Impacts of High Fructose Diet and Chronic Exercise on Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Protocol
2.2. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Measurement of NOx and TBARS
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. NADPH Oxidase and XO Activities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
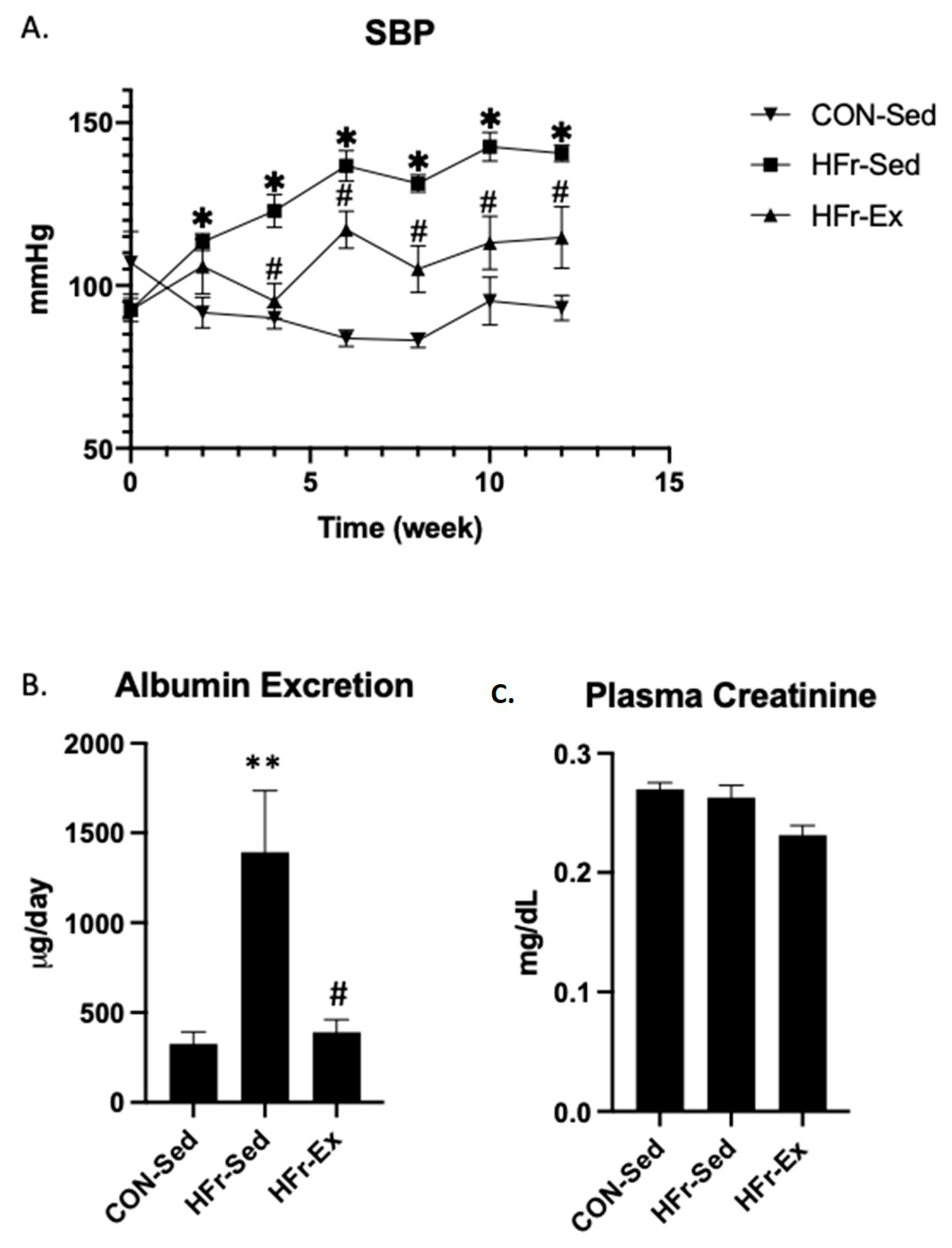
3.1. Impacts of HFr and Ex on SBP, Albuminuria, and Plasma Creatinine
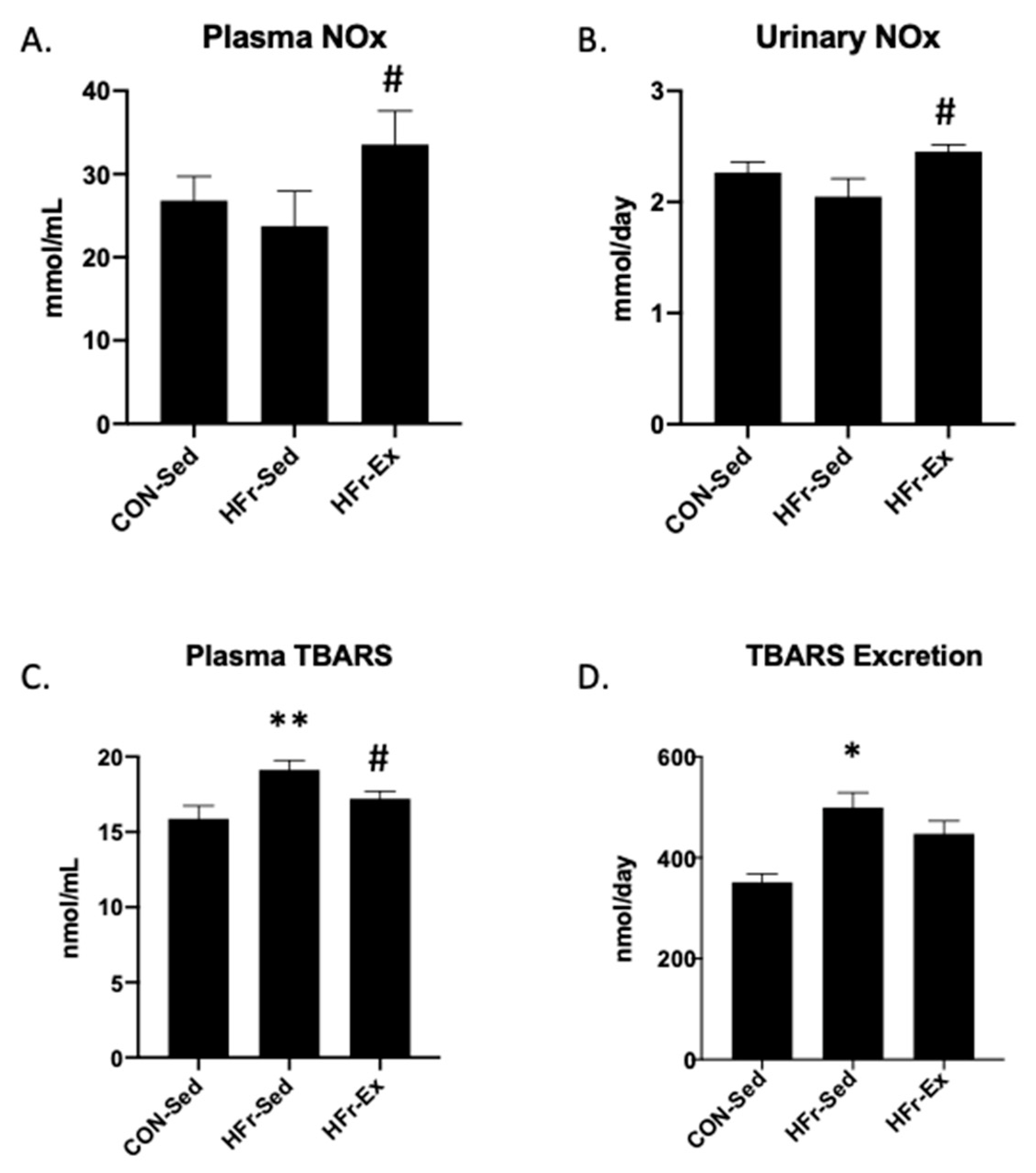
3.2. Impacts of HFr and Ex on NOx and TBARS in Plasma and Urine
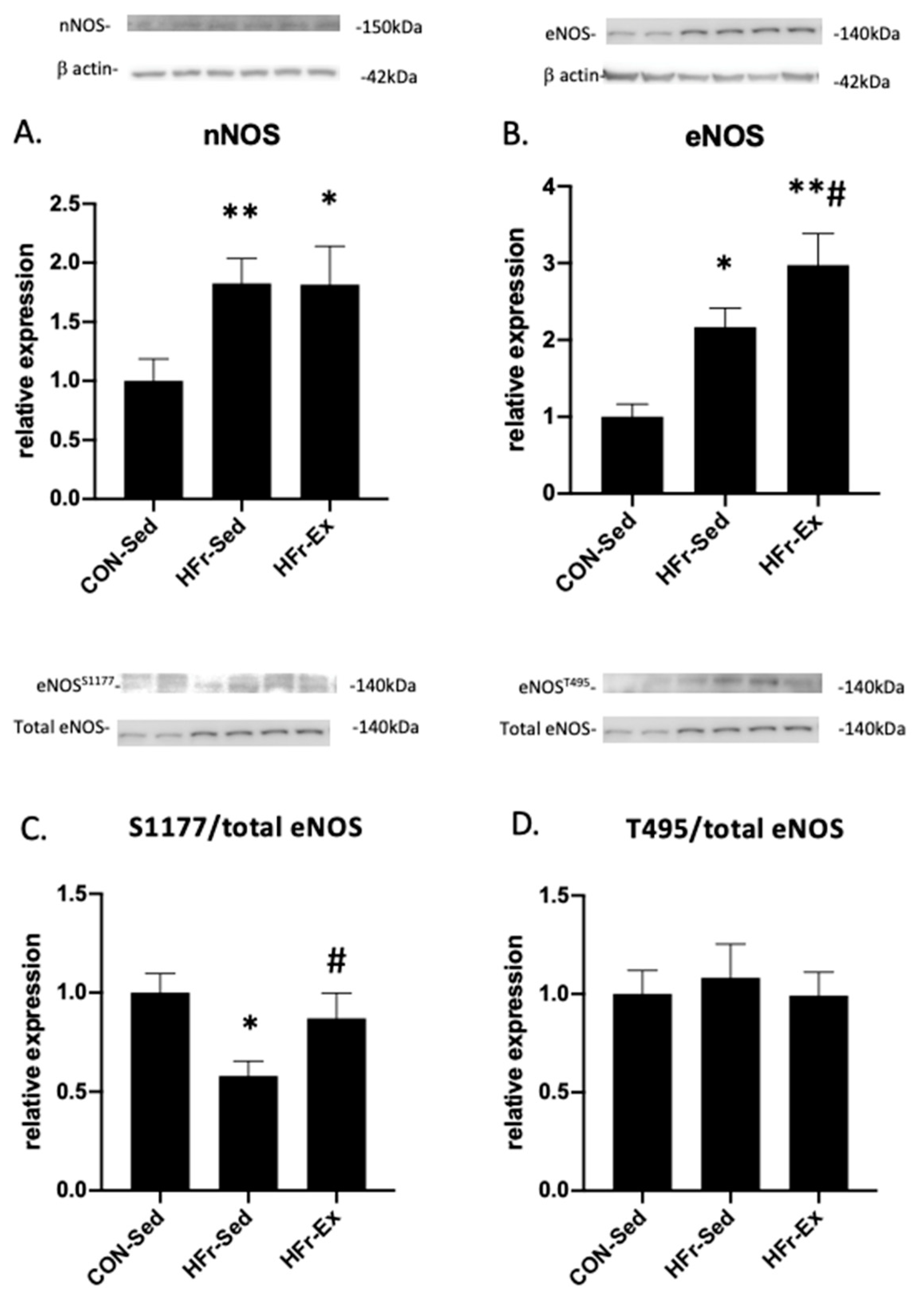
3.3. Impacts of HFr and Ex on NOS Expression and Phosphorylation
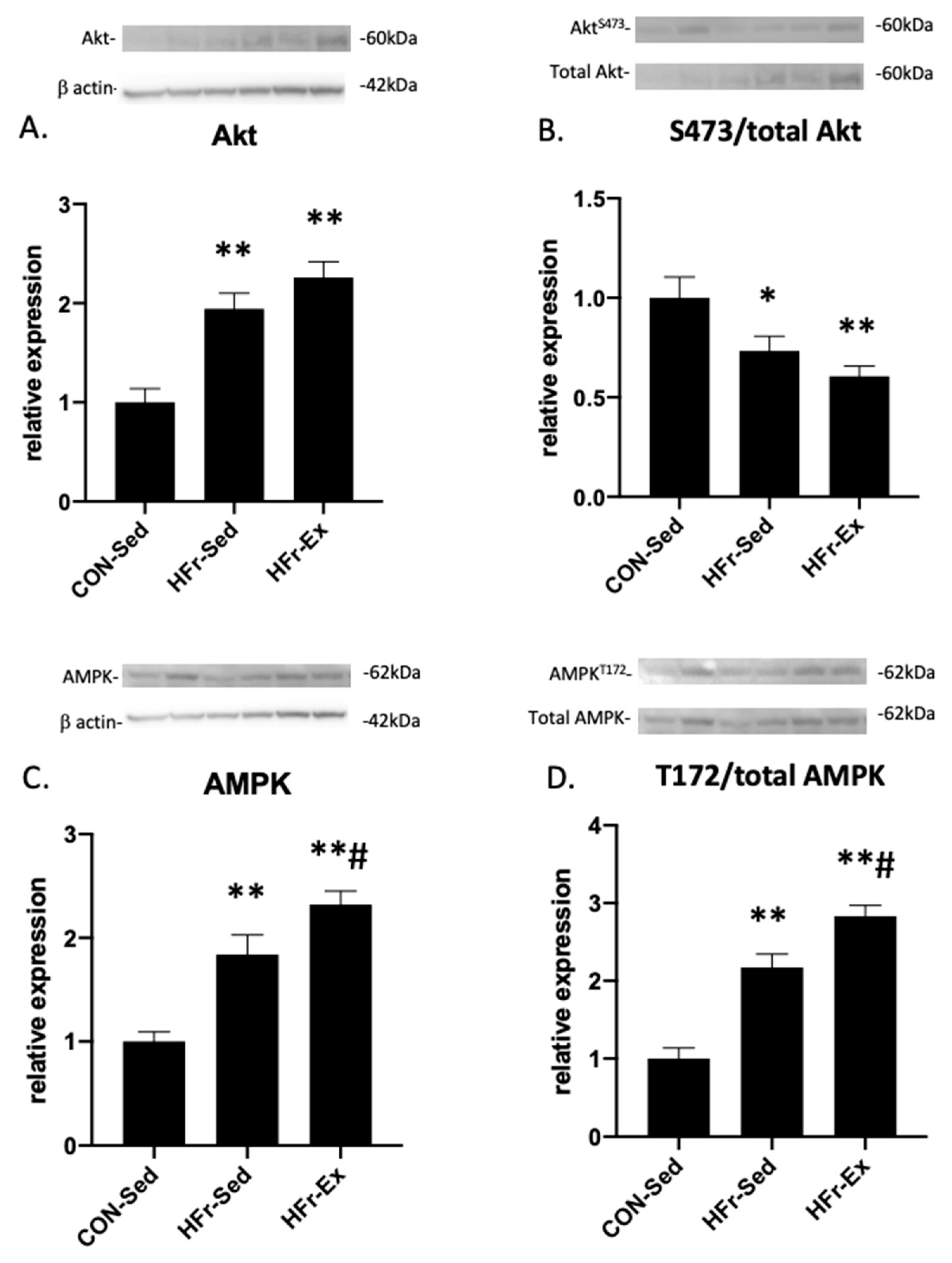
3.4. Impacts of HFr and Ex on Akt and AMPK Expression and Phosphorylation
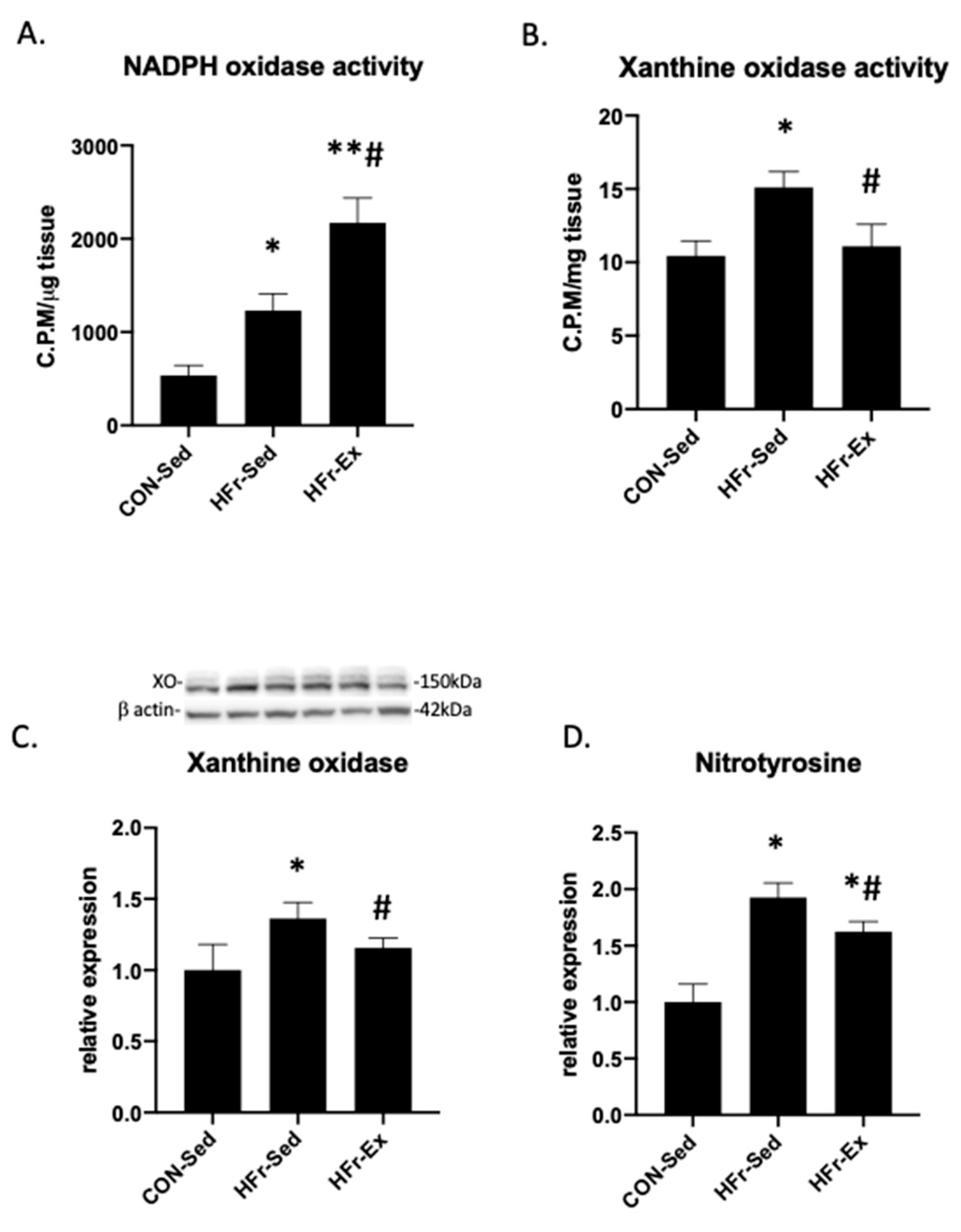
3.5. Impacts of HFr and Ex on NADPH Oxidase and XO Activity and Nitrotyrosin Levels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, T.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L. Controversies about sugars: Results from systematic reviews and meta-analyses on obesity, cardiometabolic disease and diabetes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Horst, K.W.; Serlie, M.J. Fructose consumption, lipogenesis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhope, K.L. Sugar consumption, metabolic disease and obesity: The state of the controversy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannou, S.A.; Haslam, D.E.; McKeown, N.M.; Herman, M.A. Fructose metabolism and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoham, D.A.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Kramer, H.; Luke, A.; Vupputuri, S.; Kshirsagar, A.; Cooper, R.S. Sugary soda consumption and albuminuria: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2004. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Muntner, P.; Hamm, L.L.; Jones, D.W.; Batuman, V.; Fonseca, V.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. The metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in U.S. adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Young, B.A.; Katz, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Carithers, T.C.; Norwood, A.F.; Correa, A. Patterns of Beverages Consumed and Risk of Incident Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, T.M.; Basso, O.; Darden, R.; Sandler, D.P. Carbonated beverages and chronic kidney disease. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brymora, A.; Flisinski, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Goszka, G.; Stefanska, A.; Manitius, J. Low-fructose diet lowers blood pressure and inflammation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Kohzuki, M.; Ito, O. Chronic exercise provides renal-protective effects with upregulation of fatty acid oxidation in the kidney of high fructose-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2020, 318, F826–F834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.V.; Kiat, H. The mechanisms underlying fructose-induced hypertension: A review. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Tomida, T.; Matsui, H.; Ito, T.; Okumura, K. Decrease in renal medullary endothelial nitric oxide synthase of fructose-fed, salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2002, 40, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ura, N.; Murakami, H.; Hagiwara, M.; Shimamoto, K. The role of renal natriuretic and depressor systems in insulin-resistant hypertensive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2004, 27, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, X.; Yang, S.; Edin, M.L.; Zeldin, D.C.; Wang, D.W. Increased endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression reduces hypertension and hyperinsulinemia in fructose-treated rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, P.D.; Lanzi, C.R.; Toblli, J.E.; Elesgaray, R.; Oteiza, P.I.; Fraga, C.G.; Galleano, M. Dietary (-)-epicatechin mitigates oxidative stress, NO metabolism alterations, and inflammation in renal cortex from fructose-fed rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 90, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudot, C.; Lajoix, A.D.; Jover, B.; Rugale, C. Dietary sodium restriction prevents kidney damage in high fructose-fed rats. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, B.S.; Patil, B.M. Apocynin improves endothelial function and prevents the development of hypertension in fructose fed rat. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2009, 41, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, P.; Gersch, M.S.; Mu, W.; Scherer, P.M.; Kim, K.M.; Gesualdo, L.; Henderson, G.N.; Johnson, R.J.; Sautin, Y.Y. Ketohexokinase-dependent metabolism of fructose induces proinflammatory mediators in proximal tubular cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Tapia, E.; Bautista-García, P.; Soto, V.; Avila-Casado, C.; Vega-Campos, I.P.; Nakagawa, T.; Zhao, L.; Franco, M.; Johnson, R.J. Effects of febuxostat on metabolic and renal alterations in rats with fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2008, 294, F710–F718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, S.; Nakanishi, K. Superoxide