Abstract
Understanding the triggers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer, one of the most common cancers worldwide, can provide helpful information for the development of therapeutics. RNA sequencing technology can be utilized to identify complex disease targets and therapeutic applications. In the present study, we aimed to establish the pharmacological target of Kynurenic acid (KYNA) for gastric cancer AGS cells and to identify the biological network. RNA sequencing identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between KYNA-treated and untreated cells. A total of 278 genes were differentially expressed, of which 120 genes were up-regulated, and 158 genes were down-regulated. Gene ontology results confirmed that KYNA had effects such as a reduction in genes related to DNA replication and nucleosome organization on AGS cells. Protein–protein interaction was confirmed through STRING analysis, and it was confirmed that cancer cell growth and proliferation were inhibited through KEGG, Reactome, and Wiki pathway analysis, and various signaling pathways related to cancer cell death were induced. It was confirmed that KYNA treatment reduced the gene expression of cancer-causing AP-1 factors (Fos, Jun, ATF, and JDP) in AGS cell lines derived from gastric cancer. Overall, using next-generation transcriptome sequencing data and bioinformatics tools, we confirmed that KYNA had an apoptosis effect by inducing changes in various genes, including factor AP-1, in gastric cancer AGS cells. This study can identify pharmacological targets for gastric cancer treatment and provide a valuable resource for drug development.
1. Introduction
Gastric cancer was the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in 2020 and is one of the most common cancers worldwide []. It is a malignant tumor that threatens human life and health and is mainly treated through resection []. However, chemotherapy is still used in the early stages to relieve symptoms and suppress metastasis []. Cisplatin and fluorouracil, used primarily as chemotherapeutic agents, cause various side effects in patients, including vomiting and hemotoxicity []. Therefore, there is a need to develop a therapeutically effective drug with low toxicity to treat gastric cancer.
Among approaches for cancer treatment, it is essential to understand changes in the molecular pathways and signaling mechanisms of tumor cells through drugs []. When normal cells become cancerous, various genes and proteins are involved in the transformation []. Although it is relatively difficult to identify the mechanism of action according to drug treatment, next-generation drugs focus on developing methods targeting specific genes and proteins []. Obtaining information about the target and its mechanism of action can provide precise insight into the treatment of the disease. In addition, targeted treatment methods can minimize cytotoxicity and side effects compared to conventional anticancer drugs []. It has been confirmed that tumors are caused by various factors, including genes, proteins, and metabolites [].
Network pharmacology is a study that utilizes computer network analysis and biomedical data, and helps to discover the underlying mechanisms between drugs and their target agents []. Transcriptome analysis is a method to identify differentially expressed genes during drug treatment using bioinformatics, and is a technique that helps to understand the discovery of essential genes and the mechanism of action of drugs []. It is possible to quickly identify differentially expressed genes and secure a target to accelerate treatment. However, it is still a problematic study to predict the onset of gastric cancer and to identify target factors for early treatment and treatment. Therefore, there is a need for a process to acquire more target factors to improve treatment.
The AP-1 complex is a dimeric transcription factor including Jun (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD), Fos (c-Fos, FosB, Fra2, and FosL), and ATF (ATF2, ATF3, and ATF7), and regulates a variety of cellular processes, including apoptosis, survival, migration, and differentiation [,]. It has been reported that C-Fos, together with interleukin-1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2), promotes angiogenesis in human colon cancer cells to promote tumor progression []. Therefore, AP-1 is an essential target for cancer treatment, and the related mechanism is being studied []. Therefore, this suggests that drug-mediated alteration of the corresponding biomarkers can control a variety of cells, including cancer migration, growth, and proliferation.
