Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire Using an Item Response Theory Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire
2.2. Stage 1: Translation and Transcultural Adaptation of WREQ
Pilot Test
2.3. Stage 2: Psychometric Evaluation of WREQ-C
2.3.1. Sample Size Calculation
2.3.2. Data Collection
2.3.3. Participant Recruitment
2.3.4. Development of the New WREQ-C
- (1)
- Test information of the subscale had to be maintained within 80% of the original structure of the 16-item English version of the Weight-Related Eating Behavior Questionnaire (WREQ-E)
- (2)
- The subscales retained adequate convergent construct validity (r > 0.6) as compared to the relevant Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) subscale
- (3)
- The internal consistency of the subscales needed to achieve a Cronbach’s α ≥ 0.7
2.3.5. Content Validity
2.3.6. Convergent Validity
2.3.7. Structural Validity
2.3.8. Measurement Invariance
2.3.9. Test–Retest Reliability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of the WREQ-C
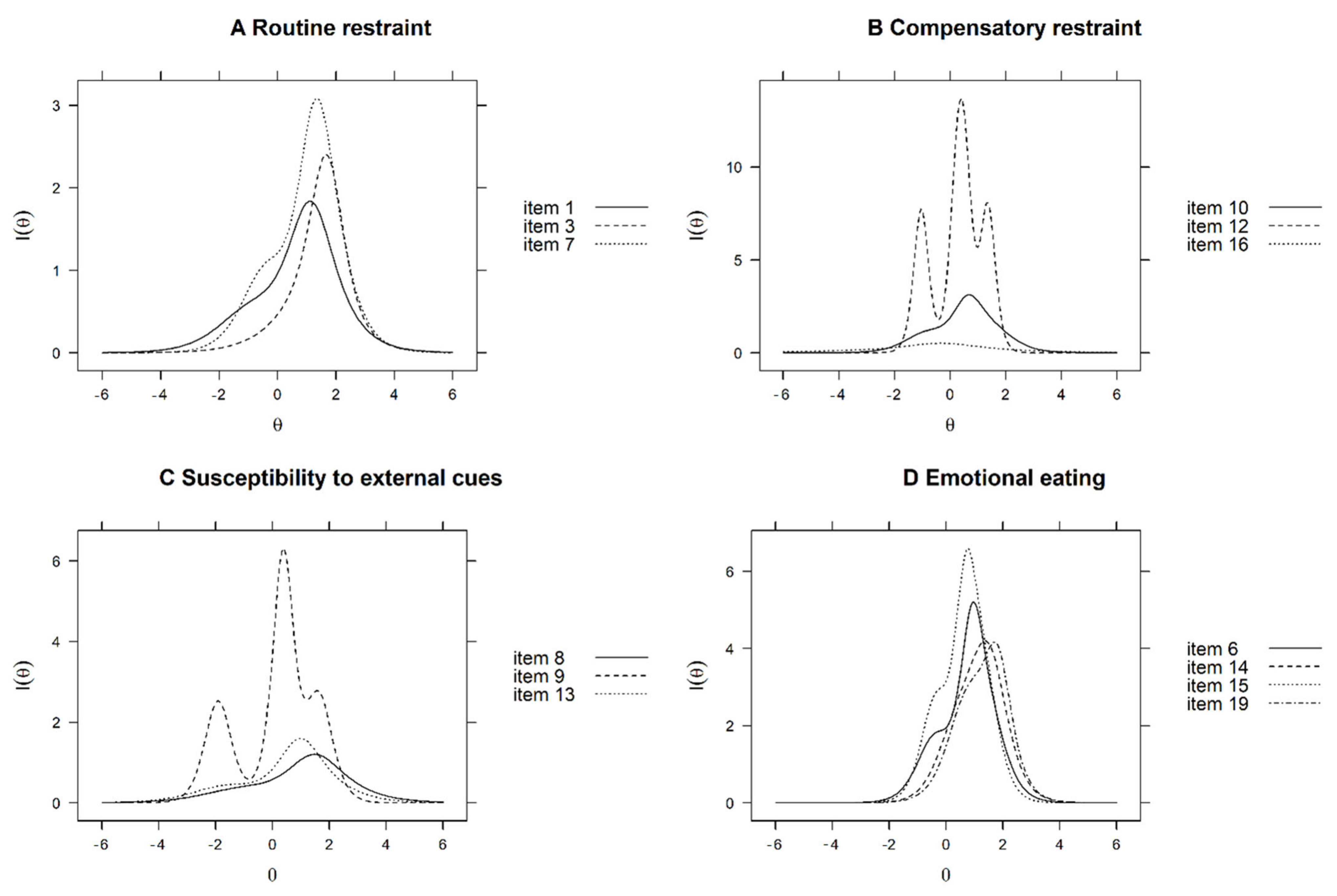
3.1.1. Routine Restraint Subscale
3.1.2. Compensatory Restraint Subscale
3.1.3. Susceptibility to External Cues Subscale
3.1.4. Emotional Eating Subscale
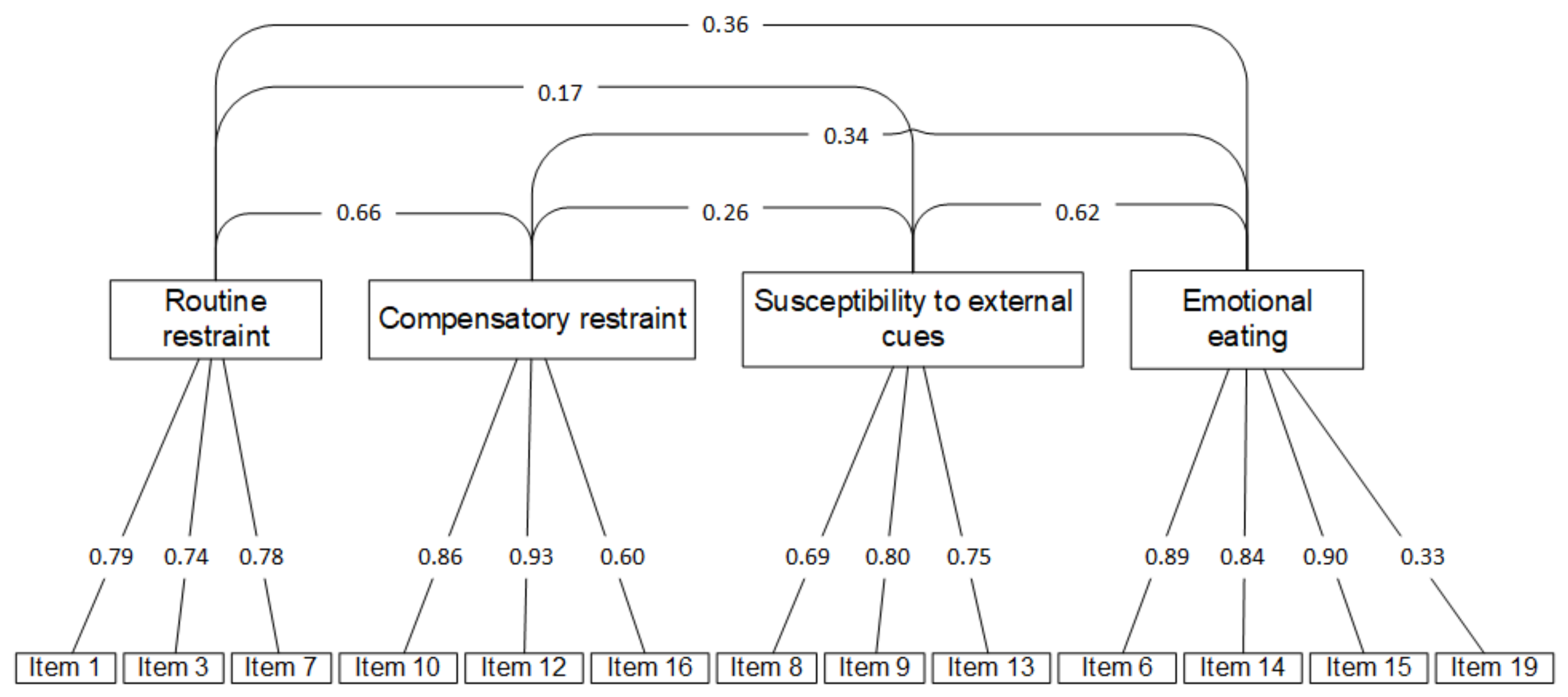
3.1.5. Structural Validity
3.1.6. Measurement Invariance
3.1.7. Test–Retest Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.; Sniehotta, F.F.; Marques, M.M.; Carraça, E.V.; Teixeira, P.J. Prevalence of Personal Weight Control Attempts in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Strien, T.; Herman, C.P.; Verheijden, M.W. Eating Style, Overeating, and Overweight in a Representative Dutch Sample. Does External Eating Play a Role? Appetite 2009, 52, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canetti, L.; Bachar, E.; Berry, E.M. Food and Emotion. Behav. Processes 2002, 60, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xi, B.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Bovet, P. Trends in the Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Abdominal Obesity Among Chinese Adults Between 1993 and 2015. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Messick, S. The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire to Measure Dietary Restraint, Disinhibition and Hunger. J. Psychosom. Res. 1985, 29, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Persson, L.O.; Sjöström, L.; Sullivan, M. Psychometric Properties and Factor Structure of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ) in Obese Men and Women. Results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzeo, S.E.; Aggen, S.H.; Anderson, C.; Tozzi, F.; Bulik, C.M. Investigating the Structure of the Eating Inventory (Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire): A Confirmatory Approach. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2003, 34, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.J.; McDowell, A.J.; Wilkinson, J.Y. The Measurement of Dietary Restraint, Disinhibition and Hunger: An Examination of the Factor Structure of the Three Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ). Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; Bergers, G.P.A.; Defares, P.B. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for Assessment of Restrained, Emotional, and External Eating Behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembre, S.; Greene, G.; Melanson, K. Development and Validation of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire. Eat. Behav. 2009, 10, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schembre, S.M.; Geller, K.S. Psychometric Properties and Construct Validity of the Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire in a Diverse Population. Obesity 2011, 19, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelen, M.O.; Reeve, B.B. Applying Item Response Theory (IRT) Modeling to Questionnaire Development, Evaluation, and Refinement. Qual. Life Res. 2007, 16 (Suppl. 1), 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Process of Translation and Adaptation of Instruments. Available online: https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/research_tools/translation/en/ (accessed on 2 February 2017).
- Motulsky, H. Intuitive Biostatistics: A Nonmathematical Guide to Statistical Thinking, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F.; Ha, S.; Zauszniewski, J.A.; Ross, R. Psychometric Properties of the Chinese Version of the Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire in a Sample of Taiwanese Parents. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H. Confirmatory Factor Analysis with Ordinal Data: Comparing Robust Maximum Likelihood and Diagonally Weighted Least Squares. Behav. Res. Methods 2016, 48, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance Structure Analysis: Conventional Criteria Versus New Alternatives. Struct. Equ. Modeling A Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiStefano, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, N.; Shi, D. Examination of the Weighted Root Mean Square Residual: Evidence for Trustworthiness? Struct. Equ. Modeling Multidiscip. J. 2018, 25, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.W.; Rensvold, R.B. Evaluating Goodness-of-Fit Indexes for Testing Measurement Invariance. Struct. Equ. Modeling Multidiscip. J. 2002, 9, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwee, C.B.; Bot, S.D.; de Boer, M.R.; van der Windt, D.A.; Knol, D.L.; Dekker, J.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C. Quality Criteria Were Proposed for Measurement Properties of Health Status Questionnaires. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007, 60, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalmers, R.P. Mirt: A Multidimensional Item Response Theory Package for the R Environment. J. Stat. Soft. 2012, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthén, L.; Muthén, B. Mplus User’s Guide, 7th ed.; Muthén and Muthén: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Linardon, J.; Mitchell, S. Rigid Dietary Control, Flexible Dietary Control, and Intuitive Eating: Evidence for Their Differential Relationship to Disordered Eating and Body Image Concerns. Eat. Behav. 