dismustase mimetic tempol decreases blood pressure by increasing renal medullary blood flow in hyperinsulinemic-hypertensive rats. Metabolism 2004, 53, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, O. Renal rehabilitation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Res. 2017, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M.; Ho, H.; Hoffman, B.B. Attenuation of fructose-induced hypertension in rats by exercise training. Hypertension 1988, 12, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Ito, O.; Cao, P.; Mori, N.; Suda, C.; Muroya, Y.; Takashima, K.; Ito, S.; Kohzuki, M. Effects of exercise training on nitric oxide synthase in the kidney of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 40, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Cao, P.; Kakihana, T.; Sato, E.; Suda, C.; Muroya, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hu, G.; Ishii, T.; Ito, O.; et al. Chronic Running Exercise Alleviates Early Progression of Nephropathy with Upregulation of Nitric Oxide Synthases and Suppression of Glycation in Zucker Diabetic Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Takahashi, J.; Sakuyama, A.; Xu, L.; Miura, T.; Muroya, Y.; Ito, D.; Kohzuki, M.; Ito, O. Exercise training delays renal disorders with decreasing oxidative stress and increasing production of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakoshi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Mori, N.; Suda, C.; Kohzuki, M.; Ito, O. Effects of exercise training on renal interstitial fibrosis and renin-angiotensin system in rats with chronic renal failure. