The Impact of Nutritional Markers and Dietary Habits on the Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Older Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
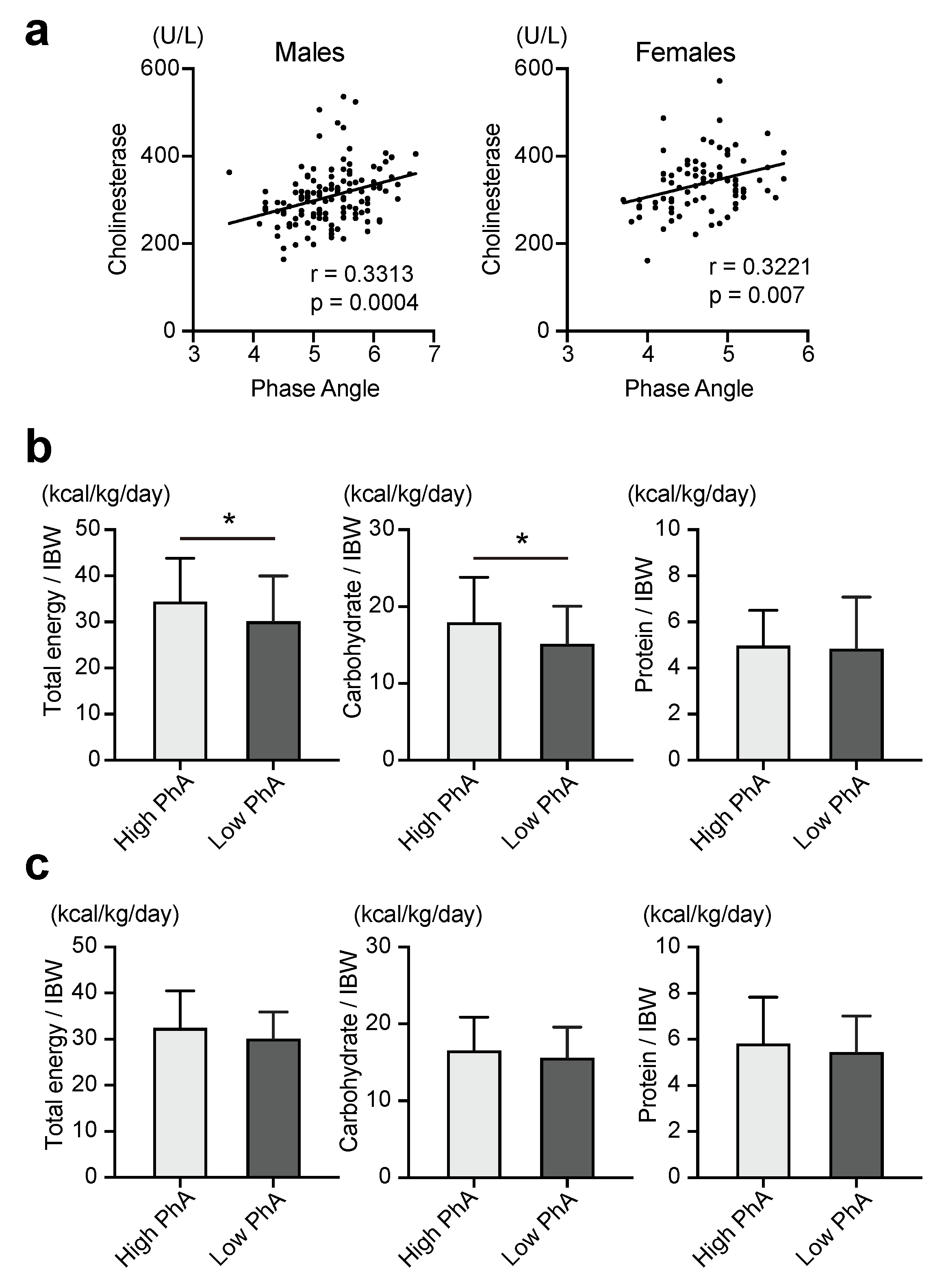
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, L.C. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Body Composition Assessment: Reflections on Accuracy, Clinical Utility, and Standardisation. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellido, D.; García-García, C.; Talluri, A.; Lukaski, H.C.; García-Almeida, J.M. Future Lines of Research on Phase Angle: Strengths and Limitations. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Oliva, A.; Ávila-Nava, A.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, E.A.; Trujillo-Mercado, A.; García-Guzmán, A.D.; Pinzón-Navarro, B.A.; Fuentes-Servín, J.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Medina-Vera, I. Association between Phase Angle and the Nutritional Status in Pediatric Populations: A Systematic Review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1142545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulasi, U.; Kuchnia, A.J.; Cole, A.J.; Earthman, C.P. Bioimpedance at the Bedside: Current Applications, Limitations, and Opportunities. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Bielemann, R.M.; Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B. Phase Angle and Its Determinants in Healthy Subjects: Influence of Body Composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical Phase Angle and Impedance Vector Analysis—Clinical Relevance and Applicability of Impedance Parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiello, R.; Amaral, M.A.; Mundstock, E.; Ziegelmann, P.K. Reference Values for the Phase Angle of the Electrical Bioimpedance: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Involving More than 250,000 Subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchnia, A.J.; Teigen, L.M.; Cole, A.J.; Mulasi, U.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Vock, D.M.; Earthman, C.P. Phase Angle and Impedance Ratio: Reference Cut-Points From the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004 From Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Data. JPEN. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Hong, N.; Kim, C.O.; Kim, H.C.; Youm, Y.; Choi, J.; Rhee, Y. The Diagnostic Value of Phase Angle, an Integrative Bioelectrical Marker, for Identifying Individuals with Dysmobility Syndrome: The Korean Urban-Rural Elderly Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kwon, O.; Shin, C.S.; Lee, S.M. Use of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Nutritional Status in Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlini, L.M.; Alves, F.D.; Ceretta, L.B.; Perry, I.S.; Souza, G.C.; Clausell, N.O. Phase Angle and Mortality: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Herpich, C.; Müller-Werdan, U. Role of Phase Angle in Older Adults with Focus on the Geriatric Syndromes Sarcopenia and Frailty. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Wirth, R.; Neubauer, M.; Eckardt, R.; Stobäus, N. The Bioimpedance Phase Angle Predicts Low Muscle Strength, Impaired Quality of Life, and Increased Mortality in Old Patients with Cancer. