Protective Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Intestinal Barrier of Mice
Highlights
- L. plantarum Q7 and L. plantarum F3-2 could protect the intestinal chemical, physical, immunological, and biological barriers of healthy mice.
- L. plantarum Q7 and L. plantarum F3-2 showed strain specificity in their protective effects on the intestinal barrier of mice.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Cultivation and Bacterial Suspension Preparation
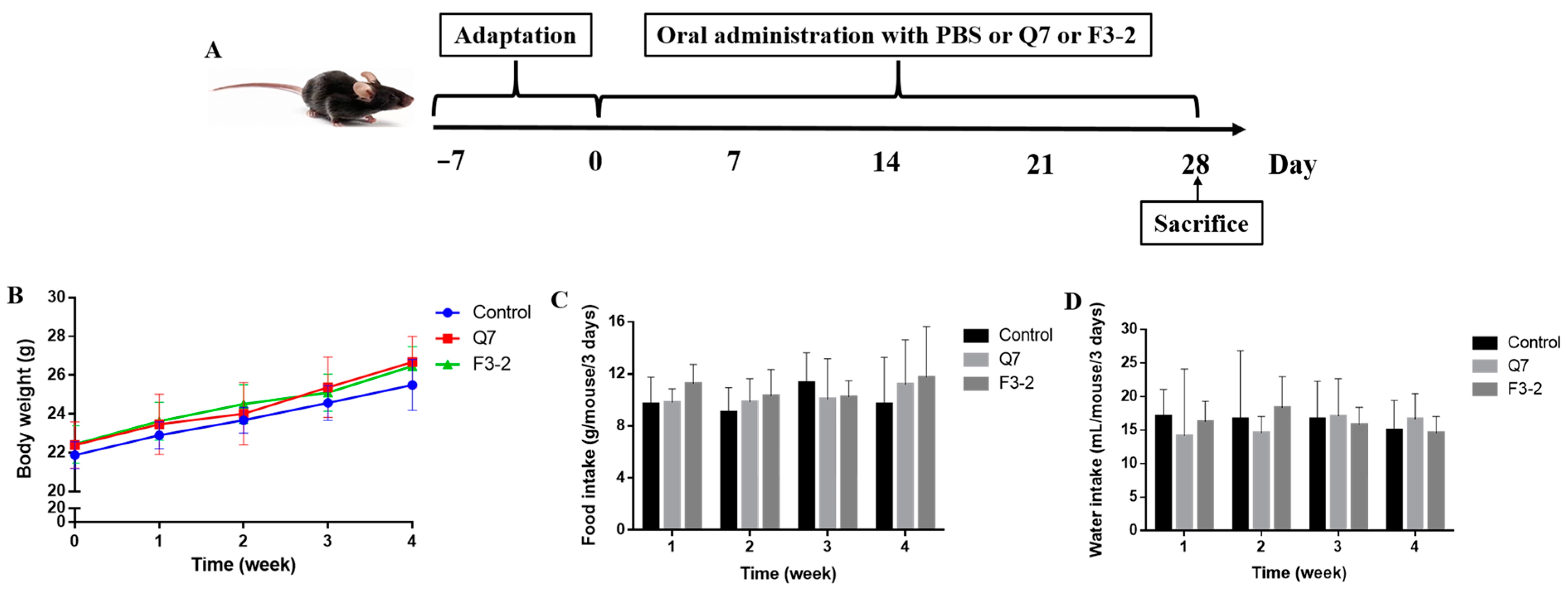
2.2. Animals and Treatments
2.3. Histomorphological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.6. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.7. SCFAs Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing L. plantarum on Physiological Indexes of Mice
3.2. Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing L. plantarum on Intestinal Chemical Barrier of Mice
3.3. Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing L. plantarum on Intestinal Physical Barrier of Mice
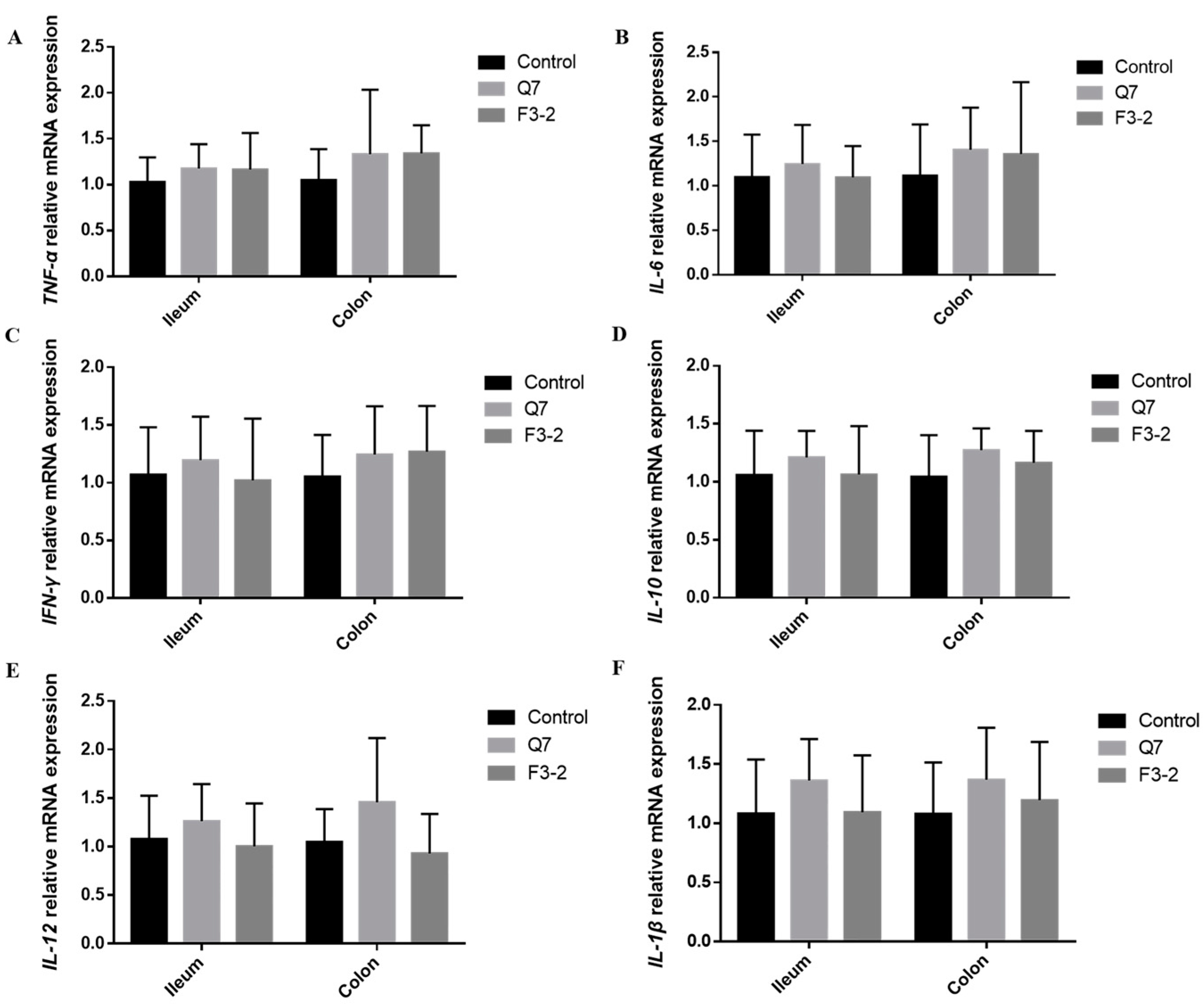
3.4. Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing L. plantarum on Intestinal Immunological Barrier of Mice
3.5. Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing L. plantarum on Intestinal Biological Barrier of Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, T.P.; Natra, B.H. Next-generation probiotics: A promising approach towards designing personalized medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damián, M.R.; Cortes-Perez, N.G.; Quintana, E.T.; Ortiz-Moreno, A.; Noguez, C.G.; Cruceño-Casarrubias, C.E.; Pardo, M.E.S.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Functional foods, nutraceuticals and probiotics: A focus on human health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vermeire, S. The intestinal barrier: A fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroent. 2017, 11, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Hao, C.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Jin, C. Aluminum induced intestinal dysfunction via mechanical, immune, chemical and biological barriers. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Wang, B. Role of gut barrier function in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 287348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, P.A.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Cani, P.D.; Mercenier, A.; MacDonald, T.T.; Garcia-Ródenas, C.L.; Wells, J.M. Can probiotics modulate human disease by impacting intestinal barrier function? Brit. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fata, G.L.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Probiotics and the gut immune system: Indirect regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ding, S.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus brevis alleviate intestinal inflammation and microbial disorder induced by ETEC in a murine model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6867962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemert, S.; Meijerink, M.; Molenaar, D.; Bron, P.A.; de Vos, P.; Kleerebezem, M.; Wells, J.M.; Marco, M.L. Identification of Lactobacillus plantarum genes modulating the cytokine response of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.Y.; Tian, X.Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, H.X.; Gong, P.M.; Lin, K.; Liu, T.J.; et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum relieved DSS-induced colitis in mice potentially by activating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics regulate gut microbiota: An effective method to improve immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ji, Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, H.; Kang, J.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, H.; Hyun, C.K.; Kim, K.T.; Holzapfel, W.H. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 regulates gut microbiota and adipose tissue accumulation in a diet-induced obesity murine model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Teng, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J. Bacteriocins: Potential for human health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5518825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Kang, S.S. In vitro antibiofilm and anti-inflammatory properties of bacteriocins produced by Pediococcus acidilactici against Enterococcus faecalis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommineni, S.; Bretl, D.J.; Lam, V.; Chakraborty, R.; Hayward, M.; Simpson, P.; Cao, Y.; Bousounis, P.; Kristich, C.J.; Salzman, N.H. Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Nature 2015, 526, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Kumar, S.; Verma, S.; Seshadri, S. Bacteriocin PJ4 from probiotic lactobacillus reduced adipokine and inflammasome in high fat diet induced obesity. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Hao, H.; Yi, H. Screening and probiotic potential evaluation of bacteriocin-producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; You, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, C.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. A fast and accurate way to determine short chain fatty acids in mouse feces based on GC-MS. J. Chromatogr. B. 2018, 1099, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.G.; Lai, Z.W.; Tan, J.S. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Purification strategies and applications in food and medical industries: A review. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabour, N.; Zihler, A.; Kheadr, E.; Lacroix, C.; Fliss, I. In vivo study on the effectiveness of pediocin PA-1 and Pediococcus acidilactici UL5 at inhibiting Listeria monocytogenes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Heeney, D.; Srisengfa, Y.; Golomb, B.; Griffey, S.; Marco, M. Bacteriocin biosynthesis contributes to the anti-inflammatory capacities of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Gentile, M.; Yeiser, J.R.; Walland, A.C.; Bornstein, V.U.; Chen, K.; He, B.; Cassis, L.; Bigas, A.; Cols, M.; et al. Mucus enhances gut homeostasis and oral tolerance by delivering immunoregulatory signals. Science 2013, 342, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeney, D.D.; Zhai, Z.; Bendiks, Z.; Barouei, J.; Martinic, A.; Slupsky, C.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriocin is associated with intestinal and systemic improvements in diet-induced obese mice and maintains epithelial barrier integrity in vitro. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, J.B.; Sharma, V.K.; Kumar, M.; Mukherjee, A. Antimicrobial peptides: Vestiges of past or modern therapeutics? Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.K.; Raffatellu, M. GI pros: Antimicrobial defense in the gastrointestinal tract. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 88, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małaczewska, J.; Kaczorek-Łukowska, E.; Wójcik, R.; Rękawek, W.; Siwicki, A.K. In vitro immunomodulatory effect of nisin on porcine leucocytes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Effects of the short-term administration of Pediococcus pentosaceus on physiological characteristics, inflammation, and intestinal microecology in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Tian, F.; Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Effect of bacteriocin-producing Pediococcus acidilactici strains on the immune system and intestinal flora of normal mice. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2022, 11, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Kerna, N.A.; Tulp, O.L. Managing the F: B ratio in DM; a review of the role of firmicutes and bacteroidetes in diabetes mellitus. Adv. Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 4, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, P.; Guo, X.; Mei, X. Compound Fu brick tea modifies the intestinal microbiome composition in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5508–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Jin, X.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus JCM 1132 strain and its mutant with different bacteriocin-producing behaviour have various in situ effects on the gut microbiota of healthy mice. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shin, Y.C.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.N.; O, E.; Kim, K.S.; Kweon, M.N. Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1892441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Huang, M.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, H.; Duan, R. Effects of short-term continuous and pulse cadmium exposure on gut histology and microbiota of adult male frogs (Pelophylax nigromaculatus) during pre-hibernation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneke, L.; Schlicht, K.; Andreani, N.A.; Hollstein, T.; Demetrowitsch, T.; Knappe, C.; Hartmann, K.; Jensen-Kroll, J.; Rohmann, N.; Pohlschneider, D.; et al. A dietary carbohydrate-gut Parasutterella-human fatty acid biosynthesis metabolic axis in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2057778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboulet-Bisson, E.; Sturme, M.H.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Donnell, M.M.; Neville, B.A.; Forde, B.M.; Claesson, M.J.; Harris, H.; Gardiner, G.E.; Casey, P.G.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus salivarius bacteriocin Abp118 on the mouse and pig intestinal microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, D.; Lok, S.; Clare, S.; Tomas, M.; Stares, M.; Scholl, D.; Donskey, C.J.; Lawley, T.D.; Govoni, G.R. A modified R-type bacteriocin specifically targeting Clostridium difficile prevents colonization of mice without affecting gut microbiota diversity. mBio 2015, 6, e02368-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Miller, R.A.; Ericsson, A.C.; Harrison, D.C.; Strong, R.; Schmidt, T.M. Changes in the gut microbiome and fermentation products concurrent with enhanced longevity in acarbose-treated mice. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Jian, S.; Guo, D.; Wen, C.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Kuang, T.; Wen, J.; Yin, Y.; Deng, B. Fecal microbiota and metabolomics revealed the effect of long-term consumption of gallic acid on canine lipid metabolism and gut health. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Genes | Forward Sequences (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F: GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG | R: ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC |
| Muc2 | F: TGCTGACGAGTGGTTGGTGAATG | R: TGATGAGGTGGCAGACAGGAGAC |
| ZO-1 | F: GCTGCCTCGAACCTCTACTC | R: TTGCTCATAACTTCGCGGGT |
| JAM-1 | F: AGTTCGTCCAAGGCAGCACAAC | R: AGAAGGTGACTCGGTCCGCATAG |
| Claudin-1 | F: GCTGGGTTTCATCCTGGCTTCTC | R: CCTGAGCGGTCACGATGTTGTC |
| RegIIIγ | F: GCTTCCTTCCTGTCCTCCATGATC | R: ATCACATCAGCATTGCTCCACTCC |
| TNF-α | F: GCGACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAG | R: GCCACAAGCAGGAATGAGAAGAGG |
| IL-6 | F: ACTTCCATCCAGTTGCCTTCTTGG | R: TTAAGCCTCCGACTTGTGAAGTGG |
| IFN-γ | F: CTGGAGGAACTGGCAAAAGGATGG | R: GACGCTTATGTTGTTGCTGATGGC |
| IL-10 | F: GAGGATCAGCAGGGGCCAGTAC | R: AAGGCAGTCCGCAGCTCTAGG |
| IL-12 | F: TCTTTGATGATGACCCTGTGCCTTG | R: GTGATTCTGAAGTGCTGCGTTGATG |
| IL-1β | F: TCGCAGCAGCACATCAACAAGAG | R: TGCTCATGTCCTCATCCTGGAAGG |
| Groups | Villus Height (μm) | Crypt Depth (μm) | Villus Height/Crypt Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 247.57 ± 19.51 b | 87.53 ± 14.44 a | 2.90 ± 0.53 b |
| Q7 | 344.82 ± 20.27 a | 84.41 ± 10.33 a | 4.14 ± 0.58 a |
| F3-2 | 337.36 ± 22.82 a | 85.01 ± 9.94 a | 4.02 ± 0.56 a |
| Groups | Acetic Acid (μg/g) | Propionic Acid (μg/g) | Butyric Acid (μg/g) | Total SCFAs (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 378.59 ± 83.50 | 242.93 ± 49.57 | 189.53 ± 39.31 | 811.04 ± 48.25 |
| Q7 | 531.15 ± 90.89 * | 320.38 ± 63.08 * | 200.78 ± 49.40 | 1052.31 ± 139.84 ** |
| F3-2 | 480.68 ± 121.61 | 257.81 ± 63.02 | 208.98 ± 35.16 | 947.46 ± 135.75 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, H. Protective Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Intestinal Barrier of Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163518
Bu Y, Liu Y, Liu Y, Cao J, Zhang Z, Yi H. Protective Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Intestinal Barrier of Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163518
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Yushan, Yisuo Liu, Yinxue Liu, Jiayuan Cao, Zhe Zhang, and Huaxi Yi. 2023. "Protective Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Intestinal Barrier of Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163518
APA StyleBu, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Cao, J., Zhang, Z., & Yi, H. (2023). Protective Effects of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Intestinal Barrier of Mice. Nutrients, 15(16), 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163518






