Enhanced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Cells of Soluble Longan Polysaccharides with a Covalent Chemical Selenylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regents and Materials
2.2. Extraction and Selenylation of Longan Polysaccharides
2.3. Cell Culture and Assay of Growth Inhibition
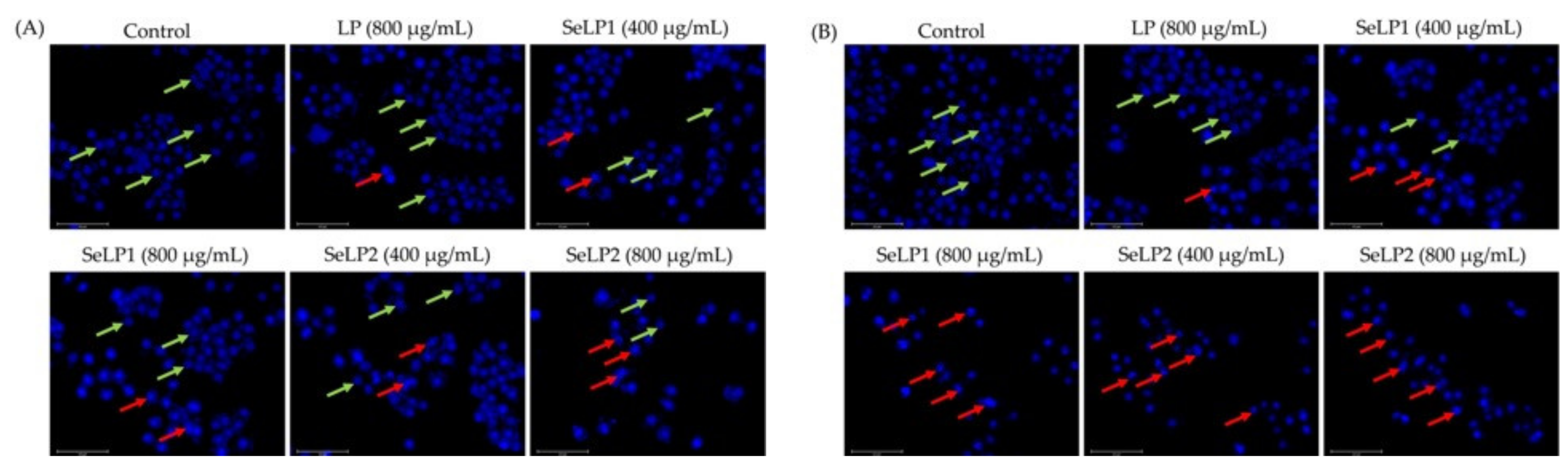
2.4. Hoechst 33258 Staining
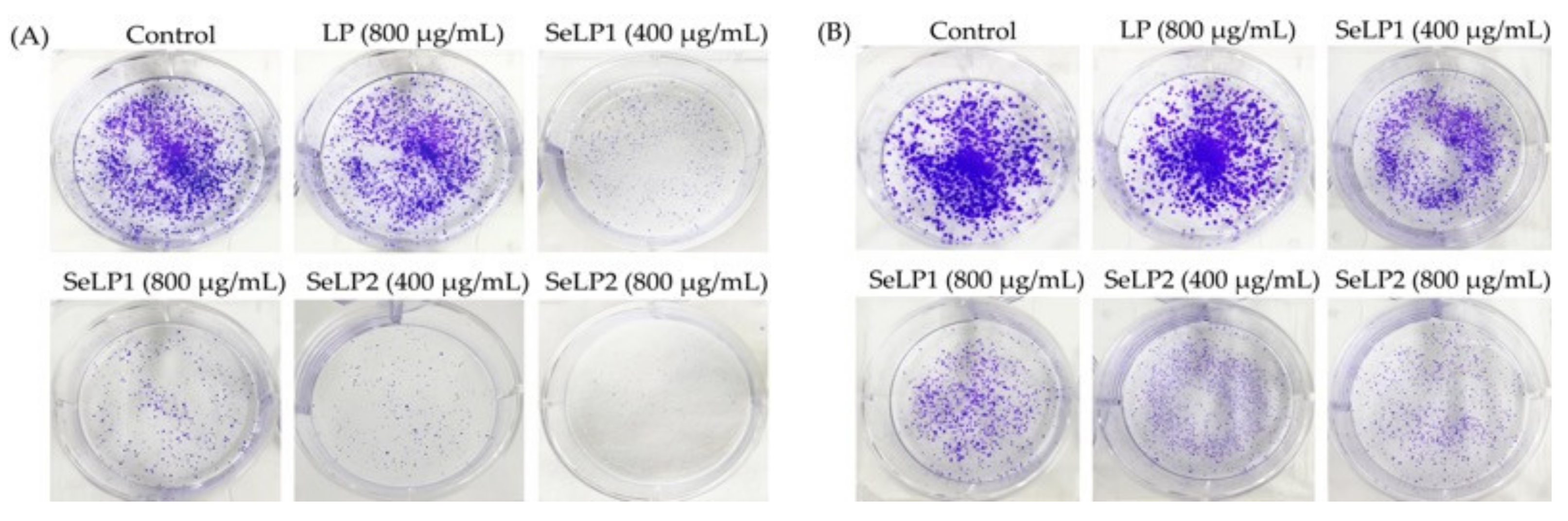
2.5. Assay of Cell Colony Formation
2.6. Analysis of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, Intracellular ROS, and Ca2+
2.7. Assay of Cell Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
2.9. Assay of Western-Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
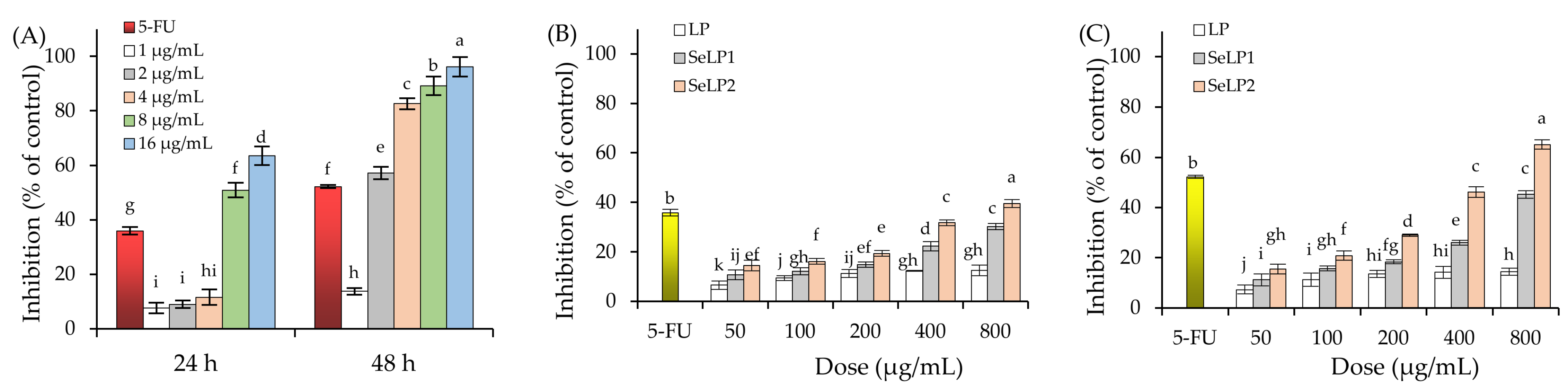
3.1. Growth Inhibition of Polysaccharide Samples on the Cells
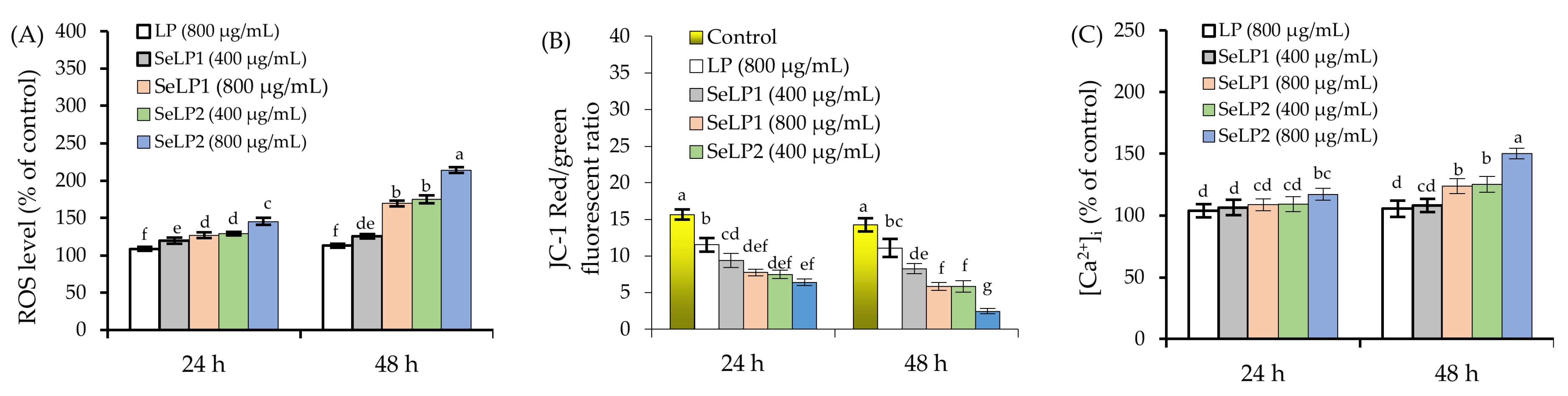
3.2. Intracellular ROS, Ca2+, and MMP Loss in Response to Polysaccharide Samples
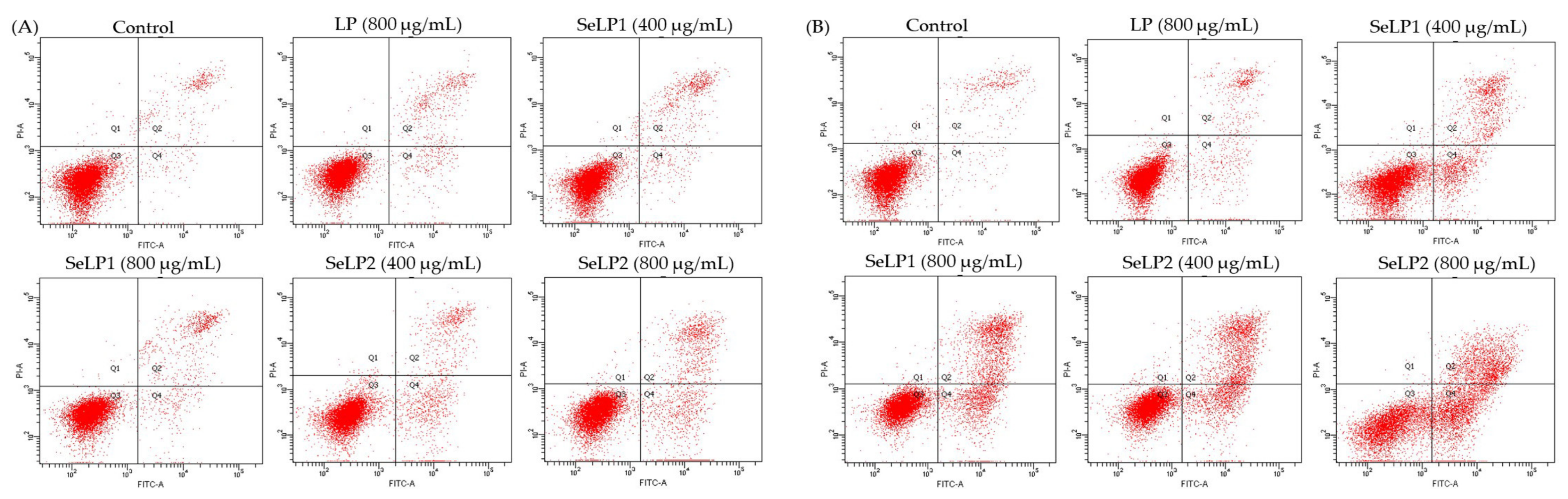
3.3. Apoptosis Induction of Polysaccharide Samples to the Cells
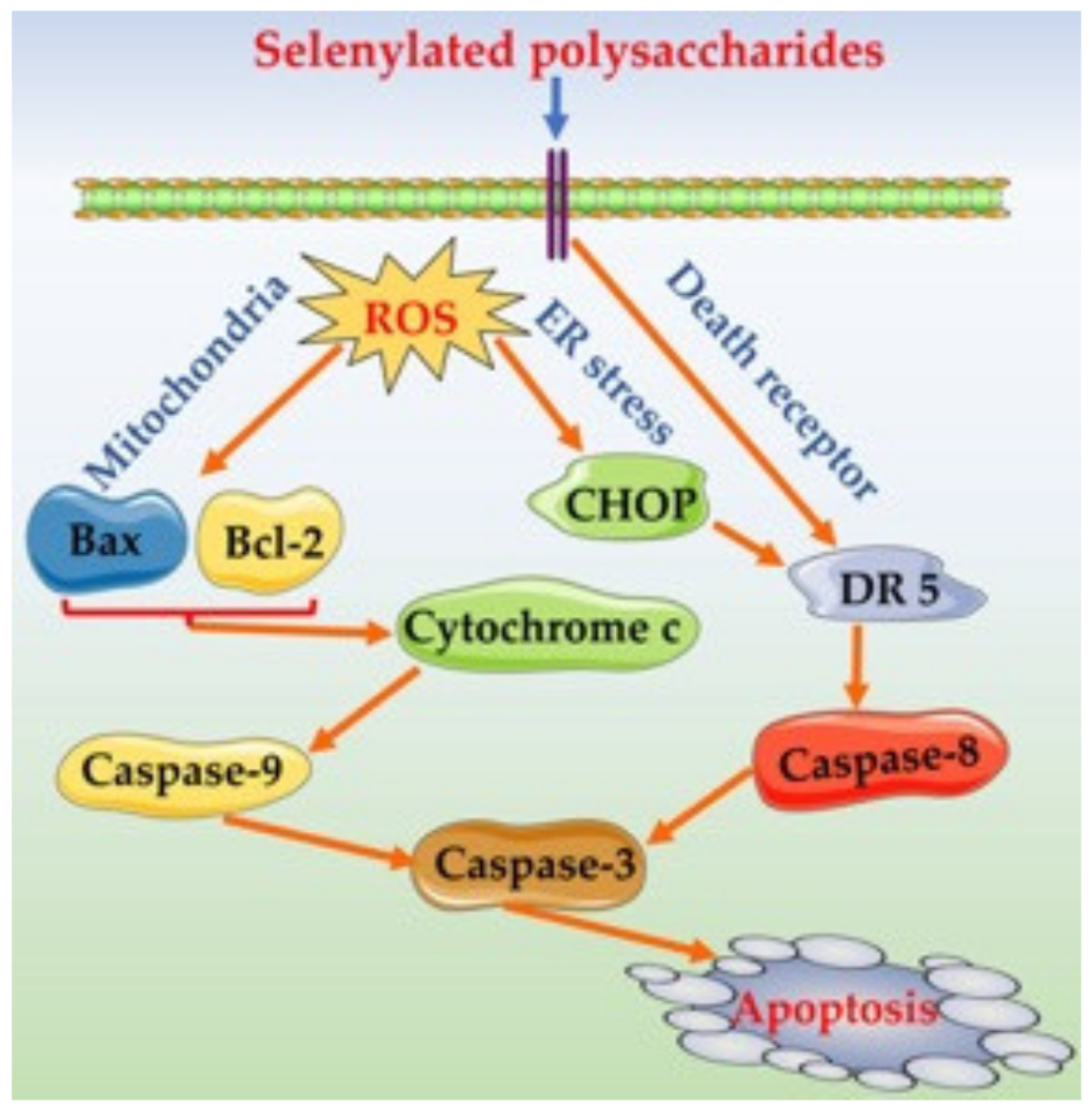
3.4. The Expression Changes of the Apoptosis-Related Genes and Proteins in the Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rayman, M.P. The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet 2000, 356, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Bao, Y.P.; Broadley, M.R.; Collings, R.; Ford, D.; Hesketh, J.E.; Hurst, R. Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2011, 14, 1337–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wen, Y.H.; Li, L.H.; Zheng, L.H. Tumoricidal effects of a selenium (Se)-polysaccharide from Ziyang green tea on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Alarcon, M.; Cabrera-Vique, C. Selenium in food and the human body: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, D.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.M.; Yu, Z.; Fu, X. A novel polysaccharide from Se-enriched ganoderma lucidum induces apoptosis of human breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D.; Sharma, A.K.; Palop, J.A. Selenium compounds, apoptosis and other types of cell death: An overview for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9649–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G.F.; Gray, W.P. Chemopreventive agents: Selenium. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 79, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Benedetti, R.; Handzlik, J.; Zwergel, C.; Battistelli, C. The innovative potential of selenium-containing agents for fighting cancer and viral infections. