Acute Effects of Low Dose of Caffeine Ingestion Combined with Conditioning Activity on Psychological and Physical Performances of Male and Female Taekwondo Athletes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
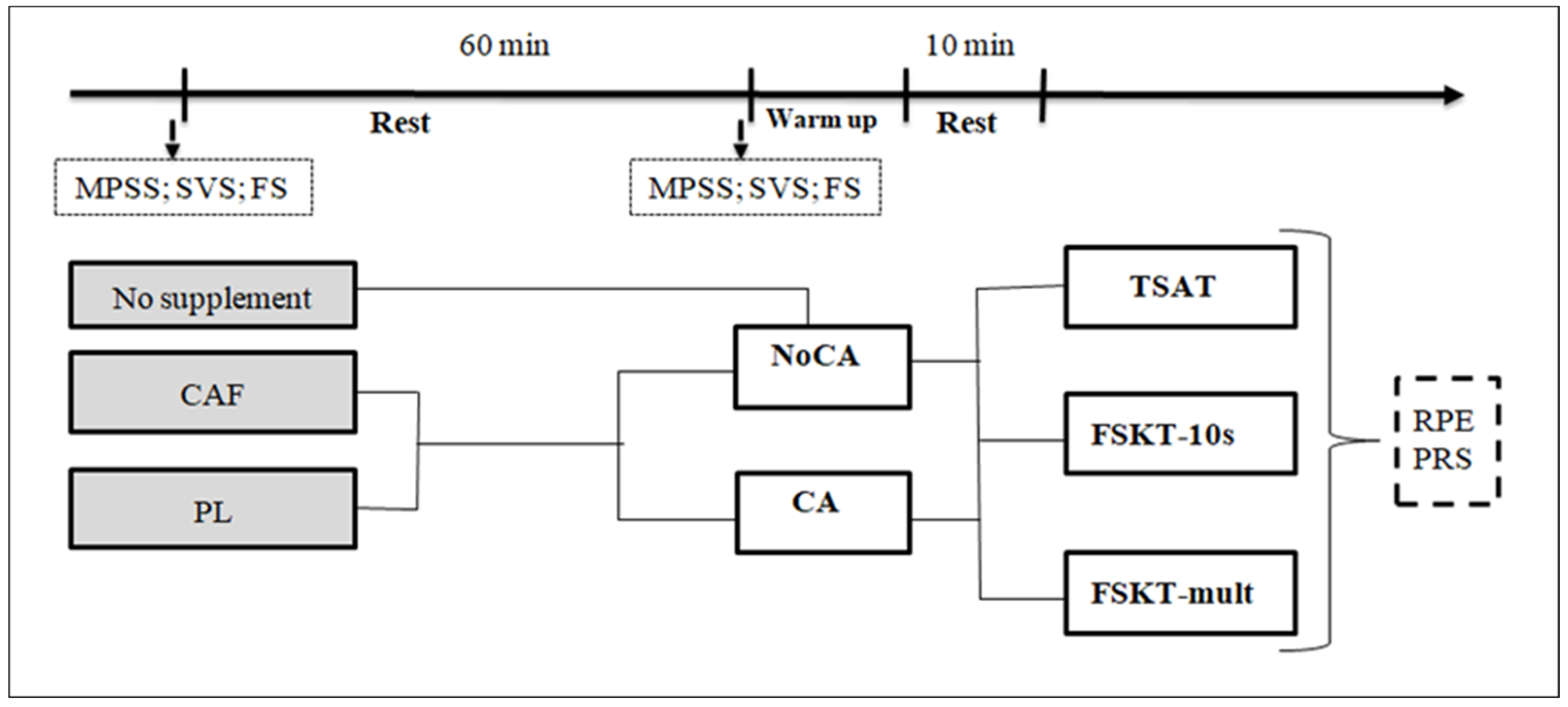
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Testing Procedure
2.3.1. Taekwondo-Specific Agility Test
2.3.2. 10 s Frequency Speed of Kick Test
2.3.3. Multiple Frequency Speed of Kick Test
2.3.4. Mood and Physical Symptoms Scale
2.3.5. Subjective Vitality Scale
2.3.6. Feeling Scale
2.3.7. Rating of Perceived Exertion
2.3.8. Perceived Recovery Status
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Taekwondo-Specific Agility Test
3.2. Frequency Speed of Kick Test
3.3. Multiple Frequency Speed of Kick Test
3.3.1. Total Number of Techniques
3.3.2. Decrement Index
3.4. Mood and Physical Symptoms Scale
3.5. Subjective Vitality Scale
3.6. Feeling Scale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| CA | Conditioning activity (single condition) |
| CAF | Caffeine (single condition) |
| DI | Kick decrement index |
| FS | Feeling Scale |
| FSKT-mult | Multiple frequency speed of kick test |
| FSKT-10s | Frequency speed of kick test |
| MPSS | Mood and Physical Symptoms Scale |
| NoCA | Without conditioning activity (single condition) |
| PAP | Post-activation potentiation |
| PAPE | Post-activation performance enhancement |
| PL | Placebo (single condition) |
| PRS | Perceived recovery status |
| RPE | Rating of perceived exertion |
| SVS | Subjective Vitality Scale |
| TSAT | Taekwondo-specific agility test |
References
- Bridge, C.A.; Ferreira da Silva Santos, J.; Chaabene, H.; Pieter, W.; Franchini, E. Physical and physiological profiles of taekwondo athletes. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 713–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornello, F.; Capranica, L.; Chiodo, S.; Minganti, C.; Tessitore, A. Time-motion analysis of youth Olympic Taekwondo combats. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Trexler, E.T.; Lazinica, B.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of caffeine intake on muscle strength and power: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Zhao, Z.; Stock, H.S.; Mehl, K.A.; Buggy, J.; Hand, G.A. Central nervous system effects of caffeine and adenosine on fatigue. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R399–R404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wang, H.S.; Tung, K.; Chao, H.H. Effects of Gender Difference and Caffeine Supplementation on Anaerobic Muscle Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gonzalez, L.M.; Sanchez-Oliver, A.J.; Mata, F.; Jodra, P.; Antonio, J.; Dominguez, R. Acute caffeine supplementation in combat sports: A systematic review. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astley, C.; Souza, D.; Polito, M. Acute Caffeine Ingestion on Performance in Young Judo Athletes. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 29, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, L.; Mackay, K.; Contreras, E.; Penailillo, L. Acute effect of caffeine ingestion on reaction time and electromyographic activity of the Dollyo Chagi round kick in taekwondo fighters. Rev. Int. Cienc. Deporte 2017, 13, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino Fernández, M.; Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Giráldez-Costas, V.; Gonzalez-Millán, C.; Matos-Duarte, M.; Gutiérrez-Hellín, J.; González-García, J. Caffeine