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Ito, O.; Rong, R.; Sakuyama, A.; Miura, T.; Ito, D.; Ogawa, Y.; Kohzuki, M. Pitavastatin Upregulates Nitric Oxide Synthases in the Kidney of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Wistar-Kyoto Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namai-Takahashi, A.; Sakuyama, A.; Nakamura, T.; Miura, T.; Takahashi, J.; Kurosawa, R.; Kohzuki, M.; Ito, O. Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor, Febuxostat Ameliorates the High Salt Intake-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2019, 32, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordish, K.L.; Kassem, K.M.; Ortiz, P.A.; Beierwaltes, W.H. Moderate (20%) fructose-enriched diet stimulates salt-sensitive hypertension with increased salt retention and decreased renal nitric oxide. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushakova, O.; Kosugi, T.; Roncal, C.; Mu, W.; Heinig, M.; Cirillo, P.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T. Fructose induces the inflammatory molecule ICAM-1 in endothelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I. Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of eNOS. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 459, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litterio, M.C.; Vazquez Prieto, M.A.; Adamo, A.M.; Elesgaray, R.; Oteiza, P.I.; Galleano, M.; Fraga, C.G. (-)-Epicatechin reduces blood pressure increase in high-fructose-fed rats: Effects on the determinants of nitric oxide bioavailability. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, R.F.; Gaique, T.G.; Bento-Bernardes, T.; Motta, N.A.; Brito, F.C.; Fernandes-Santos, C.; Castro-Pinheiro, C.; Oliveira, K.J.; Nobrega, A.C. Aerobic training prevents oxidative profile and improves nitric oxide and vascular reactivity in rats with cardiometabolic alteration. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2016, 121, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisic, J.; Koricanac, G.; Culafic, T.; Romic, S.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Kostic, M.; Pantelic, M.; Tepavcevic, S. Low intensity exercise prevents disturbances in rat cardiac insulin signaling and endothelial nitric oxide synthase induced by high fructose diet. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 420, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, O.A.; Sumlu, E.; Koca, H.B.; Pektas, M.B.; Kocabas, A.; Sadi, G.; Akar, F. Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus Helveticus on Renal Insulin Signaling, Inflammatory Markers, and Glucose Transporters in High-Fructose-Fed Rats. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhao, X.J.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.S.; Zhang, D.M.; Kong, L.D. Pterostilbene alleviates fructose-induced renal fibrosis by suppressing TGF-beta1/TGF-beta type I receptor/Smads signaling in proximal tubular epithelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahba, N.S.; Ghareib, S.A.; Abdel-Ghany, R.H.; Abdel-Aal, M.; Alsemeh, A.E. Renoprotective effects of vitamin D3 supplementation in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Ito, O.; Ito, D.; Rong, R.; Zheng, Y.; Kohzuki, M. Combination of Exercise Training and SOD Mimetic Tempol Enhances Upregulation of Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Kidney of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, 2142740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Deminice, R.; Ozdemir, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Bomkamp, M.P.; Hyatt, H. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J. Sport Health. Sci. 2020, 9, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H. Hydrogen peroxide regulation of endothelial function: Origins, mechanisms, and consequences. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.R.; Chen, K.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Hydrogen peroxide activates endothelial nitric-oxide synthase through coordinated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6017–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Ito, O.; Guo, Q.; Ito, D.; Muroya, Y.; Rong, R.; Mori, T.; Ito, S.; Kohzuki, M. Endogenous hydrogen peroxide up-regulates the expression of nitric oxide synthase in the kidney of SHR. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Xu, L.; Ito, O. Impacts of High Fructose Diet and Chronic Exercise on Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102322
Hu G, Xu L, Ito O. Impacts of High Fructose Diet and Chronic Exercise on Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney. Nutrients. 2023; 15(10):2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102322
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Gaizun, Lusi Xu, and Osamu Ito. 2023. "Impacts of High Fructose Diet and Chronic Exercise on Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney" Nutrients 15, no. 10: 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102322
APA StyleHu, G., Xu, L., & Ito, O. (2023). Impacts of High Fructose Diet and Chronic Exercise on Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney. Nutrients, 15(10), 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102322





