Inadequate Vitamin C Intake and Intestinal Inflammation Are Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiency in Young Children: Results from a Multi-Country Birth Cohort Study
Abstract
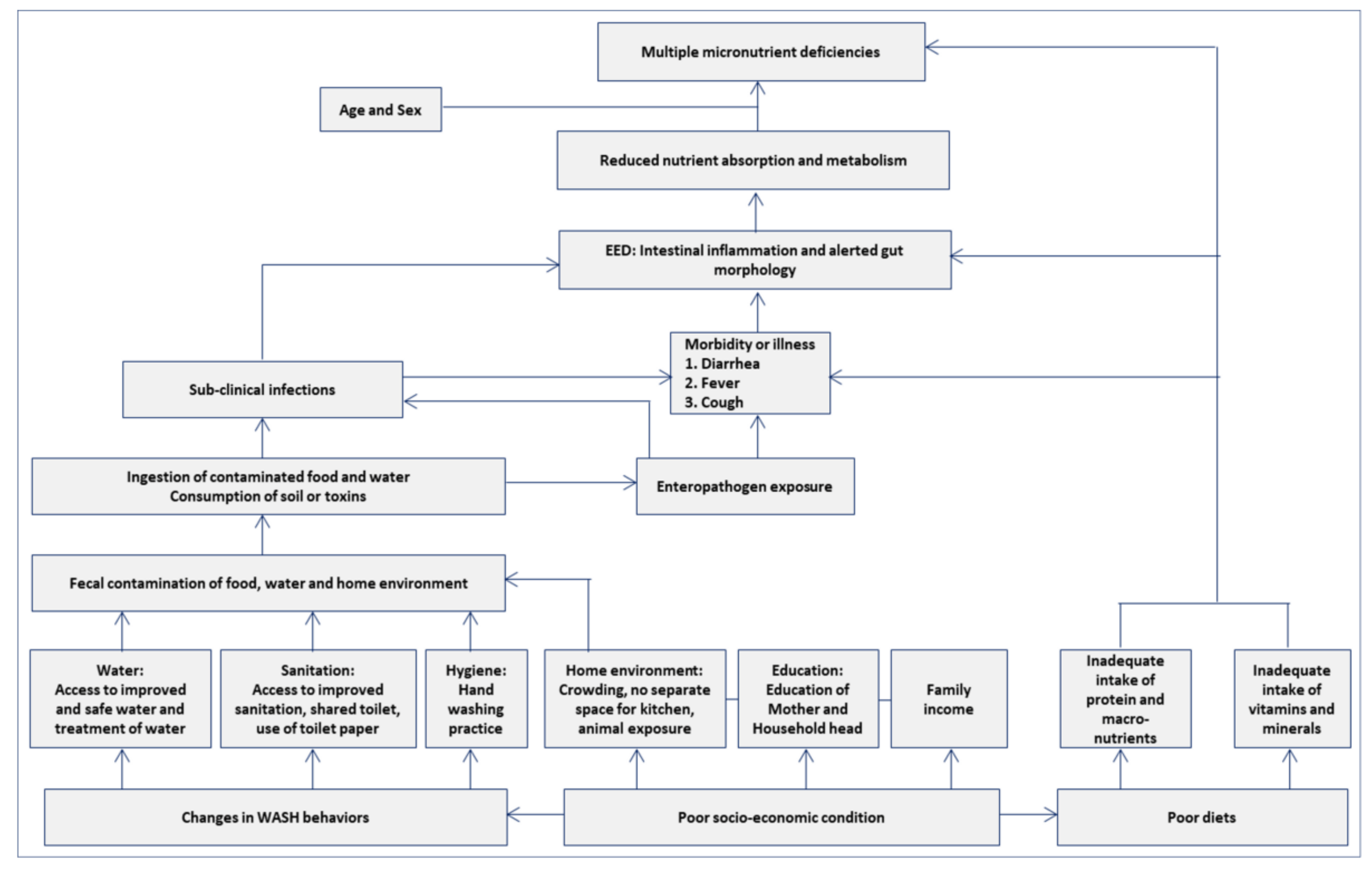
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Population, and Design
2.2. Ethics Declaration
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Biological Sample Collection
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Variables Used in This Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Socio-Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Multiple Micronutrient Deficiencies
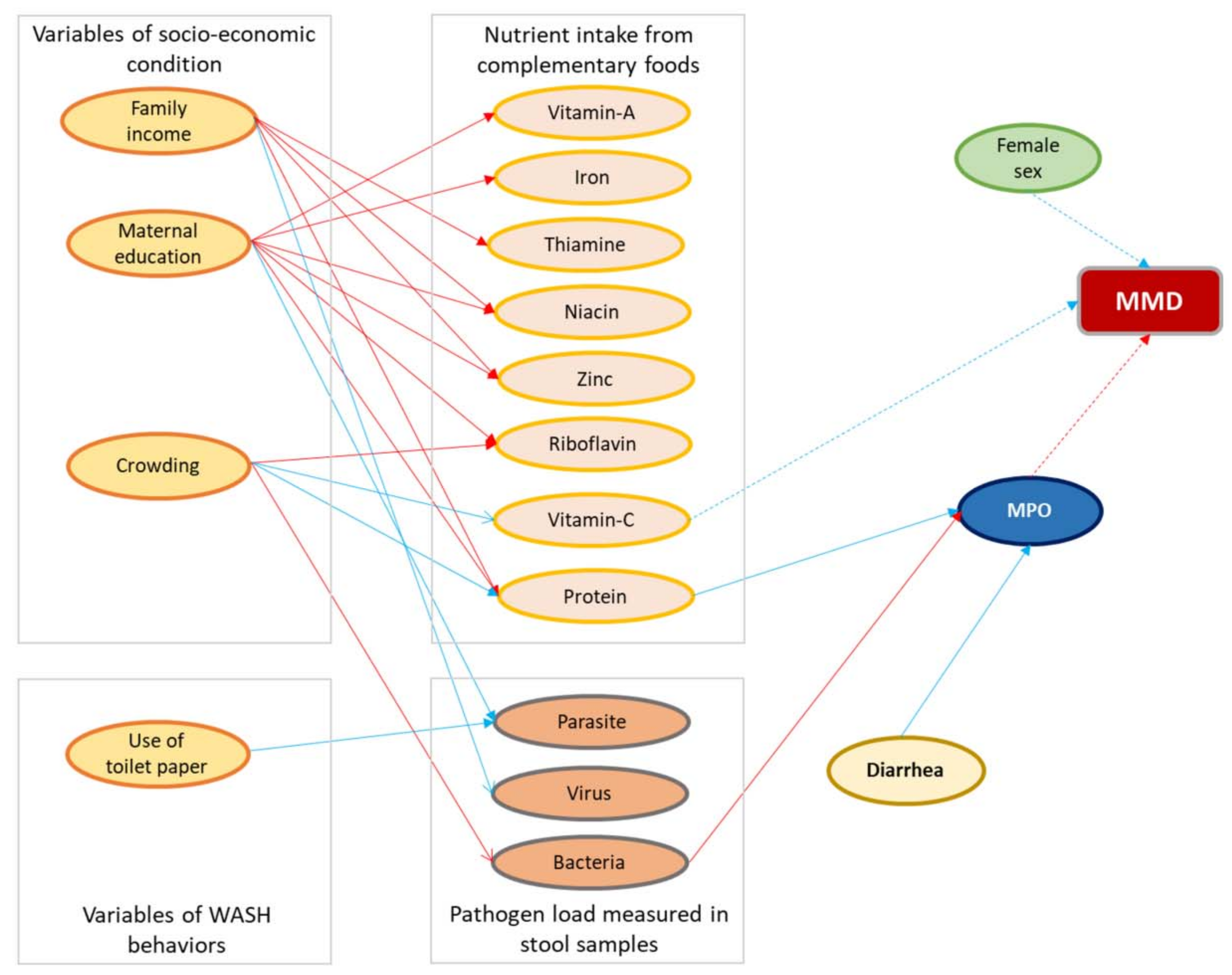
3.3. Factors Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormick, B.J.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Lee, G.O.; Schulze, K.J.; Ross, A.C.; Bauck, A.; Lima, A.A.; Maciel, B.L.; Kosek, M.N.; Seidman, J.C. Intestinal permeability and inflammation mediate the association between nutrient density of complementary foods and biochemical measures of micronutrient status in young children: Results from the MAL-ED study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; De Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, F.; Ferrari, M. Impact of micronutrient deficiencies on growth: The stunting syndrome. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2002, 46, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.M. Micronutrient deficiencies and cognitive functioning. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3927S–3931S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivera, J.A.; Hotz, C.; González-Cossío, T.; Neufeld, L.; García-Guerra, A. The effect of micronutrient deficiencies on child growth: A review of results from community-based supplementation trials. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4010S–4020S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Global micronutrient deficiencies in childhood and impact on growth and survival: Challenges and opportunities. In Meeting Micronutrient Requirements for Health and Development; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dallman, P.R. Iron deficiency and the immune response. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 46, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, T.S.; De Sanctis, V.; Yassin, M.; Wagdy, M.; Soliman, N. Chronic anemia and thyroid function. Acta Bio-Med. Atenei Parm. 2017, 88, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; De Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J.; Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. U.S. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, L.E.; Black, R.E. Zinc deficiency. In Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 257–280. [Google Scholar]