Doses of 3 mg/kg Increase Unilateral and Bilateral Vertical Jump Outcomes in Elite Traditional Jiu-Jitsu Athletes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.G.; Santos, V.R.; Felippe, L.J.; Almeida, J.W., Jr.; Bertuzzi, R.; Kiss, M.A.; Lima-Silva, A.E. Caffeine reduces reaction time and improves performance in simulated-contest of taekwondo. Nutrients 2014, 6, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Azevedo, A.P.; Guerra, M.A.; Caldas, L.C.; Guimaraes-Ferreira, L. Acute Caffeine Ingestion did not Enhance Punch Performance in Professional Mixed-Martial Arts Athletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes-Silva, J.P.; Silva Santos, J.F.; Branco, B.H.; Abad, C.C.; Oliveira, L.F.; Loturco, I.; Franchini, E. Caffeine Ingestion Increases Estimated Glycolytic Metabolism during Taekwondo Combat Simulation but Does Not Improve Performance or Parasympathetic Reactivation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.L.; Guilherme, J.; Ferreira, L.H.B.; de Souza-Junior, T.P.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. Caffeine and Exercise Performance: Possible Directions for Definitive Findings. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 574854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C. Caffeine, CYP1A2 genotype, and sports performance: Is timing important? Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southward, K.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.; Badenhorst, C.; Ali, A. The Role of Genetics in Moderating the Inter-Individual Differences in the Ergogenicity of Caffeine. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Marques-Jiménez, D.; Refoyo, I.; Del Coso, J.; León-Guereño, P.; Calleja-González, J. Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Sports Performance Based on Differences Between Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, M.A., Jr.; Caldas, L.C.; De Souza, H.L.; Vitzel, K.F.; Cholewa, J.M.; Duncan, M.J.; Guimarães-Ferreira, L. The acute effects of plyometric and sled towing stimuli with and without caffeine ingestion on vertical jump performance in professional soccer players. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blazevich, A.J.; Babault, N. Post-activation Potentiation Versus Post-activation Performance Enhancement in Humans: Historical Perspective, Underlying Mechanisms, and Current Issues. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuenca-Fernandez, F.; Smith, I.C.; Jordan, M.J.; MacIntosh, B.R.; Lopez-Contreras, G.; Arellano, R.; Herzog, W. Nonlocalized postactivation performance enhancement (PAPE) effects in trained athletes: A pilot study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.Y.; Chen, S.E.; Lum, D. Inducing postactivation potentiation with different modes of exercise. Strength Cond. J. 2020, 42, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, L.B.; Haff, G.G. Factors Modulating Post-Activation Potentiation of Jump, Sprint, Throw, and Upper-Body Ballistic Performances: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, D. Effects of various warm-up protocol on special judo fitness test performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritopoulos, S.; Theodorou, A.; Methenitis, S.; Zaras, N.; Donti, O.; Tsolakis, C. The effect of plyometric exercises on repeated strength and power performance in elite karate athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2015, 15, 310. [Google Scholar]
