Inflammation in VTA Caused by HFD Induces Activation of Dopaminergic Neurons Accompanied by Binge-like Eating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Mice with Dopamine Transporter (DAT)-Specific Deletion of IKKβ
2.3. Isolating DNA from Tissues for Detection of Recombination of Floxed Alleles
2.4. Body Composition and Food Intake
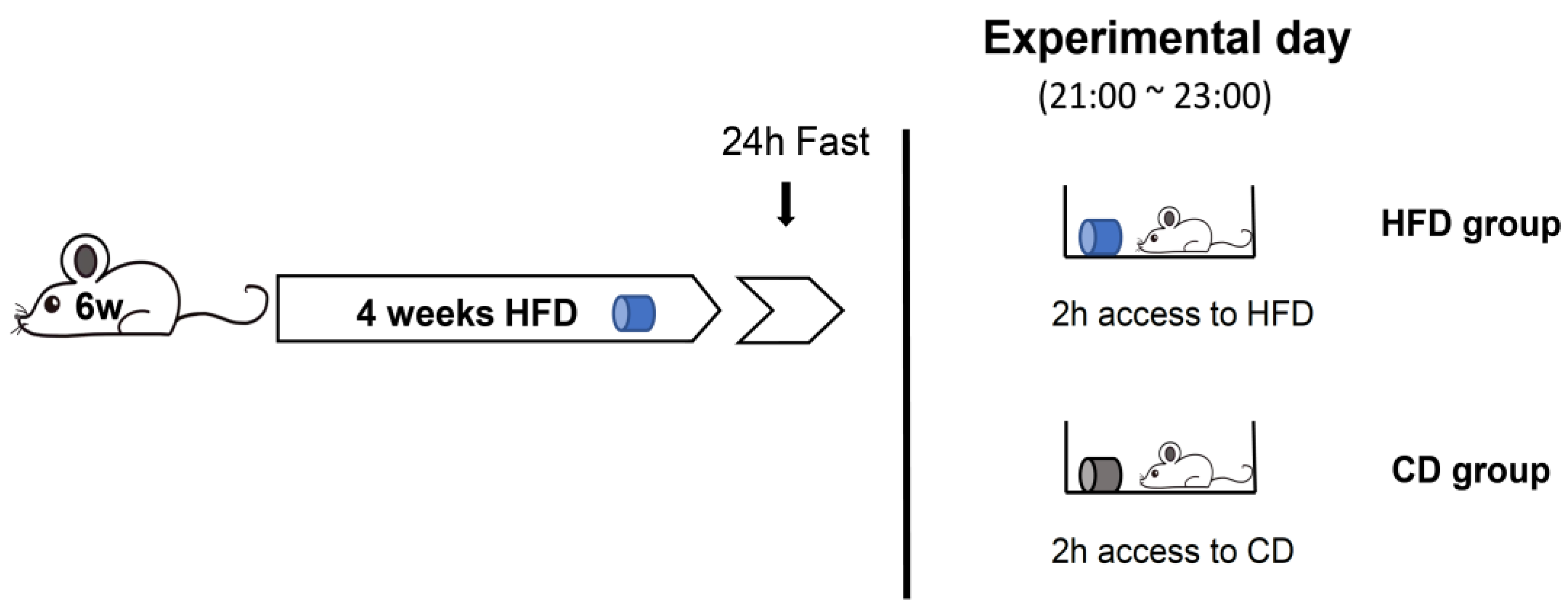
2.5. Assessment of Feeding Behaviors under Fast-Refeed Access to HFD or Chow Diet (CD)
2.6. Extraction of Brain Tissues
2.7. Determination of mRNA Levels by qRT-PCR
2.8. Intracerebroventricular Injection of Insulin
2.9. Determination of Protein Levels by Western Blot
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Dopaminergic Neuron-Specific IKKβ Deficient Mice
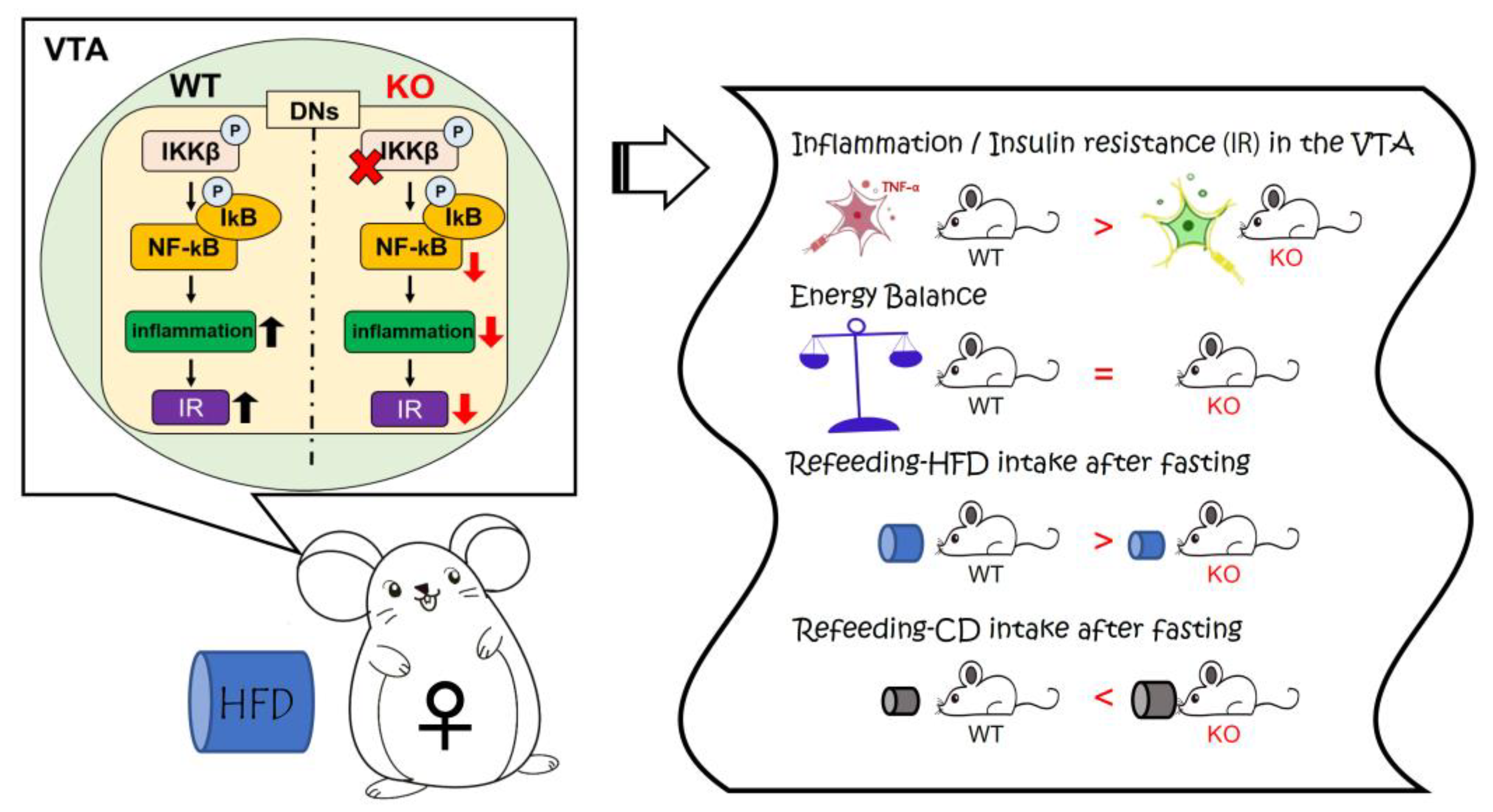
3.2. IKKβ Signaling in DNs Does Not Affect Energy Balance and Glucose Metabolism
3.3. IKKβ Deficiency in DNs Suppresses Binge Eating of HFD in Female Mice
3.3.1. Binge-like Eating under Inflammatory Conditions in the VTA
3.3.2. IKKβ Deficiency in DNs Suppresses Binge Eating of HFD in Female Mice
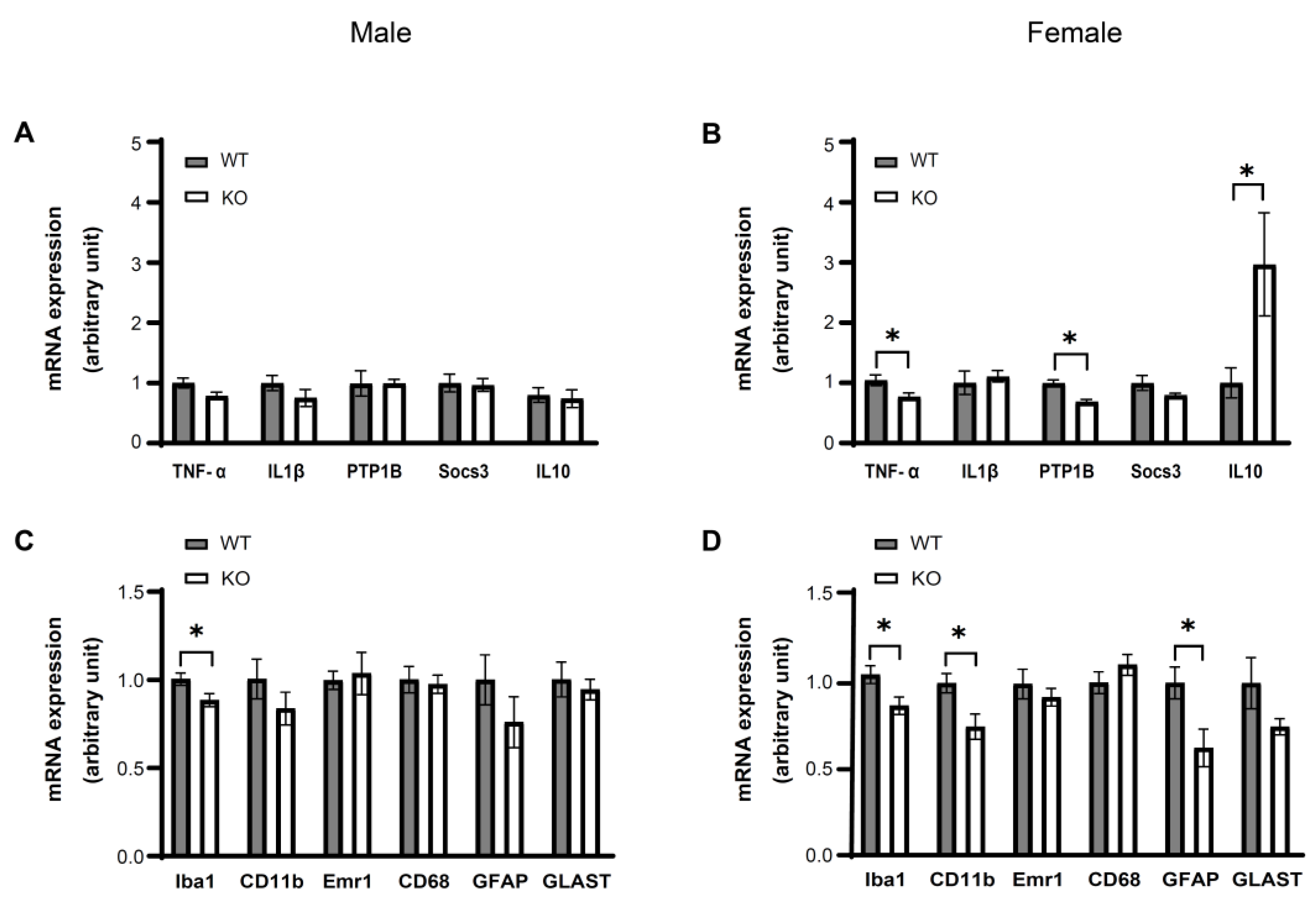
3.4. IKKβ Deficiency in the Dopamine Neurons of VTA Suppresses HFD Induced Inflammation in the VTA of Female Mice
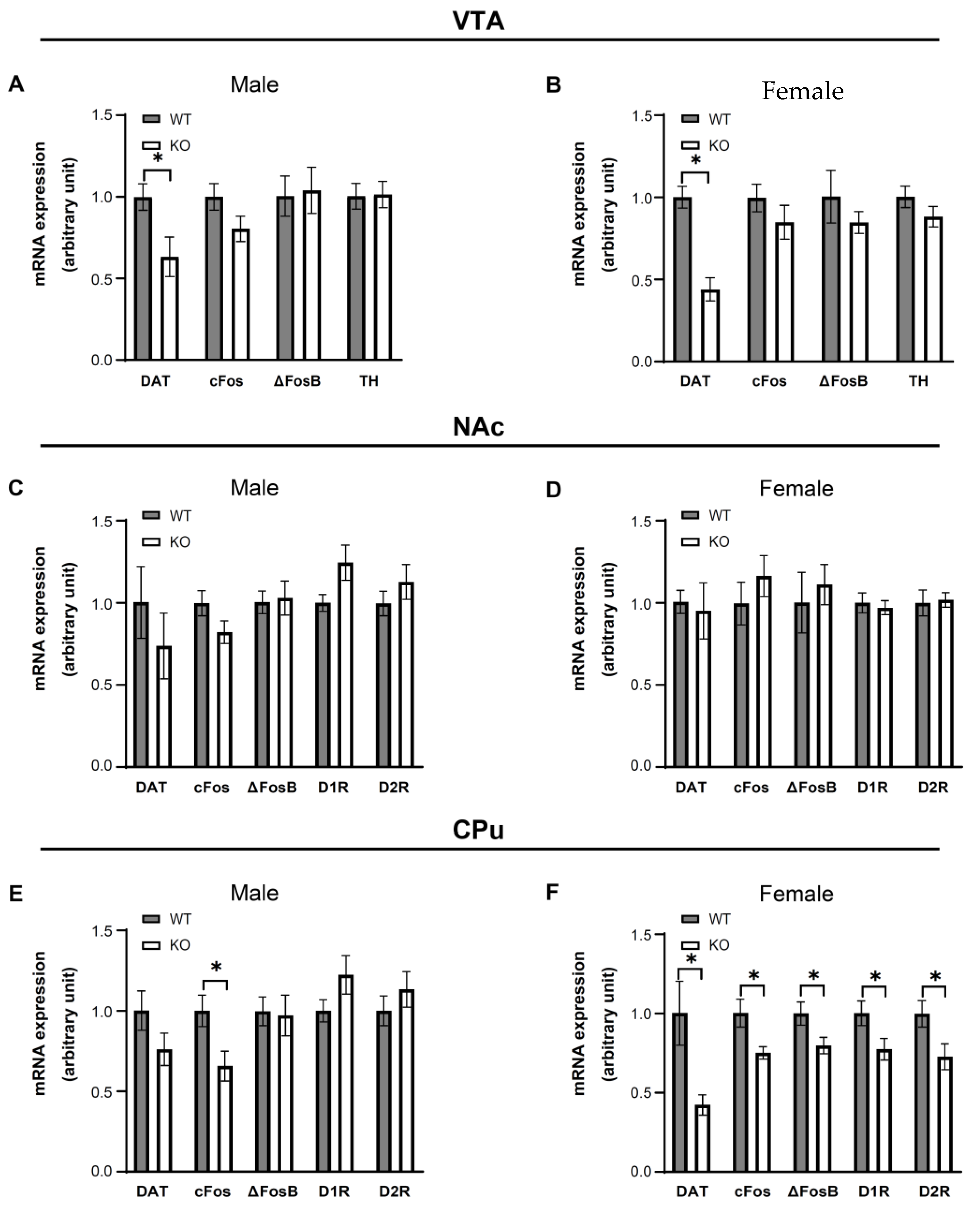
3.5. IKKβ Deficiency in the Dopamine Neurons of VTA Altered the Dopamine-Related Gene Expressions in Female Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bilano, V.; Bixby, H.; Zhou, B.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Taddei, C.; Hajifathalian, K.; Lu, Y.