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Kline, C.L.; Berg, A.; Amin, S.; Irby, R.B. The Akt inhibitor ISC-4 activates prostate apoptosis response protein-4 and reduces colon tumor growth in a nude mouse model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4474–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.T.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, J.H.; Fan, L.H.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.X.; Vang, O.; Hu, H.B. Methylseleninic acid potentiates multiple types of cancer cells to ABT-737-induced apoptosis by targeting Mcl-1 and Bad. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Long, H.R.; Wang, C.H.; Yu, L.; Zhao, M.M.; Liu, X.L. Research progress on the biological activities of selenium polysaccharides. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4834–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunzio, M.; Bordoni, A.; Aureli, F.; Cubadda, F.; Gianotti, A. Sourdough fermentation favorably influences selenium biotransformation and the biological effects of flatbread. Nutrients 2018, 10, e1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Wei, X.L. Antitumor activity of Se-containing tea polysaccharides against sarcoma 180 and comparison with regular tea polysaccharides and Se-yeast. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.J.; Li, Y.; Tuerhong, M.; Abudukeremu, M.; Cui, J.L.; Li, Y.H.; Jin, D.Q.; Xu, J.; et al. Structure features, selenylation modification, and improved anti-tumor activity of a polysaccharide from Eriobotrya japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, e118496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Hu, J.H.; Liu, S.; Guo, S.J.; Jia, Y.; Li, M.; Kong, W.B.; Liang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.L. Synthesis of Se-polysaccharide mediated by selenium oxychloride: Structure features and antiproliferative activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, e116545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.F.; Wang, C.D.; Wang, J.J.; Kumar, V.; Anwar, F.; Xiao, F.X.; Mushtaq, G.; Liu, Y.F.; Kamal, M.A.; Yuan, D. Inhibition on the growth of human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model by Se-containing polysaccharides from Pyracantha fortuneana. