Sensorial and Nutritional Properties of a Collagen-Fortified Snack Bar Designed for the Elderly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Samples
2.1.1. Preparation of the Top Layer of Bar Samples
2.1.2. Preparation of the Intermediate Layer (Puree Layer) of the Bar Samples
2.1.3. Preparation of the Base Layer of the Bar Samples
2.1.4. Combining Layers
2.2. Sensory Analysis
2.3. Ethics Committee Approval
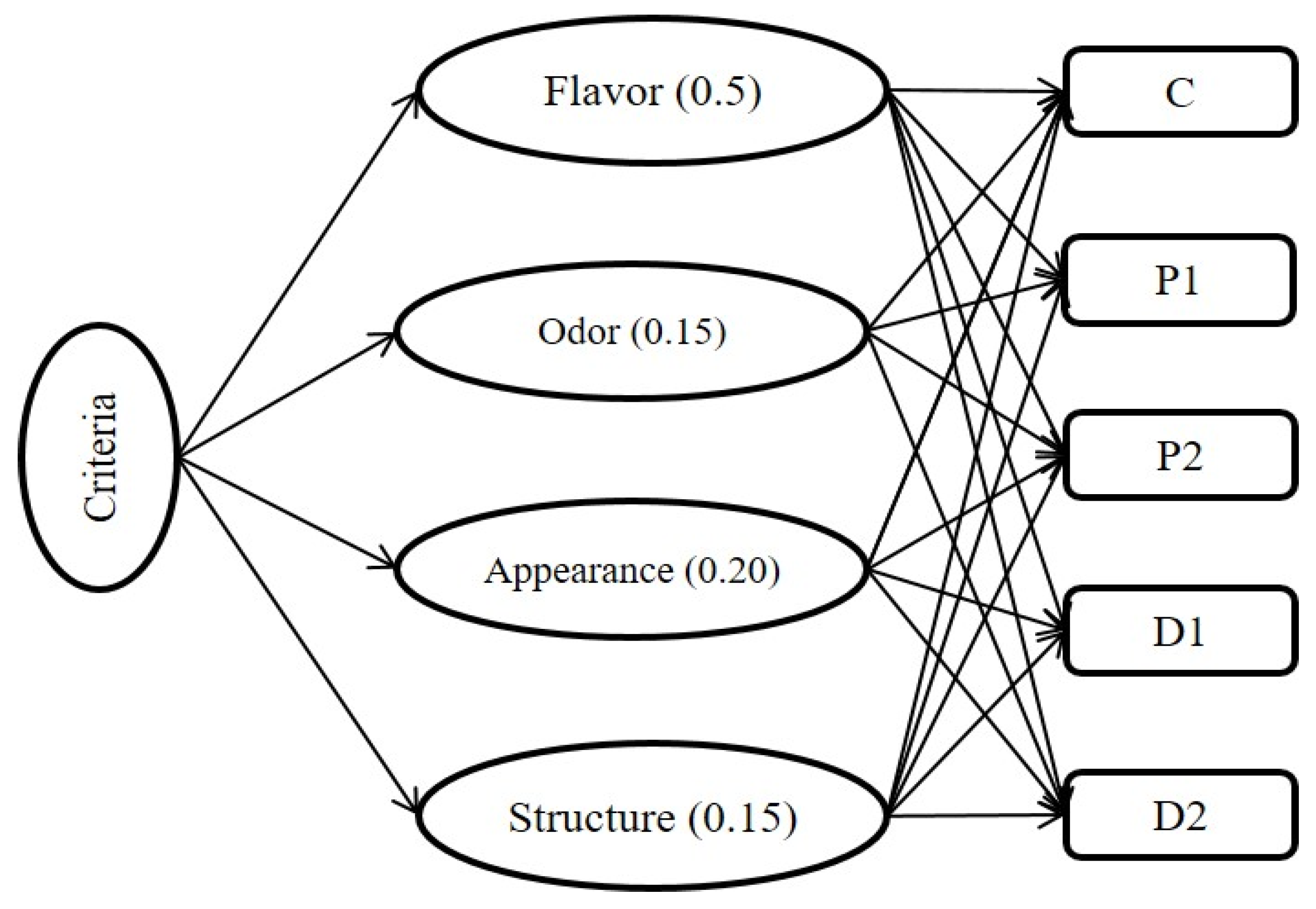
2.4. Application of the TOPSIS Technique for Sensory Analysis
TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity) Method
- Construction of the decision-making matrix with m (samples) and n (flavor, odor, appearance, and structure);
- Normalization of decision-making matrix;
- Calculate the weights for the criteria and develop the normalized weight matrix Vij = Wij × rij. The weight of each criterion was determined using the Shannon entropy method [16];
- Determining the positive and negative solutions;
- Determining the distance of the normalized weighted matrix from the ideal positive and negative points;
- Calculating the distance from the ideal point;
2.5. Nutritional Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
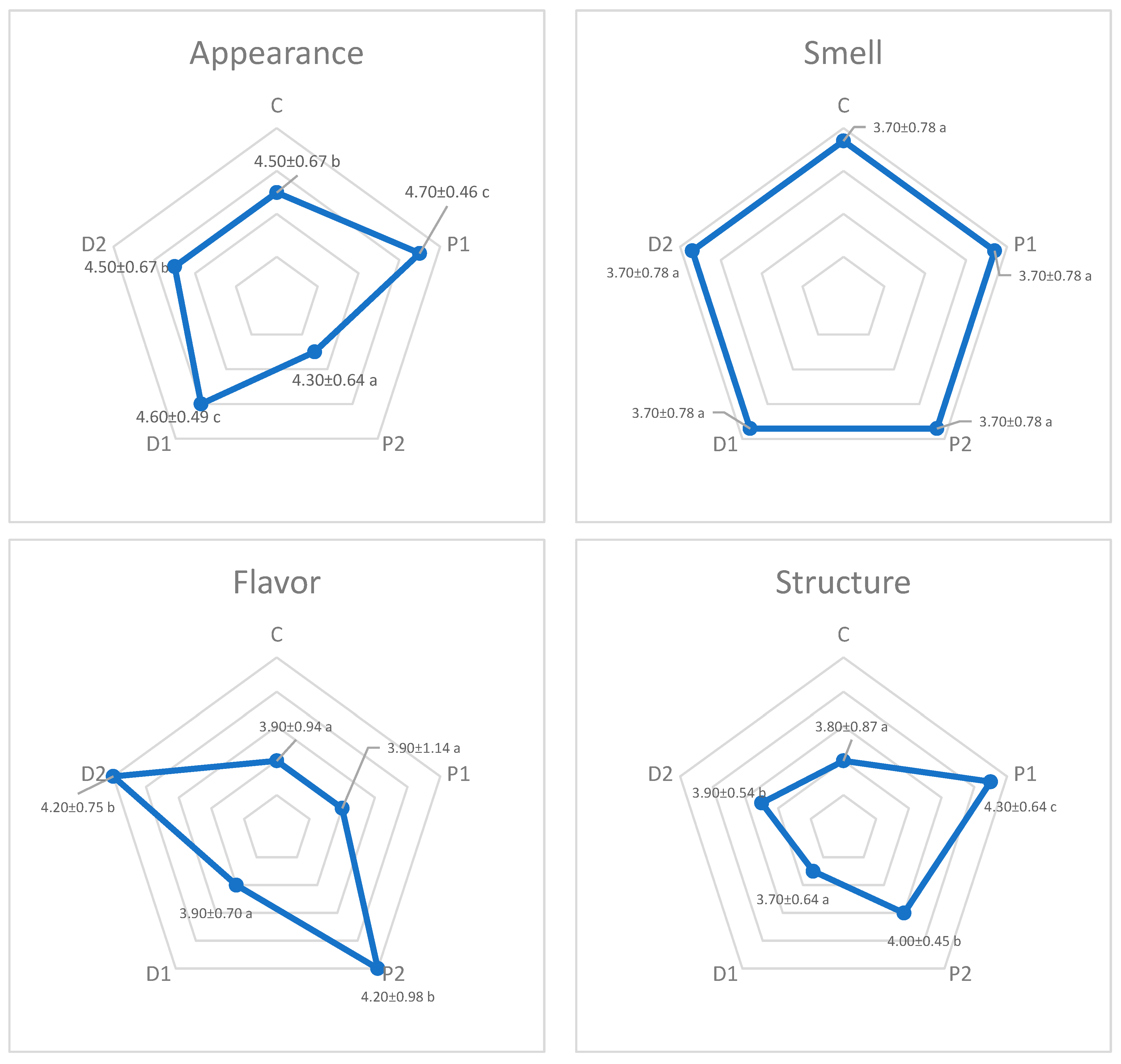
3.1. Sensory Analysis
3.2. Nutrients
4. Discussion
4.1. Sensory Properties
4.2. Nutritional Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arowosola, T.A.; Makanjuola, O.O.; Olagunju-Yusuf, O.F. The Role of Food in the Health Management of Geriatrics. In Food Security and Safety; Babalola, O.O., Ayangbenro, A.S., Ojuederie, O.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji, H.; Fırat, B. Yeme Bozuklukları ve Duygular. Fenerbahçe Üniversitesi Sos. Bilim. Derg. 2022, 2, 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, Y.; Min, S.; Song, M.; Son, S.; Lee, S. Taste sensitivity of elderly people is associated with quality of life and inadequate dietary intake. Nutrients 2021, 3, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.Y.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, X.W. Presbyphagia: Dysphagia in the elderly. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam-MacDonald, A.M.; Morrison, J.M.; Steele, C.M.; Keller, H. How swallow pressures and dysphagia affect malnutrition and mealtime outcomes in long-term care. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, J.M.; Shikany, J.M.; Thomson, C.A. The role of dietary protein intake in the prevention of sarcopenia of aging. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, F.; Gao, R. Food-derived collagen peptides: Safety, metabolism, and anti-skin-aging effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 51, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Leser, S.; Oesser, S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Cruz, G.; León-López, A.; Cruz-Gómez, V.; Jiménez-Alvarado, R.