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 173.e17–173.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, K.; Doi, T.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Nakakubo, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Kurita, S.; Ishii, H.; Shimada, H. Predictivity of Bioimpedance Phase Angle for Incident Disability in Older Adults. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundstock, E.; Amaral, M.A.; Baptista, R.R.; Sarria, E.E.; Dos Santos, R.R.G.; Filho, A.D.; Rodrigues, C.A.S.; Forte, G.C.; Castro, L.; Padoin, A.V.; et al. Association between Phase Angle from Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Level of Physical Activity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Colognesi, L.A.; Moro, T.; Paoli, A.; Casolo, A.; Santos, L.; Correia, R.R.; Lemes, Í.R.; Milanez, V.F.; Christofaro, D.D.; et al. Effect of Resistance Training on Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ichida, A.; Matsumura, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Arita, J.; Akamatsu, N.; Kaneko, J.; Kokudo, N.; Hasegawa, K. Evaluation of Preoperative Nutritional Variables to Predict Postoperative Complications after Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Nutrition 2019, 67–68S, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuzawa, N.; Naito, H. Nutritional Parameters Affecting Severity of Pneumonia and Length of Hospital Stay in Patients with Pneumococcal Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2015, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shinkai, S.; Murayama, H.; Mori, S. Comparison of Segmental Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for the Assessment of Body Composition in a Community-Dwelling Older Population. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatsky, A.L.; Zhang, J.; Udaltsova, N.; Li, Y.; Tran, H.N. Body Mass Index and Mortality in a Very Large Cohort: Is It Really Healthier to Be Overweight? Perm. J. 2017, 21, 16–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S. Murakami. K. Sasaki. S. Okubo. H. Hirota. N. Notsu. A. Fukui. M. Date. C. Comparison of Relative Validity of Food Group Intakes Estimated by Comprehensive and Brief-Type Self-Administered Diet History Questionnaires against 16 d Dietary Records in Japanese Adults. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Honda, S.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Both Comprehensive and Brief Self-Administered Diet History Questionnaires Satisfactorily Rank Nutrient Intakes in Japanese Adults. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bučan Nenadić, D.; Radić, J.; Kolak, E.; Vučković, M.; Novak, I.; Selak, M.; Radić, M. Phase Angle Association with Dietary Habits and Metabolic Syndrome in Diabetic Hypertensive Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Marra, M.; Di Gregorio, A.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) -Derived Phase Angle in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3052–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Tetsunaga, T.; Misawa, H.; Nishida, K.; Ozaki, T. Association of Phase Angle with Sarcopenia in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Patients: A Retrospective Study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Zhao, K.; Luo, G.