- Stephensen, C.B. Vitamin A, infection, and immune function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellows, A.L.; Smith, E.R.; Muhihi, A.; Briegleb, C.; Noor, R.A.; Mshamu, S.; Sudfeld, C.; Masanja, H.; Fawzi, W.W. Micronutrient deficiencies among breastfeeding infants in Tanzania. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulak, M.; Chandyo, R.K.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L.; Henjum, S.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Shrestha, P.S.; Fawzi, W.W.; Graybill, L.; Strand, T.A. Vitamin status among breastfed infants in Bhaktapur, Nepal. Nutrients 2016, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, F.; Khan, M.; Banu, C.; Qazi, M.; Akhtaruzzaman, M. The coexistence of other micronutrient deficiencies in anaemic adolescent schoolgirls in rural Bangladesh. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hettiarachchi, M.; Liyanage, C. Coexisting micronutrient deficiencies among Sri Lankan pre-school children: A community-based study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2012, 8, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.P.; Dewey, K.G.; Lin, A.; Pickering, A.J.; Byrd, K.A.; Jannat, K.; Ali, S.; Rao, G.; Dentz, H.N.; Kiprotich, M. Effects of lipid-based nutrient supplements and infant and young child feeding counseling with or without improved water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) on anemia and micronutrient status: Results from 2 cluster-randomized trials in Kenya and Bangladesh. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engle-Stone, R.; Aaron, G.J.; Huang, J.; Wirth, J.P.; Namaste, S.M.; Williams, A.M.; Peerson, J.M.; Rohner, F.; Varadhan, R.; Addo, O.Y. Predictors of anemia in preschool children: Biomarkers Reflecting Inflammation and Nutritional Determinants of Anemia (BRINDA) project. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 402S–415S. [Google Scholar]
- Manary, M.J.; Abrams, S.A.; Griffin, I.J.; Quimper, M.M.; Shulman, R.J.; Hamzo, M.G.; Chen, Z.; Maleta, K.; Manary, M.J. Perturbed zinc homeostasis in rural 3–5-y-old Malawian children is associated with abnormalities in intestinal permeability attributed to tropical enteropathy. Pediatric Res. 2010, 67, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalach, N.; Benhamou, P.; Campeotto, F.; Dupont, C. Anemia impairs small intestinal absorption measured by intestinal permeability in children. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 39, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- The MAL-ED study: A multinational and multidisciplinary approach to understand the relationship between enteric pathogens, malnutrition, gut physiology, physical growth, cognitive development, and immune responses in infants and children up to 2 years of age in resource-poor environments. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, S193–S206.
- Mal-Ed Network Investigators. Childhood stunting in relation to the pre-and postnatal environment during the first 2 years of life: The MAL-ED longitudinal birth cohort study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002408. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, L.E.; Wright, J.M.; Rice, G.; Neas, L.; Teuschler, L. Causal inference in cumulative risk assessment: The roles of directed acyclic graphs. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hornik, K.; Leisch, F.; Zeileis, A. JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 20–22 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Darnton-Hill, I.; Webb, P.; Harvey, P.W.; Hunt, J.M.; Dalmiya, N.; Chopra, M.; Ball, M.J.; Bloem, M.W.; De Benoist, B. Micronutrient deficiencies and gender: Social and economic costs. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1198S–1205S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.Y.; Chan, E.W.; Chui, C.S.; Sutcliffe, A.G.; Wong, I.C. The phenomenon of micronutrient deficiency among children in China: A systematic review of the literature. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2605–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Punalekar, S. Culture, political economy and gender marginalisation: A case of girl child in India. Soc. Change 1995, 25, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, D.S.; Frigg, M. Sight and Life Manual on Vitamin A Deficiency Disorders (VADD); Task Force Sight and Life: Basel, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, D.T.; Ninh, N.T.; Hoang, T.N.; Pham, C.T.K.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tran, T.Q.; Huynh, D.T.T. The Effectiveness of Oral Nutritional Supplements Improves the Micronutrient Deficiency of Vietnamese Children with Stunting. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 11, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bloem, M.; Wedel, M.; Egger, R.J.; Speek, A.J.; Schrijver, J.; Saowakontha, S.; Schreurs, W. Iron metabolism and vitamin A deficiency in children in Northeast Thailand. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoya, M.A.; Ngnie-Teta, I.; Séraphin, M.N.; Mamadoultaibou, A.; Boldon, E.; Saint-Fleur, J.E.; Koo, L.; Bernard, S. Prevalence and risk factors of anemia among children 6–59 months old in Haiti. Anemia 2013, 2013, 502968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J. Labor and Population Program. In Indonesian Living Standards Three Years after the Crisis: Evidence from the Indonesia Family Life Survey; deAuteurs: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P. Intrahousehold Dimensions of Micronutrient Deficiencies: A Review of the Evidence; Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Maggini, S.; Wenzlaff, S.; Hornig, D. Essential role of vitamin C and zinc in child immunity and health. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 386–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershoff, S.N. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid): New roles, new requirements? Nutr. Rev. 1993, 51, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SandstroÈm, B. Micronutrient interactions: Effects on absorption and bioavailability. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 85, S181–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, H.; Rink, L. Functional significance of zinc-related signaling pathways in immune cells. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanassova, B.D.; Tzatchev, K.N. Ascorbic acid-important for iron metabolism. Folia Med. 2008, 50, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Yao, G. Effect of vitamin C supplementations on iron deficiency anemia in Chinese children. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 1992, 5, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.C.; Mathur, R. Correction of anemia and iron deficiency in vegetarians by administration of ascorbic acid. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1995, 39, 403–406. [Google Scholar]
