Eating Behavior and Factors of Metabolic Health in Primary Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study in Greek Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Ethics Approval
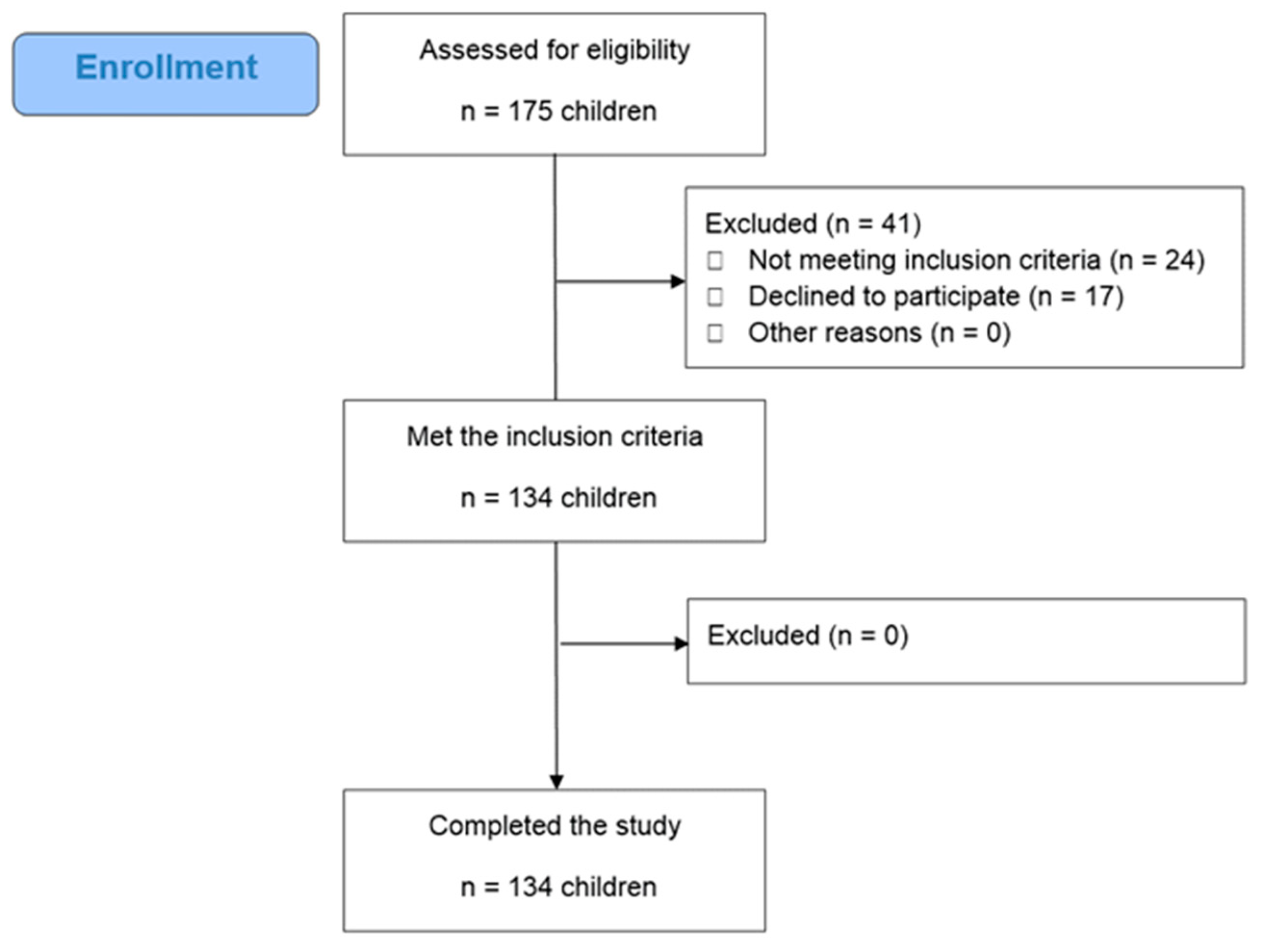
2.2. Study Design
- (a)
- community children, aged 6 to 11 years, living in Attica (Greece);
- (b)
- apparently healthy children without seasonal infection, chronic or life threatening diseases (as described below);
- (c)
- parental consent.