Kynurenic acid (KYNA) is a phenolic compound with a phenol ring and various physiological activities. It is a metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, which is the catabolic process of tryptophan []. KYNA has been reported as an inhibitor of p38 in renal cancer cells and renal cell carcinoma Caki-2 cells [], and it inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells by affecting other signaling factors such as MAPK, ERK, and AKT turnout []. The present study performed transcriptome analysis and network pharmacology analysis to identify potential targets of KYNA for gastric cancer cell AGS. We discovered AP-1 as an anti-tumor regulator that KYNA induces significant changes in AGS cells and secured primary data on changes in other genes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
AGS human gastric cancer cells (Korea Cell Line Bank, Seoul, Republic of Korea) were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco; BRL Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco; BRL Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) (Gibco; BRL Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. Kynurenic acid (KYNA) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Corp. (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Isolation of RNA for Sequencing
AGS cells were seeded into 60 mm plates at 1 × 106 and treated with 250 μM of Kynurenic acid (KYNA) for 24 h at 37 °C. After incubation, total RNAs were extracted using TRIzol. A spectrophotometer was used to measure the amount of RNA. The sequencing of isolated total RNA was then used to determine the expression levels.
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
According to the following methodology, the mRNA sequencing was prepared by Theragenbio (Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea). We created 151 bp paired-end sequencing libraries using the TruSeq stranded mRNA Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina, CA, USA). Utilizing oligo (dT) magnetic beads, mRNA molecules were specifically isolated and fragmented from 1 μg of total RNA. Through random hexamer priming, single-stranded cDNAs were created from the fragmented mRNAs. Double-stranded cDNA was created by using this as a template for second-strand synthesis. After end repair, A-tailing and adapter ligation were completed in order, and cDNA libraries were amplified using PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). The Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer (Agilent, CA, USA) was used to assess these cDNA libraries’ quality. According to the manufacturer’s library quantification methodology, they were measured using the KAPA library quantification kit (Kapa Biosystems, MA, USA). After cluster amplification of denatured templates, Illumina NovaSeq6000 (Illumina, CA, USA) was used to advance the sequencing process as paired-end (2 × 151 bp).
2.4. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.4.1. Filtering and Sequence Alignment
Adapter sequences and read ends with a Phred quality score of less than 20 were deleted throughout the filtering process, and reads less than 50 bp were also eliminated using cutadapt v.2.8. Following ENCODE standard choices and the “quantMode TranscriptomeSAM” option (refer to “Alignment” of “Help” section in the Html report) for estimation of transcriptome expression level, filtered reads were mapped to the reference genome associated with the species using the aligner STAR [].
2.4.2. Gene-Expression Estimation
By utilizing the option “strandedness”, the RSEM v.1.3.1 [] program estimated gene expression while taking into account the orientation of the reads about the library protocol. The “estimate-rspd” option was used to increase measurement accuracy. The default settings were used for all other parameters. Values for FPKM and TPM were generated to standardize depth across samples.
2.4.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
The GO database was used to analyze biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). A GO-based trend test was performed for DEG functional characterization using the Wallenius non-central hypergeometric distribution and the R package GOseq []. Following the test, selected genes with a p-value of 0.05 or below were considered statistically significant.
2.4.4. Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis
Using the TCC v.1.26.0 [] R package, DEGs were found based on the projected read counts from the previous phase. The TCC package compares tag-count data using effective normalizing techniques. Normalization factors were computed using the iterative DESeq2 []/edgeR [] technique. Using the p.adjust function of the R package with the default parameter values, the Q-value was determined based on the p-value. A q-value criterion of less than 0.05 was used to identify the DEGs and adjust for multiple testing mistakes.
2.5. STRING Network and Enrichment Pathway Analysis
The protein–protein interaction (PPI) for the top 30 genes among up-regulated and down-regulated DEGs was performed using an online tool Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING, version 9.1) (http://string-db.org (accessed on 8 February 2022)). The PPI score was set based on medium confidence (0.4). In the PPI network, each node depicts a protein, while the edges represent the strength of the relationship between proteins. Likewise, for the top 30 DEGs, all functionally enriched pathways of significantly expressed genes were determined using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), Reactome, and Wiki pathway databases. Additionally, annotated keywords were also identified.
2.6. Drug and Disease Association Analysis
Drug and disease association analyses were performed using WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis (WebGestalt), which is an online toolkit for functional genomic enrichment. The significance was set at FDR < 0.05, and the gene count was set at ≥5.
