Family Food Environments and Their Association with Primary and Secondary Students’ Food Consumption in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
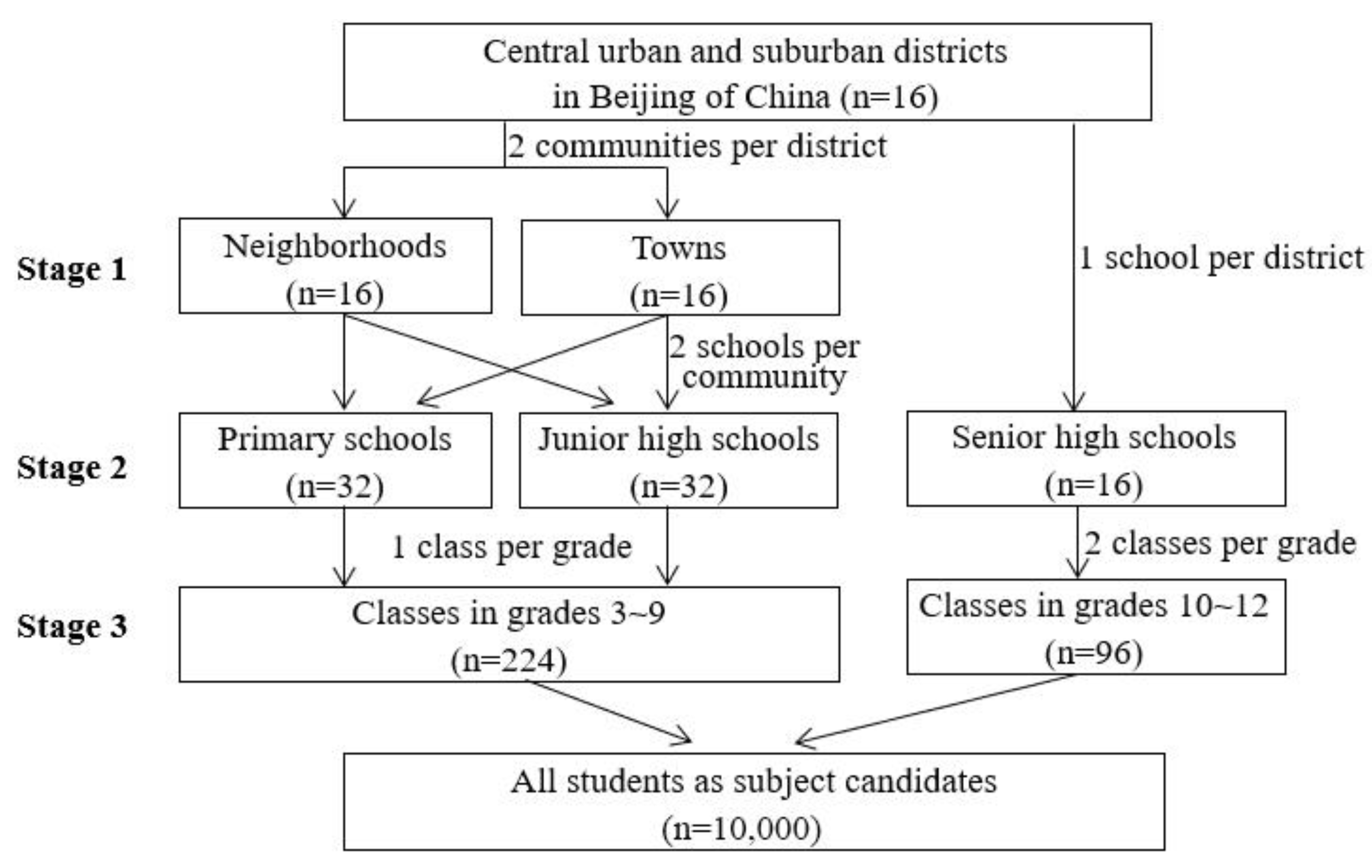
2.1. Study Design and Sampling
2.2. Family Food Environment Assessment and Demographic Measurement
2.3. Food Consumption Investigation
2.4. Anthropometric Data
2.5. Variable Value Assignment and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants and Family Food Environment
3.2. Correlations of Family Food Environment Dimensions
3.3. Family Food Environment in Relation to Students’ Food Consumption
3.4. Multiple Regression Analysis Predicting Students’ Food Consumption
3.5. Overweight in Relation to Family Food Environment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleming, C.A.; De Oliveira, J.D.; Hockey, K.; Lala, G.; Schmied, V.; Theakstone, G.; Third, A. Food and Me. How Adolescents Experience Nutrition across the World. A Companion Report to The State of the World’s Children 2019; Western Sydney University and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): Sydney, Australia, 2020; Available online: https://researchdirect.westernsydney.edu.au/islandora/object/uws:58028 (accessed on 5 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- United Nations Children’s Fund. The State of the World’s Children 2019. In Children, Food and Nutrition: Growing Well in a Changing World; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Corkins, M.R.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Golden, N.H.; Kim, J.H.; Magge, S.N.; Schwarzenberg, S.J. Nutrition in Children and Adolescents. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 100, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, X. Clustering of Poor Dietary Habits among Adolescents Aged 12 to 15 Years in 52 Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, T.; Morris, S.S.; Tumilowicz, A. Global Patterns of Adolescent Fruit, Vegetable, Carbonated Soft Drink, and Fast-Food Consumption: A Meta-Analysis of Global School-Based Student Health Surveys. Food Nutr. Bull. 2019, 40, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, J.Y.; Wolfenden, L.; Sutherland, R.; Nathan, N.; Oldmeadow, C.; McLaughlin, M.; Barnes, C.; Hall, A.; Vanderlee, L.; Yoong, S.L. A Systematic Review of the Recent Consumption Levels of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages in Children and Adolescents From the World Health Organization Regions With High Dietary-Related Burden of Disease. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2022, 34, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jan, C.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Sawyer, S.M.; et al. Economic development and the nutritional status of Chinese school-aged children and adolescents from 1995 to 2014: An analysis of five successive national surveys. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Ding, C.; Song, C.; Yuan, F.; Fan, J.; Feng, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A. The association between frequency of eating out with overweight and obesity among children aged 6-17 in China: A National Cross-sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Xu, P.; Yang, T.; Cao, W.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Pan, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Status and Its Association with Childhood Obesity among Chinese Children Aged 6–17 Years. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, S.; Arrizza, C.; Vecchi, F.; Tedeschi, S. Determinants of children’s eating behavior. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 2006S–2011S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, S.; De Cosmi, V.; Ciappolino, V.; Parazzini, F.; Brambilla, P.; Agostoni, C. Factors Influencing Children’s Eating Behaviours. Nutrients 2018, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiese, B.H.; Jones, B.L. Food and family: A socio-ecological perspective for child development. Adv. Child. Dev. Behav. 