The Effect of Enteral Immunonutrition in the Intensive Care Unit: Does It Impact on Outcomes?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
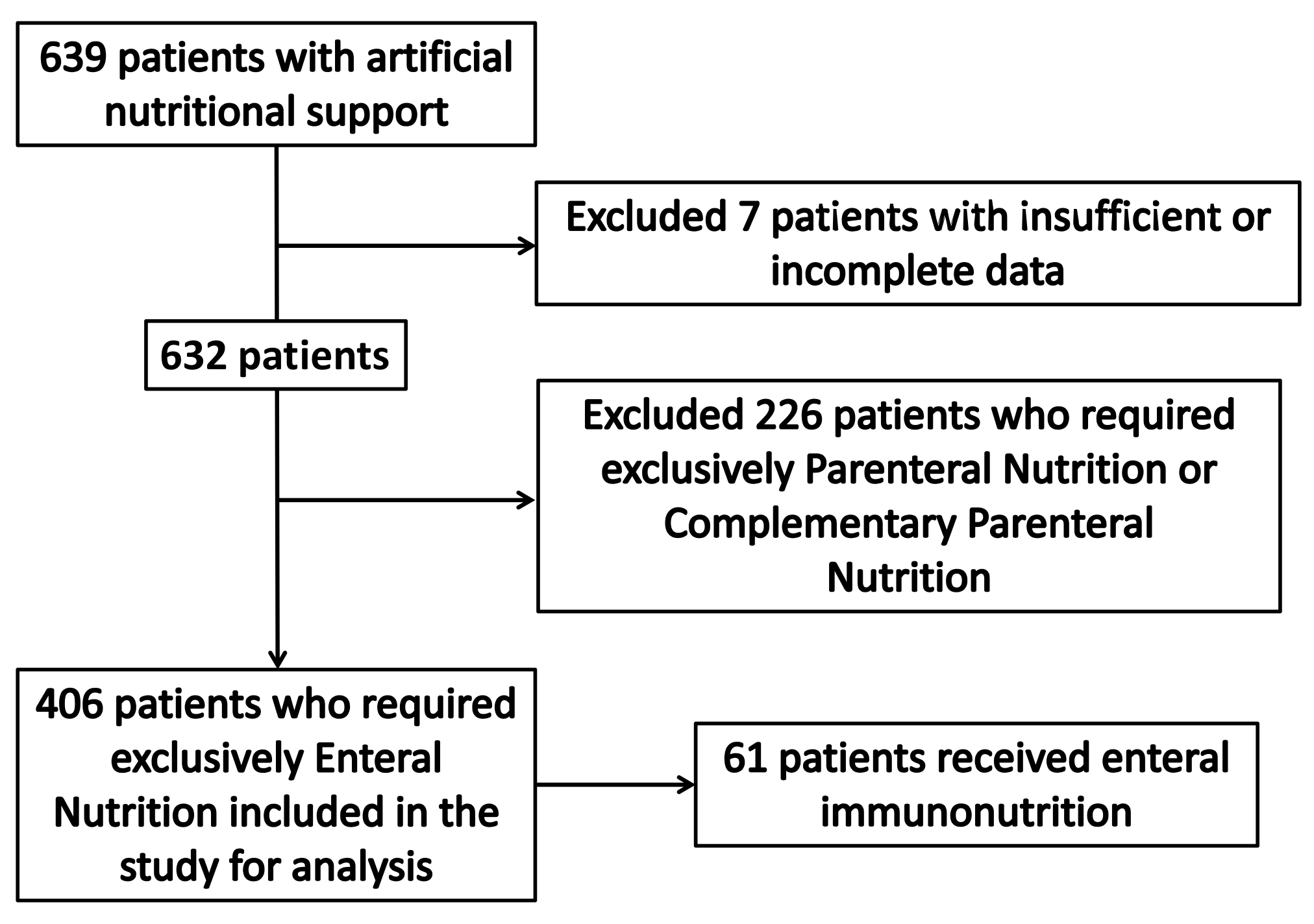
3.1. Population Included in the Study
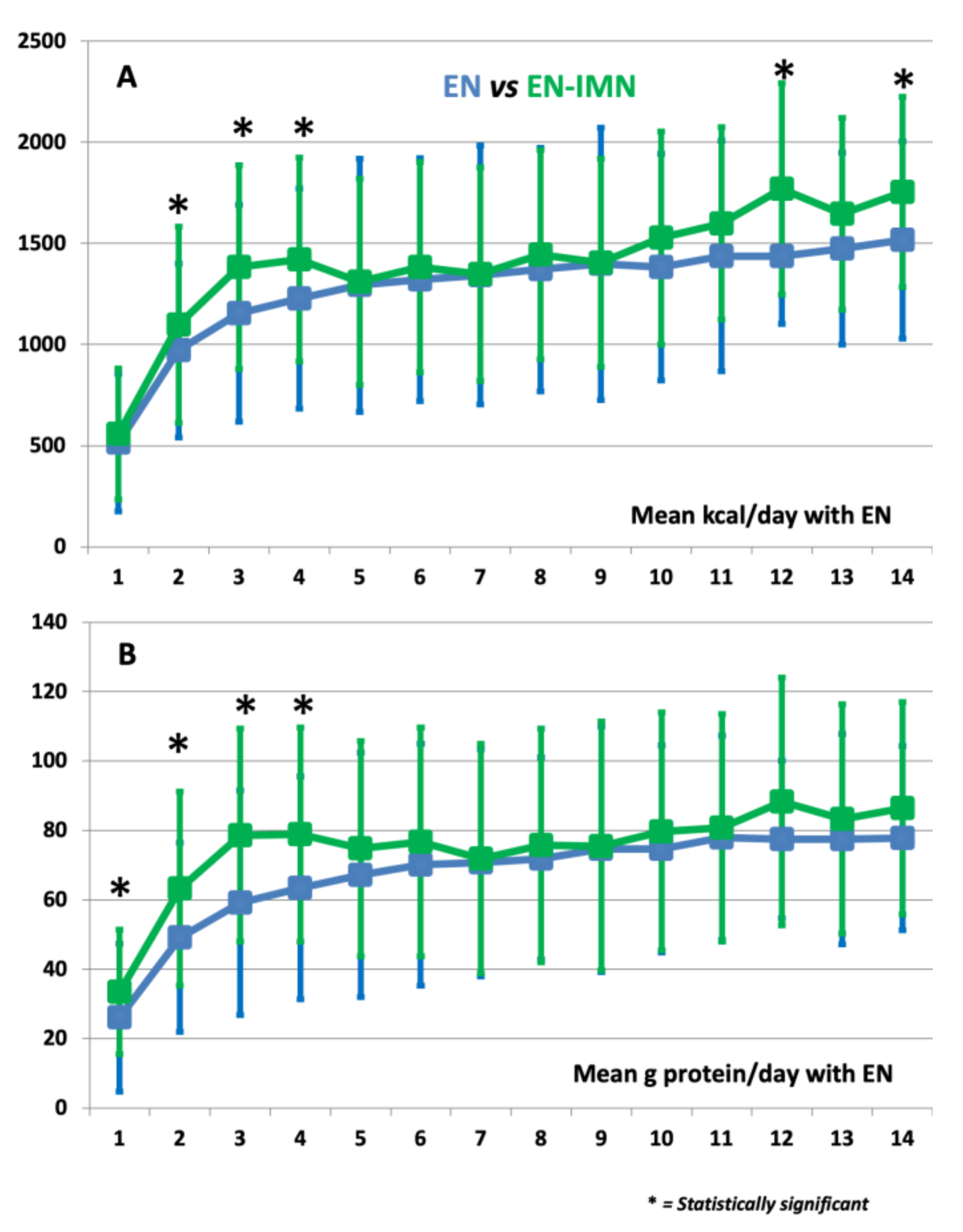
3.2. Univariate Analysis and Nutrition Delivery
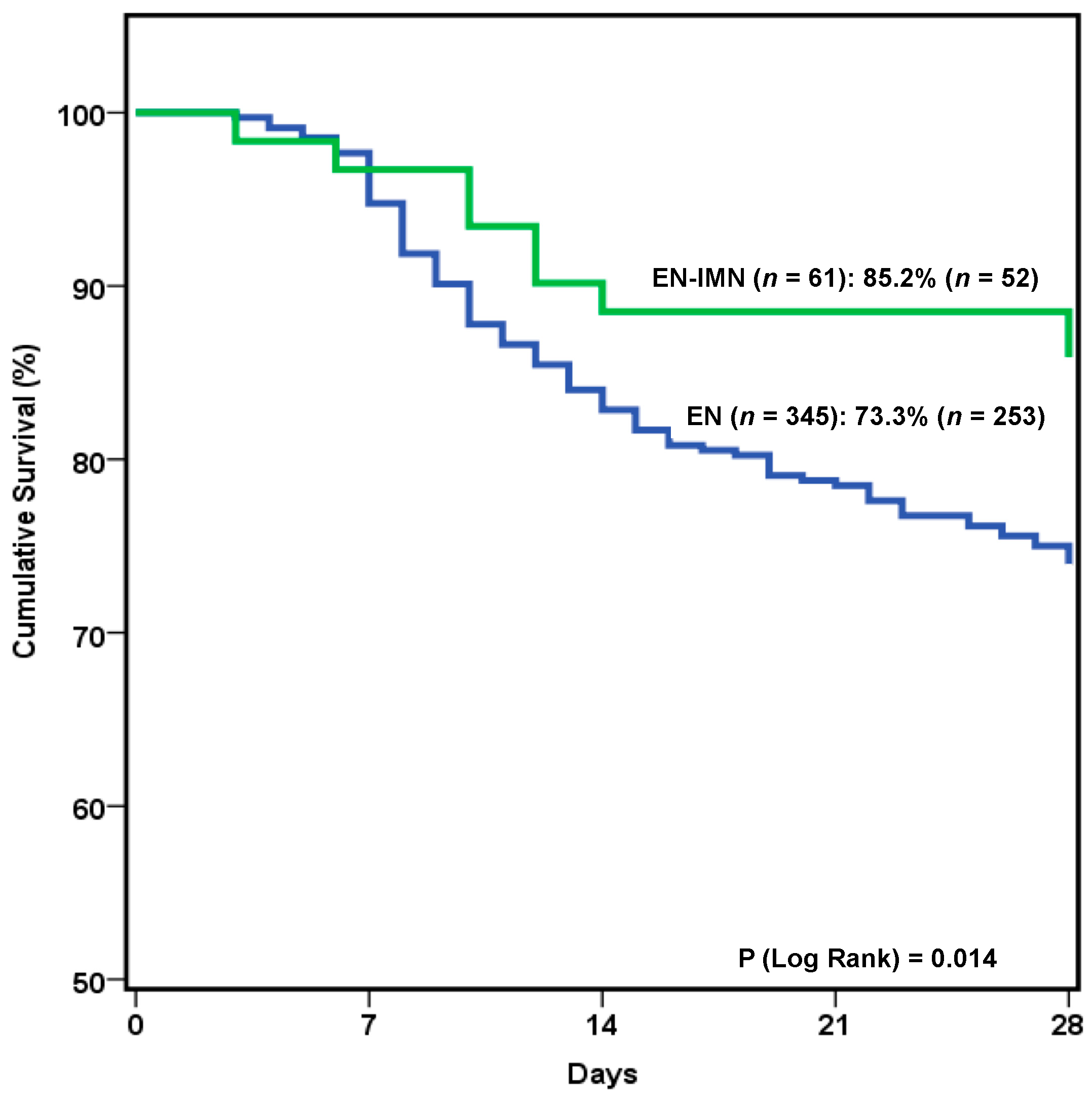
3.3. Outcome Results and Multivariate Analysis
3.4. Subgroup Analysis by Type of Patients and Laboratory Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Lew, C.C.H.; Yandell, R.; Fraser, R.J.L.; Chua, A.P.; Chong, M.F.F.; Miller, M. Association Between Malnutrition and Clinical Outcomes in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preiser, J.C.; Ichai, C.; Orban, J.C.; Groeneveld, A.B. Metabolic response to the stress of critical illness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.; et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abunnaja, S.; Cuviello, A.; Sanchez, J.A. Enteral and parenteral nutrition in the perioperative period: State of the art. Nutrients 2013, 5, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, M.S.; Martindale, R.G. Immunonutrition in Critical Illness: What Is the Role? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.J.; Miller, K.R.; Rosenthal, C.; Rosenthal, M.D. When Is It Appropriate to Use Arginine in Critical Illness? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.J.; Avenell, A.; Noble, D.W.; Campbell, M.K.; Croal, B.L.; Simpson, W.G.; Vale, L.D.; Battison, C.G.; Jenkinson, D.J.; Cook, J.A. Scottish Intensive care Glutamine or seleNium Evaluative Trial Trials Group. Randomised trial of glutamine, selenium, or both, to suplement parenteral nutrition for critically ill patients. BMJ 2011, 342, d1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyland, D.; Muscedere, J.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Cook, D.; Jones, G.; Albert, M.; Elke, G.; Berger, M.M.; Day, A.G.; Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. A randomized trial of glutamine and antioxidants in critically ill patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, T.W.; Wheeler, A.P.; Thompson, B.T.; de Boisblanc, B.P.; Steingrub, J.; Rock, P.; NIH NHLBI Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network of Investigators. Enteral omega-3 fatty acid, γ-linolenic acid, and antioxidant supplementation in acute lung injury. JAMA 2011, 306, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zanten, A.R.H.; Sztark, F.; Kaisers, U.X.; Zielmann, S.; Felbinger, T.W.; Sablotzki, A.R.; De Waele, J.J.; Timsit, J.F.; Honing, M.L.; Keh, D.; et al. High-protein enteral nutrition enriched with immune-modulating nutrients vs Standard high-protein enteral nutrition and nosocomial infections in the ICU: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montejo, J.C.; Zarazaga, A.; Lopez-Martinez, J.; Urrútia, G.; Roqué, M.; Blesa, A.L.; Celaya, S.; Conejero, R.; Galbán, C.; García de Lorenzo, A.; et al. Spanish Society of Intensive Care Medicine and Coronary Units. Immunonutrition in the intensive care unit: A systematic review and consensus statement. