Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
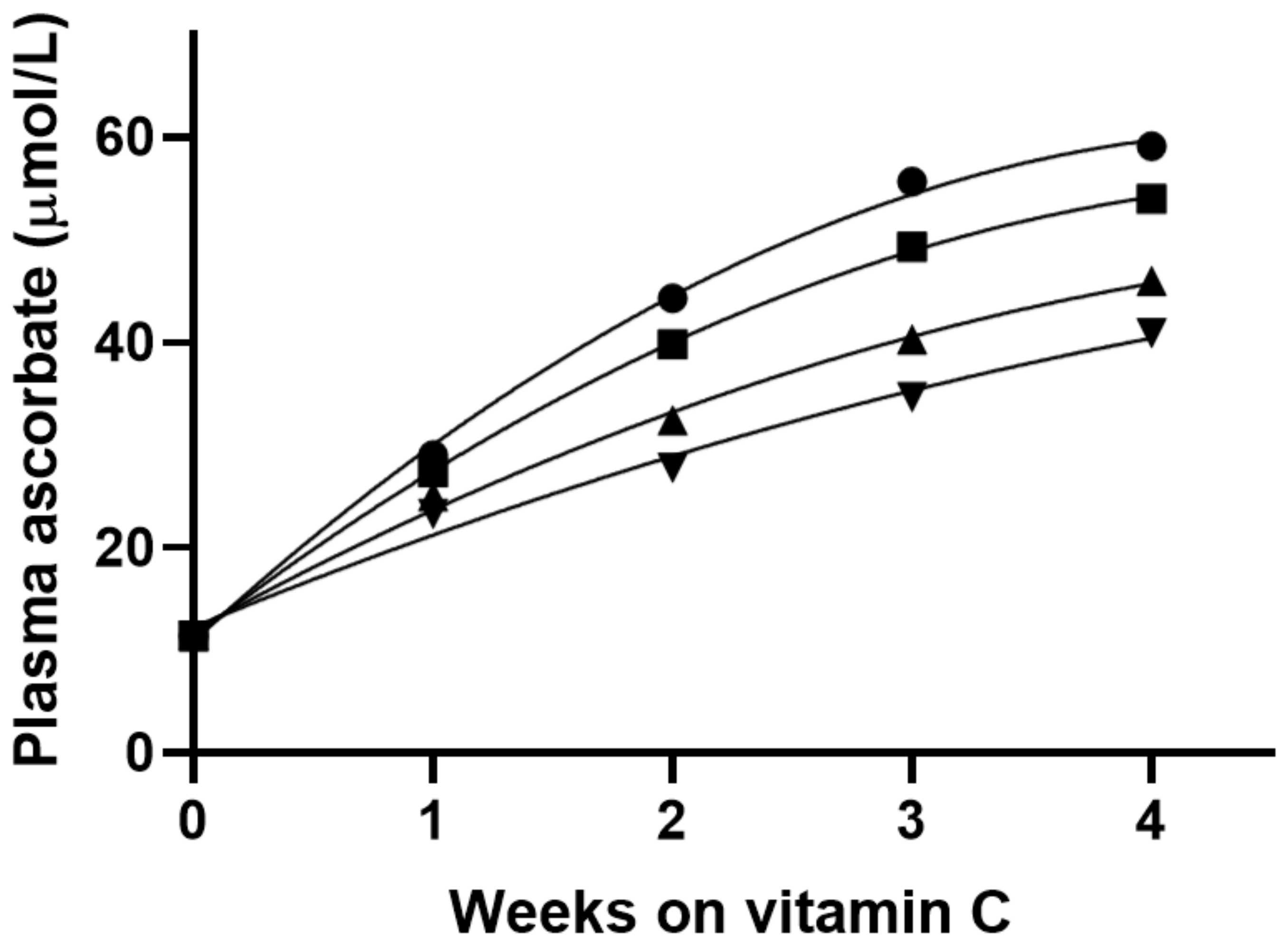
3. Results
| Body Weight Category, kg (lbs) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59 (130) | 68 (150) | 82 (180) | 91 (200) | |
| Dose (mg)/kg body weight 1 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Predicted plasma ascorbate (µmol/L) 2 | 59 | 54 | 46 | 41 |
| △ Plasma ascorbate (µmol/L) | 0 | −5 | −13 | −18 |
| Estimated vitamin C dose (mg) 3 | 109 | 97 | 84 | 77 |
| △ Vitamin C dose (mg) | 0 | 12 | 25 | 32 |
| Total vitamin C dose | 109 | 121 | 134 | 141 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, A.C.; Rowe, S. Factors Affecting Vitamin C Status and Prevalence of Deficiency: A Global Health Perspective. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Does vitamin C deficiency increase lifestyle-associated vascular disease progression? Evidence based on experimental and clinical studies. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 2084–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungert, A.; Neuhäuser-Berthold, M. The lower vitamin C plasma concentrations in elderly men compared with elderly women can partly be attributed to a volumetric dilution effect due to differences in fat-free mass. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rowe, S.; Carr, A.C. Global vitamin C status and prevalence of deficiency: A cause for concern? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Discrepancies in global vitamin C recommendations: A review of RDA criteria and underlying health perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, Á.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codoñer-Franch, P.; Valls-Bellés, V.; Arilla-Codoñer, A.; Alonso-Iglesias, E. Oxidant mechanisms in childhood obesity: The link between inflammation and oxidative stress. Transl. Res. 2011, 158, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G.; Mangels, A.R.; Patterson, B.H.; Levander, O.A.; Norkus, E.P.; Taylor, P.R. Body weight and prior depletion affect plasma ascorbate levels attained on identical vitamin C intake: A controlled-diet study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1999, 18, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Pullar, J.M.; Bozonet, S.M.; Vissers, M.C.M. Marginal Ascorbate Status (Hypovitaminosis C) Results in an Attenuated Response to Vitamin C Supplementation. Nutrients 2016, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuya, H.; Li, Y.; Hilawe, E.H.; Ota, A.; Wang, C.; Chiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Uemura, M.; Osako, A.; Ozaki, Y.; et al. Global Trend in Overweight and Obesity and Its Association with Cardiovascular Disease Incidence. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.; Willis, J.; Gearry, R.; Skidmore, P.; Fleming, E.; Frampton, C.; Carr, A. Inadequate Vitamin C Status in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Associations with Glycaemic Control, Obesity, and Smoking. Nutrients 2017, 9, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.C.; Spencer, E.; Heenan, H.; Lunt, H.; Vollebregt, M.; Prickett, T.C.R. Vitamin C Status in People with Types 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Varying Degrees of Renal Dysfunction: Relationship to Body Weight. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarena, V.; Wang, G. The epigenetic role of vitamin C in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuiper, C.; Vissers, M.C. Ascorbate as a co-factor for Fe- and 2-oxoglutarate dependent dioxygenases: Physiological activity in tumor growth and progression. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. The Pharmacokinetics of Vitamin C. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, M.; Conry-Cantilena, C.; Wang, Y.; Welch, R.W.; Washko, P.W.; Dhariwal, K.R.; Park, J.B.; Lazarev, A.; Graumlich, J.F.; King, J.; et al. Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: Evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3704–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangels, A.R.; Block, G.; Frey, C.M.; Patterson, B.H.; Taylor, P.R.; Norkus, E.P.; Levander, O.A. The bioavailability to humans of ascorbic acid from oranges, orange juice and cooked broccoli is similar to that of synthetic ascorbic acid. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition and Allergies. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for vitamin C. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3418. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, M.; Wang, Y.; Padayatty, S.J.; Morrow, J. A new recommended dietary allowance of vitamin C for healthy young women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9842–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walpole, S.C.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Edwards, P.; Cleland, J.; Stevens, G.; Roberts, I. The weight of nations: An estimation of adult human biomass. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Gu, Q.; Afful, J.; Ogden, C.L. Anthropometric reference data for children and adults: United States, 2015–2018. Vital Health Stat. 2021, 3, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Afful, J. Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Severe Obesity among Adults Aged 20 and over: United States, 1960–1962 through 2017–2018; NCHS Health E-Stats. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/obesity-adult-17-18/obesity-adult.htm (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Chumlea, W.C.; Guo, S.S.; Zeller, C.M.; Reo, N.V.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Garry, P.J.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Siervogel, R.M. Total body water reference values and prediction equations for adults. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. Synthetic or Food-Derived Vitamin C—Are They Equally Bioavailable? Nutrients 2013, 5, 4284–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carr, A.C.; Block, G.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071460
Carr AC, Block G, Lykkesfeldt J. Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071460
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarr, Anitra C., Gladys Block, and Jens Lykkesfeldt. 2022. "Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071460
APA StyleCarr, A. C., Block, G., & Lykkesfeldt, J. (2022). Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity. Nutrients, 14(7), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071460








