Astaxanthin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Ku Protein Degradation and Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Intracellular ROS Level Measurement
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.6. Cell Viability and DNA Fragmentation Determination
2.7. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide (PI)—Staining Assay
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining for γ-H2AX
2.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
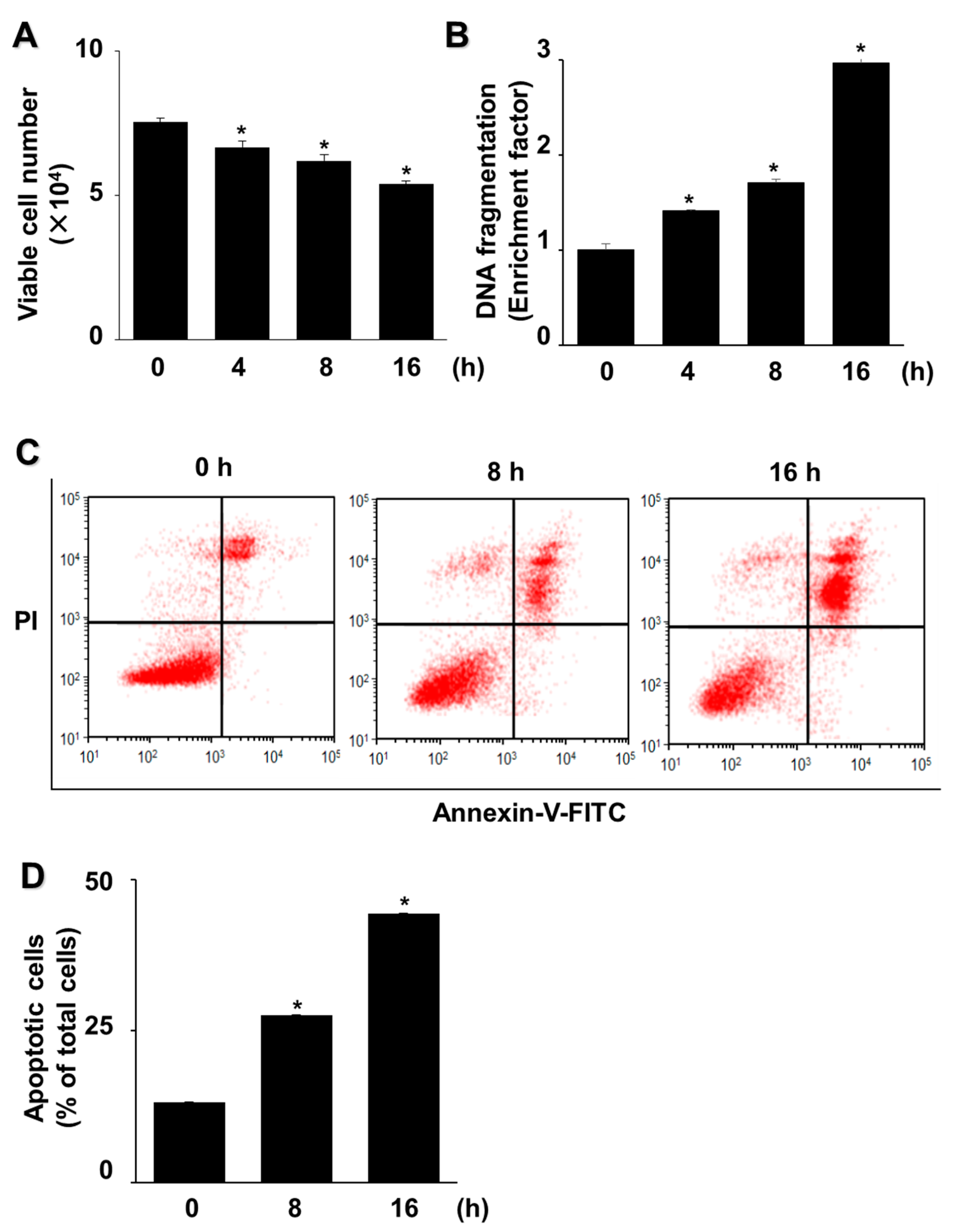
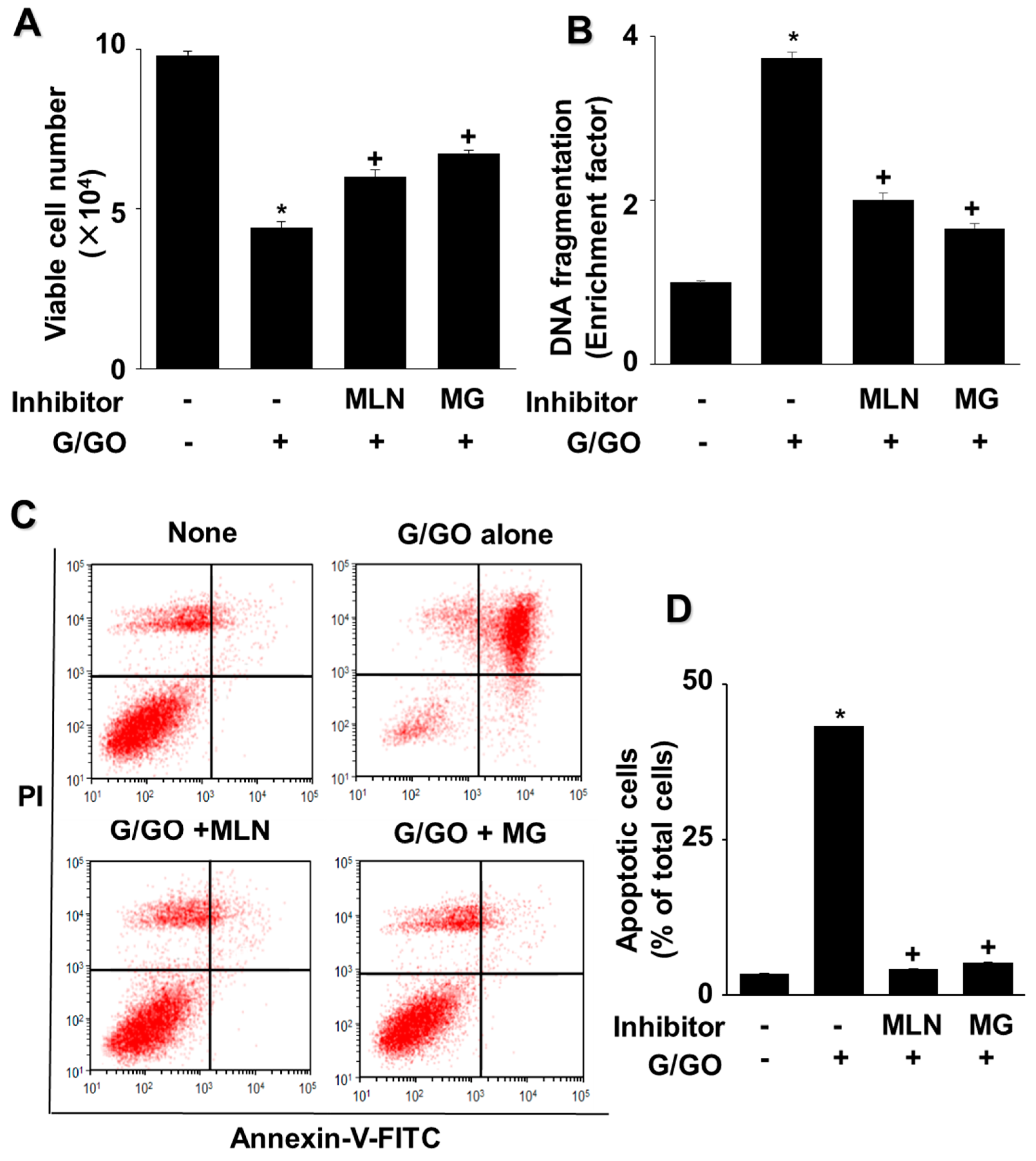
3.1. G/GO Induces Cell Death, DNA Fragmentation, and Apoptosis in AGS Cells
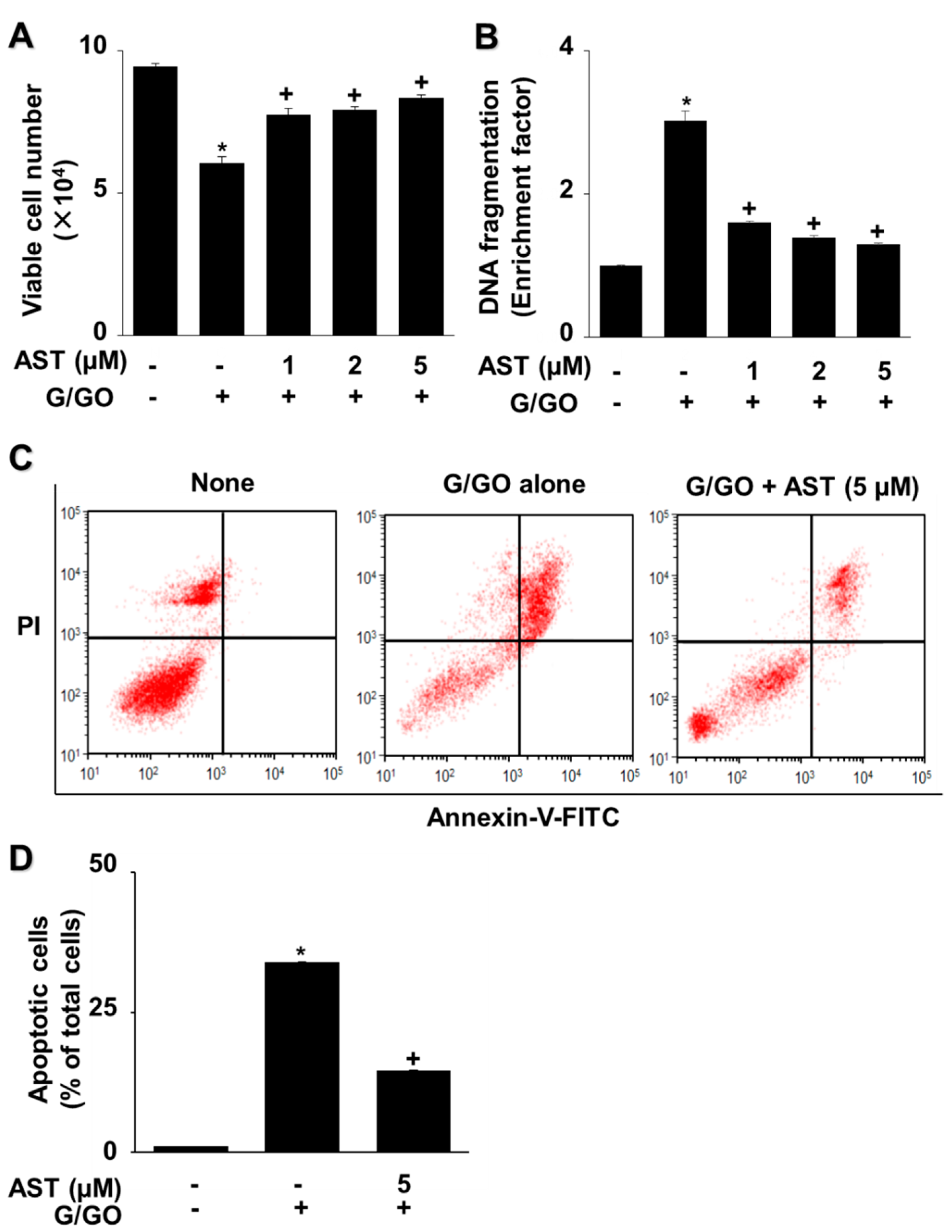
3.2. Astaxanthin Inhibits G/GO-Induced Cell Death, DNA Fragmentation, and Apoptosis in AGS Cells
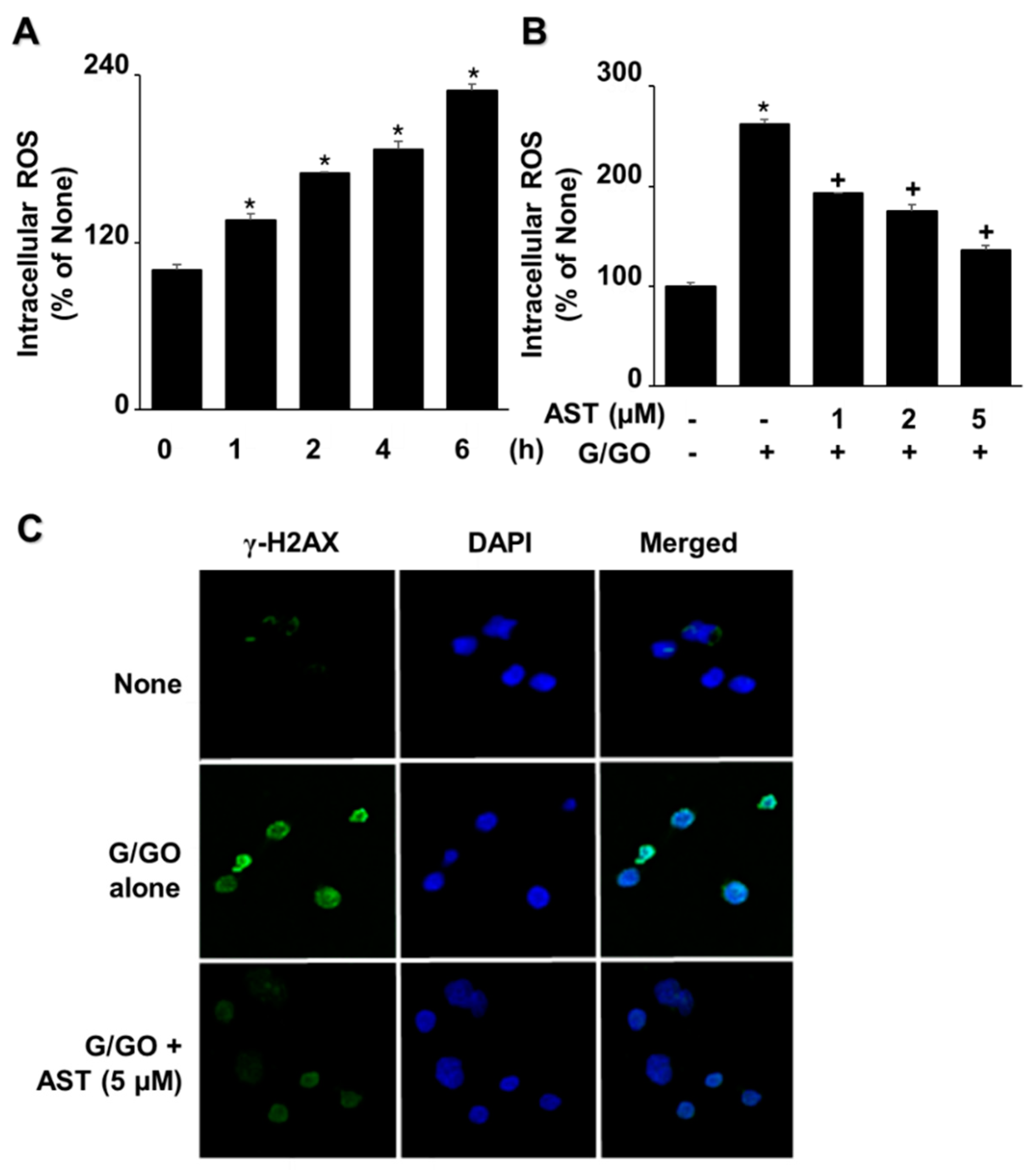
3.3. Astaxanthin Inhibits G/GO-Induced Increase in ROS Levels and γ-H2AX in AGS Cells
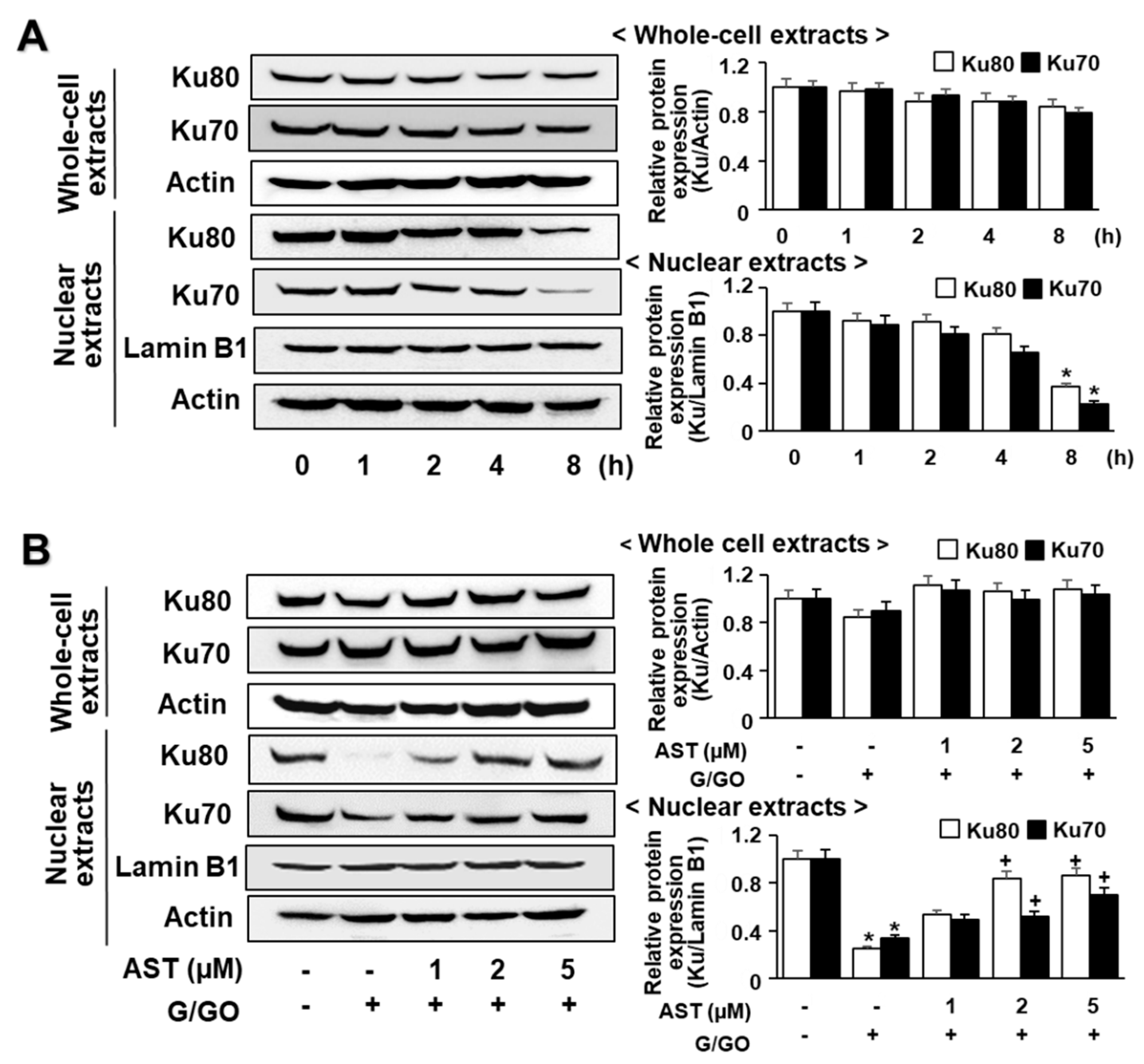
3.4. Astaxanthin Inhibits G/GO-Induced Ku70/80 Loss in AGS Cells
3.5. MLN4924 and MG132 Inhibit G/GO-Induced Cell Death, DNA Fragmentation, and Apoptosis in AGS Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Bont, R.; van Larebeke, N. Endogenous DNA damage in humans: A review of quantitative data. Mutagenesis 2004, 19, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J. Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krokan, H.E.; Bjørås, M. Base excision repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbury, C.J.; Hickson, I.D. Cellular responses to DNA damage. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, E.C. DNA damage and repair. Nature 2003, 421, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.K.; Jackson, S.P. DNA double-strand breaks: Signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gent, D.C.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J.; Kanaar, R. Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiruvella, K.K.; Liang, Z.; Wilson, T.E. Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Choi, J.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Beta-Carotene-induced apoptosis is mediated with loss of Ku proteins in gastric cancer AGS cells. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Morio, T.; Kim, K.H. Oxidative stress induces nuclear loss of DNA repair proteins Ku70 and Ku80 and apoptosis in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36676–36687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.O.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Oxidative stresss induces apoptosis via calpain- and caspase-3- mediated cleavage of ATM in pancreatic acinar cells. Free Rad. Res. 2020, 54, 7990809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.-O.; Jang, Y.-S.; Heo, J.-S.; Chung, W.-T.; Choi, K.-C.; Lee, J.-C. Apoptosis-inducing factor plays a critical role in caspase-independent, pyknotic cell death in hydrogen peroxide-exposed cells. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, Y.J.; Chong, W.S.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C. Glucosed oxidase/glucose induces apoptosis in C6 glial cells via mitochondria-dependent pathway. Biomolecules 2005, 13, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Apoptosis by Suppressing the Loss of Ku Proteins in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, R.B.; Peterson, S.R.; Wang, J.; Bear, D.G.; Bradbury, E.M.; Chen, D.J. DNA looping by Ku and the DNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 9, 4267–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, J.A.; Jackson, S.P. A means to a DNA end: The many roles of Ku. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Radulovic, M.; Figueiredo-Pereira, M.E.; Cardozo, C. The Ubiquitin-proteasome system: Potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, L.; Ghenoiu, C.; Woo, E.M.; Krutchinsky, A.N.; Chait, B.T.; Funabiki, H. Ku80 removal from DNA through double strand break-induced ubiquitylation. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S.; Lukashchuk, N.; Sczaniecka-Clift, M.; Britton, S.; Sage, C.I.; Calsou, P.; Beli, P.; Galanty, Y.; Jackson, S.P. Neddylation promotes ubiquitylation and release of Ku from DNA-damage sites. Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabut, G.; Peter, M. Function and regulation of protein neddylation. ‘Protein Modifications: Beyond the Usual Suspects’ Review Series. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, Y. MLN4924: Additional activities beyond neddylation inhibition. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2019, 6, e1618174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, S.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Dargahi, L.; Jorjani, M. Astaxanthin: A mechanistic review on its biological activities and health benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D. Astaxanthin, cell membrane nutrient with diverse clinical benefits and anti-aging potential. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction and interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, R.R.; Niu, T.T.; Chen, H.M. Astaxanthin blocks preeclampsia progression by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.X.; Zhou, H.L.; Huang, C.L.; You, C.G.; Fang, Q.; Wu, P.; Han, C.M. Astaxanthin attenuates early acute kidney injury following severe burns in rats by ameliorating oxidative stress and mitochondrial-related apoptosis. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2105–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, B.; Lin, S.; Jing, L.; Mao, C.; Xu, P.; Zuo, J. Astaxanthin inhibits apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells type II in vivo and in vitro through the ROS-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2198–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, T.; Su, J.; He, Y.; Ji, W. Hyperthermia induces apoptosis of 786-O cells through suppressing Ku80 expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Gu, Q.H.; Li, M.; Yang, H.P.; Cao, L.M.; Hu, C.P. Role of Ku70 and Bax in epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis of A549 Cells in vivo. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fell, V.L.; Schild-Poulter, C. The Ku heterodimer: Function in DNA repair and beyond. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 763, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spataro, V.; Norbury, C.; Harris, A. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 3, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.H. Role of NF-kappaB and DNA repair protein Ku on apoptosis in pancreatic acinar cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharshan, S.J.; Dyavaiah, M. Aastaxanthin protects oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage and enhances longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biogerontology 2021, 22, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santocono, M.; Zurria, M.; Berrettini, M.; Fedeli, M.; Falcioni, G. Lutein, zeaxanthin and astaxanthin protect against DNA damage in SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells induced by reactive nitrogen species. J. Phytochem. Phytobiol. B Biol. 2007, 88, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santocono, M.; Zurria, M.; Berrettini, M.; Fedeli, M.; Falcioni, G. Influence of astaxanthin, zeaxanthin and lutein on DNA damage and repair in UVA-irradiated cells. J. Phytochem. Phytobiol. B Biol. 2006, 85, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinnyi, D.; Rushkovsky, S.; Demchenko, O.; Pilinska, M. Chapter 7. Astaxanthin as a modifier of genome instability after γ-radiation. In Progress in Carotenoid Research; Zepka, L.Q., Jacob-Lopes, E., De Rosso, V.V., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Ku Protein Degradation and Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193939
Lee J, Lim JW, Kim H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Ku Protein Degradation and Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193939
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jaeeun, Joo Weon Lim, and Hyeyoung Kim. 2022. "Astaxanthin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Ku Protein Degradation and Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193939
APA StyleLee, J., Lim, J. W., & Kim, H. (2022). Astaxanthin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Ku Protein Degradation and Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients, 14(19), 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193939