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serviá Goixart, L.; López Delgado, J.C.; Grau Carmona, T. Evaluation of the degree of adherence to the nutritional recommendations in critical care patients. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma-Milla, S.; López-Plaza, B.; Santamaría, B.; de Arriba-Sánchez, A.; Bermejo, L.M.; Gómez-Candela, C. New, Immunomodulatory, Oral Nutrition Formula for Use Prior to Surgery in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: An Exploratory Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Velez, V.; Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Betancur-Zambrano, N.L.; Lopez-Suñe, N.; Rojas-Lora, M.; Torrado, H.; Ballus, J. The inflammatory response in cardiac surgery: An overview of the pathophysiology and clinical implications. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2015, 13, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, E.J.; Ma, K.C.; Murthy, S.B.; Choi, A.M.K. Danger Signals in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, A.; Zuege, D.J.; Fick, G.H.; Niven, D.J.; Berthiaume, L.R.; Stelfox, H.T.; Doig, C.J. Describing organ dysfunction in the intensive care unit: A cohort study of 20,000 patients. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drover, J.W.; Dhaliwal, R.; Weitzel, L.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Ochoa, J.B.; Heyland, D.K. Perioperative Use of Arginine-Supplemented Diets: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2011, 212, 385–399.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Drover, J.W.; Heyland, D.K. Clinical Evidence for Pharmaconutrition in Major Elective Surgery. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37 (Suppl. 5), 66S–72S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving Inflammation: Dual Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Resolution Lipid Mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Esteve, F.; Torrado, H.; Rodríguez-Castro, D.; Carrio, M.L.; Farrero, E.; Javierre, C.; Ventura, J.L.; Manez, R. Influence of acute kidney injury on short- and long-term outcomes in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: Risk factors and prognostic value of a modified RIFLE classification. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, H.; Ince, C.; De Backer, D.; Pickkers, P.; Payen, D.; Hotchkiss, J.; Kellum, J.A. A Unified Theory of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Inflammation, Microcirculatory Dysfunction, Bioenergetics, and the Tubular Cell Adaptation to Injury. Shock 2014, 41, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanmassenhove, J.; Kielstein, J.; Jörres, J.; Van Biesen, W. Management of Patients at Risk of Acute Kidney Injury. Lancet 2017, 389, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. Diet and Inflammation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa Gautier, J.B.; Martindale, R.G.; Rugeles, S.J.; Hurt, R.T.; Taylor, B.; Heyland, D.K.; McClave, S.A. How Much and What Type of Protein Should a Critically Ill Patient Receive? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32 (Suppl. 1), 6S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, U. Nutritional Laboratory Markers in Malnutrition. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, P.; Theilla, M.; Singer, P. Lipid Metabolism in Critical Illness. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary Lipids, Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Baseline Characteristics and Comorbidities | ||
| Mean age (years) | 60.8 ± 15 | |
| Sex (male) | 67.4% (274) | |
| BMI (Kg·m−2) | 28.2 ± 6.3 | |
| Alcohol | 12.81% (52) | |
| Diabetes | 25.37% (103) | |
| Hypertension | 42.36% (172) | |
| COPD | 17.98% (73) | |
| AMI | 15.02% (61) | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 5.42% (22) | |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 10.34% (42) | |
| Immunosuppression | 10.34% (42) | |
| Neoplasia | 15.27% (62) | |
| Type of patient | Medical | 71.18% (289) |
| Trauma | 15.02% (61) | |
| Surgery | 13.79% (56) | |
| APACHE II | 20 (15–25) | |
| SAPS II | 48.35 ± 17.39 | |
| SOFA (on admission) | 7.07 ± 3.2 | |
| Malnutrition (based on SGA) | 34.41% (139) | |
| mNUTRIC Score | 3.97 ± 2.15 | |
| Characteristics of nutritional support | ||
| Patients with IMN | 15.02% (61) | |
| Early enteral nutrition (<48 h) | 76.8% (310) | |
| Mean EN administration (days) | 8.5 (4–17) | |
| Mean Kcal/Kg/day * | 15.4 ± 5.2 | |
| Mean g protein/Kg/day * | 0.75 ± 0.34 | |
| EN-related complications | ↑ GRV | 11.4% (46) |
| Diarrhea | 8.6% (35) | |
| Vomiting | 1.2% (5) | |
| Aspiration | 0 | |
| Mesenteric ischemia | 0.74% (3) | |
| Outcomes | ||
| Mechanical ventilation | 97.54% (396) | |
| Days on mechanical ventilation | 13.2 ± 13.8 | |
| Vasopressor support | 73.4% (298) | |
| Days on vasopressor support | 3.26 ± 3.53 | |
| RRT needs | 10.1% (41) | |
| Respiratory tract infection | 25.12% (102) | |
| Catheter-related infections | 6.4% (26) | |
| Mean ICU stay (days) | 13 (8–22) | |
| Mean hospital stay (days) | 25 (16–42) | |
| 28-day mortality | 24.9% (101) | |
| EN n = 345 (84.98%) | EN-IMN n = 61 (15.02%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics and comorbidities | ||||
| Mean age (years) | 61.45 ± 15.13 | 56.7 ± 16.35 | 0.03 | |
