Effects of Early versus Standard Central Line Removal on the Growth of Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight: A Non-Inferiority, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Sequence Generation, Allocation Concealment, and Blinding
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
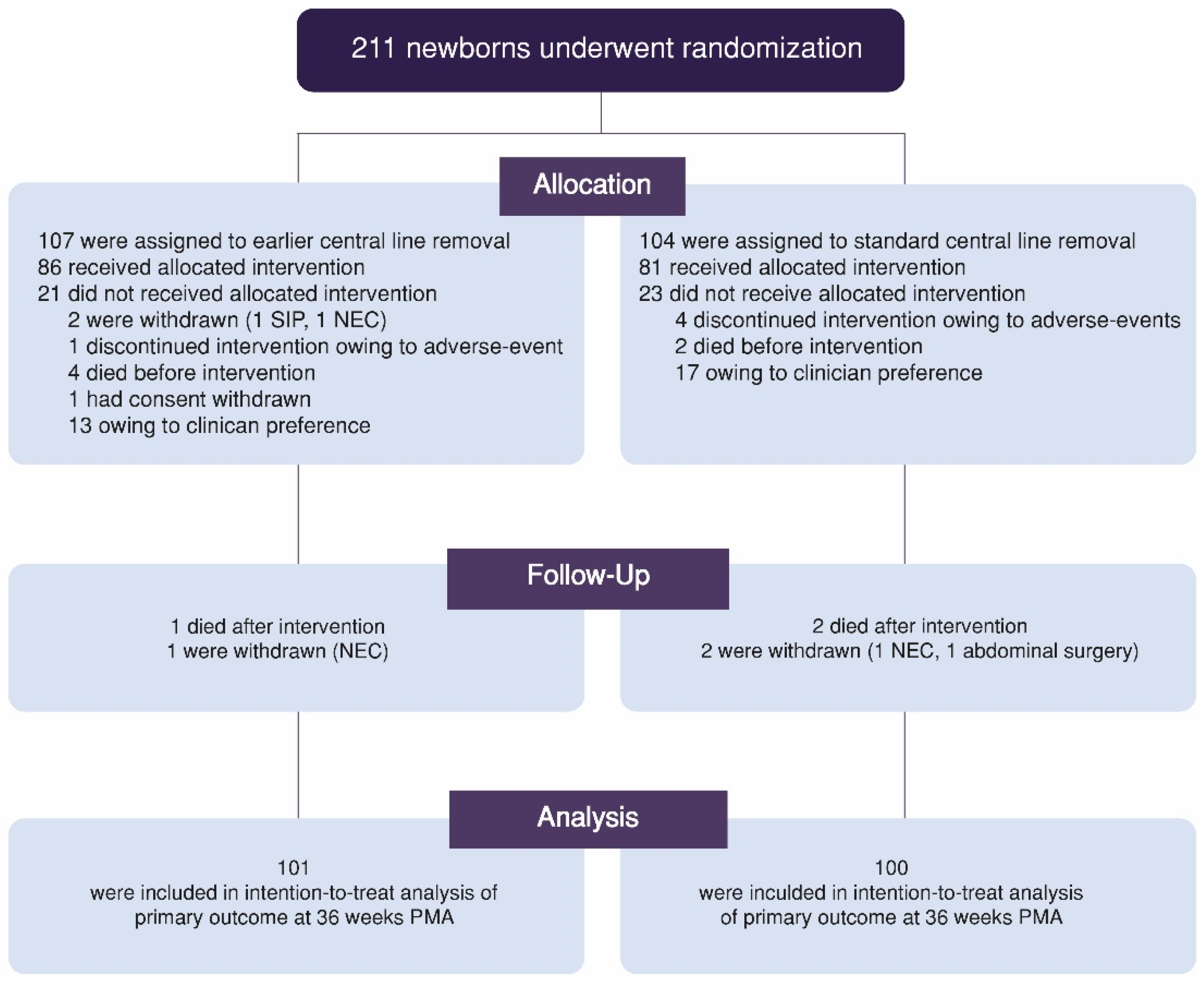
3.1. Trial Participants
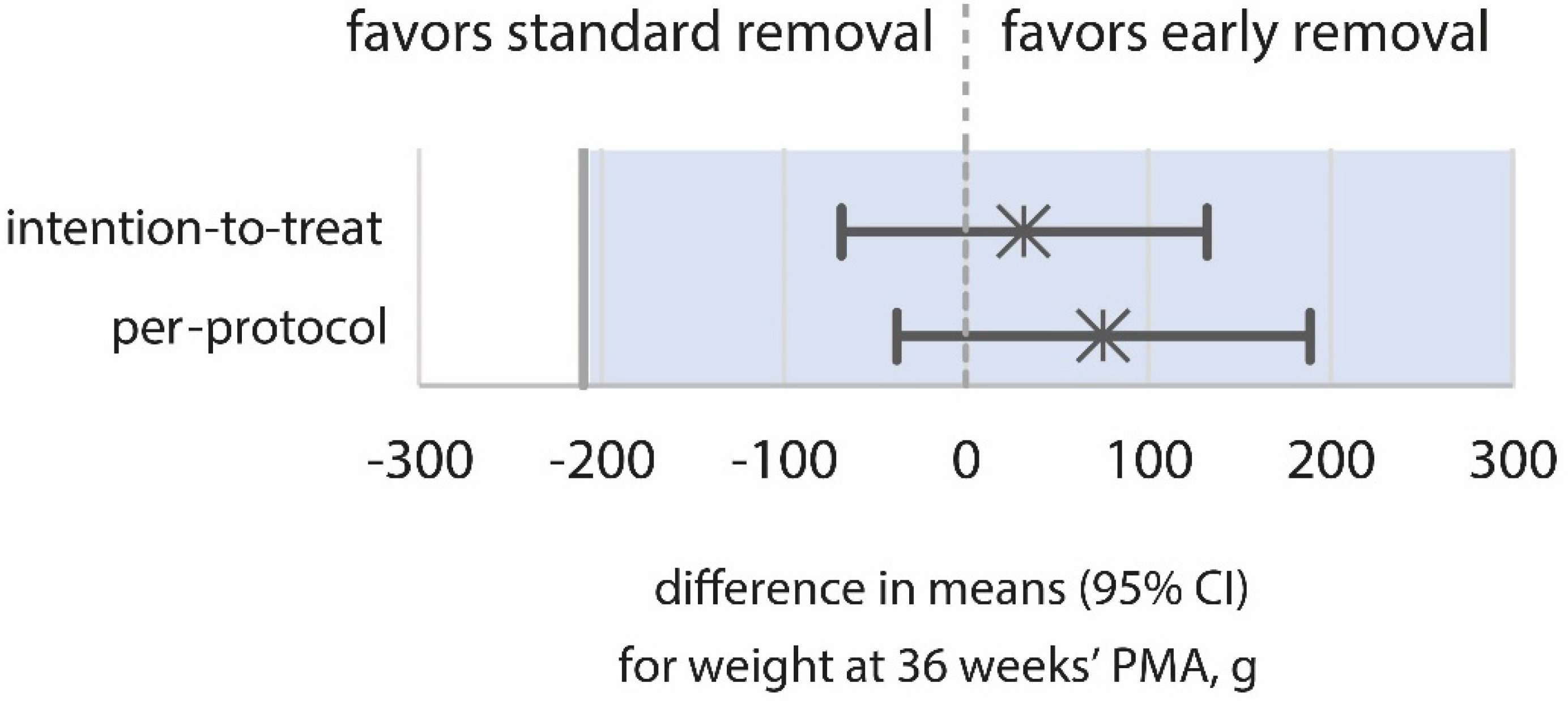
3.2. Primary Outcomes
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pettit, J. Assessment of infants with peripherally inserted central catheters: Part 1. Detecting the most frequently occurring complications. Adv. Neonatal Care 2002, 2, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Dusick, A.M.; Vohr, B.R.; Wright, L.L.; Wrage, L.A.; Poole, W.K. Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.E.; Walden, R.V.; Gargus, R.A.; Tucker, R.; McKinley, L.; Mance, M.; Nye, J.; Vohr, B.R. First-Week Protein and Energy Intakes are Associated With 18-Month Developmental Outcomes in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, S.J.; Puopolo, K.M. Prevention of Central Line–Associated Bloodstream Infections Among Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Neoreviews 2015, 16, e211–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, B.; Yee, W.; Lodha, A.; Henderson, E.; Yusuf, K.; Sauve, R. Coagulase-negative staphylococcus sepsis in preterm infants and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Adams-Chapman, I.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Hintz, S.R.; Vohr, B.; Higgins, R.D.; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neurodevelopmental and Growth Impairment Among Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants with Neonatal Infection. JAMA 2004, 292, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, V.; Hall, M.; Prieto, J.; Johnson, M. Care bundles to reduce central line-associated bloodstream infections in the neonatal unit: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 103, F422–F429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Cochran, K.M.; Provost, L.P.; Patterson, J.; Bristol, T.; Metzguer, K.; Smith, B.; Testoni, D.; McCaffrey, M.J. Reducing central line-associated bloodstream infections in North Carolina NICUs. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e1664-71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G. CONSORT 2010 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaggio, G.; Elbourne, D.R.; Pocock, S.J.; Evans, S.J.; Altman, D.G. Reporting of noninferiority and equivalence randomized trials: Extension of the CONSORT 2010 statement. JAMA 2012, 308, 2594–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romańska, J.; Margas, W.; Bokiniec, R.; Krajewski, P.; Seliga-Siwecka, J. Effect