2012, 42, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, J.; Haycraft, E.; Lytle, L.; Nicklaus, S.; Kok, F.J.; Merdji, M.; Fisberg, M.; Moreno, L.A.; Goulet, O.; Hughes, S.O. Nurturing Children’s Healthy Eating: Position statement. Appetite 2019, 137, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.; Egger, G.; Raza, F. Dissecting obesogenic environments: The development and application of a framework for identifying and prioritizing environmental interventions for obesity. Prev. Med. 1999, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.; Kaphingst, K.M.; Robinson-O’Brien, R.; Glanz, K. Creating healthy food and eating environments: Policy and environmental approaches. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andueza, N.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Cuervo, M. Effectiveness of Nutritional Strategies on Improving the Quality of Diet of Children from 6 to 12 Years Old: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adom, T.; De Villiers, A.; Puoane, T.; Kengne, A.P. A Scoping Review of Policies Related to the Prevention and Control of Overweight and Obesity in Africa. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.S.; Fisher, J.O.; Birch, L.L. Parental influence on eating behavior: Conception to adolescence. J. Law Med. Ethics 2007, 35, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grammer, A.C.; Balantekin, K.N.; Barch, D.M.; Markson, L.; Wilfley, D.E. Parent-Child influences on child eating self-regulation and weight in early childhood: A systematic review. Appetite 2022, 168, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.H.; Schoonees, A.; Sriram, U.; Faure, M.; Seguin-Fowler, R.A. Caregiver involvement in interventions for improving children’s dietary intake and physical activity behaviors. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD012547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomayko, E.J.; Tovar, A.; Fitzgerald, N.; Howe, C.L.; Hingle, M.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Muzaffar, H.; Going, S.B.; Hubbs-Tait, L. Parent Involvement in Diet or Physical Activity Interventions to Treat or Prevent Childhood Obesity: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Vizcarra, M.; Hughes, S.O.; Papaioannou, M.A. Food Parenting Practices and Feeding Styles and Their Relations with Weight Status in Children in Latin America and the Caribbean. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moal, F.; Michaud, M.; Hartwick-Pflaum, C.A.; Middleton, G.; Mallon, I.; Coveney, J. Beyond the Normative Family Meal Promotion: A Narrative Review of Qualitative Results about Ordinary Domestic Commensality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kininmonth, A.R.; Smith, A.D.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Dye, L.; Lawton, C.L.; Fildes, A. The relationship between the home environment and child adiposity: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. The Roles of Family and School Members in Influencing Children’s Eating Behaviours in China: A Narrative Review. Children 2022, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.Z.; Lwin, M.O.; Ho, S.S. The influence of parental practices on child promotive and preventive food consumption behaviors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, N.; Biddle, S.; Gorely, T. Family correlates of fruit and vegetable consumption in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleary, S.A.; Ettienne, R. The relationship between food parenting practices, parental diet and their adolescents’ diet. Appetite 2019, 135, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, N.; Moore, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J.; Ding, K.; Li, R. Perceived Parental Attitudes Are Indirectly Associated