Evaluating the Effects of Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions on Sleep Traits Using the UK Biobank Cohort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Insomnia and Sleep Duration Phenotypes in the UK Biobank
2.1.1. Ethics Approval
2.1.2. Study Population and Phenotype Definition
2.1.3. Genotype, Imputation, and Quality Control
2.2. GWAS Dataset of Gut Microbiota
2.3. GWAS Dataset of Dietary Compositions
2.4. GWAS Dataset of Dietary Habits
2.5. Genetic Correlations with Dietary Habits and Co-Localization
2.6. PRS Analysis
2.7. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Results of LDSC and Colocalization
3.2. The Results of Dietary Compositions-Gut Microbiota Interactions
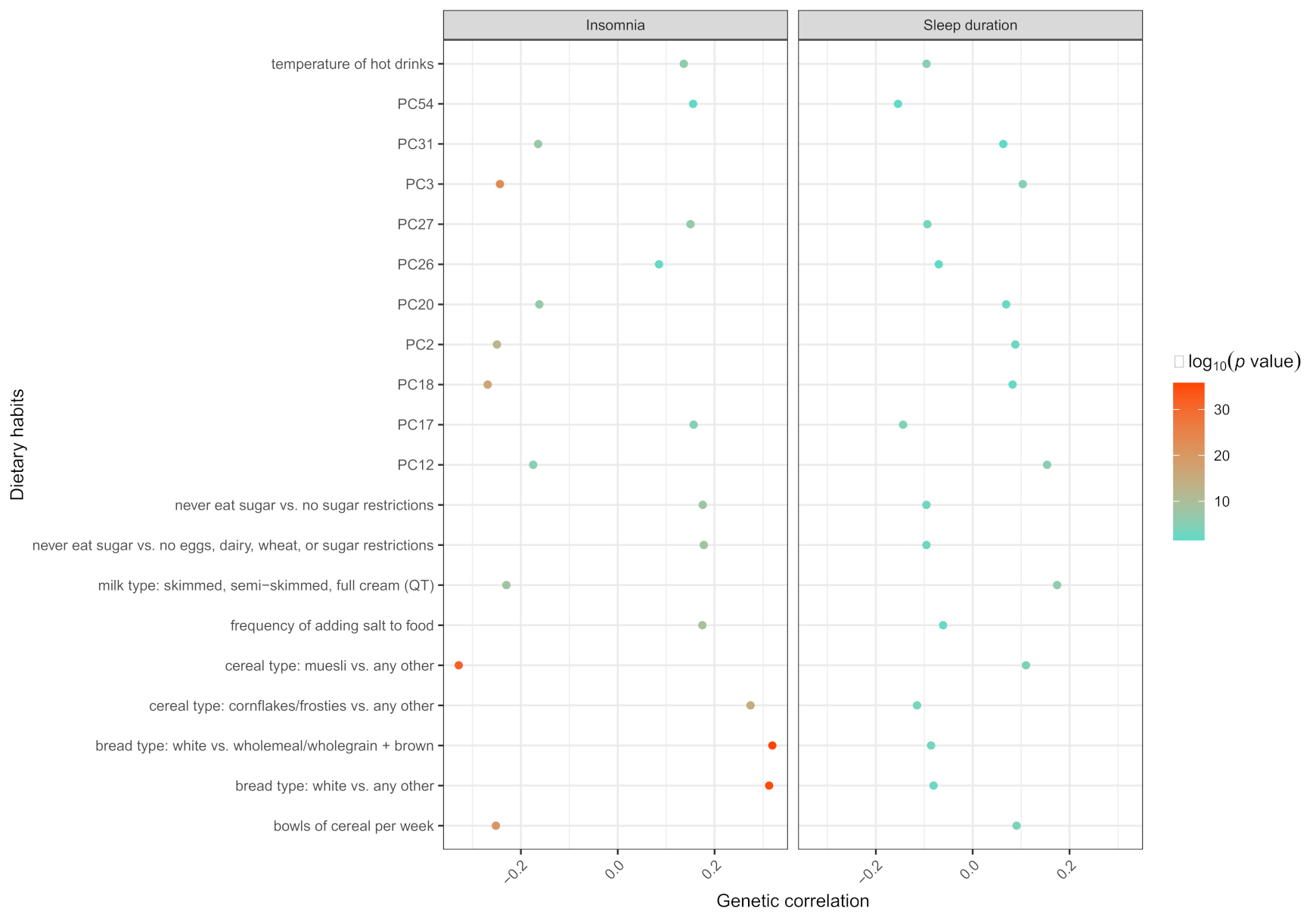
3.3. The Results of Dietary Habits-Gut Microbiota Interactions
3.4. The Common Interactions of Sleep Duration and Insomnia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buysse, D.J. Insomnia. JAMA 2013, 309, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, M.L.; Bruni, O. Insomnia in childhood and adolescence: Clinical aspects, diagnosis, and therapeutic approach. J. De Pediatr. 2015, 91 (Suppl. S1), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hysing, M.; Pallesen, S.; Stormark, K.M.; Lundervold, A.J.; Sivertsen, B. Sleep patterns and insomnia among adolescents: A population-based study. J. Sleep Res. 2013, 22, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.K.; Coulouvrat, C.; Hajak, G.; Lakoma, M.D.; Petukhova, M.; Roth, T.; Sampson, N.A.; Shahly, V.; Shillington, A.; Stephenson, J.J.; et al. Nighttime Insomnia Symptoms and Perceived Health in the America Insomnia Survey (AIS). Sleep 2011, 34, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morin, C.M.; Drake, C.L.; Harvey, A.G.; Krystal, A.D.; Manber, R.; Riemann, D.; Spiegelhalder, K. Insomnia disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.; Cho, N.; Zhang, J. Sex Differences in Insomnia: From Epidemiology and Etiology to Intervention. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wing, Y.K. Sex Differences in Insomnia: A Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2006, 29, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, D. Sleep Disorders: Insomnia. FP Essent. 2017, 460, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hoevenaar-Blom, M.P.; Spijkerman, A.M.; Kromhout, D.; van Den Berg, J.F.; Verschuren, W.M. Sleep Duration and Sleep Quality in Relation to 12-Year Cardiovascular Disease Incidence: The MORGEN Study. Sleep 2011, 34, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Tan, L. Comparing primary insomnia to the insomnia occurring in major depression and general anxiety disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 282, 112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Morin, C.; Cervena, K.; Carlander, B.; Touchon, J.; Besset, A.; Billiard, M. Family studies in insomnia. J. Psychosom. Res. 2005, 58, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lam, S.-P.; Li, S.X.; Ma, R.; Kong, A.P.S.; Chan, M.H.M.; Ho, C.-S.; Li, A.M.; Wing, Y.K. A Community-Based Study on the Association Between Insomnia and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis: Sex and Pubertal Influences. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonnet, M.H.; Arand, D.L. 24-Hour metabolic rate in insomniacs and matched normal sleepers. Sleep 1995, 18, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, B.; Dittoni, S.; Colicchio, S.; Testani, E.; Losurdo, A.; Gnoni, V.; Di Blasi, C.; Brunetti, R.; Contardi, A.; Mazza, S.; et al. Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability Modification in Chronic Insomnia Patients. Behav. Sleep Med. 2013, 12, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, L.C.; Gradisar, M.; Van Someren, E.J.; Wright, H.R.; Lushington, K. The relationship between insomnia and body temperatures. Sleep Med. Rev. 2008, 12, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.; Aggen, S.H.; Kirkpatrick, R.M.; Kendler, K.S.; Amstadter, A.B. A Longitudinal Twin Study of Insomnia Symptoms in Adults. Sleep 2015, 38, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wing, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Li, S.; Tang, N.; Lai, K.; Li, A. Familial aggregation and heritability of insomnia in a community-based study. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, N.L.; Gehrman, P.R.; Gregory, A.M.; Eaves, L.J.; Silberg, J.L. The Heritability of Insomnia Progression during Childhood/Adolescence: Results from a Longitudinal Twin Study. Sleep 2015, 38, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, J.A.; Neufeld, K.-A.M. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Microbiota-Brain-Gut Axis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Han, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, R.; Jin, K.; Yi, W. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and the central nervous system. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53829–53838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 (Suppl. S1), S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The Role of Microbiome in Insomnia, Circadian Disturbance and Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Xiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota as an Objective Measurement for Auxiliary Diagnosis of Insomnia Disorder. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Bushman, F.D.; FitzGerald, G.A. Rhythmicity of the intestinal microbiota is regulated by gender and the host circadian clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10479–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawson, S.L.; Dash, S.R.; Jacka, F.N. The Importance of Diet and Gut Health to the Treatment and Prevention of Mental Disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2016, 131, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfredi, V.; Nucci, D.; Tonzani, A. Sleep disorder, Mediterranean Diet and learning performance among nursing students: InSOMNIA, a cross-sectional study. Ann. Ig. 2018, 30, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, J.; Zhang, X.C.; Jacobi, F. Vegetarian diet and mental disorders: Results from a representative community survey. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brietzke, E.; Mansur, R.B.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Vinberg, M.; González-Pinto, A.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Ho, R.; McIntyre, R.S. Ketogenic diet as a metabolic therapy for mood disorders: Evidence and developments. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 94, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Diehl, C.; Wood, A.C.; Redline, S.; Reid, M.; Johnson, D.A.; Maras, J.E.; Jacobs, D.R.; Shea, S.; Crawford, A.; St-Onge, M.-P. Mediterranean diet pattern and sleep duration and insomnia symptoms in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Sawrey-Kubicek, L.; Beals, E.; Rhodes, C.H.; Houts, H.E.; Sacchi, R.; Zivkovic, A.M. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: A pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2020, 77, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wain, L.V.; Shrine, N.; Miller, S.; Jackson, V.E.; Ntalla, I.; Artigas, M.S.; Billington, C.K.; Kheirallah, A.K.; Allen, R.; Cook, J.P.; et al. Novel insights into the genetics of smoking behaviour, lung function, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (UK BiLEVE): A genetic association study in UK Biobank. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UK Biobank. Genotyping and Quality Control of UK Biobank, a Large-Scale, Extensively Phenotyped Prospective Resource. Available online: https://biobank.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/crystal/crystal/docs/genotyping_qc.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.A.M.