| Sex (male) | 64.93% (224) | 81.97% (50) | 0.01 | |
| BMI (Kg·m−2) | 27.24 (24.23–31.15) | 26.24 (23.44–29.33) | 0.07 | |
| Alcohol | 13.04% (45) | 11.48% (7) | 0.89 | |
| Diabetes | 25.8% (89) | 22.95% (14) | 0.75 | |
| Hypertension | 43.77% (151) | 34.43% (21) | 0.22 | |
| COPD | 20.29% (70) | 4.92% (3) | 0.003 | |
| AMI | 14.78% (51) | 16.39% (10) | 0.89 | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 5.51% (19) | 4.92% (3) | 0.99 | |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 10.14% (35) | 11.48% (7) | 0.93 | |
| Immunosuppression | 11.01% (38) | 6.56% (4) | 0.36 | |
| Neoplasia | 14.49% (50) | 19.67% (12) | 0.33 | |
| Type of patient | Medical | 75.94% (262) | 44.26% (27) | <0.001 |
| Trauma | 11.59% (40) | 34.43% (21) | ||
| Surgery | 12.46% (43) | 21.31% (13) | ||
| APACHE II | 20 (15–25) | 18 (13–23) | 0.06 | |
| SAPS II | 49.01 ± 17.43 | 44.12 ± 16.7 | 0.06 | |
| SOFA (on admission) | 7.21 ± 3.24 | 6.26 ± 2.87 | 0.03 | |
| Malnutrition (based on SGA) | 35.76% (123) | 26.67% (16) | 0.22 | |
| mNUTRIC Score | 4.08 ± 2.16 | 3.35 ± 2.05 | 0.02 | |
| Characteristics of nutritional support | ||||
| Early enteral nutrition (<48 h) | 73.9% (255) | 90.1% (55) | 0.15 | |
| Mean of EN administration (days) | 8 (4–17) | 9 (4–18) | 0.557 | |
| Mean Kcal/Kg/day * | 14.4 ± 5.69 | 16.24 ± 5.31 | 0.01 | |
| Mean g protein/Kg/day * | 0.74 ± 0.34 | 0.9 ± 0.31 | <0.001 | |
| EN-related complications | ↑ GRV | 11.30% (39) | 11.47% (7) | 0.89 |
| Diarrhea | 7.83% (27) | 13.11% (8) | 0.21 | |
| Vomiting | 1.16% (4) | 0.2% (1) | 0.56 | |
| Aspiration | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Mesenteric ischemia | 0.87% (3) | 0% (0) | 0.99 | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 97.68% (337) | 96.72% (59) | 0.65 | |
| Days on mechanical ventilation | 13.39 ± 13.88 | 12.38 ± 13.96 | 0.73 | |
| Vasopressor support | 75.65% (261) | 60.66% (37) | 0.02 | |
| Days on vasopressor support | 3.27 ± 3.48 | 3.21 ± 3.85 | 0.45 | |
| RRT needs | 11.59% (40) | 1.64% (1) | 0.03 | |
| Respiratory tract infection | 26.09% (90) | 19.67% (12) | 0.36 | |
| Catheter-related infections | 6.67% (23) | 4.92% (3) | 0.78 | |
| Mean ICU stay (days) | 14 (9–23) | 14 (8–21) | 0.69 | |
| Mean hospital stay (days) | 25 (16–41.5) | 27.5 (16–47.5) | 0.29 | |
| 28-day mortality | 26.67% (92) | 14.75% (9) | 0.07 | |
| Day | Mean kcal/day | Mean g Protein/day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN | EN-IMN | p | EN | EN-IMN | p | |
| 1 | 515 ± 324 | 557 ± 341 | 0.35 | 26.1 ± 17.9 | 33.5 ± 21.3 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 971 ± 485 | 1099 ± 430 | 0.04 | 49.2 ± 27.9 | 63.2 ± 27.3 | <0.001 |
| 3 | 1155 ± 503 | 1383 ± 536 | 0.003 | 59.1 ± 30.7 | 78.6 ± 32.3 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 1228 ± 504 | 1420 ± 544 | 0.02 | 63.4 ± 30.9 | 78.8 ± 32.1 | 0.002 |