- (a)
- children with infections (e.g., seasonal influenza), chronic diseases (e.g., celiac disease, inflammatory bowel diseases, kidney disease, malabsorption, parathyroid diseases), pediatric metabolism disorders (e.g., type 1 diabetes) or life threating diseases (e.g., cancer, congenital disorders);
- (b)
- children with cognitive disorders (e.g., autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder);
- (c)
- children under medication treatment that could affect the outcomes of the study;
- (d)
- children following a vegetarian or a vegan diet;
- (e)
- children receiving nutritional supplements including vitamins and minerals;
- (f)
- parental refusal to consent.
2.3. Clinical, Laboratory and Nutritional Data
2.3.1. Day 1: Anthropometry and Blood Analysis
2.3.2. Day 2: CRF and HGS
2.3.3. Day 3: Nutritional Behavior Assessment
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Children’s General Characteristics
4.2. Differences of Tested Variables According to Body Weight Status
4.3. Differences between Tested Variables According to Breakfast Eating Behavior
4.4. Linear Regression Analyis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight: Key Facts. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Hosseini, B.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Association between antioxidant intake/status and obesity: A systematic review of observational studies. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 175, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, P.; Melnyk, S.; Bennuri, S.C.; Delhey, L.; Reis, A.; Moura, G.R.; Børsheim, E.; Rose, S.; Carvalho, E. Redox Imbalance and Methylation Disturbances in Early Childhood Obesity. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2207125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltoglou, G.; Schoina, M.; Valsamakis, G.; Salakos, N.; Avloniti, A.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Margeli, A.; Skevaki, C.; Papagianni, M.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; et al. Interrelations among the adipocytokines leptin and adiponectin, oxidative stress and aseptic inflammation markers in pre- and early-pubertal normal-weight and obese boys. Endocrine 2017, 55, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertiš Petek, T.; Petek, T.; Močnik, M.; Marčun Varda, N. Systemic Inflammation, Oxidative stress and cardiovascular health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, E.; Özer, Ö.F.; Erek Toprak, A.; Erman, H.; Torun, E.; Kesgin Ayhan, S.; Caglar, H.G.; Selek, S.; Kocyigit, A. Oxidative stress status in childhood obesity: A potential risk predictor. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3673–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, A.I.; Mesa, M.D.; Anguita-Ruiz, A.; González-Gil, E.M.; Vázquez-Cobela, R.; Moreno, L.A.; Gil, Á.; Gil-Campos, M.; Leis, R.; Bueno, G.; et al. Antioxidants and oxidative stress in children: Influence of puberty and metabolically unhealthy status. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.; Støren, Ø.; Hertel, J.K.; Gjevestad, E.; Småstuen, M.C.; Hjelmesæth, J. Associations between cardiorespiratory fitness and weight loss in patients with severe obesity undergoing an intensive lifestyle intervention program: Retrospective cohort study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.; Nordby, P.; Stallknecht, B. Maintenance of improvements in fitness and fatness 1 year after a 3-month lifestyle intervention in overweight men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1212–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklas, B.J.; Wang, X.; You, T.; Lyles, M.F.; Demons, J.; Easter, L.; Berry, M.J.; Lenchik, L.; Carr, J.J. Effect of exercise intensity on abdominal fat loss during calorie restriction in overweight and obese postmenopausal women: A randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuveer, G.; Hartz, J.; Lubans, D.R.; Takken, T.; Wiltz, J.L.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Perak, A.M.; Baker-Smith, C.; Pietris, N.; Edwards, N.M. Cardiorespiratory fitness in youth: An important marker of health: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, e101–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahche, J.; Fakhouri, T.; Carroll, D.D.; Burt, V.