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orahilly, S. Human Genetics Illuminates the Paths to Metabolic Disease. Nature 2009, 462, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, C.R.; Keller, B.N.; Arnold, A.C.; Silberman, Y. Impact of High Fat Diet and Ethanol Consumption on Neurocircuitry Regulating Emotional Processing and Metabolic Function. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 601111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.M.; Hutson, P.H.; Herman, B.K.; Potenza, M.N. The Neurobiological Basis of Binge-Eating Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 63, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perello, M.; Valdivia, S.; Romero, G.G.; Raingo, J. Considerations about Rodent Models of Binge Eating Episodes. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, L.; Pitman, K.A.; Borgland, S.L. Mesolimbic Dopamine and Its Neuromodulators in Obesity and Binge Eating. CNS Spectr. 2015, 20, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.Y.; Haesler, S.; Vong, L.; Lowell, B.B.; Uchida, N. Neuron-Type-Specific Signals for Reward and Punishment in the Ventral Tegmental Area. Nature 2012, 482, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Borgland, S.L. Insulin Actions in the Mesolimbic Dopamine System. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 320, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann, L.J.; Schmid, S.M.; Hettel, J.; Giesen, K.; Francke, P.; Büchel, C.; Brassen, S. Central Insulin Modulates Food Valuation via Mesolimbic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Zou, J.; Qin, L. Induction of Innate Immune Genes in Brain Create the Neurobiology of Addiction. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, P.J. Common Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Obesity and Drug Addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Banno, R.; Sun, R.; Yaginuma, H.; Taki, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsunekawa, T.; Onoue, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. High-Fat Feeding Causes Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in the Ventral Tegmental Area in Mice. Neuroscience 2021, 461, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared Principles in NF-ΚB Signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.S.; Buras, E.D.; Balasubramanyam, A. The Role of the Immune System in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 616193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Karin, M.; Bai, H.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-ΚB and ER Stress Link Overnutrition to Energy Imbalance and Obesity. Cell 2008, 135, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Tsunekawa, T.; Hirose, T.; Yaginuma, H.; Taki, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Miyata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Onoue, T.; et al. GABAB Receptor Signaling in the Caudate Putamen Is Involved in Binge-like Consumption during a High Fat Diet in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiault, M.; Parnaudeau, S.; Milet, A.; Parlato, R.; Rouzeau, J.D.; Lazar, M.; Tronche, F. Analysis of Dopamine Transporter Gene Expression Pattern—Generation of DAT-ICre Transgenic Mice. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, T.; Banno, R.; Yaginuma, H.; Taki, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Onoue, T.; Takagi, H.; Hagiwara, D.; Ito, Y.; et al. GABAB Receptor Signaling in the Mesolimbic System Suppresses Binge-like Consumption of a High-Fat Diet. iScience 2019, 20, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, C.M.; Liang-Guallpa, J.; Li, C.; Wolcott, N.S.; Boone, M.H.; Southern, M.; Kobzar, N.P.; de Salgado, I.A.; Reddy, D.M.; Sun, F.; et al. High-Fat Food Biases Hypothalamic and Mesolimbic Expression of Consummatory Drives. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.L.; McKee, S.E.; Hill-Smith, T.; Grissom, N.M.; George, R.; Lucki, I.; Reyes, T.M. Removal of High-Fat Diet after Chronic Exposure Drives Binge Behavior and Dopaminergic Dysregulation in Female Mice. Neuroscience 2016, 326, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.J.; Morris, M.J. The Role of Reward Circuitry and Food Addiction in the Obesity Epidemic: An Update. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 131, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.M.; Dayas, C.V.; James, M.H.; Smith, R.J. New Directions in Modelling Dysregulated Reward Seeking for Food and Drugs. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter-Potter, L.N.; Henricks, A.M.; Berger, A.L.; Bieniasz, K.V.; Lugo, J.M.; McLaughlin, R.J. Alcohol Vapor Exposure Differentially Impacts Mesocorticolimbic Cytokine Expression in a Sex-, Region-, and Duration-Specific