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Reference Data of Phase Angle Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Overweight and Obese Chinese. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 924199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Marra, M.; Antognozzi, V.; Sammarco, R.; Ballarin, G.; Cioffi, I.; Scalfi, L.; Pasanisi, F. Comparison of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis-Derived Phase Angle in Individuals with Different Weight Status. Nutrition 2023, 108, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Soundar, E.P.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. Can Phase Angle Determined by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Assess Nutritional Risk? A Comparison between Healthy and Hospitalized Subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.E.; Queiroz, M.D.S.C.; de Albuquerque, N.M.C.; Rodrigues, J.; Wiegert, E.V.M.; Calixto-Lima, L.; de Oliveira, L.C. The Prognostic Role of Phase Angle in Advanced Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarpia, L.; Grandone, I.; Contaldo, F.; Pasanisi, F. Butyrylcholinesterase as a Prognostic Marker: A Review of the Literature. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2013, 4, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterberger, S.; Aschauer, R.; Zöhrer, P.A.; Draxler, A.; Aschauer, M.; Kager, B.; Franzke, B.; Strasser, E.-M.; Wagner, K.-H.; Wessner, B. Association of Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle with Physical Performance and Nutrient Intake of Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-Based Recommendations for Optimal Dietary Protein Intake in Older People: A Position Paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutz, N.E.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznariç, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein Intake and Exercise for Optimal Muscle Function with Aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.Y.; Ryu, H.; Ju, D.L.; Jang, M.; Oh, K.-H.; Ahn, C.; Han, S.N. Foods Contributing to Nutrients Intake and Assessment of Nutritional Status in Pre-Dialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, R.; Takahashi, F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Okamura, T.; Miki, A.; Kaji, A.; Sakai, R.; Kitagawa, N.; Senmaru, T.; Majima, S.; et al. Short Energy Intake Is Associated with Muscle Mass Loss in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Study of the KAMOGAWA-DM Cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Tamura, Y.; Yamaoka, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Umegaki, H.; Kamada, C.; Iimuro, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Ito, H.; et al. Assessing the Association between Optimal Energy Intake and All-Cause Mortality in Older Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition and Hydration in Geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria-Montesinos, D.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Navarro-Marroco, J.