Breakfast Consumption and Quality of Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Indonesia: A Study from the Indonesian Food Barometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Sample
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Breakfast Definition
2.4. Dietary Quality by NRF 9.3
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
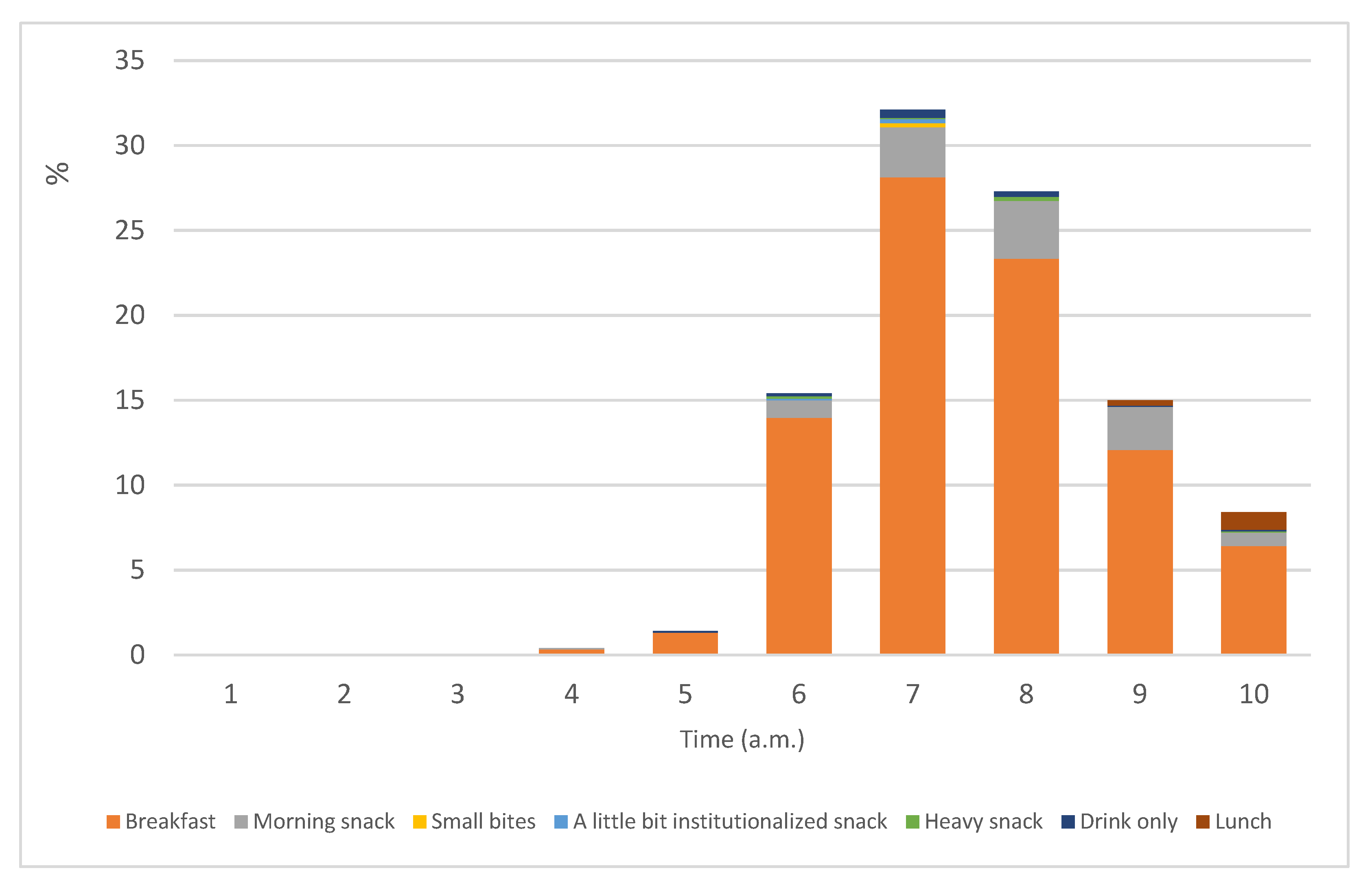
3.1. Contribution of Breaksfast to Daily Energy and Nutrient
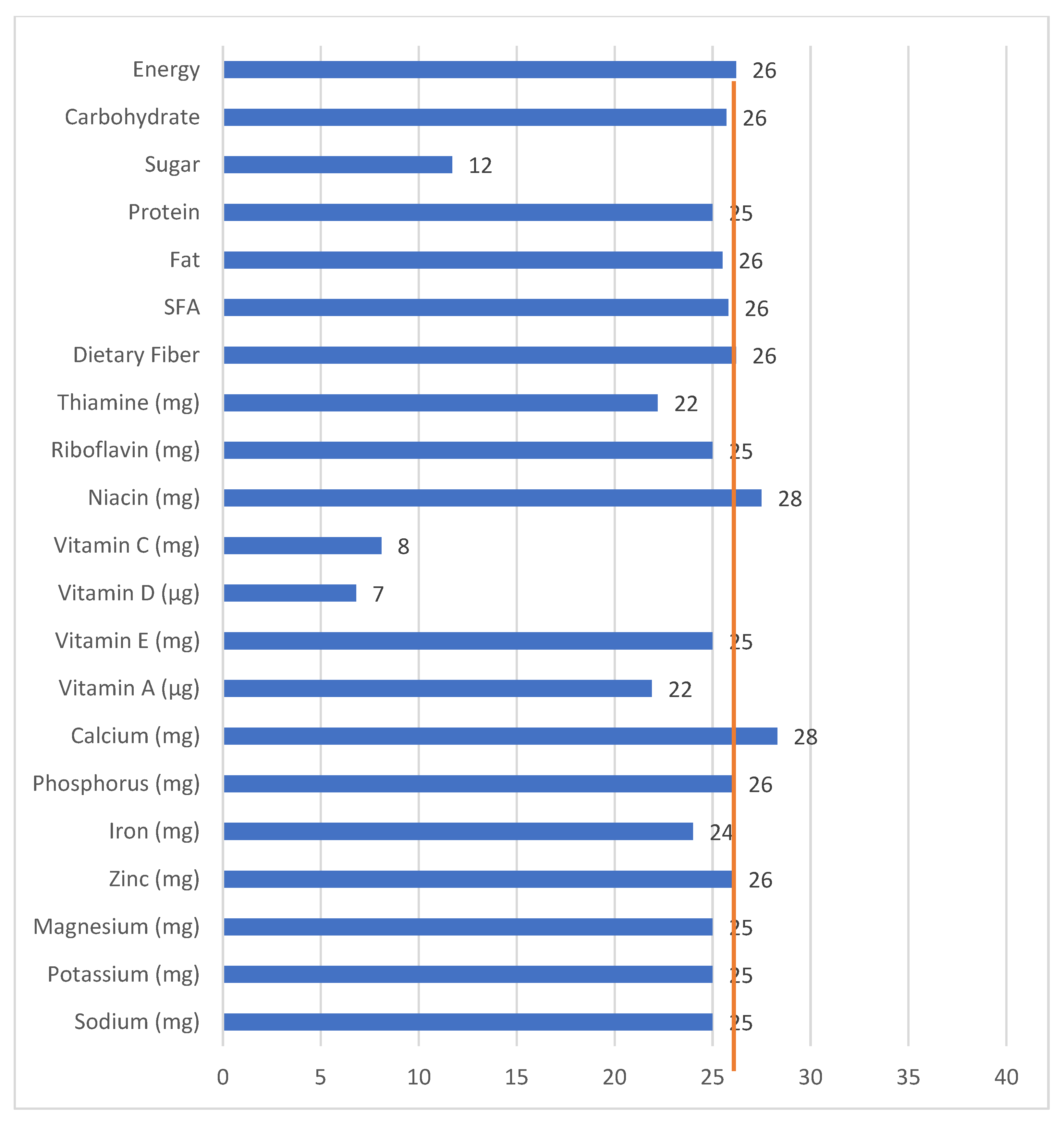
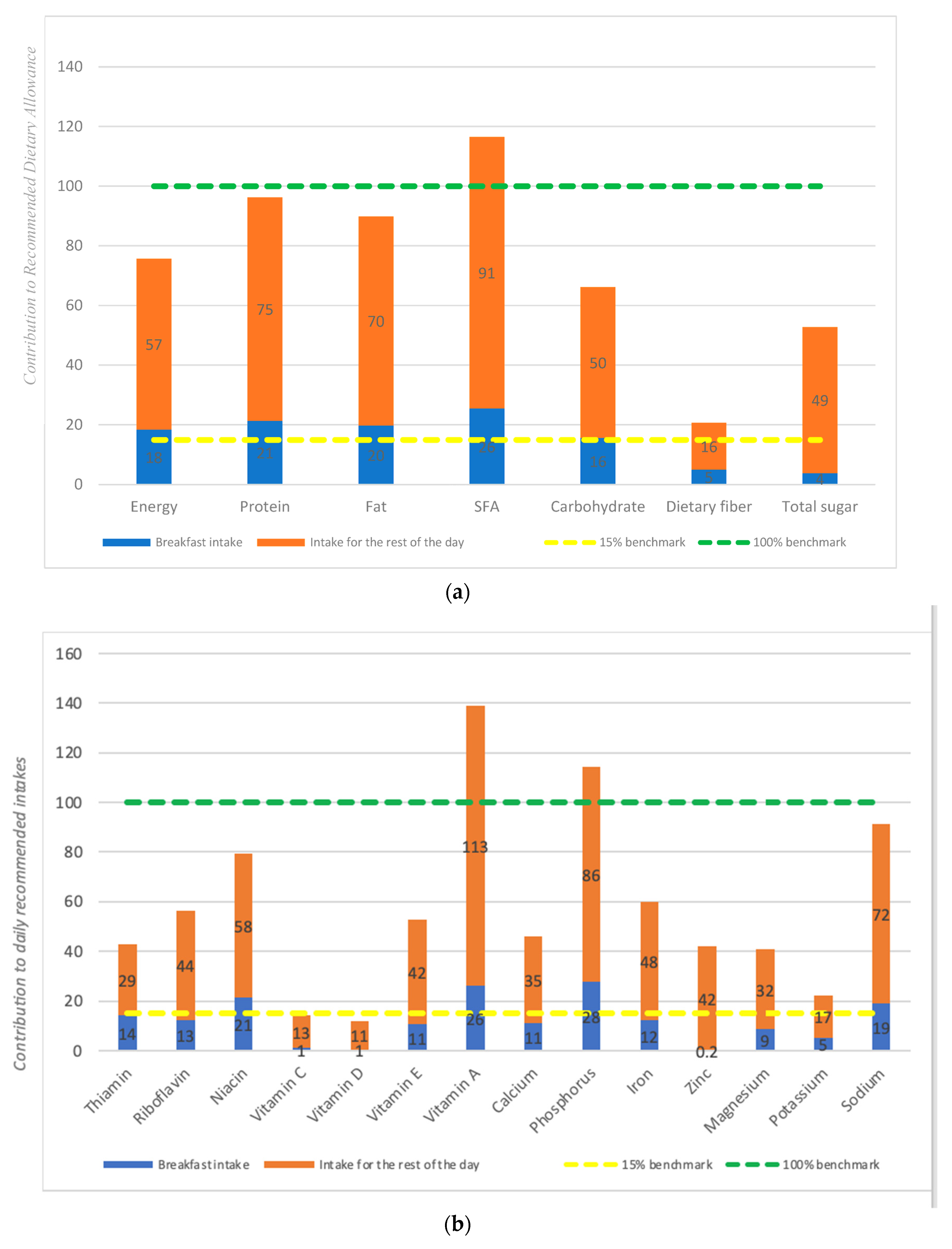
3.2. Contribution of Breaksfast to Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA)
3.3. Breakfast Intake and Diet Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Adequacy of Intake and Nutrient Contribution from Breakfast
4.2. Breakfast Intake and Diet Quality
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Health Indonesia. Basic Health Research Report; National Health Research and Development Center: Jakarata, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Atmarita, A.; Jahari, A.B.; Sudikno, S.; Soekatri, M. Asupan gula, garam, dan lemak di Indonesia: Analisis survei konsumsi makanan individu (SKMI) 2014. Gizi Indones. 2017, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Indonesia. Total Diet Study; National Health Research and Development Center: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muslihah, N.; Winarsih, S.; Soemardini, S.; Zakaria, A.; Zainudiin, Z. Kualitas diet dan hubungannya dengan pengetahuan gizi, status sosial ekonomi, dan status gizi. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2013, 8, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrin, A.P.; Hardinsyah, H.; Dwiriani, C.M. Alternatif indeks gizi seimbang untuk penilaian mutu gizi konsumsi pangan pria dewasa Indonesia. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2013, 8, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, S.; Ngatidjan, S.; Paotiana, M.; Sitompul, K.A.; Abdullah, M.; Sulistianingsih, D.P.; Shankar, A.H.; Agustina, R. Dietary quality of predominantly traditional diets is associated with blood glucose profiles, but not with total fecal Bifidobacterium in Indonesian women. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, P.A.; Briawan, D.; Ekayanti, I. Application of alternate healthy eating index to assess diet quality in male workers. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2018, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Indonesia. Indonesian Dietary Guidelines; Ministry of Health Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Min, C.; Noh, H.; Kang, Y.-S.; Sim, H.J.; Baik, H.W.; Song, W.O.; Yoon, J.; Park, Y.-H.; Joung, H. Skipping breakfast is associated with diet quality and metabolic syndrome risk factors of adults. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2011, 5, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh-Taskar, P.R.; Radcliffe, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Nicklas, T.A. Do breakfast skipping and breakfast type affect energy intake, nutrient intake, nutrient adequacy, and diet quality in young adults? NHANES 1999–2002. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, L.