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manichaikul, A.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Rich, S.S.; Daly, K.; Sale, M.; Chen, W.-M. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, J.; Sharp, K.; Shrine, N.; Wain, L.; Hall, I.; Tobin, M.; Zagury, J.-F.; Delaneau, O.; Marchini, J. Haplotype estimation for biobank-scale data sets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVean, G.A.; The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 2012, 491, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Band, G.; Marchini, J. BGEN: A binary file format for imputed genotype and haplotype data. bioRxiv 2018, 308296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.A.; Bacigalupe, R.; Wang, J.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Tito, R.Y.; Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Henckaerts, L.; Rymenans, L.; et al. Genome-wide associations of human gut microbiome variation and implications for causal inference analyses. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Thingholm, L.B.; Skiecevičienė, J.; Rausch, P.; Kummen, M.; Hov, J.R.; Degenhardt, F.; Heinsen, F.A.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Szymczak, S.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variation in vitamin D receptor and other host factors influencing the gut microbiota. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczak, M.; Nikolaus, S.; von Eberstein, H.; Croucher, P.J.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Schreiber, S. PopGen: Population-based recruitment of patients and controls for the analysis of complex genotype-phenotype relationships. Public Health Genom. 2006, 9, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hildebrand, F.; Tadeo, R.; Voigt, A.Y.; Bork, P.; Raes, J. LotuS: An efficient and user-friendly OTU processing pipeline. Microbiome 2014, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howie, B.N.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. A Flexible and Accurate Genotype Imputation Method for the Next Generation of Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, S.; Das, S. A reference panel of 64,976 haplotypes for genotype imputation. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Meddens, S.F.; de Vlaming, R.; Bowers, P.; Burik, C.A.; Linnér, R.K.; Lee, C.; Okbay, A.; Turley, P.; Rietveld, C.A.; Fontana, M.A.; et al. Genomic analysis of diet composition finds novel loci and associations with health and lifestyle. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 26, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C.; Hirschhorn, J.N. Comprehensive genomic analysis of dietary habits in UK Biobank identifies hundreds of genetic associations. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, P.-R.; Tucker, G.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.K.; Vilhjálmsson, B.J.; Finucane, H.K.; Salem, R.M.; Chasman, D.I.; Ridker, P.M.; Neale, B.M.; Berger, B.; et al. Efficient Bayesian mixed-model analysis increases association power in large cohorts. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.-R.; Kichaev, G.; Gazal, S.; Schoech, A.P.; Price, A.L. Mixed-model association for biobank-scale datasets. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.R.; Watanabe, K.; Stringer, S.; Skene, N.; Bryois, J.; Hammerschlag, A.R.; De Leeuw, C.A.; Benjamins, J.S.; Manchado, A.M.; Nagel, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of insomnia in 1,331,010 individuals identifies new risk loci and functional pathways. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dashti, H.S.; Jones, S.E.; Wood, A.R.; Lane, J.M.; Van Hees, V.T.; Wang, H.; Rhodes, J.A.; Song, Y.; Patel, K.; Anderson, S.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic loci for self-reported habitual sleep duration supported by accelerometer-derived estimates. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giambartolomei, C.; Vukcevic, D.; Schadt, E.E.; Franke, L.; Hingorani, A.; Wallace, C.; Plagnol, V. Bayesian Test for Colocalisation between Pairs of Genetic Association Studies Using Summary Statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakefield, J. Bayes factors for genome-wide association studies: Comparison with P-values. Genet. Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food Components and Dietary Habits: Keys for a Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, K.V.; Sherwin, E.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J.F. Feeding the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Diet, microbiome, and neuropsychiatry. Transl. Res. 2016, 179, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, P.; Sudo, N.; Dinan, T.; Taylor, V.; Bienenstock, J. Mood and gut feelings. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Déchelotte, P. The new link between gut–brain axis and neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Saarinen, A.; Mikkola, T.M.; Tenhunen, J.; Martinmäki, S.; Rahikainen, A.; Cheng, S.; Eklund, N.; Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.; et al. Effects of exercise and diet interventions on obesity-related sleep disorders in men: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaagura, M.; Viiard, E.; Karu-Lavits, K.; Adamberg, K. Low-carbohydrate high-fat weight reduction diet induces changes in human gut microbiota. MicrobiologyOpen 2021, 10, e1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Shekotikhina, M.; Carmona, N.E.; Lee, Y.; Mansur, R.B.; Brietzke, E.; Fus, D.; Coles, A.S.; Iacobucci, M.; et al. Characterizing the gut microbiota in adults with bipolar disorder: A pilot study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 24, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhuo, M.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Altered gut microbiota associated with symptom severity in schizophrenia. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, G.; Song, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiota changes in patients with autism spectrum disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 129, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskemoen, J.F.; Simonsen, C.; Büchmann, C.; Barrett, E.A.; Bjella, T.; Lagerberg, T.V.; Vedal, T.J.; Andreassen, O.A.; Melle, I.; Aas, M. Sleep disturbances in schizophrenia spectrum and bipolar disorders—A transdiagnostic perspective. Compr. Psychiatry 2019, 91, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souders, M.C.; Zavodny, S.; Eriksen, W.; Sinko, R.; Connell, J.; Kerns, C.; Schaaf, R.; Pinto-Martin, J. Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, A.; Struijk, E.A.; Arias-Fernandez, L.; Graciani, A.; Mesas, A.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Lopez-Garcia, E. Habitual Meat Consumption and Changes in Sleep Duration and Quality in Older Adults. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Kim, J.E.; Armstrong, C.L.; Chen, N.; Campbell, W.W. Higher-protein diets improve indexes of sleep in energy-restricted overweight and obese adults: Results from 2 randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Ahmed, M.I.; Zou, X.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Beef, Casein, and Soy Proteins Differentially Affect Lipid Metabolism, Triglycerides Accumulation and Gut Microbiota of High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-W.; Zhao, B.-C.; Yang, X.; Lei, S.-H.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Liu, K.-X. Relationships of sleep disturbance, intestinal microbiota, and postoperative pain in breast cancer patients: A prospective observational study. Sleep Breath. 2020, 25, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frugé, A.D.; Ptacek, T.; Tsuruta, Y.; Morrow, C.D.; Azrad, M.; Desmond, R.A.; Hunter, G.R.