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Fulton, J.E. Cardiorespiratory fitness levels among U.S. youth aged 12–15 years: United States, 1999–2004 and 2012. NCHS Data Brief 2014, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Zha, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, J.; Long, J.; Luo, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, S.; Luo, D.; et al. Handgrip strength-related factors affecting health outcomes in young adults: Association with cardiorespiratory fitness. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6645252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, D. Association of Grip Strength with Risk of All-Cause Mortality, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Cancer in Community-Dwelling Populations: A Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 551.e17–551.e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Ozaki, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Loenneke, J.P. Children with Low Handgrip Strength: A Narrative Review of Possible Exercise Strategies to Improve Its Development. Children 2022, 9, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Carrasco, S.; Garcia-Unanue, J.; Haapala, E.A.; Felipe, J.L.; Gallardo, L.; Lopez-Fernandez, J. Relationships of BMI, muscle-to-fat ratio, and handgrip strength-to-BMI ratio to physical fitness in Spanish children and adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juton, C.; Berruezo, P.; Torres, S.; Castañer, O.; Según, G.; Fitó, M.; Homs, C.; Gómez, S.F.; Schröder, H. Association between meal frequency and weight status in spanish children: A prospective cohort study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardeshirlarijani, E.; Namazi, N.; Jabbari, M.; Zeinali, M.; Gerami, H.; Jalili, R.B.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. The link between breakfast skipping and overweigh/obesity in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2019, 18, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzani, A.; Ricotti, R.; Caputo, M.; Solito, A.; Archero, F.; Bellone, S.; Prodam, F. A Systematic Review of the Association of Skipping Breakfast with Weight and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents. What Should We Better Investigate in the Future? Nutrients 2019, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuźbicka, K.; Rachoń, D. Bad eating habits as the main cause of obesity among children. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2013, 19, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicka, P.; Keres, J.; Ek, A.; Nordin, K.; Sandvik, P. Changing the home food environment: Parents’ perspectives four years after starting obesity treatment for their preschool aged child. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years—Indicators. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years/indicators (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Eslami, M.; Pourghazi, F.; Khazdouz, M.; Tian, J.; Pourrostami, K.; Esmaeili-Abdar, Z.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Qorbani, M. Optimal cut-off value of waist circumference-to-height ratio to predict central obesity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic studies. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 985319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, C.; Kovera, A.J.; Pietrobelli, A.; Heshka, S.; Horlick, M.; Kehayias, J.J.; Wang, Z.; Heymsfield, S.B. Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcraft, C.M.; Frankenfield, D.C. Validity test of a new open-circuit indirect calorimeter. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierenberg, D.W.; Lester, D.C. Determination of vitamins A and E in serum and plasma using a simplified clarification method and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1985, 345, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, L.S.; Lee, B.L.; New, A.L.; Ong, C.N. Determination of plasma ascorbic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. 1993, 612, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, B.; Kostianev, S.; Turnovska, T. Modified treadmill protocol for evaluation of physical fitness in pediatric age group—Comparison with Bruce and Balke protocols. Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Bulg. 2003, 27, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Beltz, N.M.; Gibson, A.L.; Janot, J.M.; Kravitz, L.; Mermier, C.M.; Dalleck, L.C. Graded exercise testing protocols for the determination of VO2max: Historical perspectives, progress, and future considerations. J. Sports Med. (Hindawi Publ. Corp.) 2016, 2016, 3968393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fess, E.E. Grip Strength. In Clinical Assessment Recommendations, 2nd ed.; Casanova, J.S., Ed.; American Society of Hand Therapists: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992; pp. 41–45, 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Gąsior, J.S.; Pawłowski, M.; Jeleń, P.J.; Rameckers, E.A.; Williams, C.A.; Makuch, R.; Werner, B. Test-retest reliability of handgrip strength measurement in children and preadolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsior, J.S.; Pawłowski, M.; Williams, C.A.; Dąbrowski, M.J.; Rameckers, E.A. Assessment of maximal isometric hand grip strength in school-aged children. Open Med. 2018, 13, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean diet quality index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.N.; Carsley, S.; Lebovic, G.; Borkhoff, C.M.; Maguire, J.L.; Parkin, P.C.; Birken, C.S. Misclassification of child body mass index from cut-points defined by rounded percentiles instead of z-scores. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Nardone, P.; Starc, G.; Hejgaard, T.; Júlíusson, P.B.; Fismen, A.-S.; Weghuber, D.; Musić Milanović, S.; García-Solano, M.; et al. Thinness, overweight, and obesity in 6- to 9-year-old children from 36 countries: The World Health Organization European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative-COSI 2015–2017. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S6), e13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambalis, K.D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Psarra, G.; Sidossis, L.S. Current data in Greek children indicate decreasing trends of obesity in the transition from childhood to adolescence; results from the National Action for Children’s Health (EYZHN) Program. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2018, 59, e36–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassapidou, M. Prevalence of childhood obesity in Greece: Results from WHO Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative 2010–2020. Public Health Toxicol. 2022, 2, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Mirmoghtadaee, P.; Najafi, H.; Keikha, M. Systematic review on the association of abdominal obesity in children and adolescents with cardio-metabolic risk factors. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Calcaterra, V.; Larizza, D.; De Silvestri, A.; Albertini, R.; Vinci, F.; Regalbuto, C.; Dobbiani, G.; Montalbano, C.; Pelizzo, G.; Cena, H. Gender-based differences in the clustering of metabolic syndrome factors in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Hernando, J.; Escribano, J.; Ferré, N.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Grote, V.; Koletzko, B.; Gruszfeld, D.; ReDionigi, A.; Verduci, E.; Xhonneux, A.; et al. Usefulness of the waist-to-height ratio for predicting cardiometabolic risk in children and its suggested boundary values. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-C.; Chen, I.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Loke, S.-S.; Wang, S.-H.; Hsiao, K.-Y. Waist-to-height ratio, waist circumference, and body mass index as indices of cardiometabolic risk among 36,642 Taiwanese adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santomauro, F.; Lorini, C.; Pieralli, F.; Niccolai, G.; Picciolli, P.; Vezzosi, S.; Bonaccorsi, G. Waist-to-height ratio and its associations with body mass index in a sample of Tuscan children in primary school. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusek, W.; Baran, J.; Leszczak, J.; Adamczyk, M.; Baran, R.; Weres, A.; Inglot, G.; Czenczek-Lewandowska, E.; Pop, T. Changes in children’s body composition and posture during puberty growth. Children 2021, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofenheimer, A.; Breyer-Kohansal, R.; Hartl, S.; Burghuber, O.C.; Krach, F.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Breyer, M.-K. Using body composition groups to identify children and adolescents at risk of dyslipidemia. Children 2021, 8, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar-Amini, M.; Khorramruz, F.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Sahebi, R.; Mohammadi-Bajgyran, M.; Mohaddes Ardabili, H.; Tayefi, M.; Darroudi, S.; Moohebati, M.; Heidari-Bakavoli, A.; et al. Association between serum vitamin E concentrations and the presence of metabolic syndrome: A population-based cohort study. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, K.; Chojnacka, A.; Górnicka, M. Tocopherols and tocotrienols-bioactive dietary compounds; what is certain, what is doubt? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, F.; Abdullah, A.; Makpol, S. Cellular uptake and bioavailability of tocotrienol-rich fraction in SIRT1-inhibited human diploid fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, E.; Sapper, T.N.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L.; Schill, K.E.; Clinton, S.K.; Bobe, G.; Traber, M.G.; Bruno, R.S. α-Tocopherol bioavailability is lower in adults with metabolic syndrome regardless of dairy fat co-ingestion: A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Franzese, A.; Ciccimarra, E.; Lucariello, S.; Savoia, M.; Capuano, G.; Migliaro, F. Vitamin E treatment in pediatric obesity-related liver disease: A randomized study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavine, J.E. Vitamin E treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children: A pilot study. J. Pediatr. 2000, 136, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.H.; Wing, R.R.; Cluss, P.; Fernstrom, M.H.; Penner, B.; Perkins, K.A.; Nudelman, S.; Marks, B.; Valoski, A. Resting metabolic rate in lean and obese children: Relationship to child and parent weight and percent-overweight change. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiauer, K.F.; Mueller, T.; Widhalm, K. Resting metabolic rate in obese children before, during and after weight loss. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1992, 16, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, D.; Schutz, Y. The effect of obesity, age, puberty and gender on resting metabolic rate in children and adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1997, 156, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzyb, A.; Domagalska-Szopa, M.; Siwiec, A.; Kwiecień-Czerwieniec, I.; Szopa, A. Cardiopulmonary capacity in overweight and obese children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 671827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinder, G.; Larsson, U.E.; Norgren, S.; Marcus, C. Insulin sensitivity, VO2max and body composition in severely obese Swedish children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeley, C.E.; Van Rompay, M.I.; Schultz, N.S.; Sacheck, J.M. Relationship between muscle strength and dyslipidemia, serum 25(OH)D, and weight status among diverse schoolchildren: A cross-sectional analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffl, M.; Chrudimsky, J.; Tufano, J.J. Using relative handgrip strength to identify children at risk of sarcopenic obesity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Zati Iwani, A.K.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Wan Mohd Zin, R.M.; Fuziah, M.Z.; Hong, J.Y.H.; Abqariyah, Y.; Mokhtar, A.H.; Wan Mohamud, W.N. TG: HDL-C ratio is a good marker to identify children affected by obesity with increased cardiometabolic risk and insulin resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 8586167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambalis, K.D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Psarra, G.; Sidossis, L.S. Breakfast skipping in Greek schoolchildren connected to an unhealthy lifestyle profile. Results from the National Action for Children’s Health Program: Breakfast Skipping and Lifestyle Factors. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 76, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, I.; Rekleiti, M.; Saridi, M.; Beliotis, E.; Toska, A.; Souliotis, K.; Wozniak, G. Prevalence of obesity in children aged 6–12 years in Greece: Nutritional behaviour and physical activity. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambalis, K.D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Psarra, G.; Sidossis, L.S. Association of cardiorespiratory fitness levels with dietary habits and lifestyle factors in schoolchildren. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utter, J.; Scragg, R.; Mhurchu, C.N.; Schaaf, D. At-home breakfast consumption among New Zealand children: Associations with body mass index and related nutrition behaviors. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Enrolled (N = 134) | Boys (N = 77) | Girls (N = 57) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometry | ||||
| Age (years); mean (SD) | 8.8 (1.8) | 8.8 (1.7) | 8.9 (1.8) | 0.709 |
| Height (m); mean (SD) | 1.4 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 0.577 |
| Weight (kg); mean (SD) | 33.6 (10.0) | 34.4 (10.9) | 32.6 (8.7) | 0.326 |