- Kosek, M.; Haque, R.; Lima, A.; Babji, S.; Shrestha, S.; Qureshi, S.; Amidou, S.; Mduma, E.; Lee, G.; Yori, P.P. Fecal markers of intestinal inflammation and permeability associated with the subsequent acquisition of linear growth deficits in infants. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahim, S.M.; Das, S.; Gazi, M.A.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T. Association of intestinal pathogens with faecal markers of environmental enteric dysfunction among slum-dwelling children in the first 2 years of life in Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2018, 23, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.M.; Das, S.; Gazi, M.A.; Alam, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Mahfuz, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Haque, R.; Sarker, S.A. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with fecal biomarkers of environmental enteric dysfunction but not with the nutritional status of children living in Bangladesh. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron homeostasis in host defence and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darnton-Hill, I.; Ahmed, F.; Samman, S. The impact of micronutrients on inflammation and health in low-and middle-income countries. In Preventive Nutrition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 597–644. [Google Scholar]
- Fahim, S.M.; Das, S.; Sanin, K.I.; Gazi, M.A.; Mahfuz, M.; Islam, M.M.; Ahmed, T. Association of fecal markers of environmental enteric dysfunction with zinc and iron status among children at first two years of life in Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| BGD | INV | NPB | PKN | BRF | PEL | TZH | ALL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrolled | 265 | 251 | 240 | 277 | 233 | 303 | 262 | 1831 |
| Blood draw at 24 months | 177 | 225 | 116 | 222 | 143 | 195 | 216 | 1294 |
| Missing hemoglobin | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 9 |
| Missing zinc | 2 | 1 | 1 | 49 | 15 | 44 | 54 | 166 |
| Missing retinol | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 |
| Missing ferritin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Analytic total | 174 | 223 | 115 | 151 | 128 | 150 | 152 | 1093 |
| BGD | BRF | INV | NPB | PEL | PKN | TZH | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 174) | (n = 128) | (n = 223) | (n = 115) | (n = 150) | (n = 151) | (n = 152) | (n = 1093) | |
| Female child, n (%) | 86 (49.4%) | 58 (45.3%) | 120 (53.8%) | 51 (44.3%) | 62 (41.3%) | 73 (48.3%) | 73 (48.0%) | 523 (47.9%) |
| Birth weight (kg), Mean ± SD | 2.81 ± 0.41 | 3.36 ± 0.52 | 2.89 ± 0.44 | 2.95 ± 0.40 | 3.13 ± 0.42 | 1.52 ± 1.46 | 3.27 ± 0.49 | 2.83 ± 0.88 |