of early versus standard central line removal on growth of very low birthweight premature infants: A protocol for a non-inferiority randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e030167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. BMC Pediatrics 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterbach, R. Żywienie pozajelitowe. In Standardy Opieki Medycznej nad Noworodkiem w Polsce, 3rd ed.; Maria Katarzyna Borszewska-Kornacka, R.B., Ed.; Media-Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2019; pp. 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mazela, J.; Chojnacka, K.; Czech-Kowalska, J.; Gawecka, A.; Gulczyńska, E.; Michalczyk, B.; Sadowska-Krawczenko, I.; Wilińska, M.; Wróblewska-Seniuk, K. Żywienie enteralne noworodka. In Standardy Opieki Medycznej nad Noworodkiem w Polsce, 3rd ed.; Maria Katarzyna Borszewska-Kornacka, R.B., Ed.; Media-Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2019; pp. 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bloodstream Infection (BSI) Events. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/psc/bsi/index.html (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- 2022 Manual of Operations, Part 2. Vermont Oxford Network. 2022. Available online: https://vtoxford.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/4405064008467-2022-Manual-of-Operations-Part-2-Release-26-1-PDF (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Cormack, B.E.; Embleton, N.D.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Bloomfield, F.H. Comparing apples with apples: It is time for standardized reporting of neonatal nutrition and growth studies. Pediatr. Res 2016, 79, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.L.; Engstrom, J.L.; Meier, P.P.; Jegier, B.J.; Kimura, R.E. Calculating postnatal growth velocity in very low birth weight (VLBW) premature infants. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.H.; Roumiantsev, S.; Singh, R. PediTools Electronic Growth Chart Calculators: Applications in Clinical Care, Research, and Quality Improvement. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh Ismail, L.; Knight, H.E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Hoch, L.; Chumlea, W.C.; International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium for the 21st Century. Anthropometric standardisation and quality control protocols for the construction of new, international, fetal and newborn growth standards: The INTERGROWTH-21st Project. BJOG 2013, 120 (Suppl. S2), 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, C.; Watson, M.; Lazidis, G.; Reeve, S.; Dods, K.; Simmer, K.; McLeod, G. Preterm human milk composition: A systematic literature review. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.K.; Kennedy, K.; Castañeda-Gutiérrez, E.; Forsyth, S.; Godfrey, K.M.; Koletzko, B.; Latulippe, M.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Rueda, R.; Schoemaker, M.H.; et al. Postnatal growth in preterm infants and later health outcomes: A systematic review. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goudoever, J.B.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Sainz de Pipaon, M. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Amino acids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, K.; Embleton, N.; Yan, W.; Senterre, T.; The ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Working Group on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Energy. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyses, H.E.; Johnson, M.J.; Leaf, A.A.; Cornelius, V.R. Early parenteral nutrition and growth outcomes in preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, E.; de Waard, M.; van Goudoever, J.B. Low- versus High-Dose and Early versus Late Parenteral Amino-Acid Administration in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neonatology 2018, 113, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozé, J.-C.; Morel, B.; Lapillonne, A.; Marret, S.; Guellec, I.; Darmaun, D.; Bednarek, N.; Moyon, T.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Benhammou, V.; et al. Association Between Early Amino Acid Intake and Full-Scale IQ at Age 5 Years Among Infants Born at Less Than 30 Weeks’ Gestation. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2135452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrem, L.; Semberova, J.; O’Sullivan, A.; Kieran, E.A.; O’Donnell, C.P.F.; White, M.J.; Miletin, J. Effect of Early Parenteral Nutrition Discontinuation on Time to Regain Birth Weight in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangia, S.; Vadivel, V.; Thukral, A.; Saili, A. Early Total Enteral Feeding versus Conventional Enteral Feeding in Stable Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Neonatology 2019, 115, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Nasser, R.; Creighton, D.; Tang, S.; Sauve, R.; Bilan, D.; Fenton, C.J.; Eliasziw, M. Weight, length, and head circumference at 36 weeks are not predictive of later cognitive impairment in very preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Early-Removal Group, n = 106 | Standard-Removal Group, n = 104 |
|---|---|---|
| Female sex—n (%) | 49 (48.5%) | 49 (49.0%) |
| Gestational age at delivery—mean ± SD, wk | 28.3 (2.3) | 28.7 (2.3) |
| Birth weight—mean ± SD, g | 1122 (259) | 1139 (233) |
| Birth weight < 1000 g—n (%) | 30 (29.7%) | 30 (30.0%) |