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Feizi, A.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Breakfast eating pattern and its association with dietary quality indices and anthropometric measurements in young women in Isfahan. Nutrition 2013, 29, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos, E.; Todd, J.E. The effects of skipping a meal on daily energy intake and diet quality. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 3346–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, R.; Caputo, M.; Monzani, A.; Pigni, S.; Antoniotti, V.; Bellone, S.; Prodam, F. Breakfast skipping, weight, cardiometabolic risk, and nutrition quality in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomized controlled and intervention longitudinal trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, N.; Obayashi, K.; Saeki, K.; Kitagawa, M.; Tone, N.; Kurumatani, N. Relationship between breakfast skipping and obesity among elderly: Cross-sectional analysis of the HEIJO-KYO study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.A.; Gottrand, F.; Huybrechts, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; González-Gross, M.; DeHenauw, S.; Group, H.S. Nutrition and lifestyle in european adolescents: The HELENA (Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence) study. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 615S–623S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M.; Rajesh, V.; Kumar, P. Effect of breakfast skipping on nutritional status and school performance of 10–16 years old children of Udupi district. Health Popul. Perspect. Issues 2014, 37, 98–117. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Gan, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Lu, Z. Breakfast skipping and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irdiani, W.; Nindya, T. Correlation between the habit of eating breakfast, nutrient intake and nutritional status of female students in SMAN 3 Surabaya. Amerta Nutr. 2017, 1, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, A.F.I.; Briawan, D.; Dwiriani, C.M. Breakfast habit and its quality of schoolgirls in Bogor District. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2012, 7, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Susanto, F. Breakfast nutrient analysis among school age children in Jakarta area, Indonesia. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Harahap, H.; Widodo, Y.; Sandjaja, S.; Khouw, I.; Deurenberg, P. Quantity and quality of breakfast of children aged 2.0 to 12.9 years in Indonesia. Gizi Indones. 2019, 42, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusun, H.; Februhartanty, J.; Mognard, E.; Anggraini, R.; Hapsari, P.W.; Poulain, J.P. Indonesian Food Barometer: Food, Cultures and Health; Seameo Recfon: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, G.; Black, A.; Jebb, S.; Cole, T.; Murgatroyd, P.; Coward, W.; Prentice, A. Critical evaluation of energy intake data using fundamental principles of energy physiology: 1. Derivation of cut-off limits to identify under-recording. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 45, 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Khusun, H.; Februhartanty, J.; Anggraini, R.; Mognard, E.; Alem, Y.; Noor, M.I.; Karim, N.; Laporte, C.; Poulain, J.