| Daily energy (Kcal) intake, Median [IQR] | 338 [272, 412] | 987 [824, 1140] | 739 [600, 894] | 392 [328, 481] | 728 [610, 876] | 619 [470, 782] | 994 [888, 1130] | 699 [452, 917] |
| Daily protein (gm) intake, Median [IQR] | 9.37 [7.83, 12.0] | 40.3 [34.3, 48.7] | 20.7 [16.4, 26.8] | 10.6 [8.09, 13.7] | 19.5 [16.3, 22.6] | 15.8 [11.9, 20.4] | 28.2 [24.6, 34.0] | 19.2 [12.2, 27.5] |
| Daily carbohydrates (gm) intake, Median [IQR] | 56.1 [45.0, 67.9] | 138 [113, 157] | 112 [93.6, 133] | 58.8 [49.4, 69.5] | 126 [109, 154] | 86.8 [69.6, 107] | 185 [163, 207] | 107 [70.0, 143] |
| Daily iron (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 1.40 [1.09, 1.78] | 14.2 [11.3, 17.4] | 2.38 [2.05, 2.95] | 1.31 [1.06, 1.70] | 3.77 [2.99, 4.80] | 2.09 [1.69, 2.78] | 8.31 [7.23, 9.14] | 2.70 [1.72, 6.90] |
| Daily folate (ug) intake, Median [IQR] | 34.3 [28.8, 44.8] | 166 [133, 201] | 82.0 [68.5, 101] | 40.3 [32.8, 53.9] | 57.8 [43.0, 71.7] | 58.7 [47.0, 78.3] | 65.0 [56.2, 77.3] | 63.6 [44.2, 88.8] |
| Daily zinc (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 1.13 [0.90, 1.42] | 9.05 [7.27, 11.0] | 2.85 [2.24, 3.69] | 1.28 [1.00, 1.71] | 2.20 [1.87, 2.74] | 1.94 [1.46, 2.54] | 5.25 [4.55, 6.03] | 2.43 [1.48, 4.54] |
| Daily thiamin (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 0.18 [0.15, 0.23] | 0.77 [0.65, 0.95] | 0.25 [0.20, 0.32] | 0.16 [0.12, 0.22] | 0.28 [0.23, 0.37] | 0.41 [0.33, 0.52] | 0.56 [0.47, 0.63] | 0.30 [0.20, 0.52] |
| Daily niacin (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 2.64 [2.08, 3.19] | 9.47 [7.51, 11.3] | 2.66 [2.12, 3.22] | 1.60 [1.25, 2.07] | 3.96 [3.13, 4.60] | 4.37 [3.43, 5.61] | 5.44 [4.63, 6.12] | 3.53 [2.44, 5.35] |
| Daily riboflavin (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 0.20 [0.15, 0.30] | 1.52 [1.27, 1.87] | 0.44 [0.29, 0.79] | 0.25 [0.17, 0.37] | 0.47 [0.35, 0.65] | 0.49 [0.36, 0.74] | 0.97 [0.64, 1.34] | 0.47 [0.28, 0.94] |
| Daily Vitamin-A (ug) intake, Median [IQR] | 52.8 [35.9, 77.4] | 955 [754, 1150] | 181 [116, 284] | 83.9 [61.0, 114] | 219 [148, 335] | 150 [93.0, 220] | 136 [91.5, 184] | 147 [81.2, 271] |
| Daily Vitamin-C (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 10.1 [6.88, 16.2] | 101 [77.2, 121] | 9.67 [7.92, 11.9] | 7.28 [5.08, 10.0] | 55.4 [28.5, 114] | 11.6 [7.38, 17.9] | 5.84 [3.96, 7.89] | 11.2 [7.11, 27.5] |
| Daily Vitamin-B6 (mg) intake, Median [IQR] | 0.26 [0.20, 0.32] | 1.03 [0.79, 1.51] | 0.27 [0.21, 0.34] | 0.23 [0.19, 0.29] | 0.37 [0.30, 0.45] | 0.42 [0.32, 0.56] | 0.15 [0.11, 0.20] | 0.30 [0.21, 0.44] |
| Daily Vitamin-B12 (ug) intake, Median [IQR] | 0.37 [0.24, 0.60] | 4.61 [3.96, 5.59] | 0.62 [0.39, 0.96] | 0.51 [0.31, 0.84] | 0.94 [0.68, 1.29] | 0.68 [0.42, 1.21] | 1.18 [0.72, 1.75] | 0.77 [0.42, 1.44] |
| EBF duration in days, Median [IQR] | 109 [59.3, 157] | 56.5 [27.0, 99.3] | 79.0 [39.5, 111] | 43.0 [17.5, 96.0] | 14.5 [6.00, 56.8] | 10.0 [5.00, 14.0] | 34.0 [19.8, 61.0] | 42.0 [14.0, 95.0] |
| Myeloperoxidase (ng/mL) in log scale, Mean ± SD | 8.31 ± 0.41 | 7.83 ± 0.73 | 8.86 ± 0.46 | 8.55 ± 0.47 | 8.83 ± 0.48 | 8.31 ± 0.55 | 8.53 ± 0.41 | 8.49 ± 0.60 |
