The Acute Effects of a Single Dose of Molecular Hydrogen Supplements on Responses to Ergogenic Adjustments during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Supplements
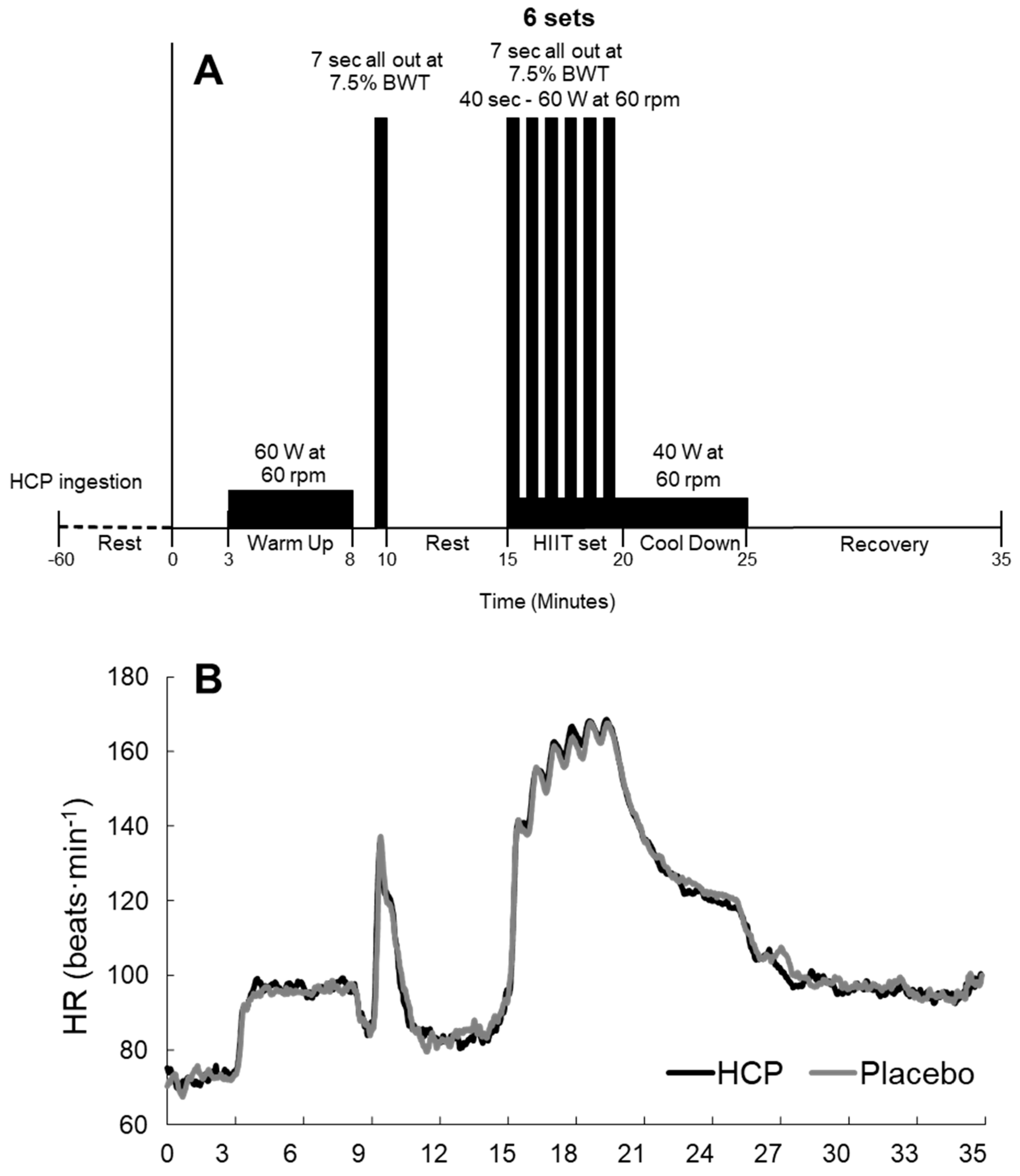
2.3. Experimental Overview
2.4. Exercise Test
2.5. Blood Sampling
2.6. Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. At Rest
3.2. HR Response during HIIT Protocol and Recovery
3.3. TR-NIRS Profiles of the RF and VL Responses during the HIIT and Recovery
3.4. Peak Power during HIIT
3.5. The Relationship between ΔPCO2, ΔHCO3− and ΔPP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.S.; Kawamura, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Nakao, A. Recent advances in hydrogen research as a therapeutic medical gas. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, J.; Wei, Y. Hydrogen, a novel therapeutic molecule, regulates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 789507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Higashida, K.; Muraoka, I. Application of molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant in sports science. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2328768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M. Molecular hydrogen in sports medicine: New therapeutic perspectives. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 36, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.A.D.; Ebine, N.; Nakae, S.; Hojo, T.; Fukuoka, Y. Application of molecular hydrogen as an antioxidant in responses to ventilatory and ergogenic adjustments during incremental exercise in humans. Nutrients 2021, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.M.; Kowalchuk, J.M.; Barstow, T.J.; Kondo, N.; Amano, T.; Shiojiri, T.; Koga, S. The relationship between muscle deoxygenation and activation in different muscles of the quadriceps during cycle ramp exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okushima, D.; Poole, D.C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Barstow, T.J.; Kondo, N.; Ohmae, E.; Koga, S. Muscle deoxygenation in the quadriceps during ramp incremental cycling: Deep vs. superficial heterogeneity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannetta, D.; Qahtani, A.; Millet, G.Y.; Murias, J.M. Quadriceps muscles O2 extraction and EMG breakpoints during a ramp incremental test. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, S.; Koppo, K.; Hespel, P. Sodium bicarbonate improves sprint performance in endurance cycling. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2021, 24, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, J.L.; Xu, H.; Mon-López, D.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Jiménez, S.L. Effect of sodium bicarbonate contribution on energy metabolism during exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, J.; Yi, L.; Hou, Z.; Benardot, D.; Cao, W. Effect of sodium bicarbonate ingestion during 6 weeks of HIIT on anaerobic performance of college students. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Zuccarello, M.; Rapoport, R.M. PCO2 and pH regulation of cerebral blood flow. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Ainslie, P.N. Regulation of cerebral blood flow and metabolism during exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 1356–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Seifert, T.; Brassard, P.; Rasmussen, P.; Vaag, A.; Nielsen, H.B.; Secher, N.H.; Van Lieshout, J.J. Impaired cerebral blood flow and oxygenation during exercise in type 2 diabetic patients. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marillier, M.; Gruet, M.; Bernard, A.C.; Verges, S.; Neder, J.A. The exercising brain: An overlooked factor limiting the tolerance to physical exertion in major cardiorespiratory diseases? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 789053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Lin, J.C.; Cheng, C.F. Effect of caffeine ingestion after creatine supplementation on intermittent high-intensity sprint performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Bailey, S.J.; Kelly, J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Influence of beetroot juice supplementation on intermittent exercise performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.S.; Rossiter, H.B.; Benson, A.P.; Amano, T.; Kondo, N.; Kowalchuk, J.M.; Koga, S. Slowed oxygen uptake kinetics in hypoxia correlate with the transient peak and reduced spatial distribution of absolute skeletal muscle deoxygenation. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rowntree, D. Statistics without Tears: A Primer for Non-Mathematicians; Charles Scribner’s Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Overholser, B.R.; Sowinski, K.M. Biostatistics Primer: Part 2. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Badr, M.S.; Mateika, J.H. Progressive argumentation and ventilatory long-term facilitation are enhanced in sleep apnea patients and are mitigated by antioxidant administration. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5451–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateika, J.H.; Narwani, G. Intermittent hypoxia and respiratory plasticity in humans and other animals: Does exposure to intermittent hypoxia promote or mitigate sleep apnea? Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.L.; Kayser, B. The effect of adding CO2 to hypoxic inspired gas on cerebral blood flow velocity and breathing during incremental exercise. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Wong, L.E.; Eves, N.D.; Koelwyn, G.J.; Smirl, J.D.; Willie, C.K.; Ainslie, P.N. Regional cerebral blood flow distribution during exercise: Influence of oxygen. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2012, 184, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subudhi, A.W.; Lorenz, M.C.; Fulco, C.S.; Roach, R.C. Cerebrovascular responses to incremental exercise during hypobaric hypoxia: Effect of oxygenation on maximal performance. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 94, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Poole, D.C.; Barstow, T.J.; Kondo, N.; Nishiwaki, M.; Okushima, D.; Koga, S. Reduction of VO2 slow component by priming exercise: Novel mechanistic insights from time-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, I.; Kemppainen, J.; Kaskinoro, K.; Peltonen, J.E.; Borra, R.; Lindroos, M.M.; Oikonen, V.; Nuutila, P.; Knuuti, J.; Hellsten, Y.; et al. Comparison of exogenous adenosine and voluntary exercise on human skeletal muscle perfusion and perfusion heterogeneity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, K.K.; Kemppainen, J.; Larmola, K.; Takala, T.O.; Peltoniemi, P.; Oksanen, A.; Ruotsalainen, U.; Cobelli, C.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P. Muscle blood flow and flow heterogeneity during exercise studied with positron emission tomography in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 83, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, K.K.; Laaksonen, M.S.; Takala, T.O.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P. Muscle oxygen extraction and perfusion heterogeneity during continuous and intermittent static exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lexell, J.; Henriksson-Larsén, K.; Sjöström, M. Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscles. 2. A study of cross-sections of whole m. vastus lateralis. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1983, 117, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korthuis, R.J. Skeletal Muscle Circulation; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 4, p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Stöcker, F.; Von Oldershausen, C.; Paternoster, F.K.; Schulz, T.; Oberhoffer, R. Relationship of post-exercise muscle oxygenation and duration of cycling exercise. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| HCP | Placebo | p Value | Effect Size a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood gas | ||||