| Birth weight < 10th percentile of gestational age—n (%) | 5 (5.0%) | 7 (7.0%) |
| Z-score for birth weight—mean ± SD | −0.12 (0.82) | −0.29 (0.82) |
| Apgar score at 5 min—median (IQR) | 8.0 (2.0) | 7.0 (1.0) |
| Cesarean delivery—n (%) | 82 (81.2%) | 91 (91.0%) |
| Received antenatal steroids, any—n (%) | 99 (98.0%) | 95 (95.0%) |
| Multiple pregnancy, any—n (%) | 37 (36.6%) | 47 (47.0%) |
| n = 100 | n = 99 | |
| HC at birth—mean ± SD, cm | 26.3 (2.5) | 26.4 (2.2) |
| HC at birth < 10th percentile of gestational age—n (%) | 7 (6.9%) | 11 (11.0%) |
| Outcome | Early-Removal Group n = 101 | Standard-Removal Group n = 100 | Effect Measure (95% CI) * | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome | ||||
| Weight at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD, g | 2232 (364) | 2200 (356) | 32 (−68 to 132) | 0.531 |
| Secondary outcomes | ||||
| n = 101 | n = 100 | |||
| Z-score for weight at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD | −1.05 (0.86) | −1.13 (0.87) | 0.08 (−0.16 to 0.32) | 0.517 |
| Change in Z-score for weight from birth to 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD | −0.94 (0.62) | −0.84 (0.64) | −0.09 (−0.27 to 0.08) | 0.302 |
| Weight < 10th percentile at 36 weeks’ PMA—n (%) | 44 (43.6%) | 42 (42.0%) | 1.07 (0.61 to 1.86) | 0.935 |
| Time to regain birth weight—mean ± SD, days | 10.62 (5.21) | 10.14 (4.92) | 0.48 (−0.93 to 1.89) | 0.499 |
| Growth velocity from birth to 36 weeks’ PMA— mean ± SD, g/kg/day | 13.6 (2.3) | 13.8 (2.5) | −0.2 (−0.8 to 0.5) | 0.645 |
| n = 89 | n = 94 | |||
| HC at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD, cm | 31.7 (1.6) | 31.8 (1.3) | −0.1 (−0.5 to 0.3) | 0.567 |
| Z-score for HC at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD | −0.54 (1.01) | −0.44 (0.89) | −0.10 (−0.38 to 0.18) | 0.479 |
| Change in Z-score for HC from birth to 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD | −0.71 (1.13) | −0.32 (0.93) | −0.39 (−0.69 to −0.09) | 0.011 |
| HC < 10th percentile at 36 weeks’ PMA—n (%) | 16 (18.0%) | 19 (20.2%) | 0.85 (0.41 to 1.79) | 0.816 |
| n = 91 | n = 95 | |||
| Length at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD, cm | 43.7 (2.2) | 44.0 (2.1) | −0.3 (−0.9 to 0.3) | 0.313 |
| Z-score for length at 36 weeks’ PMA—mean ± SD | −1.27 (0.83) | −1.11 (0.81) | −0.15 (−0.39 to 0.09) | 0.208 |
| Length < 10th percentile at 36 weeks’ PMA—n (%) | 44 (48.4%) | 39 (41.1%) | 1.34 (0.75 to 2.40) | 0.393 |
| Event | Early-Removal Group, n = 106 | Standard-Removal Group, n = 104 | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | ||||
| Death before discharge | 5 (4.7%) | 4 (3.8%) | 1.24 (0.32–4.74) | 1.000 |
| Necrotizing enterocolitis, Bell’s stage 2 or 3 | 6 (5.7%) | 4 (3.8%) | 1.50 (0.41–5.48) | 0.769 |