with Consumption of Junk Foods and Sugar-Sweetened Beverages among Chinese Adolescents through Home Food Environment and Autonomous Motivation: A Path Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hong, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, J. The Combination of School-Based and Family-Based Interventions Appears Effective in Reducing the Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, a Randomized Controlled Trial among Chinese Schoolchildren. Nutrients 2022, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, J.A.; Friend, S.; Horning, M.; Flattum, C.; Draxten, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Gurvich, O.; Garwick, A.; Story, M.; Kubik, M.Y. Family Home Food Environment and Nutrition-Related Parent and Child Personal and Behavioral Outcomes of the Healthy Home Offerings via the Mealtime Environment (HOME) Plus Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Liu, T.; Li, N.N.; Sun, J.; Cui, J.M.; Zhu, W.L. Development and assessment of homo food environment measurement questionnaire. Food Nutr. China 2020, 26, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Villberg, J.; Torsheim, T.; Tynjälä, J.; Lv, Y.; Kannas, L. Reliability and Validity of Family Affluence Scale (FAS II) among Adolescents in Beijing, China. Child Indic. Res. 2011, 5, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchley, J.; Currie, D.; Cosma, A.; Samdal, O. (Eds.) Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Study Protocol: Background, Methodology and Mandatory Items for the 2017/18 Survey; CAHRU: St Andrews, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, J.M.; Brener, N.; Thornton, J.; Harris, W.A.; Bryan, L.N.; Shanklin, S.L.; Deputy, N.; Roberts, A.M.; Queen, B.; Chyen, D.; et al. Overview and Methods for the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System - United States, 2019. MMWR-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, L.A.; Sokol, R.L. Measures of the food environment: A systematic review of the field, 2007–2015. Health Place 2017, 44, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinard, C.; Yaroch, A.; Hart, M.; Serrano, E.; McFerren, M.; Estabrooks, P. Measures of the home environment related to childhood obesity: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebremariam, M.K.; Vaque-Crusellas, C.; Andersen, L.F.; Stok, F.M.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Brug, J.; Lien, N. Measurement of availability and accessibility of food among youth: A systematic review of methodological studies. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaglioni, S.; Salvioni, M.; Galimberti, C. Influence of parental attitudes in the development of children eating behaviour. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl. S1), S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Hein, S. Parenting, Autonomy in Learning, and Development During Adolescence in China. In Child and Adolescent Development in China; Liu, Y., Grigorenko, E.L., Eds.; Wiley Periodicals: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 163, pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Chang, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. The effects of Chinese traditional feeding habits on the eating disorders and the psychological analysis. Eat. Behav. 2015, 17, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon-Daly, J.; Serpell, L. Protective factors against disordered eating in family systems: A systematic review of research. J. Eat. Disord 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodder, R.K.; O’Brien, K.M.; Tzelepis, F.; Wyse, R.J.; Wolfenden, L. Interventions for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in children aged five years and under. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 5, CD008552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, S.C.; Glanz, K.; Zhou, C.; Sallis, J.F.; Saelens, B.E. Home food environment in relation to children’s diet quality and weight status. J. Acad Nutr. Diet 2014, 114, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebestreit, A.; Intemann, T.; Siani, A.; De Henauw, S.; Eiben, G.; Kourides, Y.A.; Kovacs, E.; Moreno, L.A.; Veidebaum, T.; Krogh, V.; et al. Dietary Patterns of European Children and Their Parents in Association with Family Food Environment: Results from the I.Family Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monge-Rojas, R.; Colón-Ramos, U.; Chinnock, A.; Smith-Castro, V.; Reyes-Fernández, B. Gender-based eating norms, the family environment and food intake among Costa Rican adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 4840–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganann, R.; Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D.; Ciliska, D.; Peirson, L.J.; Warren, R.L.; Fieldhouse, P.; Delgado-Noguera, M.F.; Tort, S.; Hams, S.P.; Martinez-Zapata, M.J.; et al. Enhancing nutritional environments through access to fruit and vegetables in schools and homes among children and youth: A systematic review. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, C.; Azevedo, J.; Gregorio, M.J.; Barros, R.; Severo, M.; Padrao, P. Parental practices, preferences, skills and attitudes on food consumption of pre-school children: Results from Nutriscience Project. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | N (%) | Family Food Environment Score (Mean ± SD) | Total Score ≥ 60 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Socioeconomic Status | Family Food Availability | Family Feeding Patterns | FAMILY Food Rules | FAMILY Meal Practices | Caregiver’s Nutritional Literacy | Total Score | n (%) | ORs(95% CI) | ||
| Total | 9686(100.0) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 11.4 ± 2.2 | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.2 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.8 ± 2.9 | 65.7 ± 8.4 | 7419(76.6) | |
| Grade | ||||||||||
| 3~6 | 4092(42.2) | 4.2 ± 1.4 a | 11.9 ± 2.0 a | 8.9 ± 1.8 a | 17.1 ± 3.9 a | 12.7 ± 1.8 a | 12.9 ± 2.9 a | 67.7 ± 7.9 a | 3461(84.6) | — |
| 7~9 | 2875(29.7) | 4.3 ± 1.3 ab | 11.3 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 16.2 ± 4.5 b | 12.3 ± 1.9 b | 12.7 ± 2.9 b | 65.4 ± 8.4 b | 2170(75.5) | 0.561(0.498~0.633) * |
| 10~12 | 2719(28.1) | 4.3 ± 1.1 b | 10.9 ± 2.2 c | 8.5 ± 2.0 c | 14.7 ± 5.1 c | 11.7 ± 2.0 c | 12.7 ± 2.8 ab | 62.8 ± 8.4 c | 1788(65.8) | 0.350(0.312~0.393) * |
| Gender | ||||||||||
| Male | 4887(50.5) | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 11.4 ± 2.2 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.2 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.7 ± 2.9 | 65.6 ± 8.5 | 3706(75.8) | — |
| Female | 4799(49.5) | 4.2 ± 1.3 b | 11.5 ± 2.1 b | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.1 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.8 ± 2.8 | 65.7 ± 8.4 | 3713(77.4) | 1.090(0.992~1.197) |
| District | ||||||||||
| Urban | 3439(35.5) | 4.4 ± 1.4 a | 11.7 ± 2.1 a | 8.9 ± 1.8 a | 15.9 ± 4.5 a | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 13.3 ± 2.8 a | 66.6 ± 8.4 a | 2772(80.6) | — |
| Suburb | 6247(64.5) | 4.2 ± 1.3 b | 11.3 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 16.3 ± 4.6 b | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.5 ± 2.9 b | 65.2 ± 8.4 b | 4647(74.4) | 0.699(0.631~0.774) * |
| Number of children | ||||||||||
| 1 | 6133(63.3) | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 11.5 ± 2.1 | 8.7 ± 1.9 a | 15.9 ± 4.6 a | 12.2 ± 2.0 a | 12.9 ± 2.9 a | 65.6 ± 8.6 | 4678(76.3) | — |
| ≥2 | 3551(36.7) | 4.2 ± 1.4 b | 11.4 ± 2.2 | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 16.6 ± 4.4 b | 12.5 ± 1.8 b | 12.5 ± 2.9 b | 65.8 ± 8.2 | 2740(77.2) | 1.051(0.953~1.159) |
| Principal caregiver | ||||||||||
