The Mediation Role of Health Behaviors in the Association between Self-Regulation and Weight Status among Preschool Children: A Sex-Specific Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
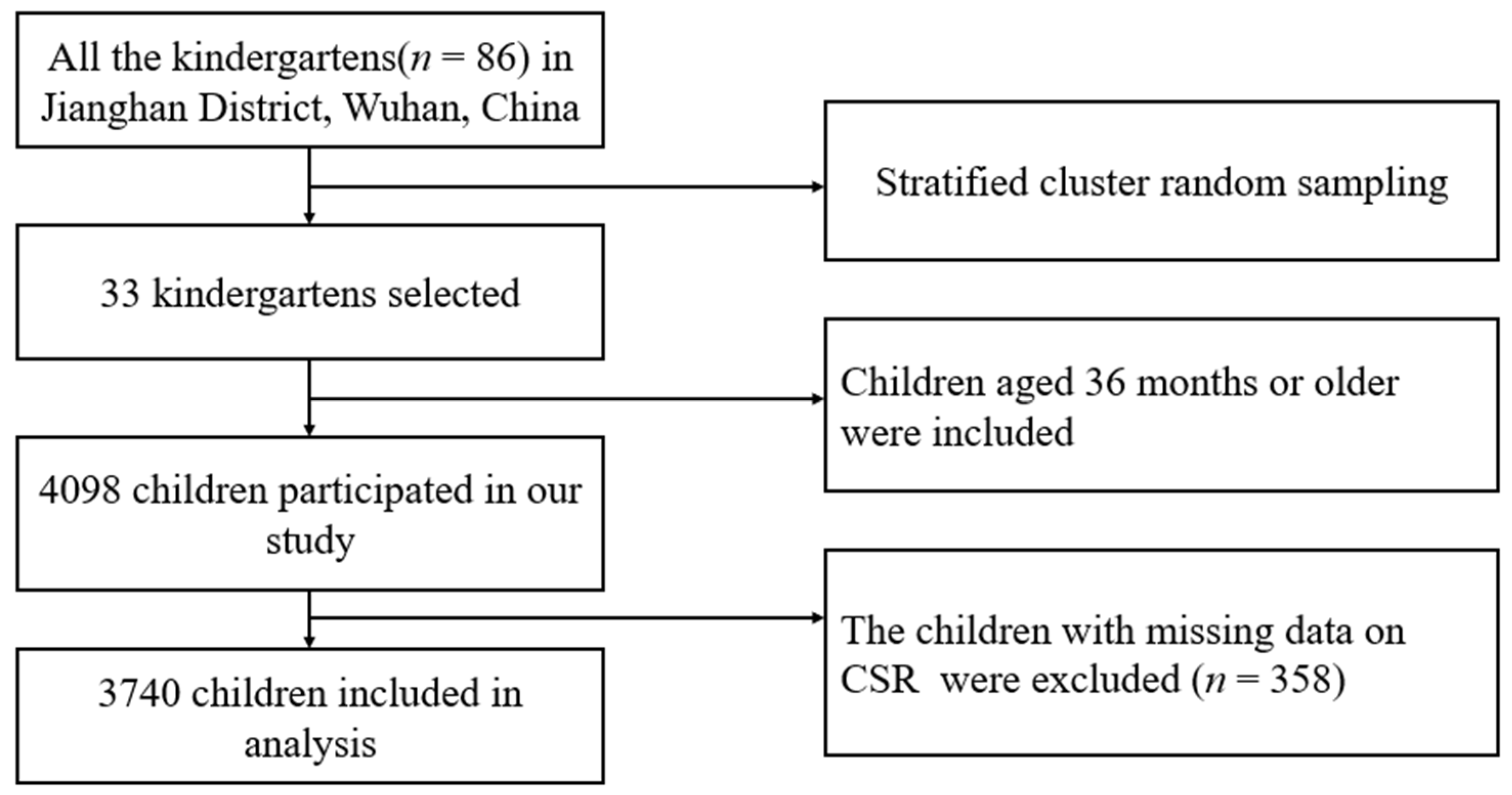
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Child Anthropometrics
2.2.2. Self-Regulation Measurement
2.3. Healthy Behaviors and Other Covariates
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Population Characteristics
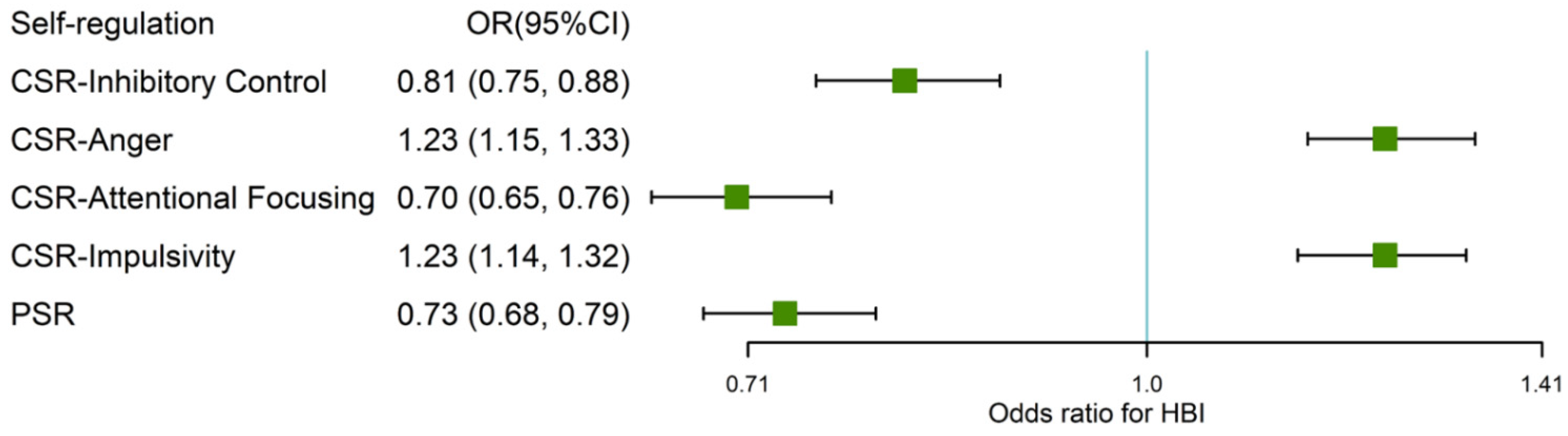
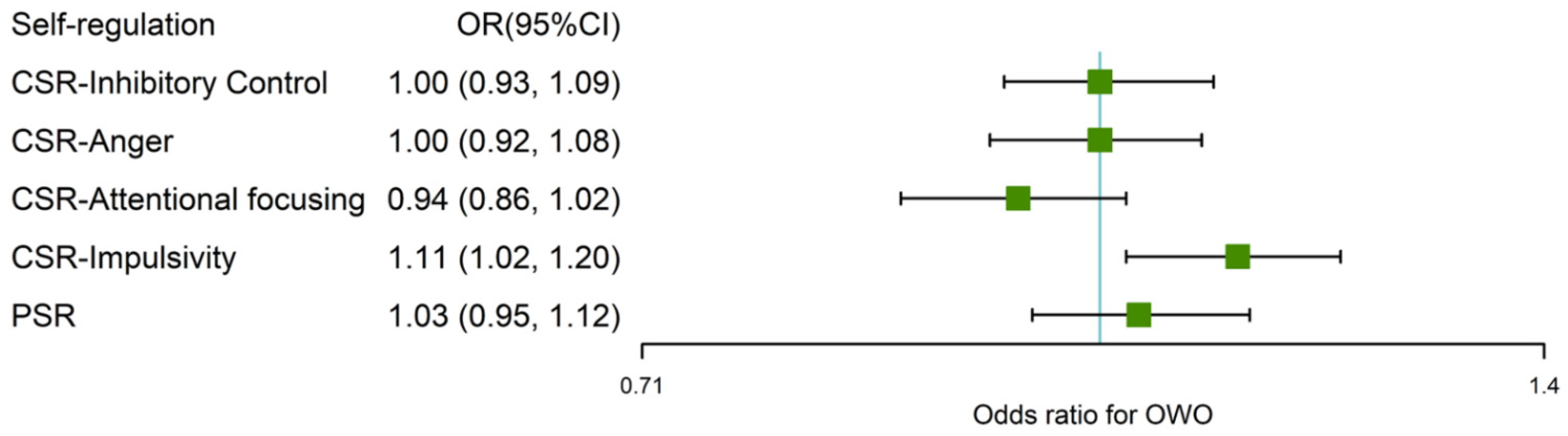
4.2. Association between SR, Health Behavior and Obesity
4.3. Mediation Analysis of HBI on Associations of Impulsivity with OWO
4.4. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capital Institute of Pediatrics; Coordinating Study Group of Nine Cities on the Physical Growth and Development of Children. A national epidemiological survey on obesity of children under seven years of age in nine cities of China in 2016. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2018, 56, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.R.; Obarzanek, E.; Franko, D.L.; Barton, B.A.; Morrison, J.; Biro, F.M.; Daniels, S.R.; Striegel-Moore, R.H. Childhood overweight and cardiovascular disease risk factors: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Growth and Health Study. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, R.; Dziura, J.; Burgert, T.S.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Taksali, S.E.; Yeckel, C.W.; Allen, K.; Lopes, M.; Savoye, M.; Morrison, J.; et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutaria, S.; Devakumar, D.; Yasuda, S.S.; Das, S.; Saxena, S. Is obesity associated with depression in children? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volger, S.; Rigassio Radler, D.; Rothpletz-Puglia, P. Early childhood obesity prevention efforts through a life course health development perspective: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijtdewilligen, L.; Waters, C.N.; Müller-Riemenschneider, F.; Lim, Y.W. Preventing childhood obesity in Asia: An overview of intervention programmes. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2016, 17, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, D.A.; Mark, S.; Howard, S.J. Self-regulation in childhood as a predictor of future outcomes: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 2020, 146, 324–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, S.E.; Keim, S.A. Parent-Child Interaction, Self-Regulation, and Obesity Prevention in Early Childhood. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlam, T.R.; Wilson, N.L.; Shoda, Y.; Mischel, W.; Ayduk, O. Preschoolers’ Delay of Gratification Predicts their Body Mass 30 Years Later. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, S.E.; Sacker, A.; Whitaker, R.C.; Kelly, Y. Self-regulation and household routines at age three and obesity at age eleven: Longitudinal analysis of the UK Millennium. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thamotharan, S.; Lange, K.; Zale, E.L.; Huffhines, L.; Fields, S. The role of impulsivity in pediatric obesity and weight status: A meta-analytic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 33, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, R.C.; Gooze, R.A. Self-regulation and Obesity Prevention A Valuable Intersection Between Developmental Psychology and Pediatrics. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, E.; Canals, J.; Arija, V.; De Henauw, S.; Michels, N. The role of emotion regulation in childhood obesity: Implications for prevention and treatment. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Matheson, B.E.; Kaye, W.H.; Boutelle, K.N. Neurocognitive correlates of obesity and obesity-related behaviors in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Berg, L.; Pieterse, K.; Malik, J.A.; Luman, M.; Willems van Dijk, K.; Oosterlaan, J.; Delemarre-van de Waal, H.A. Association between impulsivity, reward responsiveness and body mass index in children. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dore, G.A.; Elias, M.F.; Robbins, M.A.; Budge, M.M.; Elias, P.K. Relation between central adiposity and cognitive function in the Maine-Syracuse Study: Attenuation by physical activity. Ann. Behav. Med. A Publ. Soc. Behav. Med. 2008, 35, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempsey, A.; Dyehouse, J.; Schafer, J. The relationship between executive function, AD/HD, overeating, and obesity. West J. Nurs. Res. 2011, 33, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, R.D.; Rivera, J.; Silveira, P.P.; Steiner, M.; Gaudreau, H.; Hamilton, J.; Kennedy, J.L.; Davis, C.; Dube, L.; Fellows, L.; et al. Gender differences in the association between stop-signal reaction times, body mass indices and/or spontaneous food intake in pre-school children: An early model of compromised inhibitory control and obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.W.; Rosanbalm, K.; Christopoulos, C.; Hamoudi, A. Self-Regulation and Toxic Stress: Foundations for Understanding Self-Regulation from an Applied Developmental Perspective; OPRE Report; Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, J.A.; Dearth-Wesley, T.; Lewin, D.; Gioia, G.; Whitaker, R.C. Self-Regulation and Sleep Duration, Sleepiness, and Chronotype in Adolescents. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggs, N.R.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Chou, C.P.; Pentz, M.A. Relationships between executive cognitive function and lifetime substance use and obesity-related behaviors in fourth grade youth. Child Neuropsychol. 2012, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isasi, C.R.; Ostrovsky, N.W.; Wills, T.A. The association of emotion regulation with lifestyle behaviors in inner-city adolescents. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kochanska, G.; Murray, K.T.; Harlan, E.T. Effortful control in early childhood: Continuity and change, antecedents, and implications for social development. Dev. Psychol. 2000, 36, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.E.; Whitaker, R.C. Association of Self-regulation With Obesity in Boys vs Girls in a US National Sample. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaras, K.N.; Armstrong, J.M.; Klein, M.H.; Essex, M.J.; Davidson, R.J.; Goldsmith, H.H. Sex Differences in the Relationship Between Childhood Self-Regulation and Adolescent Adiposity. Obesity 2020, 28, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbart, S.P.; Rothbart, M.K. Development of Short and Very Short Forms of the Children’s Behavior Questionnaire. J. Personal. Assess. 2006, 87, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kotelnikova, Y.; Olino, T.M.; Klein, D.N.; Kryski, K.R.; Hayden, E.P. Higher- and lower-order factor analyses of the Children’s Behavior Questionnaire in early and middle childhood. Psychol. Assess. 2016, 28, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbart, M.K.; Ahadi, S.A.; Hershey, K.L.; Fisher, P. Investigations of Temperament at Three to Seven Years: The Children’s Behavior Questionnaire. Child Dev. 2001, 72, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnaly, J.C. Psychometric Theory 3; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Unger, A.; Bi, C.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Ybarra, O. The revising of the Tangney Self-Control Scale for Chinese students. Psych. J. 2016, 5, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Sun, Y.X.; Wang, Z.Y. China dietary guideline for preschool children. Chin. J. Child Health Care 2016, 25, 325–327. [Google Scholar]