| Spontaneous intestinal perforation | 3 (2.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6.03 (0.30–121.86) | 0.252 |
| Other abdominal surgeries | 1 (0.9%) | 2 (1.9%) | 0.49 (0.04–5.44) | 0.987 |
| RDS treated with a surfactant | 70 (66.0%) | 67 (64.4%) | 1.07 (0.61–1.90) | 0.920 |
| BPD—oxygen dependency at 36 weeks’ PMA | 15 (14.2%) | 12 (11.5%) | 1.26 (0.56–2.85) | 0.719 |
| PDA requiring medical treatment or surgical ligation | 21 (19.8%) | 28 (26.9%) | 0.67 (0.35–1.28) | 0.291 |
| Retinopathy of prematurity requiring treatment | 13 (12.3%) | 5 (4.8%) | 2.77 (0.95–8.07) | 0.092 |
| Metabolic bone disease | 10 (9.4%) | 14 (13.5%) | 0.67 (0.28–1.58) | 0.484 |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage grade 3 or 4 | 9 (8.5%) | 6 (5.8%) | 1.52 (0.52–4.42) | 0.619 |
| Cystic periventricular leukomalacia | 5 (4.7%) | 5 (4.8%) | 0.98 (0.28–3.49) | 1.000 |
| Early-onset sepsis | 3 (2.8%) | 1 (1.0%) | 3.00 (0.31–29.32) | 0.627 |
| Late-onset sepsis other than CLABSI | 39 (36.8%) | 29 (27.9%) | 1.51 (0.84–2.70) | 0.218 |
| Nutritional Intake, Mean ± SD | Early-Removal Group, n = 95 | Standard-Removal Group, n = 96 | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein intake—g/kg/d | ||||
| Week 1 | 2.99 (0.31) | 3.11 (0.23) | −0.12 (−0.20 to −0.04) | 0.002 |
| Week 2 | 3.41 (0.46) | 3.44 (0.44) | −0.03 (−0.16 to 0.10) | 0.607 |
| Week 3 | 3.56 (0.63) | 3.66 (0.57) | −0.10 (−0.28 to 0.07) | 0.234 |
| Week 4 | 3.56 (0.56) | 3.71 (0.48) | −0.16 (−0.31 to −0.01) | 0.041 |
| Lipid intake—g/kg/d | ||||
| Week 1 | 2.69 (0.58) | 2.79 (0.63) | −0.09 (−0.27 to 0.08) | 0.291 |
| Week 2 | 4.86 (1.15) | 5.06 (1.08) | −0.19 (−0.51 to 0.12) | 0.232 |
| Week 3 | 5.61 (0.95) | 5.83 (0.87) | −0.23 (−0.49 to 0.03) | 0.089 |
| Week 4 | 5.71 (0.87) | 5.91 (0.71) | −0.19 (−0.42 to 0.03) | 0.095 |
| Carbohydrate intake—g/kg/d | ||||
| Week 1 | 10.92 (1.17) | 11.32 (1.18) | −0.40 (−0.74 to −0.07) | 0.019 |
| Week 2 | 14.47 (1.77) | 14.98 (1.46) | −0.51 (−0.98 to −0.05) | 0.031 |
| Week 3 | 14.93 (1.70) | 15.10 (1.48) | −0.17 (−0.63 to 0.28) | 0.454 |
| Week 4 | 14.92 (1.43) | 14.86 (1.48) | 0.06 (−0.36 to 0.47) | 0.790 |
| Energy intake—kcal/kg/d | ||||
| Week 1 | 76.3 (8.5) | 79.1 (8.8) | −2.8 (−5.3 to −0.3) | 0.028 |
| Week 2 | 112.9 (15.9) | 116.3 (13.8) | −3.4 (−7.6 to 0.9) | 0.121 |
| Week 3 | 123.2 (14.8) | 126.3 (13.4) | −3.2 (−7.2 to 0.9) | 0.124 |
| Week 4 | 124.4 (13.6) | 126.8 (10.2) | −2.4 (−5.8 to 1.0) | 0.171 |
| Characteristic | Early-Removal Group, n = 100 | Standard-Removal Group, n = 102 | Effect Measure (95% CI) * | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days with a central catheter—median (IQR) | 7.5 (5.0) | 8.0 (5.0) | −0.5 | 0.064 |