2017, 26, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenhoefer, J.; von Falck, B.; Stellfeldt, A.; Fintelmann, S. Behavioural Correlates of Successful Weight Reduction Over 3 y. Results from the Lean Habits Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, P.J.; Silva, M.N.; Coutinho, S.R.; Palmeira, A.L.; Mata, J.; Vieira, P.N.; Carraça, E.V.; Santos, T.C.; Sardinha, L.B. Mediators of Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance in Middle-Aged Women. Obesity 2010, 18, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timko, C.A.; Perone, J. Rigid and Flexible Control of Eating Behavior in a College Population. Eat. Behav. 2005, 6, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 1007) | Development Sample (n = 503) | Validation Sample (n = 504) | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | n = 1006 | n = 503 | n = 504 | 0.872 |
| Females | 739 (73) | 368 (73) | 371 (74) | |
| Mean age in years (SD) | 32.6 (13.7) | 32.5 (13.5) | 32.7 (13.9) | 0.874 |
| Age groups | n = 1007 | n = 503 | n = 504 | 0.468 |
| Aged 29 years or younger | 562 (56) | 275 (55) | 287 (57) | |
| Aged 30 years or above | 445 (44) | 228 (45) | 217 (43) | |
| Mean BMI kg/m2 (SD) | 21.3 (3.0) | 21.8 (3.7) | 21.5 (3.6) | 0.367 |
| BMI category | n = 949 | n = 471 | n = 478 | 0.787 |
| Underweight | 139 (15) | 68 (14) | 71 (15) | |
| Normal weight | 508 (54) | 244 (52) | 264 (55) | |
| Overweight | 136 (14) | 71 (15) | 65 (14) | |
| Obese | 166 (17) | 88 (19) | 78 (16) | |
| Self-reported Health status | n = 1007 | n = 503 | n = 504 | 0.783 |
| Extremely well | 24 (2) | 13 (3) | 11 (2) | |
| Very well | 240 (24) | 128 (25) | 112 (22) | |
| Well | 361 (36) | 177 (35) | 184 (37) | |
| Fair | 351 (35) | 170 (34) | 181 (36) | |
| Bad | 31 (3) | 15 (3) | 16 (3) | |
| Marital status | n = 1006 | n = 502 | n = 504 | 0.037 |
| Single | 684 (68) | 344 (69) | 340 (68) | |
| Married | 294 (29) | 147 (29) | 147 (29) | |
| Divorced/Separate/widowed | 28 (3) | 11 (2) | 17 (3) | |
| Employment status | n = 1007 | n = 503 | n = 504 | 0.298 |
| Full-time | 481 (48) | 258 (51) | 223 (44) | |
| Part-time | 37 (4) | 16 (3) | 21 (4) | |
| Retired/unemployed/homemaker | 78 (8) | 33 (7) | 45 (9) | |
| Student | 411 (41) | 196 (39) | 215 (43) | |
| Education level | n = 1006 | n = 503 | n = 503 | 0.097 |
| Senior secondary or below | 118 (12) | 56 (11) | 62 (12) | |
| Diploma/certificate/associate degree | 104 (10) | 57 (11) | 47 (9) | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 510 (51) | 251 (50) | 259 (52) | |
| Master’s degree or above | 274 (27) | 139 (28) | 135 (27) | |
| Family monthly income (HKD) | n = 1000 | n = 498 | n = 502 | 0.724 |
| <9999 | 110 (11) | 53 (11) | 57 (11) | |