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W. Dietary Changes Impact the Gut Microbe Composition in Overweight and Obese Men with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 714–723.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Easson, C.; Lyle, S.M.; Kapoor, R.; Donnelly, C.P.; Davidson, E.J.; Parikh, E.; Lopez, J.V.; Tartar, J.L. Gut microbiome diversity is associated with sleep physiology in humans. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosicki, G.J.; Riemann, B.L.; Flatt, A.A.; Valentino, T.; Lustgarten, M.S. Self-reported sleep quality is associated with gut microbiome composition in young, healthy individuals: A pilot study. Sleep Med. 2020, 73, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.; Vogel, H.; Jonas, W.; Woting, A.; Blaut, M.; Schurmann, A.; Cedernaes, J. Gut microbiota and glucometabolic alterations in response to recurrent partial sleep deprivation in normal-weight young individuals. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.C.D.; Cecatti, C.; Fidélix, M.P.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Cesar, T.B.; Sivieri, K. Effect of Daily Consumption of Orange Juice on the Levels of Blood Glucose, Lipids, and Gut Microbiota Metabolites: Controlled Clinical Trials. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, S.J.; Vargas, F.; González, A.; He, S.; Jiang, P.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Knight, R.; Wright, K.P., Jr.; Lowry, C.A.; Fleshner, M.; et al. Repeated sleep disruption in mice leads to persistent shifts in the fecal microbiome and metabolome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Kong, Q.; Tian, P.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Chen, W. Targeting Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: Potential Intervention Strategies for Neurological Disorders. Engineering 2020, 6, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Singh, A.; Bokkon, I.; Mallick, B.N. REM sleep and its Loss-Associated Epigenetic Regulation with Reference to Noradrenaline in Particular. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karacan, I.; Thornby, J.I.; Anch, A.M.; Booth, G.H.; Williams, R.L.; Salis, P.J. Dose-related sleep disturbances induced by coffee and caffeine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1976, 20, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, D.P. Null hypothesis significance testing and effect sizes: Can we ‘effect’ everything … or … anything. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 51, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, D.J.M.; Bodmer, W.F. Polygenic inheritance, GWAS, polygenic risk scores, and the search for functional variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18924–18933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, X.; Ye, J.; Wen, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F. Evaluating the Effects of Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions on Sleep Traits Using the UK Biobank Cohort. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061134
Qi X, Ye J, Wen Y, Liu L, Cheng B, Cheng S, Yao Y, Zhang F. Evaluating the Effects of Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions on Sleep Traits Using the UK Biobank Cohort. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061134
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Xin, Jing Ye, Yan Wen, Li Liu, Bolun Cheng, Shiqiang Cheng, Yao Yao, and Feng Zhang. 2022. "Evaluating the Effects of Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions on Sleep Traits Using the UK Biobank Cohort" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061134
APA StyleQi, X., Ye, J., Wen, Y., Liu, L., Cheng, B., Cheng, S., Yao, Y., & Zhang, F. (2022). Evaluating the Effects of Diet-Gut Microbiota Interactions on Sleep Traits Using the UK Biobank Cohort. Nutrients, 14(6), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061134