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Gou, Y.Q.; Hu, F.D.; Liu, L.J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, P. Optimization of selenylation conditions for a pectic polysaccharide and its structural characteristic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, H.Y.; Jin, D.; Zhao, T.; Xu, C.Q.; Zhang, D.H.; Jia, Q.D.; Bai, Y.P.; et al. Anti-tumor and immunomodulatory activity of selenium (Se)-polysaccharide from Se-enriched Grifola frondose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.; Lin, H.T.; Lu, W.J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Fan, Z.Q. The role of cell wall polysaccharides disassembly in Lasiodiplodia theobromae-induced disease occurrence and softening of fresh longan fruit. Food Chem. 2021, 351, e129294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.M.; Shi, J.; Chen, F.; Ashraf, M. Extraction and pharmacological properties of bioactive compounds from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) fruit—A review. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Yang, R.L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wen, Y.Z.; Liu, S.X.; Li, C.F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Cheng, X.R.; Li, W. Structural characterization of an active polysaccharide of longan and evaluation of immunological activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Y.; Ning, Y.L.; Qi, J.; He, Z.; Jie, J.; Lin, J.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Li, F.S.; Li, X.H. Structure and antitumor and immunomodulatory activities of a water-soluble polysaccharide from dimocarpus longan pulp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5140–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, K.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; He, X.H. Evaluation of radicals scavenging, immunity-modulatory and antitumor activities of longan polysaccharides with ultrasonic extraction on in S180 tumor mice models. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, R.F.; Dong, L.H.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.X.; Jia, X.C.; Wang, G.J.; Zhang, M.W. Physicochemical properties and prebiotic activities of polysaccharides from longan pulp based on different extraction techniques. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, L.Z.; Sun, B.G.; Zhao, M.M. A comparison study on polysaccharides extracted from Laminaria japonica using different methods: Structural characterization and bile acid-binding capacity. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; He, X.X.; Wei, X.L. Preparation, structural characterization and bioactivities of Se-containing polysaccharide: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Taufek, N.; Cartwright, D.; Davies, M.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Koorts, P.; Shaw, P.N.; Sumner, R.; Lee, E.; Whitfield, K. The simultaneous analysis of eight essential trace elements in human milk by ICP-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.H.; Li, M.; Zhu, S.Y.; Guo, S.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.L. The role of Se content in improving anti-tumor activities and its potential mechanism for selenized Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharides. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.H. In vitro activities of the four structurally similar flavonols weakened by the prior thermal and oxidative treatments to a human colorectal cancer line. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, X.H. Apigenin induces both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis in human colon carcinoma HCT-116 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.N.; Bian, Z.D.; Xie, D.K.; Peng, Q. A selenium-modified ginseng polysaccharide promotes the apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 177, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.L.; Zhu, H.L.; Li, X.L.; Liu, Z.M.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, T.F.; Yu, B.; Wong, K.H. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells by surface-capping selenium nanoparticles: An effect enhanced by polysaccharide–protein complexes from polyporus rhinoceros. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 41, 9859–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, D.; Deng, Z.W.; Li, T.H.; He, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhong, S.A. A water-soluble selenium-enriched polysaccharide produced by Pleurotus ostreatus: Purification, characterization, antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bian, F.L.; Yue, L.; Jin, H.; Hong, Z.G.; Shu, G.W. Selenium-dependent antitumor immunomodulating activity of polysaccharides from roots of A. membranaceus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, S.P.; Cai, D.W.; Kong, G.Q. Induction of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in T24 cells by a selenium (Se)-containing polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba L. leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D.D.; Guo, Y.X.; Zeng, X.Q. Effect of selenylation modification on antitumor activity of peptidoglycan from Lactobacillus acidophilus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; El-Bayoumy, K. Apoptosis is a critical cellular event in cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy by selenium compounds. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.P.; Gandin, V. Selenium compounds as therapeutic agents in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 1642–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Shia, D.Y.; Liu, G.Z.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, S.J.; Hu, Y.D. Roles of Se and NO in apoptosis of hepatoma cells. Life Sci. 2000, 68, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Dong, Y.; Park, Y.M.; Ip, C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signal mediators are targets of selenium action. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9073–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalaby, A.S.G.; Ragab, T.I.M.; Mehany, A.B.M.; Helal, M.M.I.; Helmy, W.A. Antitumor and prebiotic activities of novel sulfated acidic polysaccharide from ginseng. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Huang, L.L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.H.; Ding, K. Structural characterization of a galactan from Ophiopogon japonicus and anti-pancreatic cancer activity of its acetylated derivative. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, X.Q.; Xu, X.F.; Zhang, X.W. Purification, antitumor and anti-inflammation activities of an alkali-soluble and carboxymethyl polysaccharide CMP33 from Poria cocos. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Huang, M.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Su, W.T. Phosphorylation of levan by microwave-assisted synthesis enhanced anticancer ability. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 131, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.M.; Shen, M.Y.; Hong, Y.Z.; Ye, H.D.; Huang, L.X.; Xie, J.H. Chemical modifications of polysaccharides and their anti-tumor activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, e115436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, U.; Fichna, J.; Gorlach, S. Enhancement of anticancer potential of polyphenols by covalent modifications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C.; Lai, C.S.; Chung, M.C.; Kalyanam, N.; Majeed, M.; Ho, C.T.; Ho, Y.S.; Pan, M.H. Potent anti-cancer effect of 3’-hydroxypterostilbene in human colon xenograft tumors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamvakopoulos, C.; Dimas, K.; Sofianos, Z.D.