Vitamin D Concentrations at Birth and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Adulthood: A Danish Population-Based Case-Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
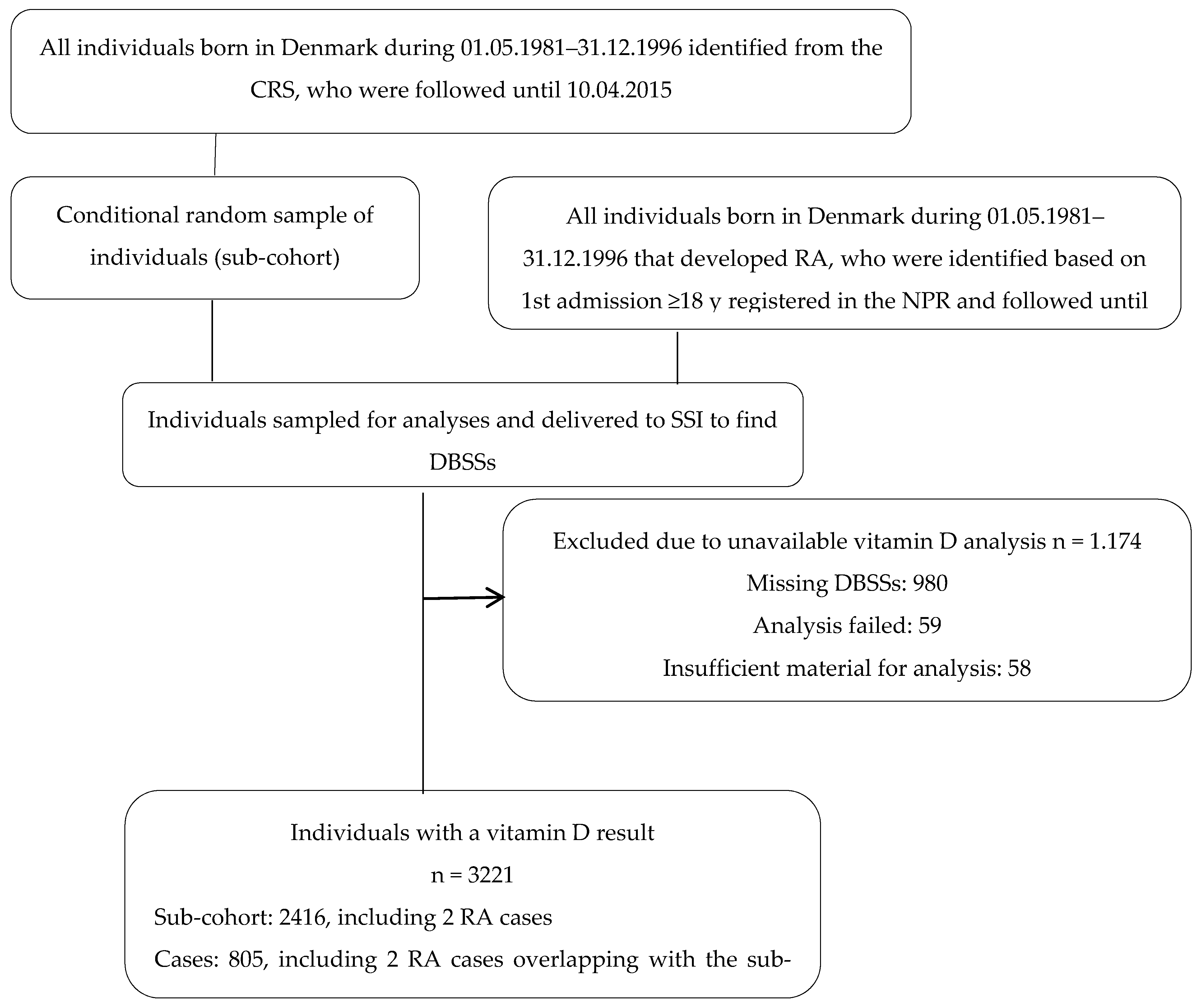
2.1. Study Population and Data Sources
2.2. Assessment of 25(OH)D Concentrations and Data Sources
2.3. Covariates and Data Sources
2.4. Power Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Davis, J.M.; Crowson, C.S.; Gabriel, S.E. Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid Arthritis and Mortality. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2010, 12, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamanos, Y.; Drosos, A. Epidemiology of Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2005, 4, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobón, G.J.; Youinou, P.; Saraux, A. The Environment, Geo-Epidemiology, and Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A288–A292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, I.C.; Steer, S.; Lewis, C.M.; Cope, A.P. Precipitating and Perpetuating Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis Immunopathology—Linking the Triad of Genetic Predisposition, Environmental Risk Factors and Autoimmunity to Disease Pathogenesis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N. Vitamin D and Rheumatic Diseases: A Review of Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin, D; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAree, T.; Jacobs, B.; Manickavasagar, T.; Sivalokanathan, S.; Brennan, L.; Bassett, P.; Rainbow, S.; Blair, M. Vitamin D Deficiency in Pregnancy—Still a Public Health Issue. Matern. Child Nutr. 2013, 9, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkhuyzen, A.A.E.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Blanken, L.M.E.; Kruithof, C.J.; Verhulst, F.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H.; McGrath, J.J. Prevalence and Predictors of Vitamin D Deficiency Based on Maternal Mid-Gestation and Neonatal Cord Bloods: The Generation R Study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 164, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thuesen, B.; Husemoen, L.; Fenger, M.; Jakobsen, J.; Schwarz, P.; Toft, U.; Ovesen, L.; Jørgensen, T.; Linneberg, A. Determinants of Vitamin D Status in a General Population of Danish Adults. Bone 2012, 50, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodda, C.P.; Benson, J.E.; Vincent, A.J.; Whitehead, C.L.; Polykov, A.; Vollenhoven, B. Maternal Vitamin D Supplementation during Pregnancy Prevents Vitamin D Deficiency in the Newborn: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disanto, G.; Chaplin, G.; Morahan, J.M.; Giovannoni, G.; Hypponen, E.; Ebers, G.C.; Ramagopalan, S. V Month of Birth, Vitamin D and Risk of Immune-Mediated Disease: A Case Control Study. BMC. Med. 2012, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disanto, G.; Watson, C.T.; Meier, U.C.; Ebers, G.C.; Giovannoni, G.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Month of Birth and Thymic Output. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Cantorna, M.T. Epigenetic Reduction in Invariant NKT Cells Following in Utero Vitamin D Deficiency in Mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 186, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chary, A.V.; Hemalatha, R.; Seshacharyulu, M.; Vasudeva Murali, M.; Jayaprakash, D.; Dinesh Kumar, B. Vitamin D Deficiency in Pregnant Women Impairs Regulatory T Cell Function. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 147, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyprian, F.; Lefkou, E.; Varoudi, K.; Girardi, G. Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D in Pregnancy and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, C.B. The Danish Civil Registration System. Scand. J. Public Health 2011, 39, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Pedersen, L.; Sørensen, H.T. The Danish Civil Registration System as a Tool in Epidemiology. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynge, E.; Sandegaard, J.L.; Rebolj, M. The Danish National Patient Register. Scand. J. Public Health 2011, 39, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M. Storage Policies and Use of the Danish Newborn Screening Biobank. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W.; Morley, R.; Anderson, C.; Ko, P.; Burne, T.; Permezel, M.; Mortensen, P.B.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; McGrath, J.J. The Utility of Neonatal Dried Blood Spots for the Assessment of Neonatal Vitamin D Status. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2010, 24, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.D.; Berry, J.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Gunter, E.; Jones, G.; Jones, J.; Makin, H.L.J.; Pattni, P.; Sempos, C.T.; Twomey, P.; et al. Hydroxyvitamin D Assays: An Historical Perspective from DEQAS. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 177, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.; Anderson, C.; Ko, P.; Jones, A.; Thomas, A.; Burne, T.; Mortensen, P.B.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; McGrath, J. A Sensitive LC/MS/MS Assay of 25OH Vitamin D3 and 25OH Vitamin D2 in Dried Blood Spots. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 403, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, R.; Abrahamsen, B.; Bauerek, M.; Holst, C.; Jensen, C.B.; Knop, J.; Raymond, K.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Stougaard, M.; Sørensen, T.I.; et al. The Influence of Early Exposure to Vitamin D for Development of Diseases Later in Life. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bliddal, M.; Broe, A.; Pottegård, A.; Olsen, J.; Langhoff-Roos, J. The Danish Medical Birth Register. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, A.C. Nutritionally Mediated Programming of the Developing Immune System. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobsen, R.; Thorsen, S.U.; Cohen, A.S.; Lundqvist, M.; Frederiksen, P.; Pipper, C.B.; Pociot, F.; Thygesen, L.C.; Ascherio, A.; Svensson, J.; et al. Neonatal Vitamin D Status Is Not Associated with Later Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: Results from Two Large Danish Population-Based Studies. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colebatch, A.N.; Edwards, C.J. The Influence of Early Life Factors on the Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 163, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Li, D.; Jeffery, L.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D, Autoimmune Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 106, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Davies, M.L.; Chen, W. Serum Vitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity: Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, S.; Freitas, Q.; Bernardo, M.; Pereira, R. Vitamin D Supplementation and Disease Activity in Patients with Immune-Mediated Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.G.; Bae, S.C.; Lee, Y.H. Association between Vitamin D Intake and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, L.E.; Raza, K.