| Parents | 9500(98.1) | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 11.5 ± 2.2 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.2 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.8 ± 2.9 a | 65.7 ± 8.4 | 7290(76.7) | — |
| Grandparents | 160 (1.7) | 3.8 ± 1.6 b | 11.0 ± 2.3 b | 8.9 ± 2.2 | 16.6 ± 4.6 | 12.2 ± 2.3 | 12.0 ± 3.1 b | 64.4 ± 8.2 | 111(69.4) | 0.687(0.489~0.964) * |
| Caregiver’s educational level | ||||||||||
| ≤Junior high school | 1603(16.5) | 3.8 ± 1.3 a | 10.7 ± 2.2 a | 8.5 ± 2.0 a | 16.1 ± 4.7 | 12.2 ± 2.0 a | 11.6 ± 2.9 a | 62.9 ± 8.4 a | 1047(65.3) | — |
| High school | 2470(25.5) | 4.1 ± 1.3 b | 11.1 ± 2.1 b | 8.5 ± 2.0 a | 16.0 ± 4.7 | 12.2 ± 1.9 a | 12.3 ± 2.8 b | 64.3 ± 8.3 b | 1789(72.4) | 1.395(1.218~1.598) * |
| Junior college | 2383(24.6) | 4.3 ± 1.3 c | 11.6 ± 2.1 c | 8.7 ± 1.8 b | 16.4 ± 4.4 | 12.3 ± 1.9 b | 12.8 ± 2.8 c | 66.2 ± 8.2 c | 1880(78.9) | 1.985(1.721~2.288) * |
| ≥College | 3230(33.3) | 4.7 ± 1.2 d | 11.9 ± 2.1 d | 8.9 ± 1.8 c | 16.2 ± 4.4 | 12.4 ± 1.9 b | 13.7 ± 2.6 d | 67.7 ± 8.1 d | 2703(83.7) | 2.724(2.371~3.130) * |
| Annual household income per capita (yuan) | ||||||||||
| <20,000 | 1685(17.4) | 3.8 ± 1.3 a | 10.9 ± 2.2 a | 8.6 ± 2.0 a | 16.3 ± 4.6 | 12.1 ± 2.0 a | 12.0 ± 2.9 a | 63.7 ± 8.4 a | 1163(69.0) | — |
| 20,000~39,999 | 2127(22.0) | 4.0 ± 1.3 b | 11.3 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 ab | 16.2 ± 4.7 | 12.3 ± 2.0 ab | 12.5 ± 2.9 b | 64.8 ± 8.4 b | 1573(74.0) | 1.274(1.106~1.468) * |
| 40,000~69,999 | 2539(26.2) | 4.2 ± 1.3 c | 11.5 ± 2.0 c | 8.7 ± 1.9 bc | 16.1 ± 4.4 | 12.4 ± 1.8 b | 12.9 ± 2.8 c | 65.8 ± 8.2 c | 1969(77.6) | 1.550(1.349~1.782) * |
| ≥70,000 | 3329(34.4) | 4.7 ± 1.3 d | 11.8 ± 2.1 d | 8.8 ± 1.9 c | 16.1 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 b | 13.3 ± 2.8 d | 67.1 ± 8.4 d | 2708(81.3) | 1.957(1.710~2.240) * |
| Dimension of Family Food Environment | Family Socioeconomic Status | Family Food Availability | Family Feeding Patterns | Family Food Rules | Family Meal Practices | Caregiver’s Nutritional Literacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family food availability | 0.061 * | |||||
| Family feeding patterns | 0.011 | 0.142 * | ||||
| Family food rules | 0.029 * | 0.276 * | 0.002 | |||
| Family meal practices | 0.032 * | 0.283 * | 0.054 * | 0.309 * | ||
| Caregiver’s nutritional literacy | 0.097 * | 0.339 * | 0.069 * | 0.133 * | 0.197 * | |
| Total score | 0.237 * | 0.633 * | 0.306 * | 0.734 * | 0.556 * | 0.585 * |
| Food Consumption During the Past 7 Days | N (%) | Family Food Environment Score (Mean ± SD) | Total Score ≥ 60 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Socioeconomic Status | Family Food Availability | Family Feeding Patterns | Family Food Rules | Family Meal Practices | Caregiver’s Nutritional Literacy | Total Score | n (%) | ORs(95% CI) | ||
| Whole grains | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 7052(72.8) | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 11.4 ± 2.1 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.1 ± 4.6 a | 12.2 ± 1.9 a | 12.7 ± 2.9 a | 65.3 ± 8.4 a | 5305(75.2) | — |
| Daily | 2630(27.2) | 4.2 ± 1.4 b | 11.7 ± 2.2 b | 8.7 ± 2.0 | 16.5 ± 4.4 b | 12.5 ± 1.9 b | 13.1 ± 2.9 b | 66.7 ± 8.4 b | 2111(80.3) | 1.282(1.146~1.435) * |
| Fruits | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 3623(37.4) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.0 ± 2.1 a | 8.6 ± 1.9 a | 15.6 ± 4.7 a | 12.0 ± 2.0 a | 12.4 ± 2.9 a | 63.7 ± 8.6 a | 2494(68.8) | — |
| Daily | 6063(62.6) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.7 ± 2.1 b | 8.8 ± 1.9 b | 16.5 ± 4.4 b | 12.5 ± 1.9 b | 13.0 ± 2.8 b | 66.8 ± 8.2 b | 4925(81.2) | 1.685(1.527~1.860) * |
| Vegetables | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 2724(28.1) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.0 ± 2.1 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 15.8 ± 4.7 a | 12.1 ± 1.9 a | 12.3 ± 2.9 a | 64.1 ± 8.4 a | 1937(71.1) | — |