| Neopterin (nmol/L) in log scale, Mean ± SD | 6.87 ± 0.45 | 7.28 ± 0.38 | 7.41 ± 0.37 | 7.47 ± 0.28 | 7.72 ± 0.37 | 6.14 ± 0.39 | 6.62 ± 0.51 | 7.07 ± 0.65 |
| α-1 antitrypsin (mg/g) in log scale, Mean ± SD | −0.95 ± 0.37 | −1.30 ± 0.49 | −1.11 ± 0.37 | −0.76 ± 0.37 | −0.98 ± 0.42 | −1.78 ± 0.58 | −1.46 ± 0.48 | −1.19 ± 0.54 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), Median [IQR] | 11.9 [10.9, 12.7] | 12.0 [10.6, 13.3] | 11.2 [10.2, 11.9] | 11.3 [10.6, 11.7] | 11.7 [11.0, 12.5] | 9.80 [8.60, 10.7] | 11.4 [10.5, 12.2] | 11.3 [10.2, 12.2] |
| Zinc (μmol/L), Median [IQR] | 11.8 [10.9, 13.2] | 13.6 [12.9, 15.4] | 8.50 [8.00, 9.20] | 11.6 [10.1, 13.0] | 14.2 [11.8, 16.7] | 8.00 [6.00, 10.6] | 11.2 [10.0, 12.7] | 11.1 [9.00, 13.3] |
| Ratinol (μmol/L), Median [IQR] | 24.0 [19.9, 28.0] | 30.7 [25.3, 35.8] | 29.2 [23.2, 36.1] | 24.5 [19.9, 30.4] | 22.8 [18.9, 28.9] | 20.6 [16.5, 25.0] | 17.2 [13.8, 20.7] | 24.1 [18.9, 30.5] |
| Ferritin (μg/L), Median [IQR] | 7.75 [4.70, 14.2] | 25.3 [15.0, 36.4] | 8.60 [4.35, 19.7] | 14.8 [7.10, 24.2] | 25.9 [12.8, 37.3] | 4.00 [2.00, 8.10] | 15.0 [7.70, 24.5] | 12.3 [5.30, 25.7] |
| Bacteria load, Mean ± SD | 0.91 ± 0.25 | 1.05 ± 0.33 | 0.79 ± 0.28 | 0.70 ± 0.22 | 0.56 ± 0.24 | 1.14 ± 0.31 | 1.04 ± 0.31 | 0.88 ± 0.34 |
| Parasite load, Mean ± SD | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.14 ± 0.20 | 0.21 ± 0.19 | 0.14 ± 0.16 | 0.32 ± 0.21 | 0.45 ± 0.23 | 0.23 ± 0.18 | 0.23 ± 0.21 |
| Virus load, Mean ± SD | 0.08 ± 0.08 | 0.03 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.07 | 0.08 ± 0.07 | 0.07 ± 0.08 | 0.09 ± 0.09 | 0.07 ± 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahim, S.M.; Alam, M.A.; Alam, J.; Gazi, M.A.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T. Inadequate Vitamin C Intake and Intestinal Inflammation Are Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiency in Young Children: Results from a Multi-Country Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071408
Fahim SM, Alam MA, Alam J, Gazi MA, Mahfuz M, Ahmed T. Inadequate Vitamin C Intake and Intestinal Inflammation Are Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiency in Young Children: Results from a Multi-Country Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071408
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahim, Shah Mohammad, Md Ashraful Alam, Jinat Alam, Md Amran Gazi, Mustafa Mahfuz, and Tahmeed Ahmed. 2022. "Inadequate Vitamin C Intake and Intestinal Inflammation Are Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiency in Young Children: Results from a Multi-Country Birth Cohort Study" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071408
APA StyleFahim, S. M., Alam, M. A., Alam, J., Gazi, M. A., Mahfuz, M., & Ahmed, T. (2022). Inadequate Vitamin C Intake and Intestinal Inflammation Are Associated with Multiple Micronutrient Deficiency in Young Children: Results from a Multi-Country Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients, 14(7), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071408