| 5 | 1293 ± 509 | 1310 ± 625 | 0.85 | 67.2 ± 31 | 74.8 ± 35.2 | 0.13 |
| 6 | 1322 ± 520 | 1382 ± 601 | 0.54 | 70.1 ± 32.9 | 76.7 ± 34.8 | 0.24 |
| 7 | 1344 ± 527 | 1348 ± 639 | 0.97 | 70.7 ± 33.1 | 71.9 ± 32.7 | 0.83 |
| 8 | 1371 ± 518 | 1445 ± 602 | 0.42 | 71.9 ± 33.7 | 75.7 ± 29.1 | 0.51 |
| 9 | 1399 ± 515 | 1404 ± 673 | 0.96 | 74.6 ± 35.8 | 75.5 ± 35.4 | 0.88 |
| 10 | 1383 ± 526 | 1527 ± 560 | 0.15 | 74.7 ± 34.3 | 79.7 ± 29.8 | 0.39 |
| 11 | 1438 ± 476 | 1599 ± 569 | 0.10 | 77.9 ± 32.8 | 80.8 ± 29.4 | 0.63 |
| 12 | 1437 ± 523 | 1770 ± 336 | 0.003 | 77.4 ± 35.7 | 88.3 ± 22.7 | 0.05 |
| 13 | 1475 ± 475 | 1647 ± 474 | 0.12 | 77.5 ± 33 | 83.3 ± 30.3 | 0.43 |
| 14 | 1517 ± 471 | 1755 ± 487 | 0.07 | 77.8 ± 30.6 | 86.4 ± 26.5 | 0.27 |
| Dependent Variable—Use of IMN | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value |
| Type of patient (trauma) | 1.490 (0.630–3.640) | 0.37 |
| Mean protein delivery (g·Kg−1·day−1) * | 6.230 (2.590–15.541) | <0.001 |
| Vasopressor support | 0.440 (0.230–0.845) | 0.012 |
| RRT Needs | 0.432 (0.231–0.850) | 0.049 |
| A | EN n= 83 (70.94%) | EN-IMN n = 34 (29.06%) | p-Value | |
| Baseline characteristics and comorbidities | ||||
| Mean age (years) | 59.59 ± 18.2 | 53.09 ± 17.53 | 0.061 | |
| Sex (male) | 72.29% (60) | 94.12% (32) | 0.012 | |
| BMI (Kg·m−2) | 27.29 (25.21–30.55) | 25.91 (23.44–27.78) | 0.036 | |
| Alcohol | 10.84% (9) | 8.82% (3) | 0.95 | |
| Diabetes | 19.28% (16) | 20.59% (7) | 0.99 | |
| Hypertension | 43.37% (36) | 20.59% (7) | 0.035 | |
| COPD | 13.25% (11) | 0 | 0.032 | |
| AMI | 10.84% (9) | 20.59% (7) | 0.27 | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 0 | 2.94% (1) | 0.29 | |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 9.64% (8) | 11.76% (4) | 0.89 | |
| Immunosuppression | 1.2% (1) | 5.88% (2) | 0.20 | |
| Neoplasia | 13.25% (11) | 17.65% (6) | 0.57 | |
| APACHE II | 18 (13–23.5) | 17.5 (12–22.75) | 0.83 | |
| SAPS II | 45.85 ± 16.51 | 43 ± 19.15 | 0.29 | |
| SOFA (on admission) | 7.25 ± 3.08 | 6.35 ± 2.88 | 0.13 | |
| Malnutrition (based on SGA) | 22.89% (19) | 18.18% (6) | 0.80 | |
| mNUTRIC Score | 3.55 ± 2.26 | 3.12 ± 2.19 | 0.37 | |
| Characteristics of nutritional support | ||||
| Early enteral nutrition (<48 h) | 78.3% (65) | 91% (31) | 0.26 | |
| Mean of EN administration (days) | 8 (3.5–17.5) | 9.5 (4–17.75) | 0.38 | |
| Mean Kcal/Kg/day * | 13.12 ± 5.74 | 17.09 ± 4.06 | <0.001 | |
| Mean g protein/Kg/day * | 0.66 ± 0.33 | 0.97 ± 0.26 | <0.001 | |
| EN-related complications | ↑ GRV | 9.64% (8) | 11.7% (4) | 0.45 |
| Diarrhea | 7.23% (6) | 17.65% (6) | 0.10 | |
| Vomiting | 1.2% (1) | 0 | 0.99 | |
| Aspiration | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Mesenteric ischemia | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 100% (83) | 100% (34) | NA | |
