Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Ethanol Extracts from Red Rice Bran Samples and Determination of Bioactive Compound Constituents
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Measurement of Serum and Hepatic Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Evaluation of Hepatic Histopathological Changes
2.5. Measurement of Hepatic Nitric Oxide (NO), ROS, and Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels
2.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioactive Constituents of RRBE
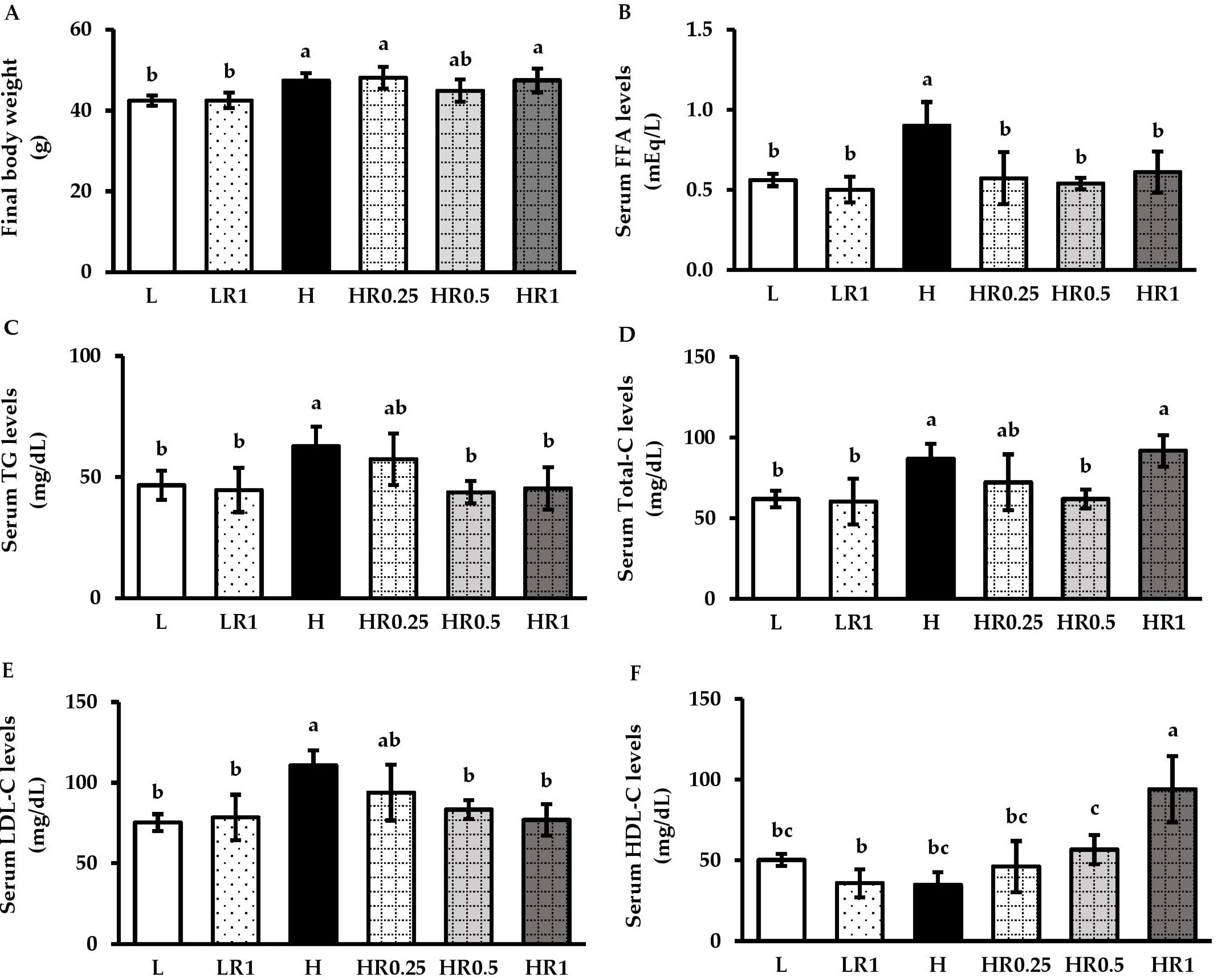
3.2. RRBE Mitigated Dyslipidemia in HFD-Fed Obese Mice
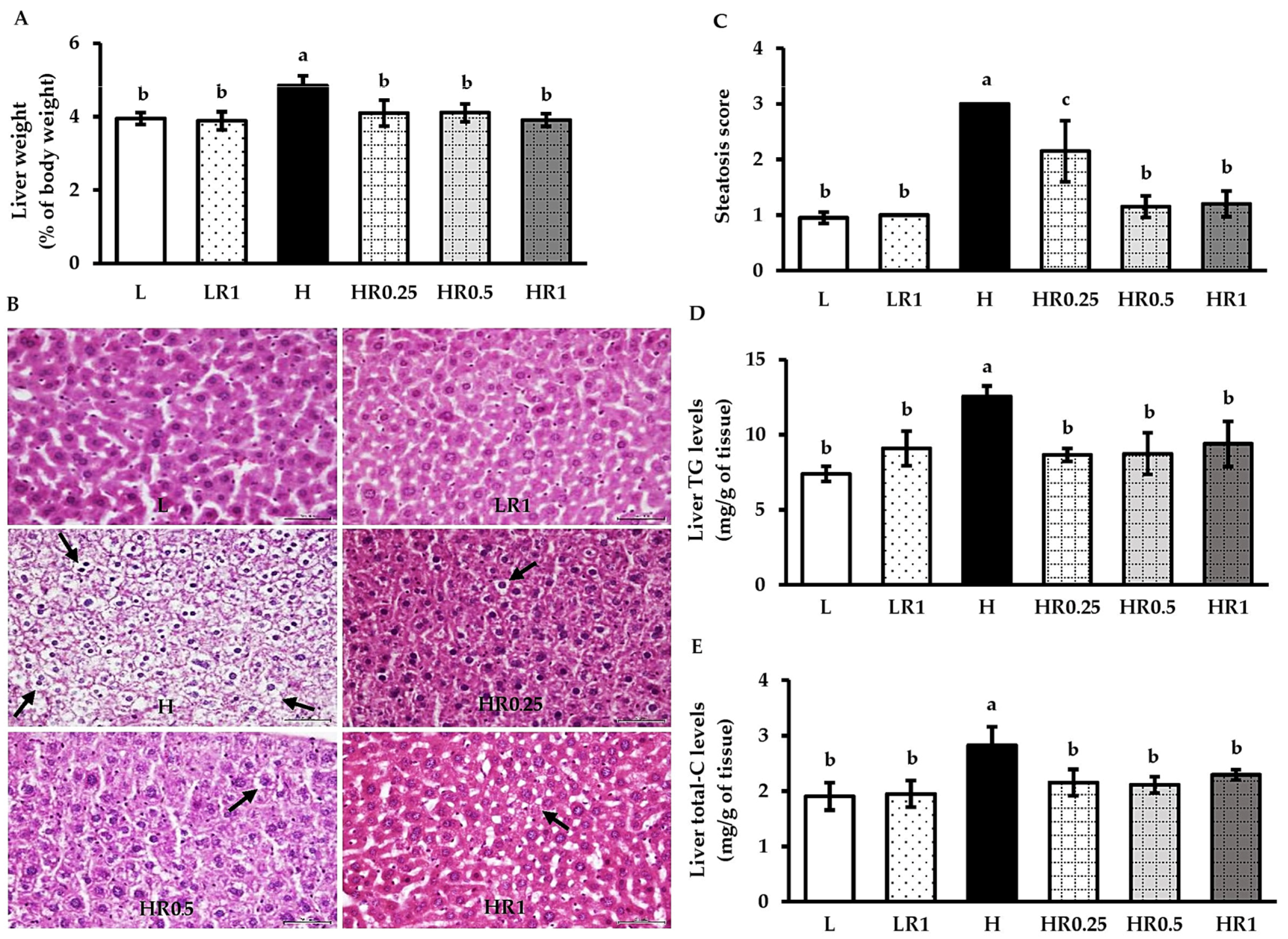
3.3. RRBE Alleviated HFD-Induced Hepatosteatosis
3.4. RRBE Regulated the Expression of Genes That Encode Key Regulators of Lipid Metabolism
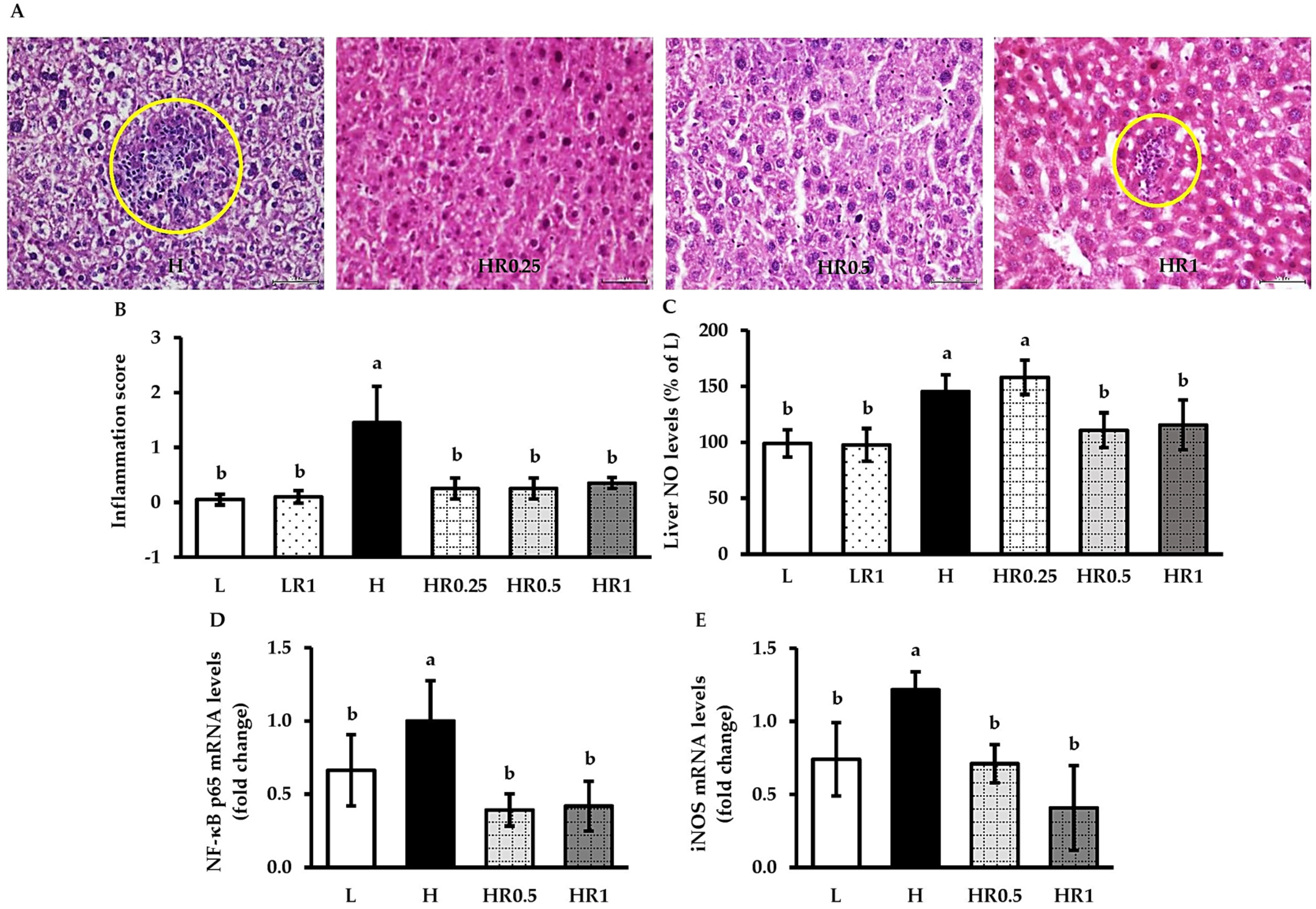
3.5. RRBE Relieved HFD-Induced Hepatic Inflammation
3.6. RRBE Suppressed HFD-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress
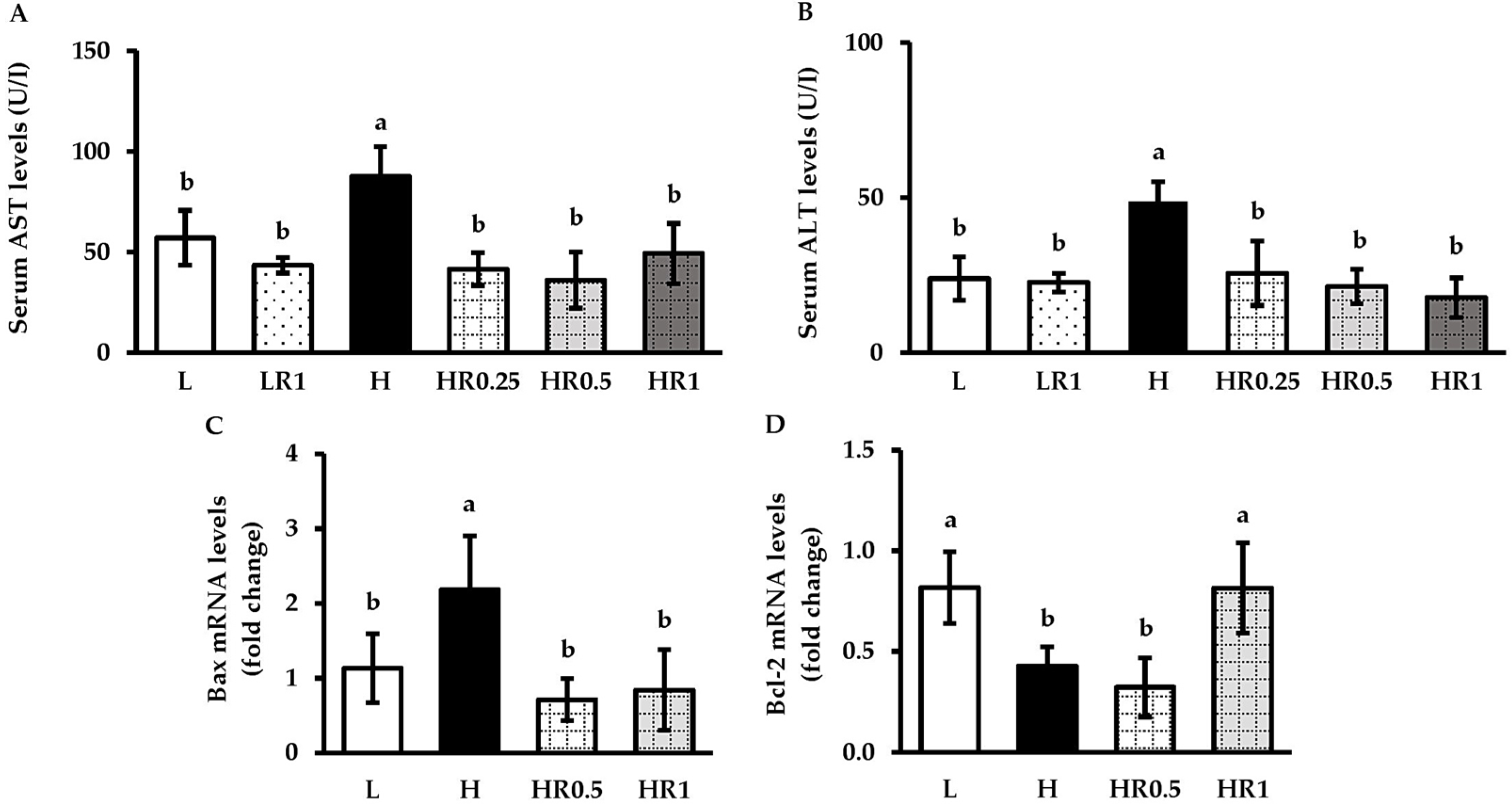
3.7. RRBE Reduced HFD-Induced Hepatic Injury and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piché, M.E.; Poirier, P.; Lemieux, I.; Després, J.P. Overview of Epidemiology and Contribution of Obesity and Body Fat Distribution to Cardiovascular Disease: An update. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The Prevalence and Incidence of NAFLD Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, T.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Sun, D.; Hou, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Yu, X.; Yang, C.; et al. Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies Related to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Basic Pathogenetic Mechanisms in the Progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 2019, 103, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, P.; González-Rodríguez, Á.; García-Monzón, C.; Valverde, Á.M. Understanding Lipotoxicity in NAFLD Pathogenesis: Is CD36 a Key Driver? Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deprince, A.; Haas, J.T.; Staels, B. Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism Links NAFLD to Cardiovascular Disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hliwa, A.; Ramos-Molina, B.; Laski, D.; Mika, A.; Sledzinski, T. The Role of Fatty Acids in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, J.T.; Marsche, G. Obesity-Related Changes in High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, F.M.; Sommano, S.R.; Riar, C.S.