| Daily | 6937(71.6) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.6 ± 2.1 b | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.3 ± 4.5 b | 12.4 ± 1.9 b | 13.0 ± 2.8 b | 66.2 ± 8.4 b | 5461(78.7) | 1.466(1.322~1.626) * |
| Dairy Products | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 4360(45.0) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.2 ± 2.2 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.0 ± 4.6 a | 12.2 ± 1.9 a | 12.5 ± 2.9 a | 64.8 ± 8.5 a | 3198(73.3) | — |
| Daily | 5322(54.9) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.6 ± 2.1 b | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.3 ± 4.5 b | 12.4 ± 1.9 b | 13.0 ± 2.9 b | 66.4 ± 8.3 b | 4219(79.3) | 1.347(1.223~1.483) * |
| Legumes | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 8401(86.7) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 11.4 ± 2.1 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.1 ± 4.5 a | 12.3 ± 1.9 a | 12.8 ± 2.9 | 65.6 ± 8.5 a | 6406(76.3) | — |
| Daily | 1283(13.2) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 11.6 ± 2.3 b | 8.6 ± 2.1 | 16.6 ± 4.6 b | 12.4 ± 1.9 b | 12.8 ± 2.9 | 66.3 ± 8.2 b | 1011(78.8) | 1.197(1.034~1.385) * |
| Fish | ||||||||||
| None | 2641(27.3) | 4.1 ± 1.3 a | 11.3 ± 2.1 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.0 ± 4.7 a | 12.2 ± 2.0 a | 12.5 ± 2.9 a | 64.7 ± 8.6 a | 1939(73.4) | — |
| Weekly | 7042(72.7) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.5 ± 2.2 b | 8.7 ± 1.9 | 16.2 ± 4.5 b | 12.3 ± 1.9 b | 12.9 ± 2.9 b | 66.0 ± 8.3 b | 5478(77.8) | 1.274(1.147~1.416) * |
| Liver | ||||||||||
| None | 6180(63.8) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.4 ± 2.1 | 8.7 ± 1.9 a | 16.2 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.7 ± 2.9 a | 65.6 ± 8.4 | 4737(76.7) | — |
| Weekly | 3494(36.1) | 4.4 ± 1.3 b | 11.5 ± 2.2 | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 16.2 ± 4.6 | 12.3 ± 1.9 | 12.9 ± 2.9 b | 65.7 ± 8.5 | 2675(76.6) | 1.147(1.036~1.269) * |
| Breakfast | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 2018(20.8) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 10.7 ± 2.1 a | 8.5 ± 2.0 a | 15.1 ± 4.9 a | 11.7 ± 1.9 a | 12.2 ± 3.0 a | 62.5 ± 8.4 a | 1290(63.9) | — |
| Daily | 7660(79.1) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.6 ± 2.1 b | 8.7 ± 1.9 b | 16.4 ± 4.4 b | 12.5 ± 1.9 b | 12.9 ± 2.8 b | 66.5 ± 8.2 b | 6121(79.9) | 1.895(1.698~2.115) * |
| Food variety yesterday | ||||||||||
| <12 | 7620(78.7) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.4 ± 2.1 | 8.7 ± 1.9 a | 16.2 ± 4.5 | 12.3 ± 1.9 a | 12.7 ± 2.9 a | 65.4 ± 8.4 a | 5768(75.7) | — |
| ≥12 | 2044(21.1) | 4.4 ± 1.4 b | 11.6 ± 2.2 | 8.8 ± 1.9 b | 16.2 ± 4.6 | 12.4 ± 1.9 b | 13.2 ± 2.8 b | 66.7 ± 8.5 b | 1635(80.0) | 1.255(1.110~1.419) * |
| Food Consumption during the Past 7 Days | N (%) | Family Food Environment Score (Mean ± SD) | Total Score ≥ 60 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Socioeconomic Status | Family Food Availability | Family Feeding Patterns | Family Food Rules | Family Meal Practices | Caregiver’s Nutritional Literacy | Total Score | n (%) | ORs(95% CI) | ||
| Sugared soft drinks | ||||||||||
| None | 2812(29.0) | 4.2 ± 1.4 a | 12.1 ± 2.0 a | 8.9 ± 1.9 a | 17.0 ± 4.3 a | 12.6 ± 1.9 a | 13.2 ± 2.8 a | 67.0 ± 8.5 a | 2369(84.2) | — |
| Weekly | 6865(70.9) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.2 ± 2.1 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 15.8 ± 4.6 b | 12.2 ± 1.9 b | 12.6 ± 2.9 b | 64.7 ± 8.3 b | 5041(73.4) | 0.582(0.517~0.654) * |
| Fried food | ||||||||||
| None | 3155(32.6) | 4.3 ± 1.4 | 11.9 ± 2.1 a | 8.8 ± 1.9 a | 16.7 ± 4.3 a | 12.5 ± 1.9 a | 13.1 ± 2.9 a | 67.3 ± 8.3 a | 2581(81.8) | — |