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.T.; Serrano-Martínez, A.; Abellán-Aynés, O.; Barcina-Pérez, P.; Hernández-Sánchez, P. Phase Angle, Handgrip Strength, and Other Indicators of Nutritional Status in Cancer Patients Undergoing Different Nutritional Strategies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Coratella, G.; Cerullo, G.; Stagi, S.; Paoli, S.; Marini, S.; Grigoletto, A.; Moroni, A.; Petri, C.; Andreoli, A.; et al. New bioelectrical impedance vector references and phase angle centile curves in 4367 adults: The need for an urgent update after 30 years. Clin Nutr. 2023, 42, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author (s) and contributor (s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor (s). MDPI and/or the editor (s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
| Characteristics | All n = 130 | High PhA n = 91 | Low PhA n = 39 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72.6 (5.0) | 71.2 (4.4) | 75.3 (5.2) | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 (3.1) | 23.5 (2.9) | 21.8 (3.1) | 0.0024 |
| Habit of smoking, current smoker, n (%) | 14 (12.7) | 12 (14.2) | 3 (8.3) | 0.3774 |
| Habit of exercise, yes, n (%) | 68 (56.2) | 53 (61.6) | 15 (41.7) | 0.0429 |
| Skipping breakfast, yes, n (%) | 6 (5.0) | 3 (3.5) | 3 (8.6) | 0.2429 |
| Fast eating speed, yes, n (%) | 64 (52.9) | 47 (55.3) | 17 (47.2) | 0.4161 |
| Getting a good sleep, yes, n (%) | 100 (82.6) | 71 (82.6) | 29 (82.9) | 0.9686 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 136.7 (17.1) | 137.5 (16.8) | 134.1 (18.4) | 0.3194 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 83.0 (11.0) | 84.3 (10.0) | 79.6 (12.7) | 0.024 |
| AST (mg/dL) | 23.6 (7.1) | 23.7 (6.9) | 23.4 (7.7) | 0.8075 |
| ALT (mg/dL) | 22.0 (10.6) | 22.4 (9.9) | 20.6 (12.4) | 0.3542 |
| γ-GTP (mg/dL) | 43.7 (43.2) | 46.9 (48.2) | 36.3 (29.2) | 0.2027 |
| Creatinine | 1.2 (2.1) | 1.2 (2.5) | 1.0 (0.2) | 0.5066 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 59.8 (12.8) | 59.4 (12.8) | 60.2 (13.0) | 0.7223 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 111.0 (19.3) | 111.1 (19.9) | 111.0 (18.5) | 0.9563 |
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | 6.0 (0.7) | 5.9 (0.7) | 6.1 (0.7) | 0.2089 |
| Triglyceride | 105.8 (47.0) | 109.3 (48.4) | 96.4 (43.7) | 0.1533 |
| HDL cholesterol | 63.7 (18.9) | 63.5 (19.3) | 64.5 (19.0) | 0.7904 |
| Total cholesterol | 197.2 (30.6) | 200.3 (29.9) | 190.1 (32.1) | 0.0819 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 7.0 (0.4) | 7.0 (0.4) | 6.9 (0.4) | 0.3683 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 (0.4) | 4.3 (0.4) | 4.2 (0.3) | 0.1524 |
| Cholinesterase (U/L) | 308.0 (65.2) | 320.3 (68.2) | 279.5 (48.2) | 0.0009 |
| Total lymphocyte count (102/uL) | 29.8 (7.8) | 30.2 (8.2) | 28.6 (6.8) | 0.2796 |
| The body composition | ||||
| Body fat mass (kg) | 15.4 (5.3) | 15.5 (4.9) | 15.0 (6.1) | 0.4961 |
| Percentage of body fat mass | 23.9 (6.2) | 23.7 (5.3) | 23.9 (8.0) | 0.8114 |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 20.0 (2.7) | 20.5 (2.5) | 19.0 (2.9) | 0.0048 |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2) | 7.3 (0.7) | 7.5 (0.7) | 6.9 (0.7) | <0.0001 |
| Percentage of skeletal muscle mass (%) | 31.9 (3.0) | 31.9 (2.5) | 31.7 (3.8) | 0.7722 |
| Habitual diet intake | ||||
| Total energy intake (kcal/day) | 1989.2 (564.7) | 2057.1 (568.9) | 1826.0 (545.0) | 0.0487 |
| Total energy intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 33.0 (9.7) | 34.5 (9.3) | 30.2 (9.8) | 0.0307 |