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Chaiyaso, T.; Prom-u-Thai, C. Status of Bioactive Compounds from Bran of Pigmented Traditional Rice Varieties and Their Scope in Production of Medicinal Food with Nutraceutical Importance. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkong, N.; Lonan, P.; Mueangchang, W.; Yadyookai, N.; Kanjoo, V.; Yoysungnoen, B. Red Rice Bran Extract Attenuates Adipogenesis and Inflammation on White Adipose Tissues in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsa-Ard, A.; Thongboontho, R.; Munkong, N.; Phromnoi, K.; Ontawong, A.; Pengnet, S.; Thim-Uam, A. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Red Rice Bran Extract Ameliorate Type I Interferon Production via STING Pathway. Foods 2022, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surarit, W.; Jansom, C.; Lerdvuthisopon, N.; Kongkham, S.; Hansakul, P. Evaluation of antioxidant activities and phenolic subtype contents of ethanolic bran extracts of Thai pigmented rice varieties through chemical and cellular assays. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Fang, W.; Chen, X.; Ling, W. Coenzyme Q10 Attenuates High-fat diet-induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Activation of the AMPK Pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkong, N.; Thim-Uam, A.; Pengnet, S.; Hansakul, P.; Somparn, N.; Naowaboot, J.; Tocharus, J.; Tocharus, C. Effects of Red Rice Bran Extract on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Huang, C.; Oua, S.; Zhang, H. Effects of Sorghum, Purple Rice and Rhubarb Rice on Lipids Status and Antioxidant Capacity in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkong, N.; Hansakul, P.; Yoysungnoen, B.; Wongnoppavich, A.; Sireeratawong, S.; Kaendee, N.; Lerdvuthisopon, N. Vasoprotective Effects of Rice Bran Water Extract on Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butsat, S.; Siriamornpun, S. Antioxidant Capacities and Phenolic Compounds of the Husk, Bran and Endosperm of Thai Rice. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettawan, A.; Kunthida, C.; Takahashi, T.; Kishi, T.; Chikazawa, J.; Sakata, Y.; Yano, E.; Watabe, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Okamoto, T. The Quality Control Assessment of Commercially Available Coenzyme Q(10)-Containing Dietary and Health Supplements in Japan. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 41, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Naowaboot, J.; Nanna, U.; Chularojmontri, L.; Songtavisin, T.; Tingpej, P.; Sattaponpan, C.; Jansom, C.; Wattanapitayakul, S. Mentha Cordifolia Leaf Extract Improves Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Obese Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 26, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naowaboot, J.; Wannasiri, S.; Pannangpetch, P. Morin Attenuates Hepatic Insulin Resistance in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, N.D.; Thalén, P.G.; Jacinto, S.M.; Ljung, B. Thiazolidinediones Increase Plasma-Adipose Tissue FFA Exchange Capacity and enhance insulin-mediated Control of Systemic FFA Availability. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Hada, N.; Sakamaki, Y.; Uno, A.; Shiga, T.; Tanaka, C.; Ito, T.; Katsume, A.; Sudoh, M. An Improved Mouse Model that Rapidly Develops Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 94, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janyou, A.; Wicha, P.; Jittiwat, J.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C.; Tocharus, J. Dihydrocapsaicin Attenuates Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Damage in Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion via Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardestani, A.; Yazdanparast, R.; Jamshidi, S.H. Therapeutic Effects of Teucrium Polium Extract on Oxidative Stress in Pancreas of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ng, J.P.; Tan, Y.; McGrath, K.; Bishop, D.P.; Oliver, B.; Chan, Y.L.; Cortie, M.B.; Milthorpe, B.K.; Valenzuela, S.M. Gold Nanoparticles Improve Metabolic Profile of Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Zhou, F.; Chen, H.; Jian, L.; Yang, Y.; Xia, F.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, B.; Li, S. Ficus hirta Vahl. Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3474723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Yuan, R.S.; Zhuang, W.