2.7. Molecular Docking Analysis
To perform molecular docking analysis, we retrieved the protein structure from PDB (https://www.rcsb.org/, accessed on 1 May 2021) using the search ID 5VPD (AP-1), and the compound structures (Dacarvazine and Kynurenic acid) were downloaded from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 May 2021). Docking analysis was performed using pyMol and USCF chimera with the default parameters. The affinity of the binding is determined using estimated free energy binding and total intermolecular energy.
2.8. Analysis of Protein Expression by Western Blot
AGS cells were seeded into 60 mm plates at 4 × 105 cells per well and treated with the indicated concentrations of KYNA of (0, 150, 200, and 250) μM for 24 h. Cells were lysed using radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (iNtRON Biotechnology, Seoul, Republic of Korea) containing phosphatase and protease inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Protein concentrations were determined using a Pierce™ BCA assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). An equal quantity of protein (10 μg) from each sample was electrophoresed on (8–15%) SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (ATTO Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and then the membrane was incubated with the primary antibodies followed by a conjugated secondary antibody to peroxidase. The obtained proteins were detected by an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratory, Hercules, CA, USA), and analyzed using the Image Lab 4.1 (Bio-Rad) program. The densitometry readings of the protein bands were normalized by comparison with the expression of β-actin as control, using the ImageJ software program (U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Antibodies of c-Fos (Cat. #2250S), c-Jun (Cat. #9165S), p-c-Fos (Cat. #5348S), and p-c-Jun (Cat. #9261S) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, Ma, USA).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All the experimental data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.2 (GraphPad Software). The results were expressed as the means ± standard deviation (SD). Results were evaluated using the Student’s t-test, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Genes and DEGs
It was confirmed in a previous study [] that KYNA treatment induces tumor cell death in AGS cells. A total of 278 DEGs (log2 (Fold Change) > 1.0 and p-value < 0.05) were identified in the KYNA treatment group, of which 120 up-regulated genes and 158 down-regulated genes were identified (Table 1). Additionally, the R-Bioconductor volcanic pilot revealed DEGs among the total genes (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Sequencing statistics data.
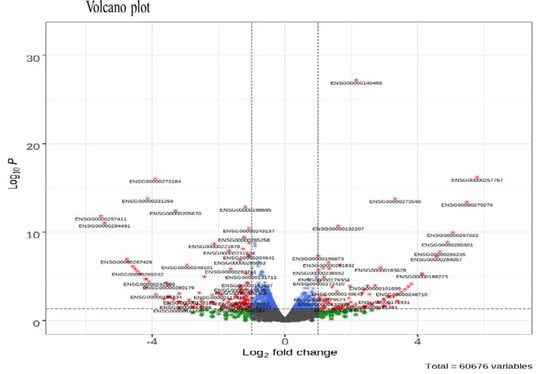
Figure 1.
Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). A total of 60,676 variables were considered for the plot. The fold-change was plotted based on log2 FC and p-value.
3.2. Functional and Enrichment Analysis
Gene ontology was used to identify a representative class of genes or proteins that were excessively changed by KYNA in AGS cells. Gene groups corresponding to molecular functions, biological processes, and cellular components were analyzed (Figure 2 and Table 2). As a result of molecular function, the structural constituent of the extracellular matrix was the most decreased, followed by a decrease in protein heterodimerization activity, showing a tendency to decrease in genes related to cell differentiation and growth. The biological process also showed a decrease in genes involved in DNA replication and nucleosome construction in cells with a similar trend. In the cellular component, genes related to extracellular regions and neuronal signaling were decreased. This suggests that KYNA suppressed the expression of genes involved in the growth and proliferation of AGS cells.
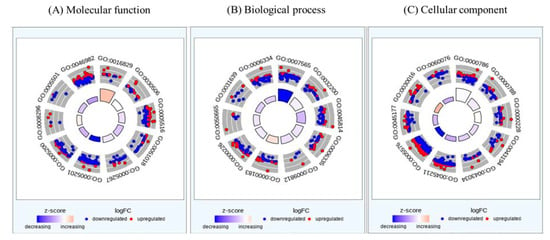
Figure 2.