- Gua, H.Y.; Zhao, X.; Qu, S.; Wu, J.X.; Yang, Y.F.; Guo, J.J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, D.M. Physical activity guideline for Chinese preschoolers aged 3-6years. Chin. J. Child Health Care 2020, 28, 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Heerman, W.J.; Sommer, E.C.; Slaughter, J.C.; Samuels, L.R.; Martin, N.C.; Barkin, S.L. Predicting Early Emergence of Childhood Obesity in Underserved Preschoolers. J. Pediatr. 2019, 213, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiersma, R.; Haverkamp, B.F.; van Beek, J.H.; Riemersma, A.M.J.; Boezen, H.M.; Smidt, N.; Corpeleijn, E.; Hartman, E. Unravelling the association between accelerometer-derived physical activity and adiposity among preschool children: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2020, 21, e12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- VanderWeele, T. Explanation in Causal Inference: Methods for Mediation and Interaction; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Steen, J.; Loeys, T.; Moerkerke, B.; Vansteelandt, S. medflex: An R Package for Flexible Mediation Analysis using Natural Effect Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, Y.F.; Tanaka, T.; Beason-Held, L.L.; An, Y.; Terracciano, A.; Sutin, A.R.; Kraut, M.; Singleton, A.B.; Resnick, S.M.; Thambisetty, M. FTO genotype and aging: Pleiotropic longitudinal effects on adiposity, brain function, impulsivity and diet. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appelhans, B.M. Neurobehavioral inhibition of reward-driven feeding: Implications for dieting and obesity. Obesity 2009, 17, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, E.P.; Evans, B.C.; Manasse, S.M.; Butryn, M.L.; Forman, E.M. Executive functioning and dietary intake: Neurocognitive correlates of fruit, vegetable, and saturated fat intake in adults with obesity. Appetite 2017, 111, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padin, A.C.; Emery, C.F.; Vasey, M.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Self-Regulation and Implicit Attitudes Toward Physical Activity Influence Exercise Behavior. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2017, 39, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, T.R.M. Risky Behavior among Youths: Some Issues from Behavioral Economics; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001; pp. 29–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rømer Thomsen, K.; Callesen, M.B.; Hesse, M.; Kvamme, T.L.; Pedersen, M.M.; Pedersen, M.U.; Voon, V. Impulsivity traits and addiction-related behaviors in youth. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhunen, V.; Bond, T.A.; Zuber, V.; Hurtig, T.; Moilanen, I.; Jarvelin, M.R.; Evangelou, M.; Rodriguez, A. The link between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and obesity-related traits: Genetic and prenatal explanations. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederkoorn, C.; Coelho, J.S.; Guerrieri, R.; Houben, K.; Jansen, A. Specificity of the failure to inhibit responses in overweight children. Appetite 2012, 59, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriver, L.H.; Dollar, J.M.; Lawless, M.; Calkins, S.D.; Keane, S.P.; Shanahan, L.; Wideman, L. Longitudinal Associations between Emotion Regulation and Adiposity in Late Adolescence: Indirect Effects through Eating Behaviors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Garcia, I.; Neseliler, S.; Morys, F.; Dadar, M.; Yau, Y.H.C.; Scala, S.G.; Zeighami, Y.; Sun, N.; Collins, D.L.; Vainik, U.; et al. Relationship between impulsivity, uncontrolled eating and body mass index: A hierarchical model. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 46, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemps, E.; Goossens, L.; Petersen, J.; Verbeken, S.; Vervoort, L.; Braet, C. Evidence for enhancing childhood obesity treatment from a dual-process perspective: A systematic literature review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 77, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total Population (n = 3740) | Normal Weight (n = 2948) | Overweight/Obesity (n = 792) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (mean (SD), months) | 55.65 (10.26) | 55.25 (10.30) | 57.16 (9.94) | <0.01 ** |
| Age n (%) | <0.01 ** | |||
| 36~48 months | 950 (25.4) | 802 (27.2) | 148 (18.7) | |
| 48~60 months | 1428 (38.2) | 1109 (37.6) | 319 (40.3) | |
| ≥60 months | 1362 (36.4) | 1037 (35.2) | 325 (41.0) | |
| Sex n (%) | <0.01 ** | |||
| Boy | 2019 (54.0) | 1503 (51.0) | 516 (65.2) | |
| Girl | 1721 (46.0) | 1445 (49.0) | 276 (34.8) | |
| Birth weight-for-length Z scores (mean (SD)) b,c | −0.19 (3.01) | −0.22 (3.02) | −0.09 (2.95) | 0.300 |
| Ever breastfeeding n (%) c | 0.278 | |||
| No | 453 (12.1) | 362 (12.3) | 91 (11.5) | |
| Yes | 3121 (83.4) | 2463 (83.5) | 658 (83.1) | |
| Current Maternal BMI (median (IQR), kg/m2) c | 20.83 (19.43, 22.77) | 20.66 (19.23, 22.49) | 21.83 (20.06, 23.88) | <0.01 ** |
| Maternal education c | 0.896 | |||
| High school or less | 794 (21.2) | 623 (21.1) | 171 (21.6) | |
| College/University | 2424 (64.8) | 1907 (64.7) | 517 (65.3) | |
| Postgraduate or above | 404 (10.8) | 323 (11.0) | 81 (10.2) | |
| Household income (n (%), RMB per month) c | 0.388 | |||
| ≤10,000 | 1014 (27.1) | 810 (27.5) | 204 (25.8) | |
| 10,001~20,000 | 1338 (35.8) | 1031 (35.0) | 307 (38.8) | |
| 20,001~40,000 | 910 (24.3) | 724 (24.6) | 186 (23.5) | |
| ≥40,001 | 293 (7.8) | 233 (7.9) | 60 (7.6) | |
| Secondhand smoke during pregnancy n (%) c | 0.970 | |||
| Never | 2640 (70.6) | 2081 (70.6) | 559 (70.6) | |
| Occasional | 1013 (27.1) | 800 (27.1) | 213 (26.9) | |
| Often | 59 (1.6) | 45 (1.5) | 14 (1.8) | |