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Collagen Hydrolysates for Skin Protection: Oral Administration and Topical Formulation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porfírio, E.; Fanaro, G. Collagen supplementation as a complementary therapy for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Rev. Bras. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2016, 19, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.L.; Dahl, W.J. A novel solution is needed to correct low nutrient intakes in elderly long-term care residents. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraç, M.G.; Dedebaş, T.; Hastaoğlu, E.; Arslan, E. Influence of using scarlet runner bean flour on the production and physicochemical, textural, and sensorial properties of vegan cakes: WASPAS-SWARA techniques. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, A.; Ares, F.; Ares, G. Sensory shelf-life estimation: A review of current methodological approaches. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Methods for Multiple Attribute Decision Making. In Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications A State of the Art Survey; Hwang, C.L., Yoon, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 58–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Xin, J.; Yang, H.; Gao, C. Application of the entropy weight and TOPSIS method in safety evaluation of coal mines. Procedia Eng. 2011, 26, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, J.; De Graaf, C.; Hulshof, T.; Jebb, S.; Livingstone, B.; Lluch, A.; Mela, D.; Salah, S.; Schuring, E.; Van Der Knaap, H.; et al. Appetite control: Methodological aspects of the evaluation of foods. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, S.; Yavuz, C. Yaşlılık ve Beslenme: Elderly and Nutrition. In Yaşlanmaya Sağlık Sosyolojisi Perspektifinden Multidisipliner Yaklaşımlar, 1st ed.; Say Şahin, D., Ed.; Ekin Yayınevi: Bursa, Türkiye, 2020; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, M.E.; Reid, R.E.R.; King, N.A. Sensory Profile of Adults with Reduced Food Intake and the Potential Roles of Nutrition and Physical Activity Interventions. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Doerr, J.M.; Peters, L.; Viard, M.; Reuter, I.; Prosiegel, M.; Weber, S.; Yeniguen, M.; Tschernatsch, M.; Gerriets, T.; et al. Age-related changes in oral sensitivity, taste and smell. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarya, S.; Singh, K.; Sabharwal, M. Changes during aging and their association with malnutrition. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesco, V.D.; Pellizzari, L.; Corrà, L.; Fontana, G. The anorexia of aging: Impact on health and quality of life. Geriatr. Care 2019, 4, 7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Randriambelonoro, M.; Perrin, C.; Valk, C.; Álvarez, B.; Schwarze, A.K. Aspects Influencing Food Intake and Approaches towards Personalising Nutrition in the Elderly. Popul. Ageing 2020, 13, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikritzi, R.; Moynihan, P.J.; Gosney, M.A.; Allen, V.J.; Methven, L. The effect of macro- and micro-nutrient fortification of biscuits on their sensory properties and on hedonic liking of older people. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.B.; Shin, W.S. Physicochemical and sensory properties of retort chicken curry mousse fortified with branched-chain amino acids for the elderly. LWT 2023, 185, 115133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoraie, N.M.; Saqaan, R.; Alharthi, R.; Alamoudi, A.; Badh, L.; Shatwan, I.M. Snacking patterns throughout the life span: Potential implications on health. Nutr. Res. 2021, 91, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, R.M.; Worsley, A.; Timperio, A.; McNaughton, S.A. Understanding meal patterns: Definitions, methodology and impact on nutrient intake and diet quality. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2015, 28, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krok-Schoen, J.L.; Jonnalagadda, S.S.; Luo, M.; Kelly, O.J.; Taylor, C.A. Nutrient intakes from meals and snacks differ with age in middle-aged and older Americans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.; Meram, C.; Bandara, N.; Wu, J. Protein and peptides for elderly health. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2018, 112, 265–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.K.; Nicklas, B.J.; Ding, J.; Harris, T.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Newman, A.B.; Lee, S.L.; Sahyoun, N.R.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B. Dietary protein intake is associated with lean mass change in older, community-dwelling adults: Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.M.B.; Sakon, P.O.R.; Paula, H.A.A.; Pinto, M.S.; Sant’Anna, M.S.L.; Araújo, T.F.; Minim, V.P.R. Protein and sensory quality of a food supplement formulated for the elderly. Acta Aliment. 2014, 43, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykänen, I.; Törrönen, R.; Schwab, U. Dairy-based and energy-enriched berry-based snacks improve or maintain nutritional and functional status in older people in home Care. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, A.D.; Visvanathan, R. Anorexia of aging–An updated short review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossen, L.; Bonham, M.; Porter, J. Can fortified, nutrient-dense and enriched foods and drink-based nutrition interventions increase energy and protein intake in residential aged care residents? A systematic review with meta-analyses. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 124, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of the Republic of Türkiye. Turkey Nutrition Guide (TÜBER) Sağlık Bakanlığı Yayınları 2022 Ankara. Available online: https://hsgm.saglik.gov.tr/tr/web-uygulamalarimiz/357.html (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Turkish Food Codex Nutrition and Health Statements Regulation. Official Journal (Number: 29960). Available online: https://www.resmigazete.gov.tr/eskiler/2017/01/20170126M1-5.htm (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Tucker, K.L. High risk nutrients in the aging population. In Handbook of Clinical Nutrition and Aging, 3rd ed.; Bales, C., Locher, J., Saltzman, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 335–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, T.C.; Frankenfeld, C.L.; Frei, B.; Shah, A.V.; Yu, C.R.; van Klinken, B.J.; Adeleke, M. Multivitamin/multimineral supplement use is associated with increased micronutrient intakes and biomarkers and decreased prevalence of inadequacies and deficiencies in middle-aged and older adults in the United States. J. Nutr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 38, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Dietary Reference Values for nutrients summary report. EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 14, e15121E. [Google Scholar]
- Keršienė, M.; Jasutienė, I.; Eisinaitė, V.; Pukalskienė, M.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Damulevičienė, G.; Knašienė, J.; Lesauskaitė, V.; Leskauskaitė, D. Development of a high-protein yoghurt-type product enriched with bioactive compounds for the elderly. LWT 2020, 131, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, A.; Novelli, A. Sarcopenia in the elderly: From clinical aspects to therapeutic options. Geriatr. Care 2019, 5, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
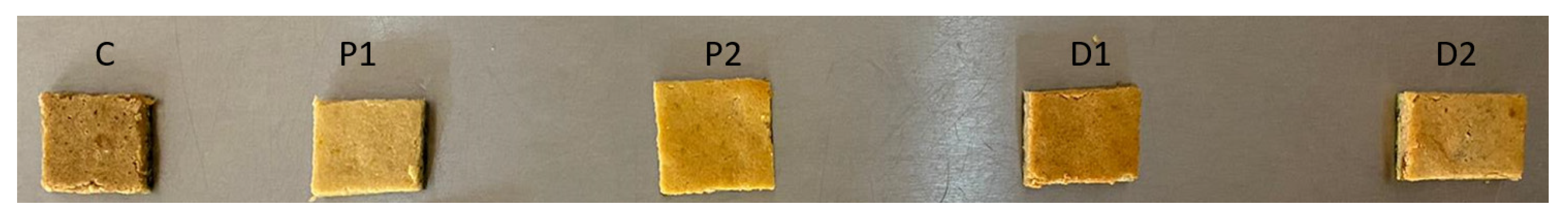
| Material Name | C | P1 | P2 | D1 | D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen (g) | - | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.33 | 0.66 |
| Pumpkin puree (g) | - | 16.6 | 16.6 | - | - |
| Tahini (ml) | - | 6.66 | 6.66 | 6.66 | 6.66 |
| Date puree (g) | - | - | - | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Normalized Decision Matrix | ||||
| Alternatives | Flavor | Odor | Appearance | Structure |
| C | 04336 | 0.4542 | 0.4450 | 0.4307 |
| P1 | 0.4336 | 0.4788 | 0.4648 | 0.4874 |
| P2 | 0.4669 | 0.4297 | 0.4253 | 0.4534 |
| D1 | 0.4336 | 0.4419 | 0.4549 | 0.4194 |
| D2 | 0.4669 | 0.4297 | 0.4450 | 0.4421 |
| Weighted Normalized Decision Matrix | ||||
