Effects of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy on the Programming of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Dams and Fetuses, Related to a Prenatal High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Specimen Collection
2.3. Blood Pressure (BP) and Body Weight (BW) Measuring
2.4. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Histological Analysis of the Placenta and Liver Tissue
2.7. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR Analysis
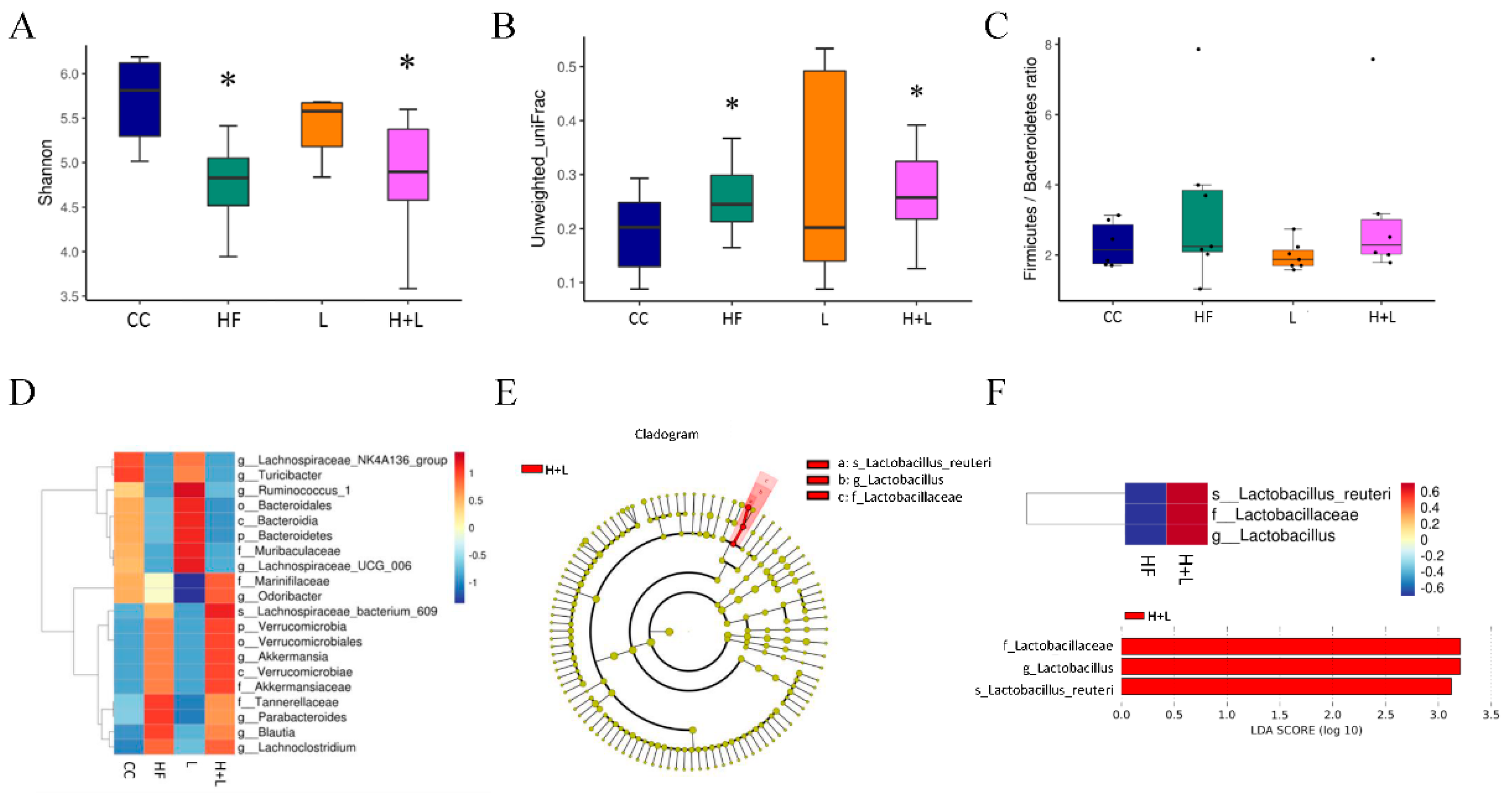
2.8. Microbial Analysis
2.9. SCFAs Analysis
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
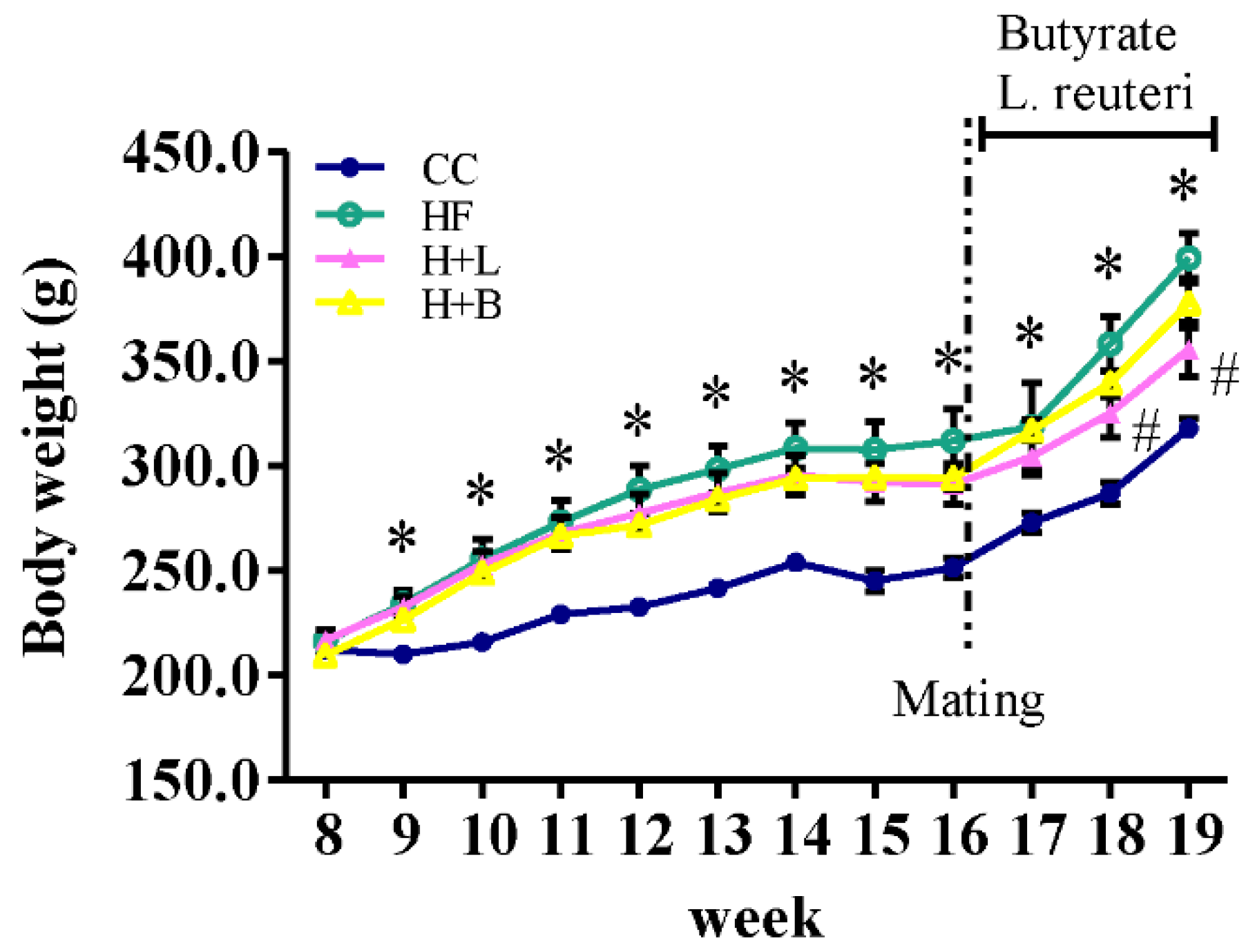
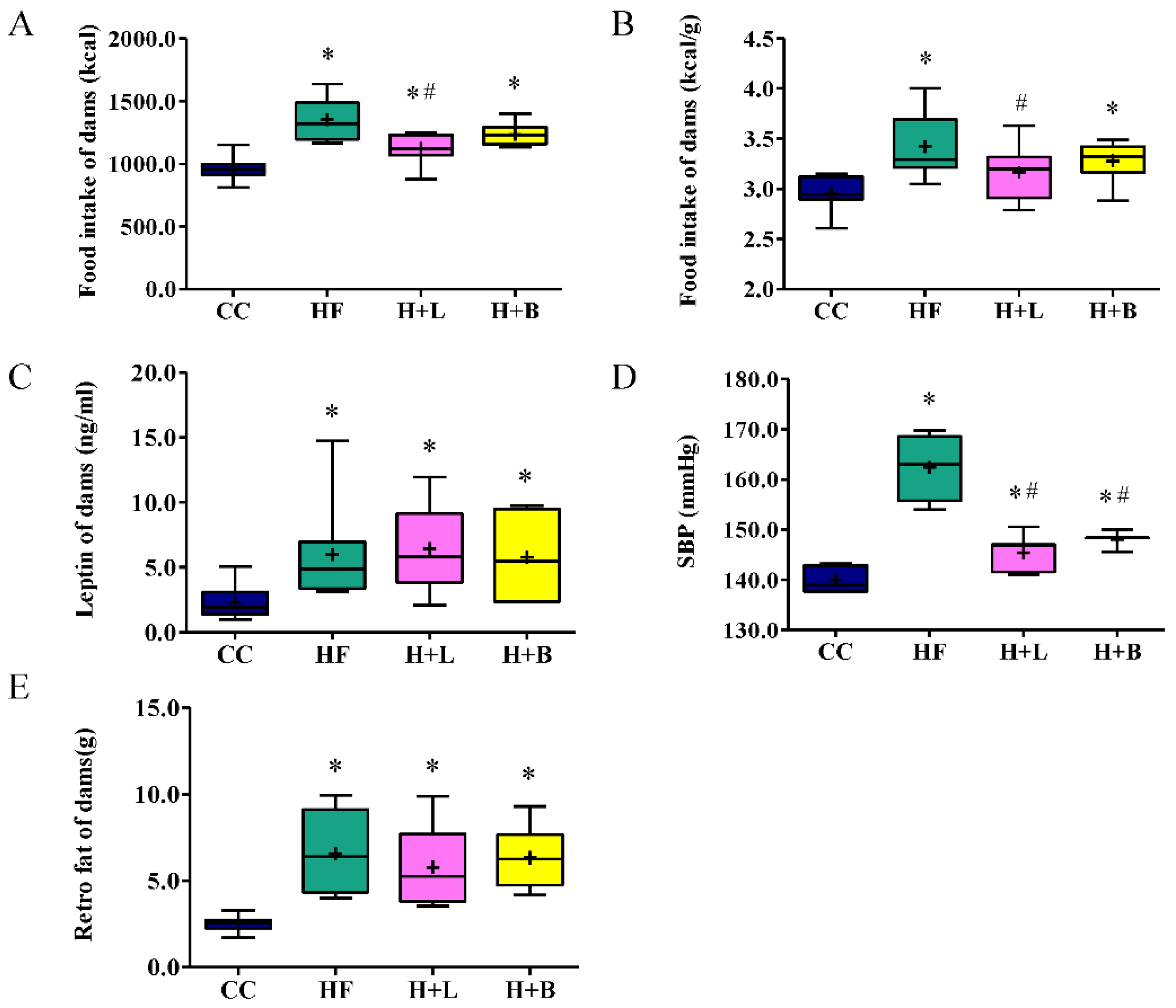
3.1. L. reuteri Intervention Ameliorates HF Diet-Related Obesity and Alters the Metabolic Profiles of Dams
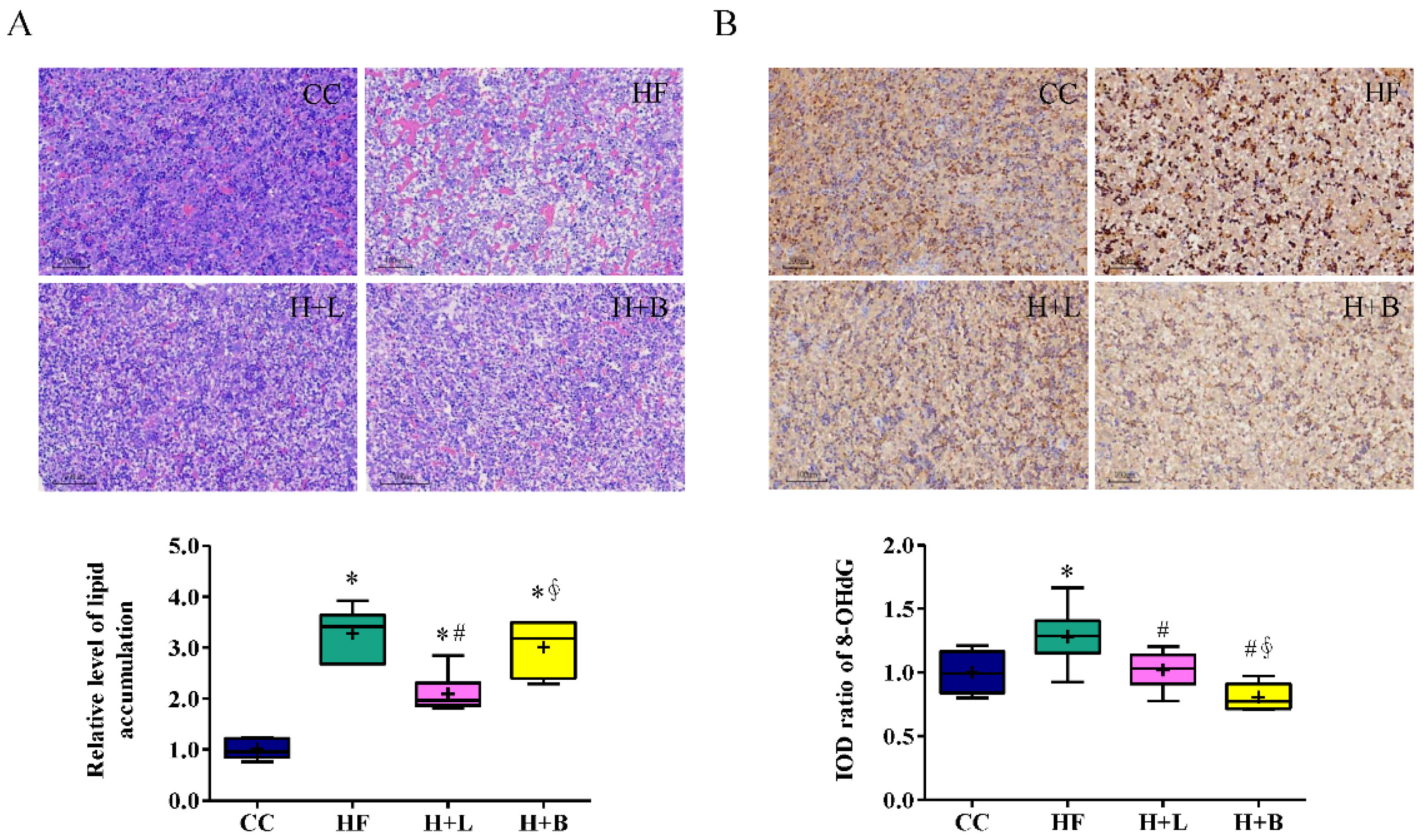
3.2. L. reuteri Is More Effective Than Butyrate in Preventing HF Diet-Induced Liver Steatosis in Pregnant Dams
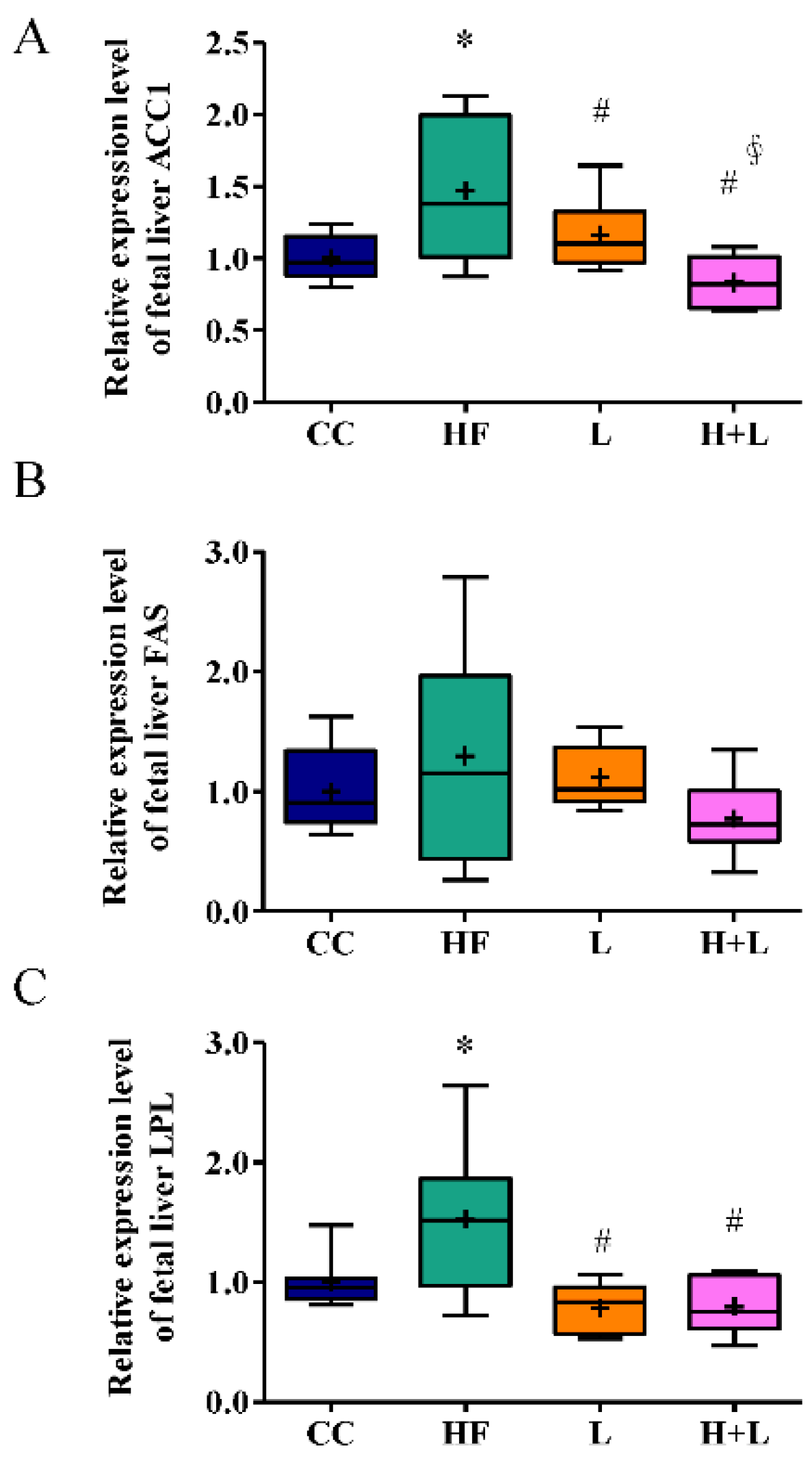
3.3. Maternal L. reuteri Intake Was an Effective Preventative Strategy for Maternal HF Diet-Induced Fetal Liver Steatosis
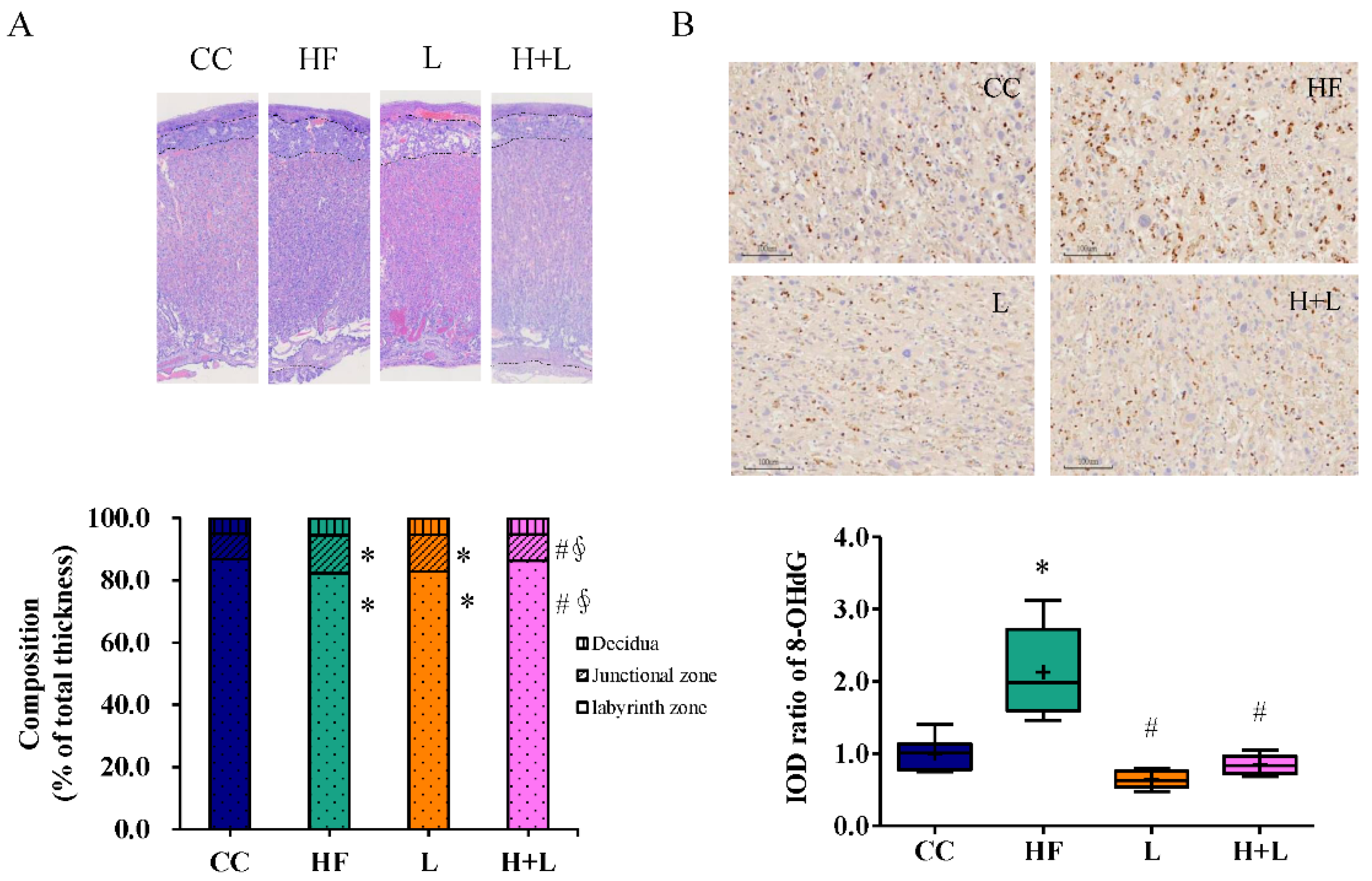
3.4. Maternal L. reuteri Treatment Can Reform Placenta Remodeling and Decrease Placental Oxidative Injury Induced by Maternal HF Diet
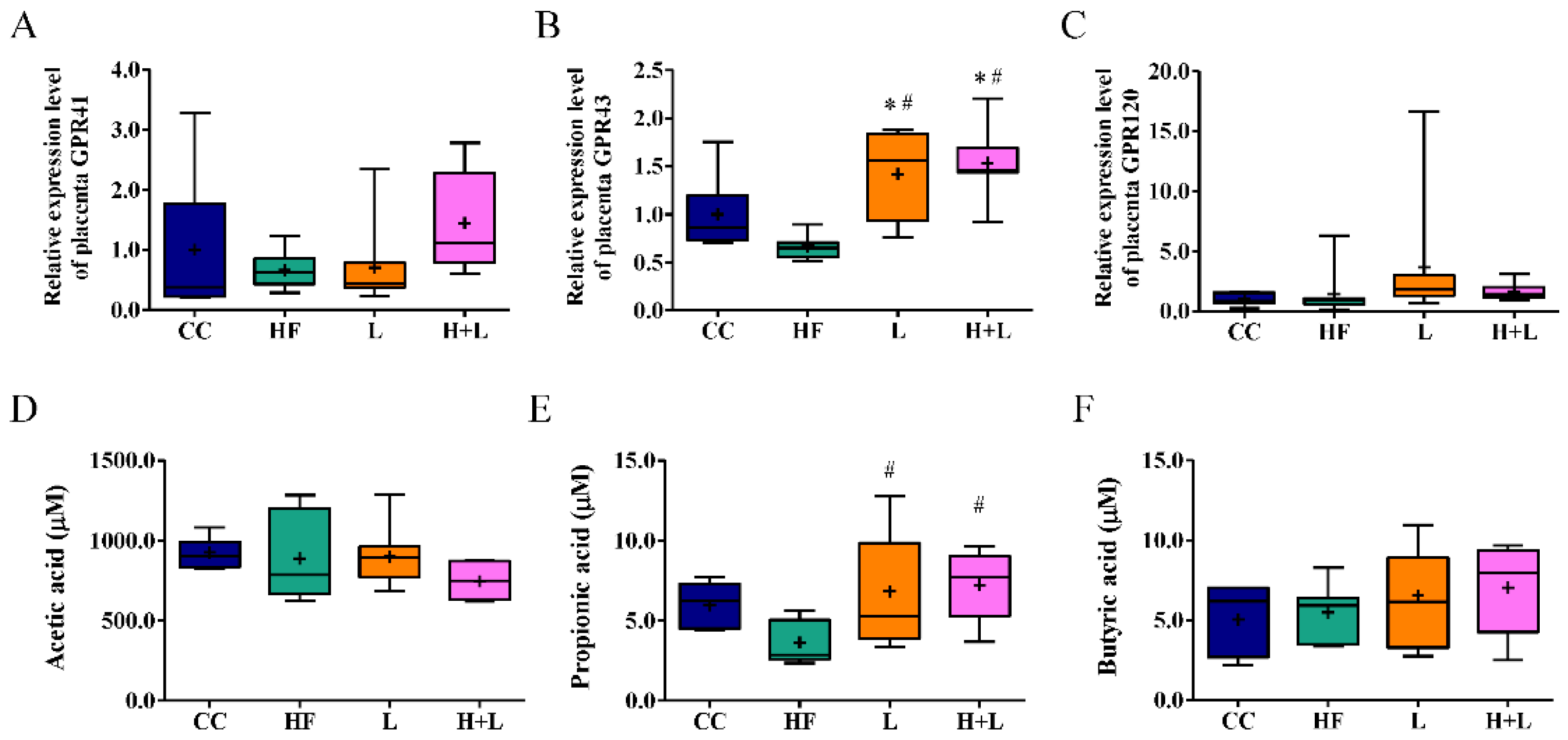
3.5. Maternal L. reuteri Therapy Modified the SCFAs Signaling Cascade