- Miarka, B.; Del Vecchio, F.B.; Franchini, E. Acute effects and postactivation potentiation in the Special Judo Fitness Test. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Garrido, N.; Valderas-Maldonado, C.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Ferreira Da Silva, J.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Vásquez-Gómez, J.; Magnani Branco, B.; Zapata-Bastias, J.; López-Fuenzalida, A.; Valdés-Badilla, P. Effects of post-activation potentiation exercises on kicking frequency, fatigue rate and jump performance in taekwondo athletes: A case study. Retos 2020, 68, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Santos, J.F.; Valenzuela, T.H.; Franchini, E. Can different conditioning activities and rest intervals affect the acute performance of taekwondo turning kick? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Tung, K.; Chao, H.H.; Wang, H.S. Effects of caffeine and sex on muscle performance and delayed-onset muscle soreness after exercise-induced muscle damage: A double-blind randomized trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 127, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, B.H.; Hester, G.M.; Palmer, T.B.; Williams, K.; Pope, Z.K.; Sellers, J.H.; Conchola, E.C.; Woolsey, C.; Estrada, C. Effect of Energy Drink Consumption on Power and Velocity of Selected Sport Performance Activities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, A.; Prat, G.; Fabbri, M.; Sanchez-Turet, M. Early effects of caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee on subjective state and gender differences. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rixon, K.P.; Lamont, H.S.; Bemben, M.G. Influence of type of muscle contraction, gender, and lifting experience on postactivation potentiation performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, V.; Guillaume, M.; Berthelot, G.; El Helou, N.; Schaal, K.; Quinquis, L.; Nassif, H.; Tafflet, M.; Escolano, S.; Hermine, O. Women and men in sport performance: The gender gap has not evolved since 1983. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Andrade, M.; Mascarin, N.C.; Foster, R.; de Jármy di Bella, Z.I.; Vancini, R.L.; Barbosa de Lira, C.A. Is muscular strength balance influenced by menstrual cycle in female soccer players? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Sanchez-Oliver, A.J.; Montoya, J.J.; Ramos-Alvarez, J.J.; Miguel-Tobal, F.; Lago-Rodriguez, A.; Jodra, P. Acute Effects of Caffeine Intake on Psychological Responses and High-Intensity Exercise Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodra, P.; Lago-Rodriguez, A.; Sanchez-Oliver, A.J.; Lopez-Samanes, A.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; San Juan, A.F.; Dominguez, R. Effects of caffeine supplementation on physical performance and mood dimensions in elite and trained-recreational athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; O’Donnell, J.; Von Hurst, P.; Foskett, A.; Holland, S.; Starck, C.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K. Caffeine ingestion enhances perceptual responses during intermittent exercise in female team-game players. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, A.; Wilk, M.; Krzysztofik, M.; Del Coso, J. Inconsistency in the Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine in Athletes Who Regularly Consume Caffeine: Is It Due to the Disparity in the Criteria That Defines Habitual Caffeine Intake? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, G.C. Different glucose levels produced by coffee and decaffeinated coffee using GH-Method: Math-physical medicine (No. 277). J. Diabetes Res. Rev. Rep. 2021, SRC/JDRR-133, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Lara, F.J.; Del Coso, J.; Portillo, J.; Areces, F.; García, J.M.; Abián-Vicén, J. Enhancement of High-Intensity Actions and Physical Performance During a Simulated Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Competition with a Moderate Dose of Caffeine. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Duncan, N.M.; Marin, P.J.; Brown, L.E.; Loenneke, J.P.; Wilson, S.M.; Jo, E.; Lowery, R.P.; Ugrinowitsch, C. Meta-analysis of postactivation potentiation and power: Effects of conditioning activity, volume, gender, rest periods, and training status. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, H.; Trabelsi, K.; Ammar, A.; Shephard, R.J.; Bragazzi, N.L. Acute Effects of an “Energy Drink” on Short-Term Maximal Performance, Reaction Times, Psychological and Physiological Parameters: Insights from a Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Counterbalanced Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaabene, H.; Negra, Y.; Capranica, L.; Bouguezzi, R.; Hachana, Y.; Rouahi, M.A.; Mkaouer, B. Validity and Reliability of a New Test of Planned Agility in Elite Taekwondo Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Santos, J.F.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Ribeiro da Mota, G.; Franchini, E. Influence of half-squat intensity and volume on the subsequent countermovement jump and frequency speed of kick test performance in taekwondo athletes. Kinesiology 2016, 48, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Wallace, M.E. Caffeine dependence in schoolchildren? Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1997, 5, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.M.; Frederick, C. On energy, personality, and health: Subjective vitality as a dynamic reflection of well-being. J. Personal. 1997, 65, 529–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, C.J.; Rejeski, W.J. Not what, but how one feels: The measurement of affect during exercise. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1989, 11, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.; Florhaug, J.A.; Franklin, J.; Gottschall, L.; Hrovatin, L.A.; Parker, S.; Doleshal, P.; Dodge, C. A New Approach to Monitoring Exercise Training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2001, 15, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.M.; Green, J.M.; Bishop, P.A.; Sjokvist, J.; Schumacker, R.E.; Richardson, M.T.; Curtner-Smith, M. A practical approach to monitoring recovery: Development of a perceived recovery status scale. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; L Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G. A scale of magnitudes for effect statistics. New View Stat. 2002, 502, 411. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Baudin, P.; Ley, A.L.; Collins, D.F. A warm-up routine that incorporates a plyometric protocol potentiates the force-generating capacity of the quadriceps muscles. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana, J.; Franchini, E.; da Silva, V.; Diefenthaeler, F. Effect of fatigue on reaction time, response time, performance time, and kick impact in taekwondo roundhouse kick. Sports Biomech. 2017, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatouros, I.