| pH | 7.354 ± 0.021 | 7.369 ± 0.018 | 0.059 | 0.881 |
| PO2 (mmHg) | 31.3 ± 5.9 | 41.3 ± 8.7 | 0.029 * | 1.081 |
| PCO2 (mmHg) | 55.0 ± 4.7 | 50.7 ± 5.0 | 0.011 † | 1.363 |
| HCO3− (mmol∙L−1) | 30.5 ± 1.6 | 29.2 ± 1.7 | 0.006 † | 1.571 |
| SO2 (%) | 54.5 ± 13.4 | 71.7 ± 12.6 | 0.022 * | 1.158 |
| BE(ecf) (mmol∙L−1) | 5.0 ± 1.5 | 3.8 ± 1.4 | 0.006 † | 1.555 |
| BE(b) (mmol∙L−1) | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 0.9 | 0.034 * | 1.034 |
| TCO2 (mmol∙L−1) | 32.3 ± 1.7 | 30.7 ± 1.8 | 0.004 † | 1.699 |
| Hct (%) | 50 ± 4 | 48 ± 4 | 0.052 | 0.915 |
| Hgb (g∙dL−1) | 17.0 ± 1.4 | 16.2 ± 1.5 | 0.033 * | 1.038 |
| Electrolytes | ||||
| Na (mmol∙L−1) | 141 ± 1 | 141 ± 1 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| K (mmol∙L−1) | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| Ca (mmol∙L−1) | 1.30 ± 0.03 | 1.28 ± 0.05 | 0.119 | 0.688 |
| Cl (mmol∙L−1) | 103 ± 1 | 103 ± 2 | 0.078 | 0.802 |
| AGap (mmol∙L−1) | 8 ± 1 | 9 ± 2 | 0.253 | 0.477 |
| AGapK (mmol∙L−1) | 13 ± 1 | 13 ± 1 | 0.289 | 0.439 |
| Metabolic status | ||||
| Lactate (mmol∙L−1) | 0.95 ± 0.18 | 1.03 ± 0.27 | 0.388 | 0.351 |
| Glucose (mg∙dL−1) | 92 ± 6 | 94 ± 9 | 0.512 | 0.264 |
| Creatinine (mg∙dL−1) | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 0.488 | 0.279 |
| TR-NIRS in the RF | ||||
| Total[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 172 ± 23 | 173 ± 25 | 0.805 | 0.080 |
| Deoxy[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 77 ± 12 | 77 ± 13 | 0.913 | 0.036 |
| StO2 (%) | 55 ± 4 | 55 ± 4 | 0.987 | 0.005 |
| TR-NIRS in the VL | ||||
| Total[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 185 ± 15 | 194 ± 16 | 0.084 | 0.613 |
| Deoxy[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 47 ± 8 | 47 ± 7 | 0.925 | 0.031 |
| StO2 (%) | 75 ± 3 | 76 ± 4 | 0.445 | 0.253 |
| Heart Rate (beats·min−1) | 69 ± 9 | 69 ± 7 | 0.912 | 0.036 |
| HCP | Placebo | p Value | Effect Size a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR-NIRS in the RF | ||||
| Total[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 183 ± 1 | 181 ± 1 | 0.031 * | 1.214 |
| Deoxy[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 104 ± 3 | 102 ± 2 | 0.092 | 0.851 |
| StO2 (%) | 43 ± 1 | 43 ± 1 | 0.272 | 0.504 |
| TR-NIRS in the VL | ||||
| Total[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 200 ± 2 | 198 ± 1 | 0.054 | 1.021 |
| Deoxy[Hb + Mb] (µM) | 60 ± 3 | 56 ± 3 | 0.018 * | 1.404 |
| StO2 (%) | 70 ± 1 | 71 ± 1 | 0.115 | 0.778 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, A.A.D.; Iwamoto, N.; Ebine, N.; Nakae, S.; Hojo, T.; Fukuoka, Y. The Acute Effects of a Single Dose of Molecular Hydrogen Supplements on Responses to Ergogenic Adjustments during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise in Humans. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193974
Alharbi AAD, Iwamoto N, Ebine N, Nakae S, Hojo T, Fukuoka Y. The Acute Effects of a Single Dose of Molecular Hydrogen Supplements on Responses to Ergogenic Adjustments during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise in Humans. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193974
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Ahad Abdulkarim D., Noriaki Iwamoto, Naoyuki Ebine, Satoshi Nakae, Tatsuya Hojo, and Yoshiyuki Fukuoka. 2022. "The Acute Effects of a Single Dose of Molecular Hydrogen Supplements on Responses to Ergogenic Adjustments during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise in Humans" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193974
APA StyleAlharbi, A. A. D., Iwamoto, N., Ebine, N., Nakae, S., Hojo, T., & Fukuoka, Y. (2022). The Acute Effects of a Single Dose of Molecular Hydrogen Supplements on Responses to Ergogenic Adjustments during High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise in Humans. Nutrients, 14(19), 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193974