| Carbohydrate intake (kcal/day) | 1031.5 (334.2) | 1081.1 (348.3) | 918.4 (286.8) | 0.0189 |
| Carbohydrate intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 17.1 (5.6) | 18.0 (5.8) | 15.2 (4.9) | 0.0157 |
| Protein intake (kcal/day) | 398.8 (100.9) | 299.3 (89.3) | 292.6 (126.6) | 0.7489 |
| Animal protein intake (g/day) | 43.6 (21.0) | 42.6 (17.5) | 44.5 (27.9) | 0.6575 |
| Vegetable protein intake (g/day) | 31.1 (8.8) | 32.3 (8.9) | 28.6 (8.5) | 0.0478 |
| Protein intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 5.0 (1.7) | 5.0 (1.5) | 4.8 (2.2) | 0.7035 |
| Protein intake per IBW (g/kg/day) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.2 (0.5) | 0.7035 |
| Fat intake (kcal/day) | 441.7 (137.1) | 448.8 (137.9) | 419.0 (136.2) | 0.2967 |
| Fat intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 7.3 (2.3) | 7.5 (2.2) | 6.9 (2.5) | 0.2763 |
| Dietary fiber intake (g/day) | 12.5 (4.4) | 12.7 (4.5) | 12.0 (4.4) | 0.4832 |
| Alcohol consumption (g/day) | 14.4 (1.9–28.7) | 15.9 (1.3–28.8) | 10.3 (2.5–29.4) | 0.7189 |
| Characteristics | All n = 82 | High PhA n = 59 | Low PhA n = 23 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 71.3 (4.9) | 69.9 (3.6) | 74.5 (6.4) | 0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.4 (3.9) | 22.8 (4.0) | 22.0 (3.4) | 0.4045 |
| Habit of smoking, current smoker, n (%) | 3 (4) | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.2243 |
| Habit of exercise, yes, n (%) | 44 (55) | 34 (58.6) | 10 (45.5) | 0.2905 |
| Skip breakfast, yes, n (%) | 2 (2.5) | 2 (3.5) | 0 (0) | 0.3777 |
| Fast eating speed, yes, n (%) | 44 (55.0) | 30 (51.7) | 14 (63.6) | 0.3389 |
| Getting a good sleep, yes, n (%) | 58 (73.4) | 43 (74.1) | 15 (71.4) | 0.8097 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 134.9 (16.3) | 134.5 (16.7) | 136.9 (15.7) | 0.5532 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 77.9 (10.9) | 79.2 (11.5) | 75.8 (8.7) | 0.2054 |
| AST (mg/dL) | 23.2 (5.2) | 23.1 (4.7) | 23.1 (6.0) | 0.9878 |
| ALT (mg/dL) | 19.4 (8.3) | 20.0 (7.7) | 17.1 (9.0) | 0.1492 |
| γ-GTP (mg/dL) | 24.4 (18.3) | 26.0 (20.4) | 20.5 (11.7) | 0.2317 |
| Creatinine | 0.7 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.0115 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 64.3 (10.8) | 62.9 (10.6) | 68.3 (10.9) | 0.043 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 103.8 (15.3) | 104.2 (16.3) | 103.1 (13.5) | 0.7728 |
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | 5.9 (0.5) | 5.9 (0.5) | 5.9 (0.3) | 0.6006 |
| Triglyceride | 89.8 (36.2) | 88.5 (36.4) | 93.7 (37.6) | 0.5685 |
| HDL cholesterol | 76.4 (15.3) | 77.3 (14.7) | 72.1 (15.3) | 0.1576 |
| Total cholesterol | 218.0 (30.0) | 217.0 (27.8) | 215.6 (32.1) | 0.8461 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 7.1 (0.4) | 7.1 (0.3) | 7.0 (0.4) | 0.1012 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 (0.3) | 4.3 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.3) | 0.0748 |
| Cholinesterase (U/L) | 335.6 (65.7) | 350.5 (60.7) | 304.9 (65.1) | 0.0036 |
| Total lymphocyte count (102/uL) | 32.5 (8.5) | 32.9 (7.3) | 30.3 (10.6) | 0.2105 |
| The body composition | ||||
| Body fat mass (kg) | 17.2 (7.1) | 17.5 (0.9) | 17.0 (1.5) | 0.7627 |