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed consent statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfrey, K.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Prescott, S.L.; Nyirenda, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Eriksson, J.G.; Broekman, B.F. Influence of maternal obesity on the long-term health of offspring. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.; Tilling, K.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Sattar, N.; Brion, M.J.; Benfield, L.; Ness, A.; Deanfield, J.; Hingorani, A.; Nelson, S.M.; et al. Association of maternal weight gain in pregnancy with offspring obesity and metabolic and vascular traits in childhood. Circulation 2010, 121, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaroli, V.; Hopkins, S.A.; Biggs, J.B.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Seneviratne, S.N.; Baldi, J.C.; McCowan, L.M.E.; Cutfield, W.S.; Hofman, P.L.; Derraik, J.G.B. The associations between maternal BMI and gestational weight gain and health outcomes in offspring at age 1 and 7 years. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.G.; Sandboge, S.; Salonen, M.K.; Kajantie, E.; Osmond, C. Long-term consequences of maternal overweight in pregnancy on offspring later health: Findings from the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montinaro, F.; Busby, G.B.; Pascali, V.L.; Myers, S.; Hellenthal, G.; Capelli, C. Unravelling the hidden ancestry of American admixed populations. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Scorletti, E.; Mosca, A.; Alisi, A.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Complications, morbidity and mortality of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2020, 111S, 154170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Roberts, E.A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 30, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Deutsch, R.; Kahen, T.; Lavine, J.E.; Stanley, C.; Behling, C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, E.; Castorani, V.; Nobili, V. The Liver in Children with Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yodoshi, T.; Orkin, S.; Arce Clachar, A.C.; Bramlage, K.; Sun, Q.; Fei, L.; Beck, A.F.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Trout, A.T.; Mouzaki, M. Muscle Mass Is Linked to Liver Disease Severity in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatrics 2020, 223, 93–99.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.W.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Tain, Y.L.; Lin, I.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, K.A.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; et al. Maternal Obesity Related to High Fat Diet Induces Placenta Remodeling and Gut Microbiome Shaping That Are Responsible for Fetal Liver Lipid Dysmetabolism. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 736944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, T.; Oakley, F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Day, C.P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Disease Spectrum. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 451–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandona, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, K.; Kedenko, L.; Antonielli, L.; Kedenko, I.; Gemeier, C.; Leitner, M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Paulweber, B.; Hackl, E. Gut microbiota dysbiosis associated with glucose metabolism disorders and the metabolic syndrome in older adults. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Wei, W.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S. CONSORT-Characteristics and metabolic phenotype of gut microbiota in NAFLD patients. Medicine 2022, 101, e29347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, S. Bridging intestinal immunity and gut microbiota by metabolites. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2019, 76, 3917–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Rescigno, M. Postbiotics: What else? Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Wang, P.M.; Tang, K.S.; Chen, C.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Tiao, M.M. Butyrate ameliorates maternal high-fat diet-induced fetal liver cellular apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, D.; Han, Y.; Ma, F.; Hu, Z.; Xin, F.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Ren, T.Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Sodium Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Steatosis by Stimulating Liver Kinase B1 and Insulin-Induced Gene. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Jing, S.; Jiakui, S.; Lei, Z.; Ying, L.; Han, L.; Xinwei, M.; Weiqin, L. Butyrate Ameliorates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Injury Via Enhancing Foxp3+ Regulatory T-Cell Function in Severe Acute Pancreatitis Model. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Turk. Soc. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibbie, J.J.; Dillon, S.M.; Thompson, T.A.; Purba, C.M.; McCarter, M.D.; Wilson, C.C. Butyrate directly decreases human gut lamina propria CD4 T cell function through histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition and GPR43 signaling. Immunobiology 2021, 226, 152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.R.; Tain, Y.L.; Sheen, J.M.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, C.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Hung, P.L.; Hsieh, K.S.; Huang, L.T. Prenatal Dexamethasone and Postnatal High-Fat Diet Decrease Interferon Gamma Production through an Age-Dependent Histone Modification in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, J.M.; Hsieh, C.S.; Tain, Y.L.; Li, S.W.; Yu, H.R.; Chen, C.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, L.T. Programming Effects of Prenatal Glucocorticoid Exposure with a Postnatal High-Fat Diet in Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Ou, Y.C.; Tang, K.S.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Tain, Y.L.; Lin, I.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Hou, C.Y.; Tsai, C.C.; et al. Metformin ameliorates maternal high-fat diet-induced maternal dysbiosis and fetal liver apoptosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, N.M.; Felix, H.R.; Sore, M.R.; Neto, M.M.A.; Campos, K.E.; Volpato, G.T. The effects of coconut oil supplementation on the body composition and lipid profile of rats submitted to physical exercise. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Huang, L.T.; Sheen, J.M.; Hou, C.Y.; Yeh, Y.T.; Chiang, C.P.; Lin, I.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Tsai, C.C.; Lin, Y.J.; et al. Resveratrol treatment improves the altered metabolism and related dysbiosis of gut programed by prenatal high-fat diet and postnatal high-fat diet exposure. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 75, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, T.; Powell, T.L. Role of placental nutrient sensing in developmental programming. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 56, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Kaser, A. Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Tzang, B.S. Lactobacillus paracasei GMNL-32, Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-89 and L. reuteri GMNL-263 ameliorate hepatic injuries in lupus-prone mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qu, Y.; Qin, B. Sodium butyrate ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by upregulating miR-150 to suppress CXCR4 expression. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, H.; Heng, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qian, S.; et al. Amelioration of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by sodium butyrate is linked to the modulation of intestinal tight junctions in db/db mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10675–10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Granados, M.J.; Franco-Robles, E. Postbiotics in human health: Possible new functional ingredients? Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, H.; Simon, T.G.; Roelstraete, B.; Stephansson, O.; Soderling, J.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Maternal obesity increases the risk and severity of NAFLD in offspring. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumbaugh, D.E.; Friedman, J.E. Developmental origins of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatric Res. 2014, 75, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, K.D.; Cagampang, F.R.; Argenton, M.; Zhang, J.; Ethirajan, P.L.; Burdge, G.C.; Bateman, A.C.; Clough, G.F.; Poston, L.; Hanson, M.A.; et al. Maternal high-fat feeding primes steatohepatitis in adult mice offspring, involving mitochondrial dysfunction and altered lipogenesis gene expression. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borengasser, S.J.; Lau, F.; Kang, P.; Blackburn, M.L.; Ronis, M.J.; Badger, T.M.; Shankar, K. Maternal obesity during gestation impairs fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial SIRT3 expression in rat offspring at weaning. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, M.A.; Chen, A.; Burdine, M.S.; Choudhury, M.; Harris, R.A.; Lane, R.H.; Friedman, J.E.; Grove, K.L.; Tackett, A.J.; Aagaard, K.M. A maternal high-fat diet modulates fetal SIRT1 histone and protein deacetylase activity in nonhuman primates. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 26, 5106–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzoub, A.M.; Nayfeh, T.; Barnard, A.; Munaganuru, N.; Dave, S.; Singh, S.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: Comparative efficacy of pharmacologic therapies for fibrosis improvement and resolution of NASH. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalic, A.J. Pharmacotherapeutic Impact on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Histology: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.-R.; Sheen, J.-M.; Hou, C.-Y.; Lin, I.-C.; Huang, L.-T.; Tain, Y.-L.; Cheng, H.