| Days on mechanical ventilation | 13.35 ± 11.56 | 10.79 ± 6.45 | 0.63 | |
| Vasopressor support | 77.1% (64) | 67.6% (23) | 0.16 | |
| Days on vasopressor support | 4.79 ± 4.18 | 3.04 ± 3.29 | 0.23 | |
| RRT needs | 9.6% (8) | 2.9% (1) | 0.28 | |
| Respiratory tract infection | 22.9% (19) | 17.6% (6) | 0.62 | |
| Catheter-related infections | 7.2% (6) | 2.9% (1) | 0.67 | |
| Mean ICU stay (days) | 14 (8–22.5) | 14.5 (8–21) | 0.70 | |
| Mean hospital stay (days) | 26 (16.5–38) | 32 (21.75–45.25) | 0.21 | |
| 28-day mortality | 19.28% (16) | 2.94% (1) | 0.022 | |
| B | EN n = 262 (90.66%) | EN-IMN n = 27 (9.34%) | p-Value | |
| Baseline characteristics and comorbidities | ||||
| Mean age (years) | 62.04 ± 14.01 | 61.26 ± 13.73 | 0.68 | |
| Sex (male) | 62.6% (164) | 66.67% (18) | 0.83 | |
| BMI (Kg·m−2) | 27.2 (24.22–31.55) | 26.35 (23.96–31.03) | 0.69 | |
| Alcohol | 13.74% (36) | 14.81% (4) | 0.77 | |
| Diabetes | 27.86% (73) | 25.93% (7) | 0.97 | |
| Hypertension | 43.89% (115) | 51.85% (14) | 0.54 | |
| COPD | 22.52% (59) | 11.11% (3) | 0.22 | |
| AMI | 16.03% (42) | 11.11% (3) | 0.78 | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 7.25% (19) | 7.41% (2) | 0.98 | |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 10.31% (27) | 11.11% (3) | 0.08 | |
| Immunosuppression | 14.12% (37) | 7.41% (2) | 0.55 | |
| Neoplasia | 14.89% (39) | 22.22% (6) | 0.39 | |
| APACHE II | 21 (16–26) | 19 (14–23.5) | 0.22 | |
| SAPS II | 50.02 ± 17.63 | 45.38 ± 13.73 | 0.34 | |
| SOFA (on admission) | 7.19 ± 3.29 | 6.15 ± 2.92 | 0.09 | |
| Malnutrition (based on SGA) | 39.85% (104) | 37.04% (10) | 0.93 | |
| mNUTRIC Score | 4.25 ± 2.1 | 3.63 ± 1.86 | 0.12 | |
| Characteristics of nutritional support | ||||
| Early enteral nutrition (<48 h) | 72.5% (190) | 88.80% (24) | 0.28 | |
| Mean of EN administration (days) | 8 (4–17.75) | 9 (3.5–17.5) | 0.90 | |
| Mean Kcal/Kg/day * | 13.81 ± 4.62 | 15.16 ± 6.48 | 0.52 | |
| Mean g protein/Kg/day * | 0.71 ± 0.32 | 0.83 ± 0.39 | 0.10 | |
| EN-related complications | ↑ GRV | 11.83% (31) | 11.11% (3) | 0.87 |
| Diarrhea | 8.02% (21) | 7.41% (2) | 0.98 | |
| Vomiting | 1.15% (3) | 3.7% (1) | 0.32 | |
| Aspiration | 0 | 0 | NA | |
| Mesenteric ischemia | 1.15% (3) | 0 | 0.99 | |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 96.95% (254) | 92.59% (25) | 0.23 | |
| Days on mechanical ventilation | 13.4 ± 14.58 | 14.62 ± 20.36 | 0.76 | |
| Vasopressor support | 75.2% (197) | 51.8% (14) | 0.018 | |
| Days on vasopressor support | 3.35 ± 3.54 | 2.48 ± 3.32 | 0.11 | |
| RRT needs | 12.2% (32) | 0 | 0.04 | |
| Respiratory tract infection | 27.1% (71) | 22.22% (6) | 0.65 | |
| Catheter-related infections | 6.49% (17) | 7.41% (2) | 0.69 | |
| Mean ICU stay (days) | 13 (9–23) | 13 (9–19.5) | 0.86 | |