Circos plot representation of gene enrichment ontology analysis plotted in terms of molecular function, biological process, and cellular component from differentially regulated genes of KYNA against AGS cells. Blue: down-regulated, Red: up-regulated.

Table 2.
List of enriched gene ontology in terms of molecular function, biological process, and cellular component.
The top 10 genes with high significance are listed with their function and z-score of the respective term.
3.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) and Enrichment Pathway of DEGs
Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis was constructed using the STRING database for the top 30 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) up and down (Figure 3), and the related enrichment pathways were analyzed (Table 3). The results of the PPI STRING analysis of up-regulated genes were divided into two groups, and down-regulated genes were divided into three groups. Up-regulated DEGs were involved in various apoptoses such as in the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and the Ras signaling pathway in the KEGG pathway analysis, and DNA damage-related results were also obtained in the Wiki pathway. In the Reactome pathway, pathways related to cell signal transduction were identified, and in the annotated keywords, results related to DNA damage, repair, and recombination were also confirmed. This suggests that KYNA induces apoptosis of AGS cells through the up-regulation of up-regulated genes. KEGG, wiki, and Reactome pathways in down-regulated genes confirmed the results of metabolic processes and DNA replication related to cell proliferation. This suggests that KYNA down-regulated genes are involved in AGS cell metabolism and DNA replication.
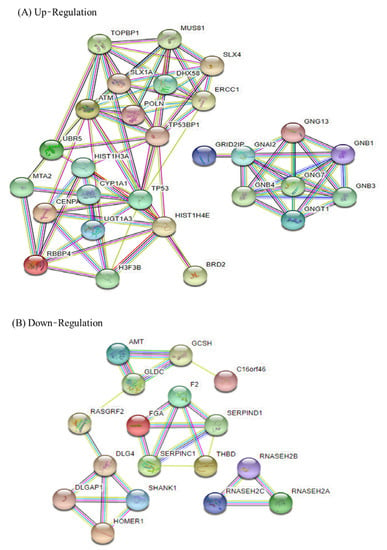
Figure 3.
Protein—protein interaction (PPI) analysis of up-regulation and down-regulation DEGs analyzed by STRING software. The network nodes represent genes (showing the interactions), and the round nodes denote individual genes. The line color indicates the type of interaction evidence.

Table 3.
KEGG, Wiki, and Reactome pathways and annotated keyword classification and functional enrichment for the up-regulation and down-regulation DEGs.
3.4. Expression Comparison of AP-1 Factors and Molecular Docking with KYNA
The expression of AP-1 factors related to tumor growth and proliferation was confirmed (Table 4). Fos, Jun, JDP (Jun dimerization protein), and ATF (Activating transcription factor) constituting AP-1 were decreased upon KYNA treatment, suggesting that KYNA inhibits the growth and proliferation of AGS cells. Additionally, ligand–protein docking analysis was performed through UCSF Chimera software. Both ligands AP-1 and KYNA were found to occupy the active site, as illustrated in Figure 4. In addition, many active sites have been shown to aid ligand binding. Active sites involved in the binding of AP-1 to KYNA were identified as ALA281, ALA168, ALA169, ALA185, GLU192, ASN165, LYS166, GLN189, GLU191, CYS285, LYS284, ARG288, ARG164, and ASP188 (Table 5). The molecular binding energy score was found to be −6.3 kcal/mol.

Table 4.
Expression comparison of AP-1 factors.
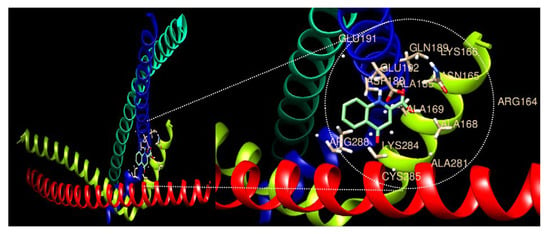
Figure 4.
Molecular docking analysis of the AP-1 complex (c-Jun and c-Fos) and Kynurenic acid. The 3D structure of AP-1 factors is bound efficiently with Kynurenic acid.