-P.; Monsivais, P. Animal and plant protein food sources in Indonesia differ across socio-demographic groups: Socio-cultural research in protein transition in Indonesia and Malaysia. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 762459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusun, H.; Monsivais, P.; Anggraini, R.; Februhartanty, J.; Mognard, E.; Alem, Y.; Noor, M.I.; Karim, N.; Laporte, C.; Poulain, J.-P. Diversity of protein food sources, protein adequacy and amino acid profiles in Indonesia diets: Socio-Cultural Research in Protein Transition (SCRiPT). J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, J.-P.; Smith, W.; Laporte, C.; Tibère, L.; Ismail, M.N.; Mognard, E.; Aloysius, M.; Neethiahnanthan, A.R.; Shamsul, A.B. Studying the Consequences of Modernization on Ethnic Food Patterns: Development of the Malaysian Food Barometer (MFB). Anthropol. Food 2015. Available online: http://aof.revues.org/7735 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Poulain, J.-P.; Laporte, C.; Tibère, L.; Mognard, E.; Ragavan, N.A.; Zadeh, A.A.; Noor, I.M. Malaysian Food Barometer (MFB): A study of the impact of compressed modernisation on food habits. Malays. J. Nutr. 2020, 26, 001–017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Indonesia. Buku Foto Makanan; National Health Research and Development Center: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bognár, A.; Piekarski, J. Guidelines for recipe information and calculation of nutrient composition of prepared foods (dishes). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2000, 13, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, M.J.; Barr, S.I.; Bellisle, F.; Drewnowski, A.; Fagt, S.; Livingstone, B.; Masset, G.; Varela Moreiras, G.; Moreno, L.A.; Smith, J. Breakfast in human nutrition: The international breakfast research initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, C.E.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C.; Hayes, D.; Jana, L.; Klinger, S.E.; Stephenson-Martin, S. The role of breakfast in health: Definition and criteria for a quality breakfast. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 12, S8–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisberg, M.; Kovalskys, I.; Previdelli, A.N.; Pereira, J.L.; Zimberg, I.Z.; Fisberg, R.; Ferrari, G.; Guajardo, V.; Group, E.S. Breakfast consumption habit and its nutritional contribution in Latin America: Results from the ELANS study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, E.A.; Richardson, J.D.; Holman, G.D.; Tsintzas, K.; Thompson, D.; Betts, J.A. The causal role of breakfast in energy balance and health: A randomized controlled trial in obese adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, J.M. Methodology, correlational analysis, and interpretation of diet diary records of the food and fluid intake of free-living humans. Appetite 1994, 23, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A. The Nutrient Rich Foods Index helps to identify healthy, affordable foods. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1095S–1101S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BPOM RI. Peraturan Badan Pengawasan Obat dan Makanan No 16 tahun 2016 Tentang Acuan Label Gizi; BPOM RI: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kementrian Kesehatan Indonesia. Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan No 30 tahun 2013 tentang Pencantuman Informasi Kandungan Gula, Garam, dan Lemak Serta Pesan Kesehatan untuk Pangan Olahan dan Pangan Siap Saji; Kementrian Kesehatan Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Custodio, M.R.S.; Toledo, M.B. Breakfast in the Philippines: Food and diet quality as analyzed from the 2018 Expanded National Nutrition Survey. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognard, E.; Sanubari, T.P.E.; Alem, Y.; Yuen, J.L.; Ragavan, N.A.; Ismail, M.N.; Poulain, J.-P. Breakfast Practices in Malaysia, Nutrient Intake and Diet Quality: A Study Based on the Malaysian Food Barometer. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Ávila, J.M.; Valero, T.; Rodriguez, P.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Breakfast consumption in Spain: Patterns, nutrient intake and quality. Findings from the ANIBES study, a study from the International Breakfast Research Initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellisle, F.; Hébel, P.; Salmon-Legagneur, A.; Vieux, F. Breakfast consumption in French children, adolescents, and adults: A nationally representative cross-sectional survey examined in the context of the International Breakfast Research Initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, S.I.; Vatanparast, H.; Smith, J. Breakfast in Canada: Prevalence of consumption, contribution to nutrient and food group intakes, and variability across tertiles of daily diet quality. A study from the International Breakfast Research Initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaal, S.; Kerr, M.A.; Ward, M.; McNulty, H.; Livingstone, M.B.E. Breakfast consumption in the UK: Patterns, nutrient intake and diet quality. A study from the international breakfast research initiative group. Nutrients 2018, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipoeto, N.I.; Lin, K.G.; Angeles-Agdeppa, I. Food consumption patterns and nutrition transition in South-East Asia. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustina, R.; Rianda, D.; Lasepa, W.; Birahmatika, F.S.; Stajic, V.; Mufida, R. Nutrient intakes of pregnant and lactating women in Indonesia and Malaysia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1030343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, K.L.; Coward, A.; Jebb, S.A. Estimating under-reporting of energy intake in dietary surveys using an individualised method. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E. Prevalence and characteristics of misreporting of energy intake in US adults: NHANES 2003–2012. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Gu, Q.; Afful, J.; Ogden, C.L. Anthropometric reference data for children and adults: United States, 2015–2018; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Perdana, F.; Hardinsyah, H. Analisis jenis, jumlah, dan mutu gizi konsumsi sarapan anak Indonesia. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2013, 8, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinsyah, H.; Aries, M. Jenis pangan sarapan dan perannya dalam asupan gizi harian anak usia 6—12 tahun di indonesia. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2012, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madanijah, S.; Briawan, D.; Rimbawan, R.; Zulaikhah, Z.; Andarwulan, N.; Nuraida, L.; Sundjaya, T.; Murti, L.; Shah, P.; Bindels, J. Nutritional status of pre-pregnant and pregnant women residing in Bogor district, Indonesia: A cross-sectional dietary and nutrient intake study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, S57–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astriningrum, E.P.; Hardinsyah, H.; Nurdin, N.M. Asupan asam folat, vitamin B12 dan vitamin C pada ibu hamil di indonesia berdasarkan studi diet total. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2017, 12, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prasetyo, T.J.; Hardinsyah, H.; Baliwati, Y.F.; Sukandar, D. The application of probability method to estimate micronutrient deficiencies prevalence of Indonesian adults. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2018, 13, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pee, S.; Bloem, M.W.; Gorstein, J.; Sari, M.; Yip, R.; Shrimpton, R. Reappraisal of the role of vegetables in the vitamin A status of mothers in Central Java, Indonesia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Persson, V.; Winkvist, A.; Hartini, T.N.S.; Greiner, T.; Hakimi, M.; Stenlund, H. Variability in nutrient intakes among pregnant women in Indonesia: Implications for the design of epidemiological studies using the 24-h recall method. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasepa, W. Association between Food Choice Motives with Fruits and Vegetables Consumption among Adult with Different Nutritional Status in Urban and Rural Area of West Java; Universitas Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Sugars Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khusun, H.; Wiradnyani, A. Calorie and Physical Activity Survey in Five Urban Population in Indonesia; SEAMEO RECFON: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khusun, H.; Wiradnyani, L.A.A.; Siagian, N. Factors associated with overweight/obesity among adults in urban Indonesia. Penelit. Gizi Dan Makanan 2015, 38, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusun, H.; Fahmida, U. Dietary patterns of obese and normal-weight women of reproductive age in urban slum areas in Central Jakarta. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, S49–S56. [Google Scholar]
- Dewi, N.U.; Tanziha, I.; Solechah, S.A. Obesity determinants and the policy implications for the prevention and management of obesity in Indonesia. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, M.; Pujianto, D.A.; Witjaksono, F.; Priliani, L.; Susanto, J.; Lukito, W.; Malik, S.G. Obesity risk and preference for high dietary fat intake are determined by FTO rs9939609 gene polymorphism in selected Indonesian adults. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 28, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Agustina, R.; Rianda, D.; Setiawan, E.A. Relationships of Child-, Parents-, and Environment-Associated Determinants with Diet Quality, Physical Activity, and Smoking Habits Among Indonesian Urban Adolescents. Food Nutr. Bull. 2022, 43, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustina, R.; Nadiya, K.; Andini, E.A.; Setianingsih, A.A.; Sadariskar, A.A.; Prafiantini, E.; Wirawan, F.; Karyadi, E.; Raut, M.K. Associations of meal patterning, dietary quality and diversity with anemia and overweight-obesity among Indonesian school-going adolescent girls in West Java. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdana, S.M.; Hardinsyah, H.; Damayanthi, E. Alternatif indeks gizi seimbang untuk penilaian mutu gizi konsumsi pangan wanita dewasa Indonesia. J. Gizi Dan Pangan 2014, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- BPOM R. Peraturan Badan Pengawas Obat Dan Makanan Nomor 22 Tahun 2019 Tentang Informasi Nilai Gizi Pada Label Pangan Olahan; BPOM, Ed.; BPOM: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Breakfast Intake (n = 1263) | Daily Intake (n = 1333) | |
|---|---|---|
| Median (25th–75th) | Median (25th–75th) | |
| Macronutrients | ||
| Energy (Kcal) | 395.8 (294.2–571.3) | 1626.2 (1314.7–2085.1) |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 50.9 (37.8–75.0) | 215 (161.2–270) |
| Carbohydrate (E%) | 55.2 (43.3–65.0) | 51.9 (44.3–59.7) |
| Total sugar (g) | 1.9 (0.5–8.3) | 26.4 (11.7–43.4) |
| Total sugar (E%) | 1.5 (0.5–9.4) | 6.5 (2.9–10.4) |
| Protein (g) | 12.8 (7.9–20.5) | 57.7 (42.9–75.3) |
| Protein (E%) | 12.7 (8.7–17.6) | 13.8 (10.8–16.9) |
| Fat (g) | 13.3 (7.6–23.4) | 60.2 (43.0–8.6) |
| Fat (E%) | 31.2 (21.4–41.1) | 33.6 (26.8–41.0) |
| SFA 1 (g) | 5.1 (2.4–10.2) | 23.3 (15.7–33.6) |
| SFA 1 (E%) | 12.2 (6.1–17.9) | 12.8 (9.5–16.9) |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 1.5 (0.5–3.0) | 6.2 (3.5–10.1) |
| Micronutrients | ||
| Thiamine (mg) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.7 (0.5–1.1) |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 1.0 (0.6–1.5) |
| Niacin (mg) | 3.2 (1.3–5.6) | 13.0 (8.8–18.7) |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 1.0 (0–5.2) | 12.8 (4.4–29.4) |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 0.1 (0–0.9) | 1.8 (0.5–3.6) |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 1.6 (0.5–3.3) | 7.9 (4.6–16.9) |
| Vitamin A (µg) | 156.4 (59.2–356.8) | 833.5 (515.3–1389.5) |
| Calcium (mg) | 120.2 (65.0–222.0) | 505.3 (345.4–721.4) |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 195.6 (108.9–303.5) | 800 (587.6–1062.3) |
| Iron (mg) | 2.7 (1.7–5.0) | 13.2 (9.7–17.8) |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.3 (0.7–2.7) | 6.2 (4.3–9.8) |
| Magnesium (mg) | 30 (15.3–59.2) | 143.4 (89.6–201.3) |
| Potassium (mg) | 244.6 (93.3–467.6) | 1048.0 (678.8–1871.0) |
| Sodium (mg) | 285.7 (114.2–593.1) | 1368.1 (836.0–2070.2) |
| Total (n = 1263) | NRF Tertile 1 (n = 407) | NRF Tertile 2 (n = 440) | NRF Tertile 3 (n = 416) | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (25th–75th) | Median (25th–75th) | Median (25th–75th) | Median (25th–75th) | |||
| Energy (Kcal) | 395.8 (294.2–571.3) | 392.2 (299.3–568.2) | 398.0 (279.8–543.4) | 401.5 (31.9–595.8) | 0.104 | 0.485 |
| Macronutrients | ||||||
