Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
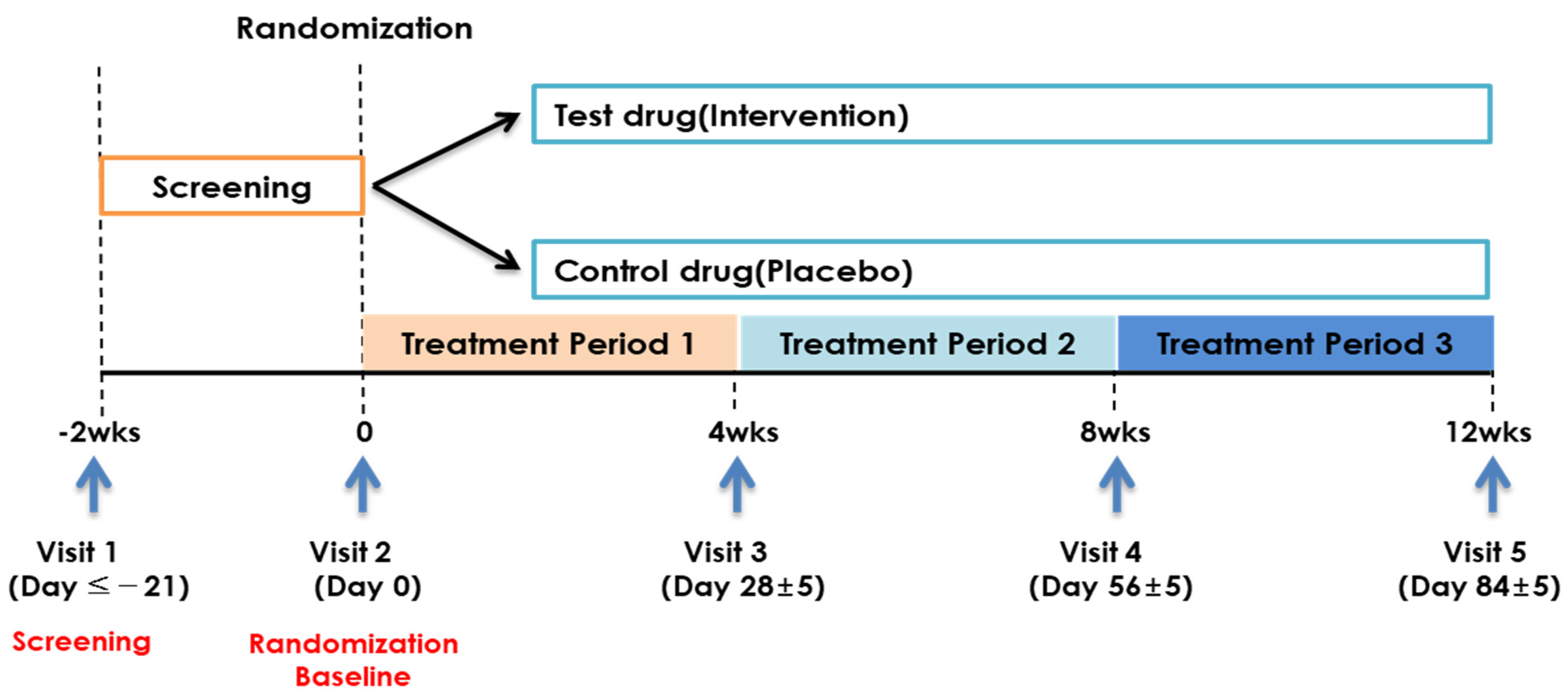
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Endpoints
2.5. Safety
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Study Endpoints
3.3. Safety
3.4. Physical Activity and Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, K.D.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M.; Klein, S.; Loos, R.J.F.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M.; Ryan, D.H.; et al. The energy balance model of obesity: Beyond calories in, calories out. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, R.J.; Astrup, A.; Cantley, L.C.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Johnson, J.D.; King, J.C.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. Competing paradigms of obesity pathogenesis: Energy balance versus carbohydrate-insulin models. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.J.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.T.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J.H. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Xu, J.Y.; Pan, X.W.; Song, X.X.; Shan, L.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Shan, P.F. Global burden of noncommunicable disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017. Endocrine 2020, 69, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukua, J.; Pekkarinen, T.; Sane, T.; Muttajoki, P. Health-related quality of life in obese outpatients losing weight with very low energy diet and behaviour modification–a 2-y follow up study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scherer, P.E.; Hill, J.A. Obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: A compendium. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1703–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; Di Domenico, M.; Donniacuo, M.; Bitti, G.; Gritti, G.; Ambrosio, P.; Quagliuolo, L.; Rinaldi, B. AT1-receptor blockade: Protective effects of irbesartan in cardiomyocytes under hypoxic stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, K.; Rokholm, B.; Kaprio, J.; Sorensen, T.I. The genetic and environmental influences on childhood obesity: A systematic review of twin and adoption studies. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.M.; Ebrahim, K.; Hashemi, M.; Shoshtari-Yeganeh, B.; Rafiei, N.; Mansourian, M.; Kelishadi, R. Association of exposure to bisphenol A with obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, E.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Gut microbiota interactions with obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: Did gut microbiote co-evolve with insulin resistance? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Obesity, diabetes, and gut microbiota: The hygiene hypothesis expanded? Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkes, M.C.; Weenen, T.C.; Brummer, R.J.; Claassen, E. The development of probiotic treatment in obesity: A review. Benef. Microbes 2013, 5, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Minami, J.; Yanagisawa, N.; Odamaki, T.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Nakajima, S.; Hamamoto, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Shimoda, T. Oral administration of Bifidobacterium breve B-3 modifies metabolic functions in adults with obese tendencies in a randomised controlled trial. J. Nutr. Sci. 2015, 4, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Satoh, T.; Odamaki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Sugahara, H.; Yaeshima, T.; Iwatsuki, K.; Kamei, A.; Abe, K. Antiobesity effects of Bifidobacterium breve strain B-3 supplementation in a mouse model with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M.; West, J.; Bell, J.D.; Harvey, N.C. Advanced body composition assessment: From body mass index to body composition profiling. J. Investig. Med. 2018, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, J.H. Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) Short Form. J. Korean. Acad. Fam. Med. 2007, 28, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.G.; Jung, J.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kwon, J.S.; Yu, S.P.; Baik, T.G. Effect of a herbal extract powder (YY 312) from Imperata cylindrical Beauvois, Citrus unshiu Markovich, and Evodia officinalis Dode on body fat mass in overweight adults: A 12 week, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group clinical trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgeraas, H.; Johnson, L.K.; Skattebu, J.; Hertel, J.K.; Hjelmesaeth, J. Effects of probiotics on body weight, body mass index, fat mass and fat percentage in subjects with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, J.; Iwabuchi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Sakane, N. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve B-3 on body fat reductions in pre-obese adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2018, 37, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Kamei, A.; Xiao, J.Z.; Iwatsuki, K.; Abe, K. Bifidobacterium breve B-3 exerts metabolic syndrome-suppressing effects in the liver of diet-induced obese mice: A DNA microarray analysis. Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadooka, Y.; Sato, M.; Imaizumi, K.; Ogawa, A.; Ikuyama, K.; Akai, Y.; Okano, M.; Kagoshima, M.; Tsuchida, T. Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Anzawa, D.; Takami, K.; Ishizuka, A.; Mawatari, T.; Kamikado, K.; Sugimura, H.; Nishijima, T. Effect of Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis GCL2505 on visceral fat accumulation in healthy Japanese adults: A randomized controlled trial. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2016, 35, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; van de Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, P.L.; Drucker, D.J. Minireview: Glucagon-Like Peptides Regulate Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in the Pancreas, Gut, and Central Nervous System. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Shimizugawa, T.; Ono, M.; Furukawa, H.J. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is a potent hyperlipidemia-inducing factor in mice and inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1770–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Imai, Y.; Shimozawa, N.; Hioki, K.; Uchida, S.; Ito, Y.; Takakuwa, K.; Matsui, J.; et al. Globular Adiponectin Protected ob/ob Mice from Diabetes and ApoE-deficient Mice from Atherosclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, D.; Hewling, S.; Kalman, D. Body Composition Changes in Weight Loss: Strategies and Supplementation for Maintaining Lean Body Mass, a Brief Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K. Long-term Weight Loss Maintenance. Korean J. Obes. 2015, 24, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Inclusion Criteria |
| (1) Age 19–60 years |
| (2) Body mass index (BMI) of ≥25 kg/m2 and <30 kg/m2 |
| (3) Able to provide written informed consent |
| Exclusion Criteria |
| (1) Severe cerebrovascular disease (cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage), heart disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and arrhythmia requiring treatment), or malignant tumor within the last six months. However, participants with a medical history of cerebrovascular disease or heart disease who were clinically stable could participate in the trial at the investigator’s discretion |
| (2) Taking drugs that affected body weight (fat absorption inhibitors and appetite suppressants, health food/supplements related to obesity, psychiatric drugs such as depression, beta-blockers, diuretics, contraceptives, steroids, and female hormones) within the last month |