Table 5.
Molecular docking studies of Kynurenic acid with the AP-1 complex and their binding energy.
The table shows the list of interacting amino acids and their binding energy.
3.5. Validation of AP-1 Factor Expression Using Western Blot Analysis
Western blot analysis of AGS cells during KYNA treatment confirmed the expression of c-Fos and c-Jun, which are AP-1 factors (Figure 5). It was confirmed that the expression of p-c-Fos and p-c-Jun proteins decreased by inhibiting phosphorylation of c-Fos and c-Jun proteins during KYNA treatment. This result was consistent with the decreased expression of AP-1 factors obtained through transcriptome analysis, further proving the role of KYNA in regulating the expression of important factors in AGS cells.
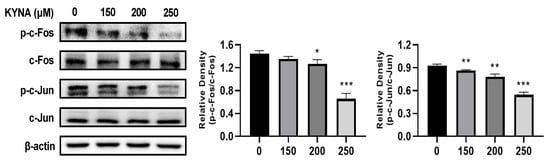
Figure 5.
Western blot validation of crucial targets of KYNA against AGS cells. Protein expression of crucial proteins c-Fos and c-Jun on KYNA-treated AGS cells for 24 hr. The results obtained from three independent experiments are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) compared with the control group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.6. Therapeutic Drug and Disease Association and Molecular Docking Analysis
Through drug and disease association analysis, the top 10 drugs significantly related to differentially regulated genes were selected (Table 6). Among the selected drugs, Dacarbazine was approved by the FDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) number; 075371, Fresenius, Kabi, Illinois, IL, USA), and it was confirmed that it was used as an anticancer drug. Drug and protein molecular docking were performed to confirm the molecular binding of Dacarbazine to AP-1 (Figure 6). In ligand–protein docking using UCSF Chimera software, it was found that a binding site was shared between the two factors, as illustrated in the figure. In addition, various active sites have been shown to aid in ligand uptake. Mutual binding amino residues were found to be GLU191, GLU193, GLU192, ASP188, GLN189, ALA185, ARG288, LYS166, ASN165, ALA169, LYS284, CYS285, CYS172, ALA168, and ALA281 (Table 7), with a molecular binding score of −5.2 kcal/mol demonstrating the molecular binding energy of autodock.

Table 6.
Results of drug and disease association analysis.
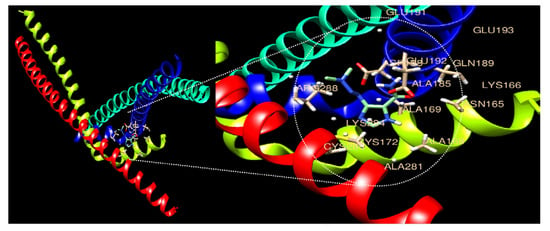
Figure 6.
Molecular docking analysis of the AP-1 complex (c-Jun and c-Fos) and Dacarbazine. The 3D structure of AP-1 factors is bound efficiently with the drug Dacarbazine.

Table 7.
Molecular docking studies of Dacarbazine with the AP-1 complex and their binding energy.
The table shows the list of interacting amino acids and their binding energy.
4. Discussion
Understanding disease-causing factors provides a roadmap for the development of new therapeutic drugs []. RNA sequencing technology is used for disease diagnosis and therapeutic applications by identifying the targets of various diseases, including cancer []. Complex relationships can be understood through network analysis, usually using bioinformatics and pharmacology to help elucidate mechanisms between drugs and their targets []. Through this, targeted drug treatment by identifying tumor-specific expressed genes can provide patients with a variety of treatment options.
The effect of KYNA on the genetic change in AGS cells was analyzed using RNA seq. A total of 60,676 genes were identified, and gene ontology changes (Figure 2) and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were confirmed between the KYNA-treated group and the KYNA-untreated group (Figure 1). Genes related to cell differentiation and growth decreased in molecular function, genes related to DNA replication and nucleosome construction decreased in biological process, and genes related to synaptic signal transduction decreased in cellular components (Table 2). Through GO analysis, it was confirmed that KYNA had a negative effect on tumor cells.