| Mean hospital stay (days) | 25 (15–42) | 22.5 (12.75–53.5) | 0.93 | |
| 28-day mortality | 29.01% (76) | 29.6% (8) | 0.98 | |
| Dependent Variable—Use of IMN | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Trauma and Surgical | ||
| Mean protein delivery (g·Kg−1·day−1) * | 5.711 (2.876–6.892) | 0.02 |
| Vasopressor support | 0.850 (0.641–1.278) | 0.19 |
| In-hospital mortality | 1.012 (0.929–1.129) | 0.09 |
| Medical | ||
| Mean protein delivery (g·Kg−1·day−1) * | 4.630 (3.041–6.801) | 0.001 |
| Vasopressor support | 0.687 (0.520–1.181) | 0.11 |
| RRT needs | 0.905 (0.850–1.620) | 0.35 |
| EN | EN-IMN | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum protein | ||||
| Albumin (mg·dL−1) | Day 1 | 30.37 ± 6.08 | 33.57 ± 7.18 | 0.002 |
| Day 3 | 28.17 ± 5.39 | 29.12 ± 5.70 | 0.35 | |
| Day 7 | 27.78 ± 5.83 | 28.04 ± 5.35 | 0.81 | |
| ICU discharge | 29.88 ± 6.09 | 29.73 ± 5.66 | 0.88 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | −3.85 ± 5.83 | −4.48 ± 6.17 | 0.001 | |
| Prealbumin (mg·L−1) | Day 1 | 153.28 ± 81.05 | 178.77 ± 50.14 | 0.04 |
| Day 3 | 150.43 ± 80.31 | 150.28 ± 56.90 | 0.99 | |
| Day 7 | 213.14 ± 110.06 | 201.78 ± 92.87 | 0.68 | |
| ICU discharge | 216.28 ± 92.82 | 207.64 ± 102.97 | 0.75 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 59.47 ± 101.54 | 31.27 ± 97.55 | 0.38 | |
| Total Protein (g·dL−1) | Day 1 | 5.72 ± 0.87 | 5.96 ± 0.96 | 0.12 |
| Day 3 | 5.29 ± 0.75 | 5.47 ± 0.81 | 0.25 | |
| Day 7 | 5.37 ± 0.76 | 5.35 ± 0.91 | 0.91 | |
| ICU discharge | 5.81 ± 0.97 | 6.13 ± 0.81 | 0.04 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 0.29 ± 1.12 | 0.78 ± 0.92 | 0.27 | |
| Lipid profile | ||||
| Total Cholesterol (mg·dL−1) | Day 1 | 132 ± 39 | 136 ± 41 | 0.58 |
| Day 3 | 128 ± 42 | 132 ± 32 | 0.63 | |
| Day 7 | 143 ± 41 | 127 ± 36 | 0.16 | |
| ICU discharge | 156 ± 49 | 144 ± 45 | 0.35 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 21 ± 52 | 7.9 ± 30 | 0.17 | |
| HDL (mg·dL−1) | Day 1 | 38.1 ± 18.9 | 38.1 ± 15.1 | 0.98 |
| Day 3 | 60.9 ± 26.2 | 77.1 ± 13.6 | 0.50 | |
| Day 7 | 33.9 ± 19.7 | 25.9 ± 11.2 | 0.18 | |
| ICU discharge | 34.03 ± 17.2 | 31.5 ± 7 | 0.59 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | −2.8 ± 6.8 | 1.5 ± 8.9 | 0.26 | |
| LDL (mg·dL−1) | Day 1 | 65.8 ± 31.4 | 75.9 ± 32.9 | 0.16 |
| Day 3 | 158.9 ± 25.7 | 246.1 ± 43.7 | 0.37 | |
| Day 7 | 84.3 ± 49.4 | 69.4 ± 25.1 | 0.35 | |
| ICU discharge | 91.4 ± 39.6 | 87.7 ± 44.3 | 0.75 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 25.7 ± 13.5 | 2.5 ± 23.5 | 0.03 | |
| Triglycerides (mg·dL−1) | Day 1 | 135 ± 73 | 128 ± 69 | 0.61 |
| Day 3 | 156 ± 99 | 133 ± 47 | 0.08 | |
| Day 7 | 168 ± 104 | 160 ± 107 | 0.77 | |
| ICU discharge | 160 ± 89 | 136 ± 64 | 0.20 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 26 ± 106 | −10 ± 39 | 0.02 | |