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z.L.; Wyche, J.H.; Pantazis, P. Metabolism and anticancer activity of the curcumin analogue, dimethoxycurcumin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Shen, B.X.; Nie, S.L.; Duan, Z.H.; Chen, K.S. A combination of selenium and polysaccharides: Promising therapeutic potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.J.; Duan, Y.Q.; He, Y.Q.; Xiang, H.; Sun, W.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Ma, H.L. Characterization, antioxidant, antineoplastic and immune activities of selenium modified Sagittaria sagittifolia L. polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, e110913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Genes | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Bax | Forward: 5′-CCAGAGGCGGGGGATGATT-3′ Reverse: 5′-CTGATCAGTTCCGGCACCTT-3′ | Human |
| Bcl-2 | Forward: 5′-CTTTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTCA-3′ Reverse: 5′-GGGCCGTACAGTTCCACAAA-3′ | Human |
| Caspase-3 | Forward: 5′-TTGAGACAGACAGTGGTGTTGATGATG-3′ Reverse: 5′-ATAATAACCAGGTGCTGTGGAGTATGC-3′ | Human |
| Caspase-8 | Forward: 5′-CAAACTTCACAGCATTAGGGAC-3′ Reverse: 5′-ATGTTACTGTGGTCCATGAGTT-3′ | Human |
| Caspase-9 | Forward: 5′-CTGCTGCGTGGTGGTCATTCTC-3′ Reverse: 5′-CACAATCTTCTCGACCGACACAGG-3′ | Human |
| CHOP | Forward: 5′-TAAAGATGAGCGGGTGGCAG-3′ Reverse: 5′-CTGCCATCTCTGCAGTTGGA-3′ | Human |
| Cytochrome c | Forward: 5′-GAGTAATAATTGGCCACTGCCT-3′ Reverse: 5′-AATCAGGACTGCCCAACAAAA-3′ | Human |
| DR5 | Forward: 5′-CTGATCACCCAACAAGACCTAG-3′ Reverse: 5′-GATGCAATCTCTACCGTCTTCT-3′ | Human |
| β-Actin | Forward: 5′-CCACCATGTACCCTGGCAT-3′ Reverse: 5′-ACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCAC-3′ | Human |
| Cell Group | Total Apoptotic Proportion (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | |
| Control | 5.1 ± 0.1 e | 5.4 ± 0.3 d |
| LP (800 μg/mL) | 7.9 ± 0.7 d | 8.3 ± 0.2 d |
| SeLP1 (400 μg/mL) | 9.5 ± 0.4 c | 20.2 ± 0.7 c |
| SeLP1 (800 μg/mL) | 10.0 ± 0.9 c | 31.6 ± 1.9 b |
| SeLP2 (400 μg/mL) | 12.1 ± 0.4 b | 33.5 ± 2.8 b |
| SeLP2 (800 μg/mL) | 16.2 ± 1.7 a | 46.2 ± 3.2 a |
| Gene | Cell Group and Relative Expression Fold | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LP (800 μg/mL) | SeLP1 (400 μg/mL) | SeLP1 (800 μg/mL) | SeLP2 (400 μg/mL) | SeLP2 (800 μg/mL) | |
| Bax | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 |