The association of 30 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was confirmed through protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis. The up-regulated genes showed interaction in a total of two groups, and the down-regulated genes consisted of a total of three groups (Figure 3). Up-regulated interacting genes affected various signaling pathways, including the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway in the KEGG pathway. In the Wiki pathway, signaling pathways related to the ATM signaling pathway and DNA damage were also shown, and in the Reactome pathway, results such as cell-cycle checkpoint and DNA repair were shown. Down-regulated genes obtained results related to cell proliferation, metabolism, and DNA replication in the KEGG, wiki, and Reactome pathways (Table 3). These results suggest that KYNA induces apoptosis of AGS.
AP-1 [], which affects various regulatory processes including tumor growth, proliferation, migration, cell cycle, and apoptosis, has members Jun, Fos, and ATF []. In particular, Fos and Jun are involved in DNA synthesis and G0-G1 during the cell cycle and are known to generate CD8 T-lymphocytes of T-cells []. In addition, c-Fos expression in gastric cancer cells is associated with lymph node metastasis, invasion, and short survival, and has been reported to have a poor prognosis []. In this study, as a result of analyzing the expression level of AP-1 members, it was confirmed that Fos, Jun, ATF, and JDP were decreased upon KYNA treatment (Table 4). Additionally, as a result of confirming the binding affinity of KYNA and the AP-1 complex (Jun and Fos) through molecular docking analysis, a binding force of −6.3 kcal/mol was confirmed (Figure 4 and Table 5). In addition, as a result of analyzing the protein expression of Jun and Fos through Western blot analysis, it was confirmed that AP-1 factors decreased in a concentration-dependent manner when KYNA was treated (Figure 5). This suggests that KYNA treatment in AGS cells suppresses the expression of AP-1 factors, thereby inhibiting tumor growth and proliferation. The top 10 drugs related to DEGs were obtained through drug and disease association analysis (Table 6). Among them, Dacarbazine was approved by the FDA and confirmed to be used as an anticancer agent []. As a result of confirming the binding affinity between Dacarbazine and the AP-1 complex (Jun and Fos) through molecular docking analysis, a binding force of −5.2 kcal/mol was shown (Figure 6 and Table 7). AP-1, which induces tumor growth and proliferation, showed a somewhat higher binding force with KYNA than Dacarbazine, which is currently used as a drug. This suggests that KYNA induces inhibition of AP-1.
KYNA is a physiologically active ingredient found in various herbs [] which induces apoptosis through cell-cycle regulation and signaling pathways in colorectal and renal cancer cells []. It has also been reported to inhibit cell proliferation and growth through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in adenocarcinoma []. It has been demonstrated that KYNA has a direct effect on the gastric wall to prevent gastric ulcers []. In a previous study, KYNA was confirmed to induce apoptosis in gastric cancer-derived AGS cells []. In this study, it was confirmed that KYNA inhibits the growth and proliferation of cancer cells through the identification of biomarkers. These results suggest that KYNA can have an anti-tumor effect in gastric cancer, and it is judged that it can be used as basic data for the development of gastric cancer therapeutics.