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D in Rheumatoid Arthritis-towards Clinical Application. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, C.M.; Cantorna, M.T.; DeLuca, H.F. Expression of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Receptor in the Immune System. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 374, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.-J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, A.C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerina, K.; Baum, W.; Axmann, R.; Heiland, G.R.; Distler, J.H.; Smolen, J.; Hayer, S.; Zwerina, J.; Schett, G. Vitamin D Receptor Regulates TNF-Mediated Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Z.; Imani, D.; Yousefi, H.; Abbasifard, M. Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Gene Polymorphism and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3555–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Snyder, L.; Lin, Y.D.; Yang, L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T Cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heath, A.K.; Williamson, E.J.; Ebeling, P.R.; Kvaskoff, D.; Eyles, D.W.; English, D.R. Measurements of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Archived Dried Blood Spots Are Reliable and Accurately Reflect Those in Plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3319–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.; Schmidt, S.A.J.; Sandegaard, J.L.; Ehrenstein, V.; Pedersen, L.; Sørensen, H.T. The Danish National Patient Registry: A Review of Content, Data Quality, and Research Potential. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thygesen, L.; Ersbøll, A. When the Entire Population Is the Sample: Strengths and Limitations in Register-Based Epidemiology. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.; Klarlund, M.; Jacobsen, S.; Svendsen, A.J.; Frisch, M. Validity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnoses in the Danish National Patient Registry. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Pedersen, C.B.; Anderson, C.; Ko, P.; Burne, T.H.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; Mortensen, P.B. Neonatal Vitamin D Status and Risk of Schizophrenia: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saraf, R.; Morton, S.M.B.; Camargo, C.A.; Grant, C.C. Global Summary of Maternal and Newborn Vitamin D Status—A Systematic Review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 12, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cases | Random Subcohort | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 805 | 2416 | |
| 25(OH)D nmol/L median [IQR] | 24.9 (15.4; 36.9) | 23.9 (13.6; 36.4) | 0.15 |
| Case n (%) | |||
| No | 0 (0.0) | 2414 (99.9) | |
| Yes | 805 (100.0) | 2 (0.1) | |
| Offspring sex n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 201 (25.0) | 1234 (51.1) | |
| Female | 604 (75.0) | 1182 (48.9) | |
| Maternal ethnicity n (%) | 0.011 | ||
| Western | 784 (97.4) | 2303 (95.3) | |
| Non-Western | 21 (2.6) | 113 (4.7) | |
| Maternal age in years median [IQR] | 27 (24; 30) | 27 (24; 31) | 0.04 |
| Maternal education n (%) | 0.015 | ||