| BMI (kg/m2); mean (SD) | 17.8 (3.1) | 18.1 (3.4) | 17.5 (2.5) | 0.301 |
| Z-score weight; mean (SD) | 0.9 (1.2) | 1.0 (1.2) | 0.6 (1.0) | 0.042 |
| Z-score height; mean (SD) | 0.8 (1.1) | 0.9 (1.1) | 0.6 (1.0) | 0.064 |
| Z-score BMI; mean (SD) | 0.6 (1.2) | 0.7 (1.3) | 0.4 (1.1) | 0.156 |
| Weight status based on z-score BMI; N (%) | ||||
| <−2, underweight | 2 (1.9) | 1 (1.3) | 1 (1.8) | - |
| −2 to +0.99, normal weight | 85 (81.7) | 48 (62.3) | 37 (64.9) | 0.531 |
| ≥1, overweight/obese | 47 (35.1) | 28 (36.4) | 19 (33.3) | 0.393 |
| WC (cm); mean (SD) | 61.1 (8.7) | 62.0 (9.5) | 59.8 (7.4) | 0.149 |
| WHtR; mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.6) | 0.4 (0.7) | 0.4 (0.0) | 0.564 |
| FM (%); mean (SD) | 23.7 (9.5) | 22.4 (10.4) | 25.4 (7.9) | 0.070 |
| FM (kg); mean (SD) | 8.6 (5.8) | 8.5 (6.7) | 8.8 (4.3) | 0.777 |
| FFM (%); mean (SD) | 76.3 (9.6) | 77.5 (10.6) | 74.6 (7.9) | 0.082 |
| FFM (kg); mean (SD) | 25.0 (5.7) | 25.8 (5.5) | 24.0 (5.8) | 0.064 |
| TBW (%); mean (SD) | 63.7 (9.2) | 64.6 (9.9) | 62.4 (8.0) | 0.169 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness and strength | ||||
| RMR (kcal/day); mean (SD) | 1565.5 (278.9) | 1628.0 (276.2) | 1479.8 (261.4) | 0.003 |
| RMR (kcal/kg/day); mean (SD) | 49.0 (10.0) | 49.6 (9.8) | 48.1 (10.3) | 0.414 |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min); mean (SD) | 49.9 (9.5) | 52.5 (10.2) | 47.0 (7.6) | 0.003 |
| HRmax (bpm); mean (SD) | 202.9 (11.3) | 201.9 (10.5) | 204.2 (12.3) | 0.297 |
| HGS (kg); mean (SD) | 15.2 (5.2) | 16.3 (5.4) | 13.2 (4.7) | 0.018 |
| Blood indices | ||||
| Vit A (mg/L); mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.852 |
| Vit E (mg/L); mean (SD) | 10.9 (2.6) | 10.9 (2.8) | 10.8 (2.4) | 0.859 |
| Vit C (mg/L); mean (SD) | 5.6 (1.3) | 5.6 (1.0) | 5.6 (1.7) | 0.826 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL); mean (SD) | 164.3 (26.8) | 166.1 (25.1) | 161.8 (29.1) | 0.366 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL); mean (SD) | 53.2 (12.2) | 53.5 (11.1) | 52.7 (12.6) | 0.729 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL); mean (SD) | 99.6 (23.6) | 101.5 (22.4) | 97.1 (26.2) | 0.288 |
| TG (mg/dL); mean (SD) | 57.4 (19.1) | 55.5 (16.5) | 59.9 (22.0) | 0.196 |
| TG/HDL-C ratio; mean (SD) | 1.2 (0.7) | 1.1 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.8) | 0.268 |
| Meals | ||||
| Daily breakfast (YES/NO); N (%) | 101 (75.4)/23 (17.2) | 58 (75.3)/13 (16.9) | 43 (75.4)/10 (17.5) | 0.937 |
| Daily snacking at school (YES/NO); N (%) | 98 (73.1)/22 (16.4) | 52 (67.5)/15 (19.5) | 46 (80.7)/7 (12.3) | 0.197 |
| Parameters: Mean (SD) | Normal Weight (N = 85) | Overweight/Obese (N = 47) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometry | |||
| z-score BMI | −0.05 (0.7) | 1.9 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| z-score height | 0.6 (1.0) | 1.1 (1.1) | 0.002 |
| z-score weight | 0.3 (0.8) | 2.0 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 8.8 (1.8) | 8.8 (1.7) | 0.897 |
| Height (m) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 0.076 |
| Weight (kg) | 29.9 (7.3) | 40.7 (10.8) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 16.2 (1.5) | 20.9 (2.8) | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 57.4 (5.8) | 68.1 (8.9) | <0.001 |
| WHtR | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.05) | <0.001 |
| FM (%) | 18.9 (6.4) | 32.4 (8.2) | <0.001 |
| FM (kg) | 5.6 (2.7) | 13.7 (6.5) | <0.001 |
| FFM (%) | 81.1 (6.4) | 67.5 (8.3) | <0.001 |
| FFM (kg) | 24.0 (5.6) | 27.0 (5.5) | 0.004 |
| TBW (%) | 67.5 (7.7) | 56.4 (7.0) | <0.001 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness and strength | |||
| RMR (kcal/kg/day) | 52.9 (9.0) | 42.3 (8.1) | <0.001 |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | 52.4 (8.4) | 46.1 (10.1) | <0.001 |
| HRmax (bpm) | 202.8 (11.7) | 203.0 (10.7) | 0.932 |
| HGS (kg) | 14.8 (4.8) | 15.8 (5.9) | 0.371 |
| Blood indices | |||
| Vit A (mg/L) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.582 |
| Vit E (mg/L) | 10.9 (2.4) | 10.5 (2.9) | 0.435 |
| Vit C (mg/L) | 5.5 (1.1) | 5.7 (1.7) | 0.591 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 165.0 (27.5) | 163.3 (26.0) | 0.736 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 53.2 (11.9) | 53.3 (12.8) | 0.968 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 100.2 (24.5) | 98.6 (22.4) | 0.719 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 57.9 (20.0) | 56.9 (17.5) | 0.764 |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | 1.2 (0.7) | 1.2 (0.6) | 0.859 |