| Inflammatory markers | ||||
| CRP (mg·L−1) | Day 1 | 26.65 ± 45.89 | 54.82 ± 76.97 | 0.07 |
| Day 3 | 77.34 ± 106.35 | 91.55 ± 148.97 | 0.54 | |
| Day 7 | 95.51 ± 120.77 | 67.96 ± 125.95 | 0.17 | |
| ICU discharge | 58.11 ± 77.22 | 77.30 ± 62.61 | 0.25 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | −64.41 ± 140.70 | −17.12 ± 91.08 | 0.11 | |
| Leukocytes (×109·L−1) | Day 1 | 14.69 ± 6.27 | 13.84 ± 5.29 | 0.18 |
| Day 3 | 10.61 ± 5.28 | 9.54 ± 4.46 | 0.04 | |
| Day 7 | 8.8 ± 6.12 | 10.1 ± 5.65 | 0.18 | |
| ICU discharge | 11.15 ± 5.59 | 9.72 ± 3.26 | 0.11 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | −2.5 ± 7.3 | −2.7 ± 5.5 | 0.84 | |
| Lymphocytes (×109·L−1) | Day 1 | 1.77 ± 1.42 | 1.69 ± 0.92 | 0.58 |
| Day 3 | 1.59 ± 1.66 | 1.09 ± 0.76 | 0.37 | |
| Day 7 | 0.92 ± 0.6 | 1.22 ± 0.84 | 0.30 | |
| ICU discharge | 1.56 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 0.65 | 0.15 | |
| Δ (day 1-ICU discharge) | 0.096 ± 1.49 | −0.003 ± 1.10 | 0.63 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Grau-Carmona, T.; Trujillano-Cabello, J.; García-Fuentes, C.; Mor-Marco, E.; Bordeje-Laguna, M.L.; Portugal-Rodriguez, E.; Lorencio-Cardenas, C.; Vera-Artazcoz, P.; Macaya-Redin, L.; et al. The Effect of Enteral Immunonutrition in the Intensive Care Unit: Does It Impact on Outcomes? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091904
Lopez-Delgado JC, Grau-Carmona T, Trujillano-Cabello J, García-Fuentes C, Mor-Marco E, Bordeje-Laguna ML, Portugal-Rodriguez E, Lorencio-Cardenas C, Vera-Artazcoz P, Macaya-Redin L, et al. The Effect of Enteral Immunonutrition in the Intensive Care Unit: Does It Impact on Outcomes? Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091904
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Delgado, Juan Carlos, Teodoro Grau-Carmona, Javier Trujillano-Cabello, Carlos García-Fuentes, Esther Mor-Marco, Maria Luisa Bordeje-Laguna, Esther Portugal-Rodriguez, Carol Lorencio-Cardenas, Paula Vera-Artazcoz, Laura Macaya-Redin, and et al. 2022. "The Effect of Enteral Immunonutrition in the Intensive Care Unit: Does It Impact on Outcomes?" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091904
APA StyleLopez-Delgado, J. C., Grau-Carmona, T., Trujillano-Cabello, J., García-Fuentes, C., Mor-Marco, E., Bordeje-Laguna, M. L., Portugal-Rodriguez, E., Lorencio-Cardenas, C., Vera-Artazcoz, P., Macaya-Redin, L., Martinez-Carmona, J. F., Mateu-Campos, L., Gero-Escapa, M., Gastaldo-Simeon, R., Vila-García, B., Flordelis-Lasierra, J. L., Montejo-Gonzalez, J. C., Servia-Goixart, L., & the ENPIC Study Group. (2022). The Effect of Enteral Immunonutrition in the Intensive Care Unit: Does It Impact on Outcomes? Nutrients, 14(9), 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091904