| Elementary school | 313 (38.9) | 843 (34.9) | |
| Highschool | 320 (39.8) | 1040 (43.1) | |
| University | 138 (17.1) | 468 (19.4) | |
| Unknown | 34 (4.2) | 65 (2.7) | |
| Parity n (%) | 0.60 | ||
| Primiparous | 376 (46.7) | 1103 (45.7) | |
| Multiparous | 429 (53.3) | 1313 (54.4) | |
| Season of birth n (%) | 0.98 | ||
| Winter | 405 (50.3) | 1214 (50.3) | |
| Summer | 400 (49.7) | 1202 (49.8) | |
| Gestational age n (%) | 0.73 | ||
| ≥37 weeks | 756 (93.9) | 2277 (94.3) | |
| <37 weeks | 49 (6.1) | 139 (5.8) | |
| Birth weight in grams median [IQR] | 3450 (3150; 3800) | 3470 (3128; 3810) | 0.39 |
| Maternal RA n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 694 (86.2) | 2220 (91.9) | |
| Yes | 111 (13.8) | 196 (8.1) | |
| Paternal RA n (%) | 0.10 | ||
| No | 714 (88.7) | 2191 (90.7) | |
| Yes | 91 (11.3) | 225 (9.3) |
| Quintiles Limit, (nmol/L) | Crude (n = 3221) | Adjusted a (n = 3221) |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 [0–12.1] | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Q2 [12.1–19.6] | 0.89 (0.67–1.18) | 0.89 (0.66–1.19) |
| Q3 [19.6–28.0] | 1.06 (0.80–1.40) | 1.13 (0.84–1.52) |
| Q4 [28.0–40.1] | 1.15 (0.88–1.51) | 1.17 (0.88–1.57) |
| Q5 [40.1–114.9] | 1.12 (0.85–1.48) | 1.19 (0.88–1.60) |
| Quintiles | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude (n = 1435) | Adjusted b (n = 1435) | Crude (n = 1786) | Adjusted b (n = 1786) | |
| Q1 | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Q2 | 0.91 (0.54–1.55) | 0.96 (0.54–1.70) | 0.85 (0.60–1.21) | 0.84 (0.59–1.20) |
| Q3 | 0.97 (0.58–1.62) | 0.97 (0.56–1.67) | 1.10 (0.60–1.56) | 1.12 (0.78–1.60) |
| Q4 | 1.39 (0.86–2.27) | 1.46 (0.88–2.45) | 1.10 (0.83–1.66) | 1.20 (0.84–1.71) |
| Q5 | 1.25 (0.76–2.05) | 1.31 (0.75–2.28) | 1.05 (0.74–1.48) | 1.06 (0.74–1.52) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoso, I.; Specht, I.O.; Thorsteinsdottir, F.; Thorbek, M.J.; Keller, A.; Stougaard, M.; Cohen, A.S.; Händel, M.N.; Kristensen, L.E.; Heitmann, B.L. Vitamin D Concentrations at Birth and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Adulthood: A Danish Population-Based Case-Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030447
Cardoso I, Specht IO, Thorsteinsdottir F, Thorbek MJ, Keller A, Stougaard M, Cohen AS, Händel MN, Kristensen LE, Heitmann BL. Vitamin D Concentrations at Birth and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Adulthood: A Danish Population-Based Case-Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(3):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030447
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoso, Isabel, Ina Olmer Specht, Fanney Thorsteinsdottir, Marta Jadwiga Thorbek, Amélie Keller, Maria Stougaard, Arieh S. Cohen, Mina Nicole Händel, Lars Erik Kristensen, and Berit Lilienthal Heitmann. 2022. "Vitamin D Concentrations at Birth and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Adulthood: A Danish Population-Based Case-Cohort Study" Nutrients 14, no. 3: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030447
APA StyleCardoso, I., Specht, I. O., Thorsteinsdottir, F., Thorbek, M. J., Keller, A., Stougaard, M., Cohen, A. S., Händel, M. N., Kristensen, L. E., & Heitmann, B. L. (2022). Vitamin D Concentrations at Birth and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Adulthood: A Danish Population-Based Case-Cohort Study. Nutrients, 14(3), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030447