| Patients with central catheters reinserted during 7 days after intervention—n (%) | 3 (3.0%) | 3 (2.9%) | 1.02 (0.20–5.18) | 1.000 |
| Patients with peripheral catheters inserted after intervention—n (%) | 56 (56.0%) | 28 (27.5%) | 3.36 (1.87–6.05) | 0.000071 |
| Number of peripheral catheters per patient inserted after intervention—median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.3) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.0 | 0.517 |
| Duration of PN delivered through the peripheral catheter after intervention—median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.3) | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 | 0.163 |
| Event | Early-Removal Group, n = 106 | Standard-Removal Group, n = 104 |
|---|---|---|
| CLABSI-rate-events/1000 catheter-days | 10.35 | 10.20 |
| Cardiac tamponade—n (%) | 1 (0.9%) | 0 |
| Peritoneal effusion—n (%) | 0 | 1 (1.0%) |
| Soft-tissue infiltration—n (%) | 0 | 2 (1.9%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romańska, J.; Wawrzoniak, T.; Krajewski, P.; Seliga-Siwecka, J.; Brunets, N.; Lehman, I.; Bokiniec, R.; Adamska, E.; Królak-Olejnik, B.; Modzelewski, J.; et al. Effects of Early versus Standard Central Line Removal on the Growth of Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight: A Non-Inferiority, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224766
Romańska J, Wawrzoniak T, Krajewski P, Seliga-Siwecka J, Brunets N, Lehman I, Bokiniec R, Adamska E, Królak-Olejnik B, Modzelewski J, et al. Effects of Early versus Standard Central Line Removal on the Growth of Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight: A Non-Inferiority, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2022; 14(22):4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224766
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomańska, Justyna, Tomasz Wawrzoniak, Paweł Krajewski, Joanna Seliga-Siwecka, Natalia Brunets, Izabela Lehman, Renata Bokiniec, Ewa Adamska, Barbara Królak-Olejnik, Jan Modzelewski, and et al. 2022. "Effects of Early versus Standard Central Line Removal on the Growth of Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight: A Non-Inferiority, Randomized Clinical Trial" Nutrients 14, no. 22: 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224766
APA StyleRomańska, J., Wawrzoniak, T., Krajewski, P., Seliga-Siwecka, J., Brunets, N., Lehman, I., Bokiniec, R., Adamska, E., Królak-Olejnik, B., Modzelewski, J., & Szczapa, T. (2022). Effects of Early versus Standard Central Line Removal on the Growth of Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight: A Non-Inferiority, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 14(22), 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14224766