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.G. Schisandra Polysaccharide Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Downregulating Expression of SREBPs in NAFLD Mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Gu, A.X.; Huang, B.Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.P.; Shan, A.S. Dietary Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Alleviates the Liver Injury Induced by Long-Term High-Fat Diets in Sprague Dawley Rats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 959906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattace Raso, G.; Simeoli, R.; Russo, R.; Iacono, A.; Santoro, A.; Paciello, O.; Ferrante, M.C.; Canani, R.B.; Calignano, A.; Meli, R. Effects of Sodium Butyrate and Its Synthetic Amide Derivative on Liver Inflammation and Glucose Tolerance in an Animal Model of Steatosis Induced by High Fat Diet. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Zhan, G.; Li, G.; Du, W.; Tan, H. MicroRNA-26a-Interleukin (IL)-6-IL-17 Axis Regulates the Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Murine Model. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 187, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, Q.; Tong, X.; Liu, L.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Deng, Y.; Jia, X.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M. Rice Bran Phenolic Extract Supplementation Ameliorates Impaired Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Fed Mice through AMPK Activation in Liver. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, R.; Huang, F.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Jia, X.; Chi, J.; Ma, Y.; Deng, M.; Chen, Y.; et al. Hydrolyzed Bound Phenolics from Rice Bran Alleviate Hyperlipidemia and Improve Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in High-Fat-Diet Fed Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Mong, M.C.; Yin, M.C. Effects of Protocatechuic Acid on Trans Fat Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10247–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Q.; Yang, T.; Liang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Shen, J.; Fu, X.; Tang, Y.; Luo, F. Oryzanol Modifies High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity, Liver Gene Expression Profile, and Inflammation Response