| Carbohydrate (g) | 50.9 (37.8–75.0) | 51.1 (36.4–72.9) | 48.9 (31.7–75.9) | 54.1 (42.0–79.6) | 0.007 * | 0.900 |
| Total sugar (g) | 1.9 (0.5–8.3) | 1.3 (0.3–8.3) | 2.0 (0.5–10.5) | 2.0 (0.7–6.5) | 0.391 | 0.030 * |
| Protein (g) | 12.8 (7.9–20.5) | 12.2 (6.8–16.6) | 12.6 (7.4–20.8) | 15.2 (10.0–25.0) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Fat (g) | 13.3 (7.6–23.4) | 13.1 (7.7–22.0) | 13.2 (7.8–22.2) | 13.7 (7.2–24.9) | 0.859 | 0.738 |
| SFA 1 (g) | 5.1 (2.4–10.2) | 5.4 (2.5–12.9) | 4.8 (2.7–9.2) | 5.0 (2.3–9.1) | 0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 1.5 (0.5–3.0) | 1.3 (0.4–2.7) | 1.4 (0.5–2.7) | 2.1 (0.6–4.3) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Micronutrient | ||||||
| Thiamin (mg) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.1 (0.1–0.3) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | <0.001 * | 0.015 * |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 0.1 (0.1–0.3) | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 0.3 (0.2–0.5) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Niacin (mg) | 3.2 (1.3–5.6) | 2.8 (0.8–5.0) | 3.1 (1.3–5.9) | 4.3 (2.6–6.8) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 1.0 (0–5.2) | 0.3 (0–3.8) | 0.5 (0–3.8) | 2.6 (0–8.6) | <0.001 * | 0.015 * |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 0.1 (0–0.9) | 0.1 (0–0.9) | 0 (0–0.9) | 0 (0–0.9) | 0.470 | 0.895 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 1.6 (0.5–3.3) | 1.5 (0.6–3.7) | 1.4 (0.5–2.7) | 1.8 (0.5–3.4) | 0.009 * | 0.167 |
| Vitamin A (µg) | 156.4 (59.2–356.8) | 106.6 (32.3–301.2) | 174.2 (61.8–328.2) | 211.0 (73.7–447.8) | <0.001 * | 0.002 * |
| Potassium (mg) | 244.6 (93.3–467.6) | 163.8 (70.4–340.9) | 253.9 (88.2–470.4) | 316.1 (140.3–696.7) | <0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| Calcium (mg) | 120.2 (65.0–222.0) | 89.8 (60.6–176.4) | 111.0 (59.9–204.0) | 174.0 (85.2–322.1) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 195.6 (108.9–303.5) | 171.9 (92.5–260.9) | 189.5 (107.1–285.4) | 240.0 (138.7–373.5) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Iron (mg) | 2.7 (1.7–5.0) | 2.5 (1.7–3.9) | 2.5 (1.6–4.6) | 3.6 (2.0–6.5) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.3 (0.7–2.7) | 1.1 (0.6–2.0) | 1.4 (0.6–2.6) | 1.6 (1.0–3.0) | <0.001 * | 0.187 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 30.0 (15.3–59.2) | 24.8 (12.1–44.0) | 29.6 (14.9–49.8) | 52.5 (18.8–75.3) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Sodium (mg) | 285.7 (114.2–593.1) | 359.6 (142.4–764.2) | 335.3 (130.5–589.2) | 221.1 (78.6–426.2) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Total (n = 1263) | NRF Tertile 1 (n = 407) | NRF Tertile 2 (n = 440) | NRF Tertile 3 (n = 416) | p-Value 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumers | Median (25th–75th) | Consumers | Median (25th–75th) | Consumers | Median (25th–75th) | Consumers | Median (25th–75th) | ||
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | ||||||
| Cereal grains and pasta (g) | 947 (74.9) | 120 (100-200) | 303 (74.3) | 120 (90-200) | 321 (73) | 120 (90-200) | 323 (77.7) | 105 (100-180) | 0.819 |
| Vegetables and vegetable products (g) | 436 (34.5) | 45 (30–80) | 102 (25.1) | 40 (30–60) | 138 (31.4) | 45 (30–60) | 196 (47.1) | 60 (30–90) | 0.023 * |