| Weekly | 6526(67.4) | 4.3 ± 1.3 | 11.2 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 15.9 ± 4.6 b | 12.2 ± 1.9 b | 12.6 ± 2.9 b | 64.9 ± 8.4 b | 4834(74.1) | 0.723(0.649~0.806) * |
| Fast food | ||||||||||
| None | 4564(47.1) | 4.2 ± 1.3 a | 11.7 ± 2.1 a | 8.8 ± 1.9 a | 16.5 ± 4.4 a | 12.5 ± 1.9 a | 13.0 ± 2.9 a | 66.7 ± 8.3 a | 3640(79.8) | — |
| Weekly | 5119(52.8) | 4.3 ± 1.3 b | 11.2 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 1.9 b | 15.9 ± 4.6 b | 12.1 ± 1.9 b | 12.6 ± 2.9 b | 64.7 ± 8.4 b | 3777(73.8) | 0.738(0.670~0.814) * |
| Snacks | ||||||||||
| ≤6 days | 8412(86.8) | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 11.5 ± 2.1 a | 8.7 ± 1.9 a | 16.2 ± 4.5 a | 12.3 ± 1.9 a | 12.8 ± 2.9 | 65.8 ± 8.4 a | 6464(76.8) | — |
| Daily | 1272(13.1) | 4.4 ± 1.3 b | 11.3 ± 2.2 b | 8.6 ± 2.1 b | 15.7 ± 4.6 b | 12.1 ± 1.9 b | 12.9 ± 2.9 | 64.9 ± 8.5 b | 954(75.0) | 0.952(0.828~1.095) |
| Independent Variable | Daily Fruit Consumption | Daily Vegetable Consumption | Weekly Sugared Soft Drink Consumption | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | p | ORs (95%CI) | B | p | ORs (95%CI) | B | p | ORs (95%CI) | |
| constant term | −0.242 | 0.014 | 0.227 | 0.026 | 1.239 | <0.001 * | |||
| Grade | |||||||||
| 3~6 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| 7~9 | −0.212 | <0.001 * | 0.809(0.728~0.898) | 0.238 | <0.001 * | 1.269(1.135~1.418) | 0.491 | <0.001 * | 1.634(1.466~1.820) |
| 10~12 | −0.809 | <0.001 * | 0.445(0.400~0.495) | −0.012 | 0.840 | 0.989(0.884~1.105) | 0.633 | <0.001 * | 1.884(1.678~2.115) |
| Gender (Female) | 0.302 | <0.001 * | 1.352(1.241~1.473) | 0.257 | <0.001 * | 1.293(1.182~1.415) | −0.278 | <0.001 * | 0.757(0.692~0.828) |
| District (Suburb) | 0.209 | 0.555 | 1.209(0.935~1.132) | −0.093 | 0.071 | 0.911(0.823~1.008) | −0.026 | 0.614 | 0.975(0.882~1.077) |
| Number of children (≥2) | −0.067 | 0.152 | 0.935(0.853~1.025) | −0.033 | 0.506 | 0.968(0.879~1.065) | 0.001 | 0.989 | 1.001(0.909~1.101) |
| Principal caregiver (grandparents) | 0.317 | 0.071 | 1.373(0.974~1.937) | 0.047 | 0.791 | 1.048(0.741~1.482) | −0.214 | 0.220 | 0.807(0.573~1.137) |
| Caregiver’s education | |||||||||
| ≤Junior high school | — | — | — | — | |||||
| High school | 0.294 | <0.001 * | 1.341(1.174~1.532) | 0.111 | 0.116 | 1.118(0.973~1.284) | −0.004 | 0.961 | 0.996(0.857~1.158) |
| Junior college | 0.493 | <0.001 * | 1.637(1.422~1.885) | 0.261 | 0.001 * | 1.298(1.120~1.504) | −0.098 | 0.214 | 0.907(0.777~1.058) |
| ≥College | 0.608 | <0.001 * | 1.838(1.591~2.123) | 0.417 | <0.001 * | 1.517(1.303~1.766) | −0.290 | <0.001 * | 0.748(0.640~0.874) |
| Household income per capita (yuan) | |||||||||
| <20,000 | — | — | — | — | |||||
| 20,000~39,999 | 0.128 | 0.062 | 1.136(0.993~1.299) | 0.182 | 0.012 * | 1.199(1.042~1.381) | −0.035 | 0.634 | 0.965(0.834~1.117) |
| 40,000~69,999 | 0.193 | 0.004 * | 1.213(1.062~1.386) | 0.115 | 0.105 | 1.122(0.976~1.289) | 0.019 | 0.795 | 1.019(0.883~1.177) |
| ≥70,000 | 0.306 | <0.001 * | 1.358(1.186~1.555) | 0.123 | 0.088 | 1.131(0.982~1.302) | 0.154 | 0.037 * | 1.166(1.009~1.348) |
| Family food environment score (≥60) | 0.456 | <0.001 * | 1.578(1.428~1.744) | 0.338 | <0.001 * | 1.402(1.263~1.556) | −0.524 | <0.001 * | 0.592(0.526~0.667) |
| Independent Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | β | p | B | β | p | |
| constant term | 10.857 | <0.001 * | 10.554 | <0.001 * | ||
| Grade | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.013 * | 0.029 | 0.024 | 0.024 * |
| Gender | 0.087 | 0.013 | 0.200 | 0.061 | 0.009 | 0.363 |
| District | −0.222 | −0.031 | 0.003 * | −0.208 | −0.029 | 0.005 * |
| Number of children | 0.041 | 0.006 | 0.572 | 0.037 | 0.005 | 0.609 |
| Principal caregiver | −0.050 | −0.002 | 0.810 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 0.886 |
| Caregiver’s education | 0.314 | 0.100 | <0.001 * | 0.278 | 0.088 | <0.001 * |
| Household income | 0.093 | 0.030 | 0.006 * | 0.070 | 0.022 | 0.043 * |