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Leontsini, D.; Taxildaris, K.; Aggelousis, N.; Kostopoulos, N.; Buckenmeyer, P. Evaluation of plyometric exercise training, weight training, and their combination on vertical jumping performance and leg strength. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2000, 14, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yetter, M.; Moir, G.L. The acute effects of heavy back and front squats on speed during forty-meter sprint trials. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Coso, J.; Salinero, J.J.; Gonzalez-Millan, C.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Perez-Gonzalez, B. Dose response effects of a caffeine-containing energy drink on muscle performance: A repeated measures design. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2012, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillin, N.A.; Bishop, D. Factors modulating post-activation potentiation and its effect on performance of subsequent explosive activities. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, R. Dietary Supplements and the High-Performance Athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazi, H.; Hoseinihaji, M.; Eghbali, E. The effects of different doses of caffeine on performance, rating of perceived exertion and pain perception in teenagers female karate athletes. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woolf, K.; Bidwell, W.K.; Carlson, A.G. The Effect of Caffeine as an Ergogenic Aid in Anaerobic Exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2008, 18, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, X. Cognition and brain activation in response to various doses of caffeine: A near-infrared spectroscopy study. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PL + NoCA | CAF + NoCA | PL + CA | CAF + CA | Control | Overall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSAT (s) | M | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.4 £ |
| F | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ±0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | |
| Overall | 6.1 ± 0.5 | 5.9 ± 0.4 α | 5.7 ± 0.5 $,§ | 5.5 ± 0.4 *,≠ | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.4 | |
| FSKT-10s (n) | M | 25 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | 29 ± 2 | 24 ± 2 | 27 ± 2d |
| F | 23 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 b,c | 24 ± 1 a | 26 ± 1 * | 22 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | |
| Overall | 24 ± 2 | 25 ± 1 | 26 ± 1 | 28 ± 1 * | 23 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | |
| FSKT-mult (kicks’ number) (n) | M | 117 ± 7 h | 121 ± 8 | 126 ± 4 | 138 ± 7 f | 107 ± 6 g | 122 ± 6 d |
| F | 105 ± 6 | 110 ± 10 | 111 ± 9 | 119 ± 6 f | 95 ± 10 | 108 ± 8 | |
| Overall | 111 ± 6 | 116 ± 9 * | 118 ± 6 *,e | 128 ± 7 * | 101 ± 8 | 115 ± 7 | |
| FSKT-mult (DI) (%) | M | 9 ± 2 | 6 ± 3 | 7 ± 2 | 4 ± 1 | 11 ± 3 | 7 ± 2 d |
| F | 10 ± 2 | 8 ± 2 | 7 ± 4 | 6 ± 3 | 13 ± 4 | 9 ± 3 | |
| Overall | 10 ± 2 i | 7 ± 2 i | 7 ± 3 i | 5 ± 2 *,§ | 12 ± 3 | 8 ± 2 | |
| Before | After | Overall | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL + NoCA | CAF + NoCA | PL + CA | CAF + CA | Overall | PL + NoCA | CAF + NoCA | PL + CA | CAF + CA | Overall | |||
| MPSS (a.u.) | M | 53 ± 9 | 48 ± 4 | 45 ± 6 | 47 ± 7 | 48 ± 7 | 56 ± 9 c | 55 ± 6 c | 49 ± 6 | 53 ± 6 | 53 ± 7 | 51 ± 7 |
| F | 44 ± 7 | 49 ± 9 | 46 ± 2 | 43 ± 4 | 45 ± 5 | 49 ± 9 | 46 ± 2 e | 43 ± 4 d | 47 ± 7 d | 46 ± 5 | 46 ± 5 | |
| Overall | 48 ± 8 | 49 ± 6 a | 45 ± 4 | 45 ± 5 | 47 ± 6 | 52 ± 9 | 53 ± 8 | 46 ± 5 | 50 ± 6 | 50 ± 7 b | 49 ± 6 | |