| Percentage of body fat mass | 31.5 (8.1) | 31.3 (8.4) | 32.9 (7.0) | 0.4097 |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 14.0 (2.5) | 14.4 (2.5) | 12.9 (2.3) | 0.0144 |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2) | 5.9 (0.8) | 6.1 (0.7) | 5.6 (0.7) | 0.0035 |
| Percentage of skeletal muscle mass (%) | 26.7 (3.3) | 27.1 (3.4) | 25.5 (2.8) | 0.0428 |
| Habitual diet intake | ||||
| Total energy intake (kcal/day) | 1651.3 (369.7) | 1679.3 (388.7) | 1540.1 (286.3) | 0.1455 |
| Total energy intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 32.1 (7.5) | 32.5 (7.9) | 30.2 (5.7) | 0.2328 |
| Carbohydrate intake (kcal/day) | 851.5 (221.8) | 860.2 (222.4) | 798.9 (201.1) | 0.2823 |
| Carbohydrate intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 16.5 (4.3) | 16.6 (4.3) | 15.7 (3.9) | 0.3869 |
| Protein intake (kcal/day) | 269.2 (89.6) | 299.3 (94.2) | 278.0 (69.5) | 0.3552 |
| Animal protein intake (g/day) | 46.5 (19.2) | 47.5 (20.0) | 42.3 (16.1) | 0.2907 |
| Vegetable protein intake (g/day) | 27.6 (6.9) | 27.3 (7.0) | 27.2 (6.4) | 0.9715 |
| Protein intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 5.8 (1.9) | 5.8 (2.0) | 5.5 (1.5) | 0.4685 |
| Protein intake per IBW (g/kg/day) | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.5) | 1.4 (0.4) | 0.4685 |
| Fat intake (kcal/day) | 418.5 (125.5) | 428.5 (133.3) | 391.7 (27.3) | 0.2641 |
| Fat intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 8.1 (2.6) | 8.3 (2.7) | 7.6 (2.1) | 0.3379 |
| Dietary fiber intake (g/day) | 12.1 (3.9) | 11.8 (3.9) | 12.5 (3.6) | 0.5153 |
| Alcohol consumption (g/day) | 0.0 (0.0–0.8) | 0.0 (0.0–8.2) | 0.0 (0.0–0.3) | 0.938 |
| Characteristics | Men | Women | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| Age (years) | −0.5286 | <0.0001 | −0.4051 | 0.0006 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.3207 | 0.0006 | 0.0774 | 0.5274 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 0.0608 | 0.5302 | −0.0694 | 0.5739 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 0.1782 | 0.0638 | 0.0204 | 0.8686 |
| AST (mg/dL) | 0.1157 | 0.231 | 0.0265 | 0.8301 |
| ALT (mg/dL) | 0.2381 | 0.0126 | 0.1767 | 0.1496 |
| γ-GTP (mg/dL) | 0.1598 | 0.0971 | 0.0968 | 0.4324 |
| Creatinine | −0.0137 | 0.8872 | 0.191 | 0.1187 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.0296 | 0.76 | −0.1504 | 0.2209 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.0377 | 0.697 | 0.1648 | 0.1793 |
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | −0.0245 | 0.8004 | 0.214 | 0.0797 |
| Triglyceride | 0.1557 | 0.106 | −0.1034 | 0.2841 |
| HDL cholesterol | −0.0644 | 0.506 | 0.1318 | 0.4013 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.1076 | 0.2653 | −0.0316 | 0.2841 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 0.1379 | 0.151 | 0.1949 | 0.1085 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.102 | 0.2889 | 0.2988 | 0.0126 |
| Cholinesterase (U/L) | 0.3313 | 0.0004 | 0.3221 | 0.007 |
| Total lymphocyte count (/uL) | 0.1152 | 0.2308 | 0.1343 | 0.2713 |
| The body composition | ||||
| Body fat mass (kg) | 0.0759 | 0.4328 | −0.0316 | 0.7982 |
| Percentage of body fat mass (%) | −0.0231 | 0.8112 | −0.137 | 0.2653 |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 0.3946 | <0.0001 | 0.3534 | 0.0031 |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (kg/m2) | 0.4241 | <0.0001 | 0.3562 | 0.0027 |
