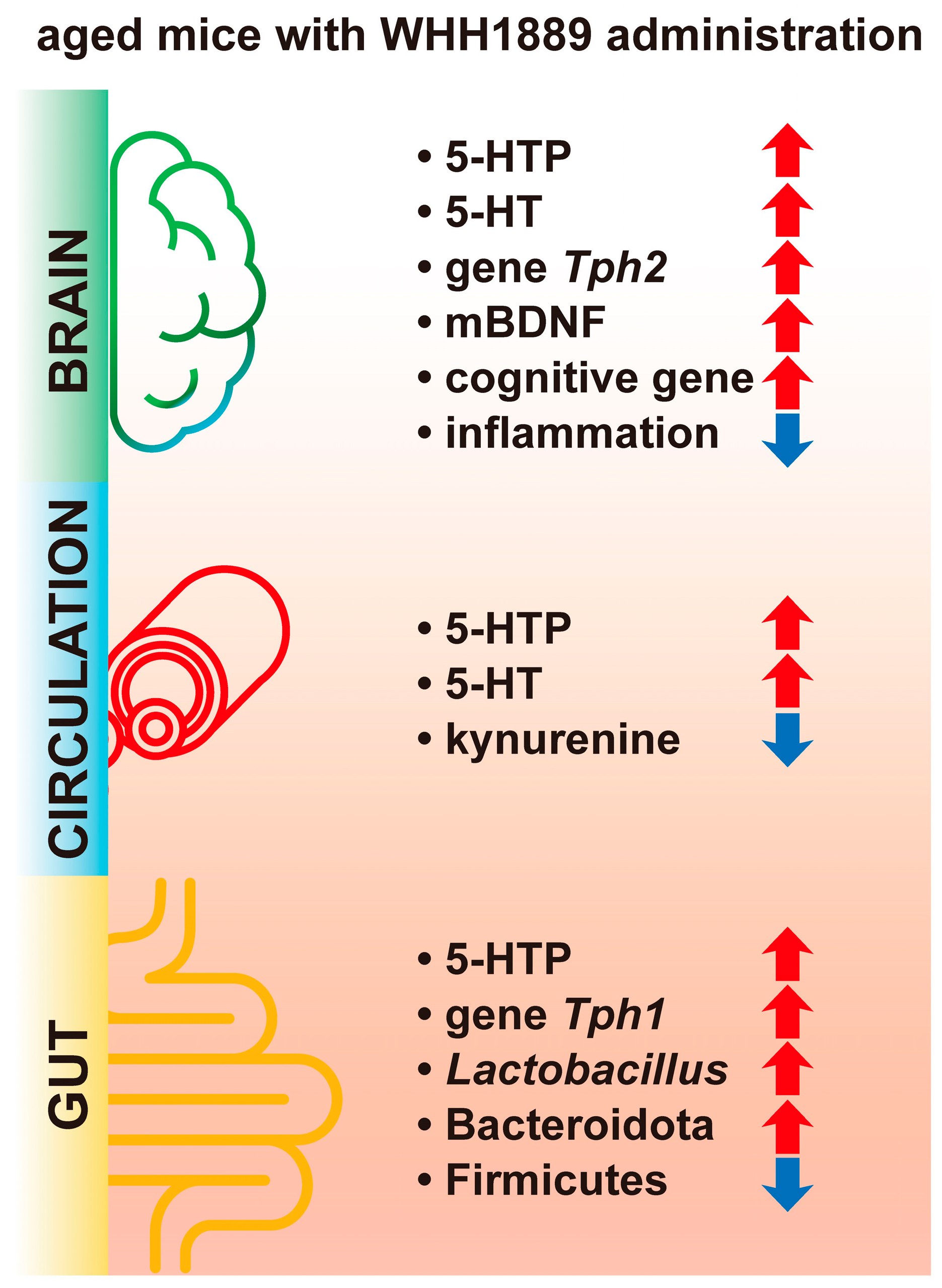
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bettio, L.E.B.; Rajendran, L.; Gil-Mohapel, J. The effects of aging in the hippocampus and cognitive decline. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.; Buzsaki, G.; Eichenbaum, H.; Nadel, L.; Ranganath, C.; Redish, A.D. Viewpoints: How the hippocampus contributes to memory, navigation and cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ning, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Yin, L.; et al. Age-related shifts in gut microbiota contribute to cognitive decline in aged rats. Aging 2020, 12, 7801–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.H.; Chou, P.Y.; Hou, A.T.; Huang, C.L.; Shiu, W.L.; Wang, S. Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 improves cognitive deficits via modulating the hippocampal gene expression and the gut microbiota in D-galactose-induced aging mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5240–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Maudsley, S.; Martin, B. BDNF and 5-HT: A dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L.t.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, E.; Le Gall, G.; Pontifex, M.G.; Sami, S.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G.; Muller, M.; Vauzour, D. Microbial-derived metabolites as a risk factor of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsegiani, A.S.; Shah, Z.A. The influence of gut microbiota alteration on age-related neuroinflammation and cognitive decline. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Mohanty, D. Psychobiotics: A new approach for treating mental illness? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroojzadeh, P.; Bostanabad, S.Y.; Lotfi, H. Psychobiotics: The influence of gut microbiota on the gut-brain axis in neurological disorders. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1952–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Jiang, J.; Yang, T.; Ma, L.; Fu, Z. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium improves physiological function and cognitive ability in aged mice by the regulation of gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.R.; Shin, M.; Mun, D.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeong, D.Y.; Song, M.; Ko, G.; Unno, T.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S. Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum strain JDFM216 improves cognitive behavior and modulates immune response with gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, H.M.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, D.H. Alleviation of cognitive impairment by gut microbiota lipopolysaccharide production-suppressing Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10750–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Liao, Y.C.; Lee, M.C.; Lin, K.J.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chiou, S.Y.; Young, S.L.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, C.C.; Watanabe, K. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 attenuates aging-associated muscle weakness, bone loss, and cognitive impairment by modulating the gut microbiome in mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 708096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraffa, G. Lactobacillus helveticus: Importance in food and health. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Chen, C.L.; Ke, X.Q.; Yu, Y.X.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.C.; Wang, H.F.; Li, Y.J. Ingestion of Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889 improves depressive and anxiety symptoms induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in mice. Benef. Microbes 2022, 13, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordzij, M.; Dekker, F.W.; Zoccali, C.; Jager, K.J. Sample size calculations. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 118, c319–c323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.J.; Kim, K.A.; Hwang, Y.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Anti-inflammaging effects of Lactobacillus brevis OW38 in aged mice. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Wang, B.; Shi, R.; Ye, J.; Xia, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X. Leucine-restricted diet ameliorates obesity-linked cognitive deficits: Involvement of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9404–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, S.; Ni, L.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, A.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z. Bisphenol A impairs cognitive function and 5-HT metabolism in adult male mice by modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Ma, S.Y.; Chen, M.W.; Lin, X.; Hong, Y.L.; Feng, Y. Determination of the levels of two types of neurotransmitter and the anti-migraine effects of different dose-ratios of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Gastrodia elata. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkidesh, B.S.; Shankar, S.R.; Narasimhamurthy, R.K.; Rao, S.B.S.; Mumbrekar, K.D. Radioprotective potential of probiotics against gastrointestinal and neuronal toxicity: A preclinical study. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Luo, L.; Bian, X.; Liu, R.H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, K.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, L. Pu-erh tea restored circadian rhythm disruption by regulating tryptophan metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5610–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, A.; Banfi, D.; Bistoletti, M.; Giaroni, C.; Baj, A. Tryptophan metabolites along the microbiota-gut-brain axis: An interkingdom communication system influencing the gut in health and disease. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920928984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ano, Y.; Ohya, R.; Kondo, K.; Nakayama, H. Iso-alpha-acids, hop-derived bitter components of beer, attenuate age-related inflammation and cognitive decline. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, A.; Santelli, L.; Tomassini, V.; Bosnell, R.; Smith, S.; De Stefano, N.; Johansen-Berg, H. Age-related changes in grey and white matter structure throughout adulthood. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiese, K. Cognitive impairment and dementia: Gaining insight through circadian clock gene pathways. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, M. Organization and dynamics of PDZ-domain-related supramodules in the postsynaptic density. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Gu, L.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum combined with Galactooligosaccharides supplement: A neuroprotective regimen against neurodegeneration and memory impairment by regulating short-chain fatty acids and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8619–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.I.; Miller, D.L.; Roecklein, K.A. The aging hippocampus: Interactions between exercise, depression, and BDNF. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza, M.; Ziontz, J.; Cantero, J.L. Low-grade inflammation in the relationship between sleep disruption, dysfunctional adiposity, and cognitive decline in aging. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 42, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. The kynurenine pathway as a therapeutic target in cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1211–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumaah, M.R.; Bhatia, U.; Roach, J.; Gunstad, J.; Azcarate Peril, M.A. The gut microbiome, mild cognitive impairment, and probiotics: A randomized clinical trial in middle-aged and older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Dynamic network modeling of gut microbiota during Alzheimer’s disease progression in mice. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2172672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, C.; Li, R.; Liu, K.; Jin, G.; Ge, R.; Tang, F.; Cui, S. High-altitude Tibetan fermented milk ameliorated cognitive dysfunction by modified gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mo, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, Z.; Chen, L.; Rong, S.; Yang, W.; Xu, S.; et al. Yeast beta-glucan alleviates cognitive deficit by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites in Abeta(1)(-)(42)-induced AD-like mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Du, H.; Li, Z.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, F.; He, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Decoding the contributions of gut microbiota and cerebral metabolism in acute liver injury mice with and without cognitive dysfunction. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 29, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, S.J.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Westbrook, R.F.; Morris, M.J. Minocycline-induced microbiome alterations predict cafeteria diet-induced spatial recognition memory impairments in rats. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlinar, B.; Stocca, G.; Corradetti, R. Endogenous serotonin facilitates hippocampal long-term potentiation at CA3/CA1 synapses. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Primer Sequences | GenBank Accession | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sirt1 | F-5′-TCCTTGGAGACTGCGATGTTA-3′ R-5′-GTGGCAACTCTGATAAATGAACC-3′ | NM_001159589.2 | 60 |
| FoxO3 | F-5′-GGACGACCTGCTGGATAACAT-3′ R-5′-CCTGGATAGTCTGCATGGGTG-3′ | NM_001376967.1 | 60 |
| PSD95 | F-5′-GGGAGATGGAGTATGAGGAGA-3′ R-5′-TGATAAAGATGGATGGGTCGT-3′ | NM_001109752.1 | 60 |
| Spinophilin | F-5′-AGGACTATGACCGACGCAATG-3′ R-5′-TCCAGCTCCACAGGAAACAG-3′ | NM_172261.3 | 60 |
| Tph2 | F-5′-TGGAGCAGGGTTACTTTCGT-3′ R-5′-AAGCAGGTCGTCTTTGGGT-3′ | NM_173391.3 | 60 |
| Tph1 | F-5′-AACAAAGACCATTCCTCCGAAAG-3′ R-5′-TGTAACAGGCTCACATGATTCTC-3′ | NM_001136084 | 60 |
| Gapdh | F-5′-AACAGCAACTCCCACTCTTCC-3′ R-5′-TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC-3′ | NM_008084.4 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, K.; Chen, C.; Ke, X.; Fan, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, S. Improvements of Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice by Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889, a Novel Strain with Psychobiotic Properties. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173852
Gao K, Chen C, Ke X, Fan Q, Wang H, Li Y, Chen S. Improvements of Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice by Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889, a Novel Strain with Psychobiotic Properties. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173852
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Kan, Cailing Chen, Xueqin Ke, Qiuling Fan, Haifeng Wang, Yanjun Li, and Su Chen. 2023. "Improvements of Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice by Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889, a Novel Strain with Psychobiotic Properties" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173852
APA StyleGao, K., Chen, C., Ke, X., Fan, Q., Wang, H., Li, Y., & Chen, S. (2023). Improvements of Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Mice by Lactobacillus helveticus WHH1889, a Novel Strain with Psychobiotic Properties. Nutrients, 15(17), 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173852