| Legumes and legume products (g) | 420 (33.3) | 80 (45–100) | 80 (19.6) | 50 (30–80) | 140 (31.8) | 75 (40–100) | 200 (48.1) | 90 (50–125) | <0.001 * |
| Beverages and sugar-sweetened beverages (g) | 233 (18.4) | 15 (2–25) | 69 (16.9) | 14 (7–25) | 92 (20.8) | 18 (2–25) | 72 (17.3) | 15 (2–25) | 0.968 |
| Finfish and shell fish products (g) | 225 (17.8) | 40 (30–60) | 43 (10.5) | 50 (40–70) | 74 (16.8) | 50 (40–70) | 109 (26.2) | 40 (20–60) | 0.040 * |
| Snack (g) | 219 (17.3) | 60 (25–100) | 82 (20.1) | 50 (25–110) | 77 (17.4) | 60 (25–100) | 60 (14.5) | 100 (50–120) | 0.286 |
| Eggs and egg products (g) | 182 (14.4) | 60 (60–60) | 78 (19.1) | 60 (60–60) | 59 (13.4) | 60 (60–60) | 45 (10.9) | 60 (40–60) | 0.001 * |
| Sweets (g) | 126 (10) | 20 (15–20) | 34 (8.4) | 20 (15–20) | 55 (12.6) | 20 (10–20) | 36 (8.8) | 20 (10–20) | 0.538 |
| Poultry products (g) | 123 (9.8) | 40 (30–60) | 35 (8.5) | 40 (30–50) | 46 (10.5) | 50 (30–60) | 43 (10.2) | 30 (30–50) | 0.044 * |
| Baked products (g) | 118 (9.3) | 60 (40–75) | 53 (12.9) | 70 (30–75) | 43 (9.7) | 54 (40–75) | 23 (5.4) | 70 (39–75) | 0.696 |
| Spices and herbs (g) | 63 (5) | 10 (10–10) | 20 (5) | 10 (10–10) | 17 (3.8) | 10 (5–20) | 26 (6.3) | 10 (5–10) | 0.283 |
| Fats and oils (g) | 54 (4.3) | 5 (3–10) | 27 (6.5) | 4 (2–12.5) | 20 (4.4) | 8 (5–8) | 8 (1.9) | 5 (2–5) | 0.090 |
| Beef products (g) | 43 (3.4) | 50 (40–90) | 17 (4.1) | 90 (50–100) | 18 (4.2) | 40 (30–50) | 8 (1.8) | 50 (50–50) | 0.006 * |
| Fruits and fruit juice (g) | 35 (2.8) | 120 (50–200) | 11 (2.7) | 50 (30–300) | 9 (1.9) | 120 (100–150) | 15 (3.7) | 200 (50–200) | 0.570 |
| Dairy and dairy products (g) | 27 (2.1) | 27 (21–40) | 5 (1.2) | 27 (27–27) | 10 (2.3) | 40 (21–40) | 12 (2.8) | 27 (10–200) | 0.604 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khusun, H.; Anggraini, R.; Februhartanty, J.; Mognard, E.; Fauzia, K.; Maulida, N.R.; Linda, O.; Poulain, J.-P. Breakfast Consumption and Quality of Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Indonesia: A Study from the Indonesian Food Barometer. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173792
Khusun H, Anggraini R, Februhartanty J, Mognard E, Fauzia K, Maulida NR, Linda O, Poulain J-P. Breakfast Consumption and Quality of Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Indonesia: A Study from the Indonesian Food Barometer. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173792
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhusun, Helda, Roselynne Anggraini, Judhiastuty Februhartanty, Elise Mognard, Khalida Fauzia, Nursyifa Rahma Maulida, Ony Linda, and Jean-Pierre Poulain. 2023. "Breakfast Consumption and Quality of Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Indonesia: A Study from the Indonesian Food Barometer" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173792
APA StyleKhusun, H., Anggraini, R., Februhartanty, J., Mognard, E., Fauzia, K., Maulida, N. R., Linda, O., & Poulain, J.-P. (2023). Breakfast Consumption and Quality of Macro- and Micronutrient Intake in Indonesia: A Study from the Indonesian Food Barometer. Nutrients, 15(17), 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173792