| Alternatives | Flavor | Odor | Appearance | Structure |
| C | 0.2168 | 0.0681 | 0.0890 | 0.0646 |
| P1 | 0.2168 | 0.0718 | 0.0930 | 0.0731 |
| P2 | 0.2335 | 0.0644 | 0.0851 | 0.0680 |
| D1 | 0.2168 | 0.0663 | 0.0910 | 0.0629 |
| D2 | 0.2335 | 0.0644 | 0.0890 | 0.0663 |
| Samples | Si+ | Si− | Pi | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.0195 | 0.0057 | 0.2253 | 5 |
| P1 | 0.0167 | 0.0149 | 0.4713 | 3 |
| P2 | 0.0120 | 0.0174 | 0.5933 | 2 |
| D1 | 0.0204 | 0.0062 | 0.2334 | 4 |
| D2 | 0.0108 | 0.0175 | 0.6185 | 1 |
| Nutrients | C | P1 | P2 | D1 | D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 308.3 | 352.5 | 353.7 | 376.4 | 377.6 |
| Protein (g) | 6.8 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 8.8 |
| Fat (g) | 13.1 | 16.4 | 16.4 | 16.4 | 16.4 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 40.0 | 42.1 | 42.1 | 47.8 | 47.8 |
| Fibre (g) | 3.1 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| Vitamin A (µg) | 260.4 | 276.5 | 276.5 | 261.0 | 261.0 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 6.1 | 13.0 | 17.9 | 11.3 | 16.2 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 4 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Vitamin B12 (µg) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Folic acid (µg) | 47.1 | 59.1 | 59.1 | 55.2 | 55.2 |
| Calcium (mg) | 64.7 | 96.3 | 96.3 | 99.1 | 99.1 |
| Phosphorous (mg) | 174.6 | 232.0 | 232.0 | 230.7 | 230.7 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 50.0 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 61.7 | 61.7 |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.3 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| Glycine (mg) | 333.6 | 511.8 | 621.7 | 518.7 | 628.6 |
| Proline (mg) | 431.7 | 515.1 | 545.1 | 524.3 | 554.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hastaoğlu, F.; Hastaoğlu, E.; Bağlam, N.; Taş, İ.N. Sensorial and Nutritional Properties of a Collagen-Fortified Snack Bar Designed for the Elderly. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163620
Hastaoğlu F, Hastaoğlu E, Bağlam N, Taş İN. Sensorial and Nutritional Properties of a Collagen-Fortified Snack Bar Designed for the Elderly. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163620
Chicago/Turabian StyleHastaoğlu, Fatma, Emre Hastaoğlu, Nurcan Bağlam, and İrem Nur Taş. 2023. "Sensorial and Nutritional Properties of a Collagen-Fortified Snack Bar Designed for the Elderly" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163620
APA StyleHastaoğlu, F., Hastaoğlu, E., Bağlam, N., & Taş, İ. N. (2023). Sensorial and Nutritional Properties of a Collagen-Fortified Snack Bar Designed for the Elderly. Nutrients, 15(16), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163620