| (3) Obese or overweight due to endocrine diseases such as hypothyroidism and Cushing’s syndrome |
| (4) Maintenance treatment for gastrointestinal disorders (gastric ulcer, chronic digestive disorder, and irritable bowel syndrome) |
| (5) Psychologically significant medical history or current disease (schizophrenia, epilepsy, anorexia, and bulimia) or a history of alcohol and other drug abuse |
| (6) Judgment of inability to exercise due to musculoskeletal disorders |
| (7) Fasting blood sugar of ≥126 mg/dL, random blood sugar of ≥200 mg/dL, or patients with diabetes taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin |
| (8) Uncontrolled hypertension (blood pressure >160/100 mmHg measured after a 10-min rest) |
| (9) Alanine aminotransferase(AST) or Alkaline phosphatase(ALT) level at least 2.5 times higher than the laboratory’s upper limit of normal |
| (10) Creatinine levels more than twice the upper limit of normal in the testing institute |
| (11) Weight loss ≥5% within the last three months |
| (12) Participation in a commercial obesity program within the last three months |
| (13) Participation in an obesity clinical trial within the last six months |
| (14) Pregnancy, lactation, or was planning to become pregnant during the study period |
| (15) An allergic reaction to the food study drug |
| (16) Others were considered unsuitable for the study at the discretion of the principal investigator |
| (17) The intake of probiotics within the last month |
| BB-3 Group (n = 42) | Placebo Group (n = 41) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 15 (35.71) | 11 (26.83) | 0.3829 1 |
| Female | 27 (64.29) | 30 (73.17) | ||
| Age, years | 46.55 ± 9.76 | 45.02 ± 9.23 | 0.3361 2 | |
| Height, cm | 164.17 ± 9.15 | 162.22 ± 8.87 | 0.3343 2 | |
| Weight, kg | 72.71 ± 8.22 | 70.82 ± 8.17 | 0.2948 3 | |
| Body mass index | 26.93 ± 1.29 | 26.85 ± 1.38 | 0.7325 2 | |
| Waist circumference, cm | 88.39 ± 4.58 | 87.62 ± 5.55 | 0.4928 3 | |
| Hip circumference, cm | 99.04 ± 3.66 | 98.60 ± 3.89 | 0.6003 3 | |
| Fat mass index, g | 25,446.90 ± 4405.20 | 26,163.00 ± 3809.42 | 0.4311 3 | |
| Fat-free mass index, g | 47,094.50 ± 8707.45 | 44,334.07 ± 8532.53 | 0.0965 2 | |
| Family history of obesity | Yes No | 16 (38.10) 26 (61.90) | 16 (39.02) 25 (60.98) | 0.9307 1 |
| BB-3 Group (n = 42) | Placebo Group (n = 41) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Body fat mass, g | V2 | 25,446.90 ± 4405.20 | 26,163.00 ± 3809.42 |
| V5 | 24,859.86 ± 4382.83 | 26,098.63 ± 4022.56 | |
| V5-V2 | −587.05 ± 1004.42 | −64.37 ± 933.76 | |
| p-value | 0.0005 1 | 0.6613 1 | |
| Difference V5-V2 (Tx-Px) | −522.68 ± 970.17 | ||
| LS mean difference 5 | −528.56 | ||
| p-value | 0.0170 3 | ||
| Body fat percentage (%) | V2 | 36.60 ± 6.67 | 38.73 ± 6.14 |
| V5 | 36.28 ± 6.77 | 38.64 ± 6.25 | |
| V5-V2 | −0.32 ± 1.26 | −0.09 ± 0.97 | |
| p-value | 0.1097 1 | 0.5431 1 | |
| Difference V5-V2 (Tx-Px) | −0.22 ± 1.12 | ||
| LS mean difference 5 | −0.23 | ||
| p-value | 0.3760 3 | ||
| Fat-free mass, g | V2 | 47,094.50 ± 8707.45 | 44,334.07 ± 8532.53 |
| V5 | 46,622.79 ± 8539.42 | 44,362.80 ± 8454.12 | |
| V5-V2 | −471.71 ± 1500.65 | 28.73 ± 840.49 | |
| p-value | 0.0916 2 | 0.8279 1 | |
| Difference V5-V2 (Tx-Px) | −500.45 ± 1220.14 | ||
| p-value | 0.1172 4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, H.K.; Youn, S.J.; Choi, Y.; Eun, S.W.; Shin, S.M. Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010028
Sung HK, Youn SJ, Choi Y, Eun SW, Shin SM. Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Hyun Kyung, Sang Jun Youn, Yong Choi, Sang Won Eun, and Seon Mi Shin. 2023. "Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010028
APA StyleSung, H. K., Youn, S. J., Choi, Y., Eun, S. W., & Shin, S. M. (2023). Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 15(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010028