| Family food environments | 0.092 | 0.226 | <0.001 * | — | — | — |
| Family socioeconomic status | — | — | — | 0.078 | 0.030 | 0.003 * |
| Family food availability | — | — | — | 0.219 | 0.137 | <0.001 * |
| Family feeding pattern | — | — | — | −0.017 | −0.009 | 0.343 |
| Family food rules | — | — | — | 0.038 | 0.050 | <0.001 * |
| Family meal practices | — | — | — | 0.141 | 0.079 | <0.001 * |
| Caregiver’s nutritional literacy | — | — | — | 0.111 | 0.093 | <0.001 * |
| F = 100.273, p < 0.05 | F = 71.574, p < 0.05 | |||||
| Independent Variable | B | p | ORs (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| constant term | 0.024 | 0.853 | |
| Grade | |||
| 3~6 | — | — | |
| 7~9 | −0.122 | 0.026 * | 0.885(0.794~0.986) |
| 10~12 | −0.342 | <0.001 * | 0.710(0.632~0.797) |
| Gender (Female) | −0.870 | <0.001 * | 0.419(0.383~0.458) |
| District (Suburb) | 0.299 | <0.001 * | 1.349(1.223~1.487) |
| Number of children (≥2) | −0.093 | 0.051 | 0.911(0.830~1.000) |
| Principal caregiver (grandparents) | −0.040 | 0.822 | 0.961(0.676~1.364) |
| Caregiver’s education | |||
| ≤Junior high school | — | — | |
| High school | 0.078 | 0.277 | 1.081(0.939~1.244) |
| Junior college | 0.151 | 0.044 * | 1.163(1.004~1.348) |
| ≥College | 0.094 | 0.223 | 1.098(0.944~1.278) |
| Caregiver’s weight status | |||
| Normal | — | — | |
| Overweight | 0.455 | <0.001 * | 1.576(1.429~1.737) |
| Obese | 0.823 | <0.001 * | 2.278 (1.973~2.631) |
| Wasted | −0.292 | 0.024 * | 0.747 (0.579~0.963) |
| Household income per capita | |||
| <20,000 | — | — | |
| 20,000~39,999 | −0.084 | 0.235 | 0.919(0.800~1.056) |
| 40,000~69,999 | −0.220 | 0.002 * | 0.803(0.699~0.922) |
| ≥70,000 | −0.302 | <0.001 * | 0.739(0.643~0.850) |
| Family food environments (≥ 60) | 0.122 | 0.026 * | 1.130(1.014~1.258) |
| Food consumption | |||
| Whole grains (daily) | −0.167 | 0.002 * | 0.846(0.761~0.941) |
| Fruits (daily) | 0.085 | 0.109 | 1.089(0.981~1.208) |
| Vegetables (daily) | −0.004 | 0.943 | 0.996(0.892~1.112) |
| Vitamin A-rich vegetables (daily) | −0.003 | 0.960 | 0.997(0.902~1.103) |
| Dairy products (daily) | 0.010 | 0.834 | 1.010(0.919~1.111) |
| Legumes (daily) | 0.179 | 0.011 * | 1.196(1.042~1.372) |
| Fungi and algae (weekly) | −0.040 | 0.488 | 0.960(0.857~1.077) |
| Fish (weekly) | −0.023 | 0.667 | 0.977(0.879~1.086) |
| Liver (weekly) | 0.017 | 0.733 | 1.017(0.923~1.121) |
| Sugared soft drinks (weekly) | 0.038 | 0.479 | 1.039(0.935~1.154) |
| Fried food (weekly) | −0.022 | 0.683 | 0.979(0.882~1.086) |
| Fast food (weekly) | −0.099 | 0.043 * | 0.905(0.822~0.997) |
| Breakfast (daily) | −0.086 | 0.137 | 0.918(0.819~1.028) |
| Snacks (daily) | −0.276 | <0.001 * | 0.759(0.662~0.869) |
| Food variety (≥12) | 0.092 | 0.099 | 1.096(0.983~1.223) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Yu, X.; Yu, Y.; Guo, D.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W. Family Food Environments and Their Association with Primary and Secondary Students’ Food Consumption in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091970
Zhang R, Yu X, Yu Y, Guo D, He H, Zhao Y, Zhu W. Family Food Environments and Their Association with Primary and Secondary Students’ Food Consumption in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091970
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rong, Xiaohui Yu, Yingjie Yu, Dandan Guo, Hairong He, Yao Zhao, and Wenli Zhu. 2022. "Family Food Environments and Their Association with Primary and Secondary Students’ Food Consumption in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091970
APA StyleZhang, R., Yu, X., Yu, Y., Guo, D., He, H., Zhao, Y., & Zhu, W. (2022). Family Food Environments and Their Association with Primary and Secondary Students’ Food Consumption in Beijing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 14(9), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091970