| Percentage of skeletal muscle mass (%) | −0.002 | 0.8364 | 0.2524 | 0.0379 |
| Habitual diet intake | ||||
| Total energy intake (kcal/day) | 0.1303 | 0.1747 | 0.288 | 0.0164 |
| Total energy intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 0.1828 | 0.0537 | 0.222 | 0.0667 |
| Carbohydrate intake (kcal/day) | 0.1747 | 0.068 | 0.247 | 0.0408 |
| Carbohydrate intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 0.2 | 0.0362 | 0.1967 | 0.1052 |
| Protein intake (kcal/day) | −0.0293 | 0.7613 | 0.161 | 0.0608 |
| Animal protein intake (g/day) | −0.1032 | 0.2855 | 0.1581 | 0.1978 |
| Vegetable protein intake (g/day) | 0.161 | 0.0945 | 0.0782 | 0.5264 |
| Protein intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | −0.0093 | 0.9231 | 0.1085 | 0.3748 |
| Fat intake (kcal/day) | 0.0248 | 0.7972 | 0.2269 | 0.0608 |
| Fat intake per IBW (kcal/kg/day) | 0.0422 | 0.6615 | 0.1804 | 0.1381 |
| Dietary fiber intake (g/day) | 0.0255 | 0.792 | −0.0032 | 0.9791 |
| Men | Women | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted | Unadjusted | Adjusted | |||||
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.2 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | ||||
| (per 1 year increase) | (1.10–1.31) | <0.0001 | (1.09–1.37) | 0.0004 | (1.08–1.37) | 0.0002 | (1.07–1.39) | 0.003 |
| Habit of exercise | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.43 | ||||
| (yes) | (0.20–0.98) | 0.0451 | (0.17–1.10) | 0.0886 | (0.22–1.58) | 0.2928 | (0.13–1.42) | 0.1645 |
| Total energy intake per IBW | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.97 | ||||
| (per 1 kcal/kg/day increase) | (0.91–1.00) | 0.0262 | (0.89–1.00) | 0.0346 | (0.89–1.03) | 0.2312 | (0.89–1.05) | 0.3976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kajiyama, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Okamura, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kitagawa, N.; Hamaguchi, M.; Fukui, M. The Impact of Nutritional Markers and Dietary Habits on the Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Older Individuals. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163599
Kajiyama S, Nakanishi N, Yamamoto S, Ichikawa T, Okamura T, Hashimoto Y, Kitagawa N, Hamaguchi M, Fukui M. The Impact of Nutritional Markers and Dietary Habits on the Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Older Individuals. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163599
Chicago/Turabian StyleKajiyama, Shintaro, Naoko Nakanishi, Shinta Yamamoto, Takahiro Ichikawa, Takuro Okamura, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Noriyuki Kitagawa, Masahide Hamaguchi, and Michiaki Fukui. 2023. "The Impact of Nutritional Markers and Dietary Habits on the Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Older Individuals" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163599
APA StyleKajiyama, S., Nakanishi, N., Yamamoto, S., Ichikawa, T., Okamura, T., Hashimoto, Y., Kitagawa, N., Hamaguchi, M., & Fukui, M. (2023). The Impact of Nutritional Markers and Dietary Habits on the Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Older Individuals. Nutrients, 15(16), 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163599