| Overall (n = 3740) | Boys (n = 2019) | Girls (n = 1721) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | p | β | p | β | p | |
| Mediator: HBI a | ||||||
| Direct effects | 0.092 | 0.026 * | 0.109 | 0.044 * | 0.060 | 0.364 |
| Indirect effects | 0.011 | 0.007 ** | 0.010 | 0.032 * | 0.011 | 0.124 |
| Total effect | 0.103 | 0.013 * | 0.119 | 0.027 * | 0.071 | 0.277 |
| Proportion mediated, % | 10.67 | 8.40 | 15.49 | |||
| Mediator: Diet b | ||||||
| Direct effects | 0.097 | 0.020 * | 0.114 | 0.035 * | 0.063 | 0.340 |
| Indirect effects | 0.006 | 0.043 * | 0.005 | 0.155 | 0.008 | 0.126 |
| Total effect | 0.103 | 0.013 * | 0.119 | 0.028 * | 0.071 | 0.277 |
| Proportion mediated, % | 5.83 | 4.20 | 11.26 | |||
| Mediator: Screen time c | ||||||
| Direct effects | 0.093 | 0.025 * | 0.111 | 0.040 * | 0.058 | 0.374 |
| Indirect effects | 0.010 | 0.010 * | 0.008 | 0.090 | 0.013 | 0.054 |
| Total effect | 0.103 | 0.013 * | 0.119 | 0.027 * | 0.071 | 0.277 |
| Proportion mediated, % | 9.71 | 6.72 | 18.31 | |||
| Mediator: Sleep d | ||||||
| Direct effects | 0.100 | 0.017 * | 0.118 | 0.029 * | 0.061 | 0.346 |
| Indirect effects | 0.003 | 0.148 | 0.001 | 0.553 | 0.010 | 0.118 |
| Total effect | 0.103 | 0.013 * | 0.119 | 0.027 * | 0.071 | 0.277 |
| Proportion mediated, % | 2.91 | 0.84 | 14.08 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W.; Tuerxun, P.; Li, C.; Chang, R.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. The Mediation Role of Health Behaviors in the Association between Self-Regulation and Weight Status among Preschool Children: A Sex-Specific Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091692
Xu K, Zhang Y, Dong W, Tuerxun P, Li C, Chang R, Qi H, Zhang Y, Zhang J. The Mediation Role of Health Behaviors in the Association between Self-Regulation and Weight Status among Preschool Children: A Sex-Specific Analysis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091692
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ke, Yuanyuan Zhang, Wenli Dong, Paiziyeti Tuerxun, Chunan Li, Ruixia Chang, Haiqin Qi, Ya Zhang, and Jianduan Zhang. 2022. "The Mediation Role of Health Behaviors in the Association between Self-Regulation and Weight Status among Preschool Children: A Sex-Specific Analysis" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091692
APA StyleXu, K., Zhang, Y., Dong, W., Tuerxun, P., Li, C., Chang, R., Qi, H., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2022). The Mediation Role of Health Behaviors in the Association between Self-Regulation and Weight Status among Preschool Children: A Sex-Specific Analysis. Nutrients, 14(9), 1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091692