| SVS (a.u.) | M | 29 ± 4 | 31 ± 3 g | 27 ± 5 | 29 ± 4 g | 29 ± 4 | 28 ± 10 | 33 ± 4 | 28 ± 6 | 34 ± 4 | 31 ± 6 | 30 ± 5 f |
| F | 24 ± 6 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 2 | 24 ± 4 | 26 ± 4 | 25 ± 9 | 30 ± 5 | 27 ± 3 | 29 ± 3 | 28 ± 5 | 27 ± 4 | |
| Overall | 26 ± 5 | 29 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 a | 27 ± 4 | 27 ± 4 | 26 ± 10 | 31 ± 5 | 28 ± 4 | 32 ± 4 | 29 ± 6 | 28 ± 5 | |
| FS (a.u.) | M | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 g | 1 ± 2 | 1 ± 3 g | 2 ± 2 | 2 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 g | 1± 2 | 4 ± 1 g | 2 ± 2 | 2 ± 2 f |
| F | 1 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | 1 ± 2 | 0.3 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 3 | 2 ± 2 | 1 ± 3 | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 2 | 1 ± 2 | |
| Overall | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | 1 ± 2 | 1 ± 2 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 3 | 2 ± 2 | 1 ± 2 | 3 ± 1 | 2 ± 2 | 2 ± 2 | |
| PL + NoCA | CAF + NoCA | PL + CA | CAF + CA | Control | Overall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPE (a.u.) | M | 7.5 ± 1.5 | 7.4 ± 0.8 | 7.1 ± 1.2 | 7.6 ± 1.0 | 7.0 ± 1.1 | 7.3 ± 1.1 |
| F | 6.9 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 1.4 | 7.9 ± 1.2 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 7.7 ± 1.0 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | |
| Overall | 7.2 ± 1.5 | 7.25 ± 1.1 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | |
| PRS (a.u.) | M | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 2.7 ± 1.5 | 3.0 ± 1.7 | 3.2 ± 1.3 | 2.8 ± 1.3 |
| F | 2.7 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 2.1 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | |
| Overall | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 2.7 ± 1.6 | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouergui, I.; Mahdi, N.; Delleli, S.; Messaoudi, H.; Chtourou, H.; Sahnoun, Z.; Bouassida, A.; Bouhlel, E.; Nobari, H.; Ardigò, L.P.; et al. Acute Effects of Low Dose of Caffeine Ingestion Combined with Conditioning Activity on Psychological and Physical Performances of Male and Female Taekwondo Athletes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030571
Ouergui I, Mahdi N, Delleli S, Messaoudi H, Chtourou H, Sahnoun Z, Bouassida A, Bouhlel E, Nobari H, Ardigò LP, et al. Acute Effects of Low Dose of Caffeine Ingestion Combined with Conditioning Activity on Psychological and Physical Performances of Male and Female Taekwondo Athletes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030571
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuergui, Ibrahim, Nourhene Mahdi, Slaheddine Delleli, Hamdi Messaoudi, Hamdi Chtourou, Zouheir Sahnoun, Anissa Bouassida, Ezdine Bouhlel, Hadi Nobari, Luca Paolo Ardigò, and et al. 2022. "Acute Effects of Low Dose of Caffeine Ingestion Combined with Conditioning Activity on Psychological and Physical Performances of Male and Female Taekwondo Athletes" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030571
APA StyleOuergui, I., Mahdi, N., Delleli, S., Messaoudi, H., Chtourou, H., Sahnoun, Z., Bouassida, A., Bouhlel, E., Nobari, H., Ardigò, L. P., & Franchini, E. (2022). Acute Effects of Low Dose of Caffeine Ingestion Combined with Conditioning Activity on Psychological and Physical Performances of Male and Female Taekwondo Athletes. Nutrients, 14(3), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030571