5. Conclusions
Transcriptome analysis results provide potential insights into tumor therapeutics in KYNA-treated AGS cells. In this study, it was found that KYNA induces the expression of genes that responds to apoptosis and, in particular, up-regulates the expression of AP-1 factors. In addition, the results of this study show the effect of KYNA on the gene expression of AGS cells, and provide a novel research method that can be used to confirm the effects of other drugs on other cancer cells. Results suggest that KYNA can be considered for the development of treatment for gastric cancer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H.K.; Methodology, H.H.K. and S.E.H.; Software, H.H.K. and M.Y.P.; Validation, S.H.J.; Formal analysis, H.H.K. and S.H.J.; Investigation, P.B.B.; Resources, A.A.; Data curation, C.K.W.; Writing-original draft preparation, H.H.K.; Writing-review and editing, H.H.K.; Visualization, J.D.H. and M.A.; Supervision, G.S.K.; Project administration, J.K.S., H.W.K. and G.S.K.; Funding acquisition, G.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (grant no. 2020R1A2B5B01001807 and 2022R1A6A3A01086899).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.C.; Nilsson, M.; Grabsch, H.I.; van Grieken, N.C.; Lordick, F. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2020, 396, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaretto, L.; Sousa, P.L.; Mari, J.J. Chemotherapy versus support cancer treatment in advanced gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sastre, J.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Diaz-Rubio, E. Chemotherapy for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baretton, G.B.; Aust, D.E. Current biomarkers for gastric cancer. Pathologe 2017, 38, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.L.; Fock, K.M. Clinical epidemiology of gastric cancer. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Villanueva, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J.M. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, G.; Wu, J.; Guo, S.; Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. A bioinformatics investigation into molecular mechanism of Yinzhihuang granules for treating hepatitis B by network pharmacology and molecular docking verification. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Transcriptome analysis and identification of key genes involved in 1-deoxynojirimycin biosynthesis of mulberry (Morus alba L.). PeerJ 2018, 6, e5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Ding, Y.; Wild, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Small molecule inhibitors targeting activator protein 1 (AP-1). J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6930–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.F.; Eferl, R. Fos/AP-1 proteins in bone and the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, A.C.; Chu, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Chien, C.W.; Cheng, J.J.; Yang, S.H.; Jiang, J.K.; Lee, T.C. Interleukin-1 Receptor Type 2 Acts with c-Fos to Enhance the Expression of Interleukin-6 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A in Colon Cancer Cells and Induce Angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 22212–22224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, P.; Casalino, L.; Talotta, F.; Yaniv, M.; Weitzman, J.B. Deciphering AP-1 function in tumorigenesis: Fra-ternizing on target promoters. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2633–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Turski, W.A.; Rajtar, G. Kynurenic acid inhibits colon cancer proliferation in vitro: Effects on signaling pathways. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Zurawska, M.; Kis, J.; Starownik, R.; Zgrajka, W.; Bar, K.; Turski, W.A.; Rzeski, W. Kynurenic acid in human renal cell carcinoma: Its antiproliferative and antimigrative action on Caki-2 cells. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nishiyama, T.; Shimizu, K.; Kadota, K. TCC: An R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Ha, S.E.; Park, M.Y.; Bhosale, P.B.; Abusaliya, A.; Won, C.K.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, G.S. Cellular Regulation of Kynurenic Acid-Induced Cell Apoptosis Pathways in AGS Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.; Bazhin, A.V.; Westphalen, C.B.; Renz, B.W.; Jacob, S.N.; Lampert, C.; Werner, J.; Angele, M.K.; et al. Angiogenesis-Related Gene Expression Signatures Predicting Prognosis in Gastric Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byron, S.A.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.R.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Carpten, J.D.; Craig, D.W. Translating RNA sequencing into clinical diagnostics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakle, N.S.; More, S.A.; Mokale, S.N. A network pharmacology-based approach to explore potential targets of Caesalpinia pulcherima: An updated prototype in drug discovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesely, P.W.; Staber, P.B.; Hoefler, G.; Kenner, L. Translational regulation mechanisms of AP-1 proteins. Mutat. Res. 2009, 682, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarubin, T.; Han, J. Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grausz, J.D.; Fradelizi, D.; Dautry, F.; Monier, R.; Lehn, P. Modulation of c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in normal human lymphocytes by calcium ionophore A23187 and phorbol ester. Eur. J. Immunol. 1986, 16, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.P.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.A.; Yang, H.K.; Lee, H.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, W.H. Prognostic significance of loss of c-fos protein in gastric carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2007, 13, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: 21st List 2019. 2019. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/325771 (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Zgrajka, W.; Bartnik, M.; Kocki, T.; Turski, W.A. Distribution, synthesis, and absorption of kynurenic acid in plants. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavin, G.B.; Pinsky, C. Kynurenic acid attenuates experimental ulcer formation and basal gastric acid secretion in rats. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1989, 64, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).