| 10,000–19,999 | 178 (18) | 86 (17) | 92 (18) | |
| 20,000–29,999 | 196 (20) | 98 (20) | 98 (20) | |
| 30,000–39,999 | 154 (15) | 72 (15) | 82 (16) | |
| 40,000–59,999 | 170 (17) | 95 (19) | 75 (15) | |
| 60,000 or above | 192 (19) | 94 (19) | 98 (20) | |
| Mean WREQ-C score (SD) | n = 1007 | n = 503 | n = 504 | |
| Routine restraint (1–5) | 2.0 (0.9) | 2.0 (0.8) | 2.0 (0.9) | 0.516 |
| Compensatory restraint (1–5) | 2.8 (1.0) | 2.8 (1.0) | 2.8 (1.0) | 0.274 |
| External eating (1–5) | 2.5 (0.8) | 2.5 (0.8) | 2.6 (0.9) | 0.262 |
| Emotional Eating (1–5) | 2.1 (0.9) | 2.0 (0.9) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.465 |
| Factor Score Determinacy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | n | X2 (df) | CFI | TFI | RMSEA | WRMR | Compensatory Restraint | Routine Restraint | External Eating | Emotional Eating |
| Total | 503 | 277.5 (59) | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 1.22 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
| Males | 128 | 215.6 (59) | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.09 | 1.07 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| Females | 375 | 217.8 (59) | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 1.31 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| aged ≤ 29 years | 255 | 205.4 (59) | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 1.19 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| aged ≥ 30 years | 248 | 206.1 (59) | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.07 | 1.17 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| underweight/normal weight | 326 | 210.5 (59) | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 1.26 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| overweight/obese | 144 | 208.2 (59) | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 1.10 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, M.; Smith, R.; Chau, P.-H.; Chung, C.-Y.; Schembre, S.M.; Fong, D.Y.T. Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire Using an Item Response Theory Approach. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081627
Ho M, Smith R, Chau P-H, Chung C-Y, Schembre SM, Fong DYT. Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire Using an Item Response Theory Approach. Nutrients. 2022; 14(8):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081627
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Mandy, Robert Smith, Pui-Hing Chau, Cheuk-Yan Chung, Susan M. Schembre, and Daniel Y. T. Fong. 2022. "Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire Using an Item Response Theory Approach" Nutrients 14, no. 8: 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081627
APA StyleHo, M., Smith, R., Chau, P.-H., Chung, C.-Y., Schembre, S. M., & Fong, D. Y. T. (2022). Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of a Weight-Related Eating Questionnaire Using an Item Response Theory Approach. Nutrients, 14(8), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081627