in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8374–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Xiang, D.; Lei, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D. Vitamin E Ameliorates Lipid Metabolism in Mice with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Nrf2/CES1 Signaling Pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 3182–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.; Tang, H.; Song, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Effects of Protocatechuic Acid on Ameliorating Lipid Profiles and Cardio-Protection Against Coronary Artery Disease in High Fat and Fructose Diet Fed in Rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presa, N.; Clugston, R.D.; Lingrell, S.; Kelly, S.E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Jana, S.; Kassiri, Z.; Gómez-Muñoz, A.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L.; et al. Vitamin E Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase Deficient Mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, M.I.M.; Sayed, R.H.; El-Yamany, M.F.; El-Naggar, R.A.; Eliwa, H. Rosuvastatin and Co-Enzyme Q10 Improve High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats via Ameliorating Inflammatory and Oxidative Burden. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Tian, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, M.; Mei, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S. Metabolic Changes of Hepatocytes in NAFLD. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 710420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ho, C.T.; Long, P.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X. Preventive Efficiency of Green Tea and Its Components on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5306–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luci, C.; Bourinet, M.; Leclère, P.S.; Anty, R.; Gual, P. Chronic Inflammation in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 597648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiseler, M.; Schwabe, R.; Hampe, J.; Kubes, P.; Heikenwälder, M.; Tacke, F. Immune Mechanisms Linking Metabolic Injury to Inflammation and Fibrosis in Fatty Liver Disease–Novel Insights into Cellular Communication Circuits. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1136–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbia, D.; Cannella, L.; De Martin, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in NAFLD–NASH–HCC Transition—Focus on NADPH Oxidases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthorn, W.; Chatuphonprasert, W.; Chulasiri, M.; Jarukamjorn, K. Thai Red Rice Extract Provides Liver Protection in Paracetamol-Treated Mice by Restoring the Glutathione System. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jia, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M. Rice Bran Phenolic Extract Protects Against Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice by Alleviating Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis, Barrier Dysfunction, and Liver Inflammation Mediated by the Endotoxin-TLR4-NF-κB Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wu, C.; He, Y.; Guo, M.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Dong, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; et al. Rice Bran Phenolic Extract Confers Protective Effects against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice by Alleviating Mitochondrial Dysfunction via the PGC-1α-TFAM Pathway Mediated by microRNA-494-3p. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12284–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bioactive Constituents | Content |
|---|---|
| Protocatechuic acid (μg/g) | 277.94 ± 7.69 |
| γ-oryzanol (μg/g) | 481.81 ± 18.80 |
| Vitamin E (μg α-tocopherol/g) | 3.18 ± 0.01 |
| Coenzyme Q10 (μg/g) | 9.81 ± 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munkong, N.; Somnuk, S.; Jantarach, N.; Ruxsanawet, K.; Nuntaboon, P.; Kanjoo, V.; Yoysungnoen, B. Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010246
Munkong N, Somnuk S, Jantarach N, Ruxsanawet K, Nuntaboon P, Kanjoo V, Yoysungnoen B. Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010246
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunkong, Narongsuk, Surasawadee Somnuk, Nattanida Jantarach, Kingkarnonk Ruxsanawet, Piyawan Nuntaboon, Vaiphot Kanjoo, and Bhornprom Yoysungnoen. 2023. "Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010246
APA StyleMunkong, N., Somnuk, S., Jantarach, N., Ruxsanawet, K., Nuntaboon, P., Kanjoo, V., & Yoysungnoen, B. (2023). Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice. Nutrients, 15(1), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010246