-H.; Lai, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Tiao, M.-M.; et al. Effects of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy on the Programming of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Dams and Fetuses, Related to a Prenatal High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194004
Yu H-R, Sheen J-M, Hou C-Y, Lin I-C, Huang L-T, Tain Y-L, Cheng H-H, Lai Y-J, Lin Y-J, Tiao M-M, et al. Effects of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy on the Programming of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Dams and Fetuses, Related to a Prenatal High-Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194004
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hong-Ren, Jiunn-Ming Sheen, Chih-Yao Hou, I-Chun Lin, Li-Tung Huang, You-Lin Tain, Hsin-Hsin Cheng, Yun-Ju Lai, Yu-Ju Lin, Mao-Meng Tiao, and et al. 2022. "Effects of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy on the Programming of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Dams and Fetuses, Related to a Prenatal High-Fat Diet" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 4004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194004
APA StyleYu, H.-R., Sheen, J.-M., Hou, C.-Y., Lin, I.-C., Huang, L.-T., Tain, Y.-L., Cheng, H.-H., Lai, Y.-J., Lin, Y.-J., Tiao, M.-M., & Tsai, C.-C. (2022). Effects of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy on the Programming of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Dams and Fetuses, Related to a Prenatal High-Fat Diet. Nutrients, 14(19), 4004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194004