| Bcl-2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.0 |
| Caspase-3 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| Caspase-8 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| Caspase-9 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.0 |
| CHOP | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| Cytochrome c | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| DR5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| Protein | Relative Expression Fold | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LP | SeLP1 | SeLP2 | 5-FU | DEVD | DEVD and SeLP2 | |
| Bax | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| Bcl-2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| CHOP | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| Cleaved Csapase-3 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | NA | NA |
| Cleaved Caspase-8 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | NA | NA |
| Cleaved Caspase-9 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| Cytochrome c | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| DR5 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | NA | NA |
| Procaspase-3 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | NA | NA | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.-H.; Tang, Z.-M.; Xiong, C.; Wu, F.-F.; Zhao, J.-R.; Zhao, X.-H. Enhanced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Cells of Soluble Longan Polysaccharides with a Covalent Chemical Selenylation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091710
Yu Y-H, Tang Z-M, Xiong C, Wu F-F, Zhao J-R, Zhao X-H. Enhanced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Cells of Soluble Longan Polysaccharides with a Covalent Chemical Selenylation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091710
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Ya-Hui, Zhi-Mei Tang, Cen Xiong, Fei-Fei Wu, Jun-Ren Zhao, and Xin-Huai Zhao. 2022. "Enhanced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Cells of Soluble Longan Polysaccharides with a Covalent Chemical Selenylation" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091710
APA StyleYu, Y.-H., Tang, Z.-M., Xiong, C., Wu, F.-F., Zhao, J.-R., & Zhao, X.-H. (2022). Enhanced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Cells of Soluble Longan Polysaccharides with a Covalent Chemical Selenylation. Nutrients, 14(9), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091710