| Meals | |||
| Daily breakfast (YES/NO); N (%) | 68 (80.0)/9 (10.6) | 31 (66.0)/14 (29.8) | 0.009 |
| Daily snacking at school (YES/NO); N (%) | 62 (72.9)/15 (17.6) | 34 (72.3)/7 (14.9) | 0.478 |
| Parameters: Mean Values (SD) | Consuming Breakfast | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily or Most of the Days (N = 101) | Sometimes/No (N = 23) | p-Value | |
| z-score BMI | 0.5 (1.3) | 1.2 (1.2) | 0.012 |
| z-score height | 0.8 (1.1) | 0.6 (1.2) | 0.393 |
| z-score weight | 0.8 (1.2) | 1.2 (1.3) | 0.175 |
| Age (years) | 8.6 (1.8) | 9.4 (1.3) | 0.042 |
| Height (m) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 0.165 |
| Weight (kg) | 32.3 (9.4) | 37.9 (10.0) | 0.012 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 17.4 (3.0) | 19.5 (3.3) | 0.002 |
| WC (cm) | 60.0 (8.3) | 65.5 (9.6) | 0.006 |
| WHtR | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.025 |
| FM (%) | 23.1 (9.5) | 27.7 (9.2) | 0.041 |
| FM (kg) | 8.2 (5.5) | 11.1 (6.5) | 0.029 |
| FFM (%) | 76.9 (9.5) | 72.4 (9.2) | 0.044 |
| FFM (kg) | 24.2 (5.3) | 26.8 (5.0) | 0.035 |
| TBW (%) | 64.0 (9.4) | 60.2 (7.9) | 0.082 |
| RMR (kcal/kg/day) | 49.6 (9.9) | 44.6 (7.3) | 0.035 |
| VO2 max (mL/kg/min) | 49.7 (10.1) | 48.6 (6.3) | 0.642 |
| HRmax (bpm) | 202.2 (12.0) | 205.2 (8.5) | 0.304 |
| HGS (kg) | 14.5 (5.0) | 16.2 (3.8) | 0.159 |
| Vit A (mg/L) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.531 |
| Vit E (mg/L) | 10.9 (2.8) | 10.7 (2.3) | 0.769 |
| Vit C (mg/L) | 5.5 (1.4) | 5.7 (1.1) | 0.733 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 163.8 (27.7) | 163.0 (23.5) | 0.895 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 52.8 (12.1) | 54.9 (11.8) | 0.460 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 99.5 (24.1) | 96.9 (22.1) | 0.629 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 57.2 (19.8) | 56.1 (15.6) | 0.814 |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | 1.2 (0.7) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.524 |
| Tested Associations | Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model 1 | Adjusted Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | p-Value | Beta | p-Value | Beta | p-Value | |
| z-BMI | ||||||
| FFM (kg) | 0.414 | <0.001 | 0.823 | <0.001 | 0.258 | 0.009 |
| FM (kg) | 0.709 | <0.001 | 0.845 | <0.001 | 0.461 | <0.001 |
| Plasma vitamin E (mg/L) | −0.286 | 0.001 | −0.293 | 0.001 | −0.161 | 0.004 |
| Eating breakfast regularly | −0.218 | 0.016 | −0.237 | 0.010 | −0.082 | 0.173 |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | ||||||
| FFM (kg) | 0.135 | 0.143 | 0.122 | 0.367 | 0.092 | 0.560 |
| FM (kg) | −0.258 | 0.005 | −0.425 | <0.001 | −0.602 | <0.001 |
| HGS (kg) | ||||||
| FFM (kg) | 0.869 | <0.001 | 0.658 | <0.001 | 0.627 | <0.001 |
| FM (kg) | 0.450 | <0.001 | 0.248 | <0.001 | 0.066 | 0.520 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 0.207 | 0.055 | 0.118 | 0.094 | 0.063 | 0.343 |
| TG/HDL-C | −0.224 | 0.037 | −0.103 | 0.142 | −0.075 | 0.247 |
| RMR (kcal/day) | ||||||
| FFM (kg) | 0.704 | <0.001 | 0.638 | <0.001 | 0.464 | <0.001 |
| FM (kg) | 0.504 | <0.001 | 0.335 | <0.001 | 0.028 | 0.812 |
| Eating breakfast regularly | 0.212 | 0.020 | 0.213 | 0.005 | 0.196 | 0.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gioxari, A.; Amerikanou, C.; Peraki, S.; Kaliora, A.C.; Skouroliakou, M. Eating Behavior and Factors of Metabolic Health in Primary Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study in Greek Children. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163592
Gioxari A, Amerikanou C, Peraki S, Kaliora AC, Skouroliakou M. Eating Behavior and Factors of Metabolic Health in Primary Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study in Greek Children. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163592
Chicago/Turabian StyleGioxari, Aristea, Charalampia Amerikanou, Sevasti Peraki, Andriana C. Kaliora, and Maria Skouroliakou. 2023. "Eating Behavior and Factors of Metabolic Health in Primary Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study in Greek Children" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163592
APA StyleGioxari, A., Amerikanou, C., Peraki, S., Kaliora, A. C., & Skouroliakou, M. (2023). Eating Behavior and Factors of Metabolic Health in Primary Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study in Greek Children. Nutrients, 15(16), 3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163592