Manner. Neuroscience 2017, 346, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, S.F.; Razmpour, R.; Lutton, E.M.; Tallarida, C.S.; Heldt, N.A.; Cannella, L.A.; Persidsky, Y.; Rawls, S.M.; Ramirez, S.H. Adolescent Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Chronic Mesolimbic Neuroinflammation with Concurrent Enhancement in the Rewarding Effects of Cocaine in Mice during Adulthood. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, J.P.; Bravo, J.; Freitas, J.; Barbosa, M.A.; Santos, S.G.; Summavielle, T.; Almeida, M.I. TNF-Alpha-Induced Microglia Activation Requires MiR-342: Impact on NF-KB Signaling and Neurotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellhauser, L.; Belsham, D.D. Activation of the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Receptor GPR120 Mediates Anti-Inflammatory Actions in Immortalized Hypothalamic Neurons. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, R.C.; Bence, K.K. Central Regulation of Metabolism by Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabolotny, J.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Welsh, L.A.; Kershaw, E.E.; Neel, B.G.; Kahn, B.B. Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Expression Is Induced by Inflammation in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14230–14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, T.; Banno, R.; Mizoguchi, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Tominaga, T.; Onoue, T.; Hagiwara, D.; Ito, Y.; Iwama, S.; Goto, M.; et al. Deficiency of PTP1B Attenuates Hypothalamic Inflammation via Activation of the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in Microglia. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, N.T.; Sweigart, K.L.; Lakoski, J.M.; Norgren, R.; Hajnal, A. Restricted Feeding with Scheduled Sucrose Access Results in an Upregulation of the Rat Dopamine Transporter. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbs, R.K.; Unger, E.L.; Corwin, R.L.W. 2-Hydroxyestradiol Enhances Binge Onset in Female Rats and Reduces Prefrontal Cortical Dopamine in Male Rats. Horm. Behav. 2013, 63, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D.K.; Singh, S.; Shi, Q.; Pardee, A.B.; Iglehart, J.D. Crossroads of Estrogen Receptor and NF-kappaB Signaling. Sci. STKE 2005, 2005, pe27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerri, S.; Mus, L.; Blandini, F. Parkinson’s Disease in Women and Men: What’s the Difference? J. Parkinsons Dis. 2019, 9, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.B.; Chartoff, E. Sex Differences in Neural Mechanisms Mediating Reward and Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, J.A.; Logsdon, M.K.; Turner, C.A.; Gonzalez, I.L.; Leonardo, N.B.; Becker, J.B. Sex Differences in Vulnerability to Addiction. Neuropharmacology 2021, 187, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, R.; Sugiyama, M.; Wang, S.; Kuno, M.; Sasaki, T.; Hirose, T.; Miyata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsunekawa, T.; Onoue, T.; et al. Inflammation in VTA Caused by HFD Induces Activation of Dopaminergic Neurons Accompanied by Binge-like Eating. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183835
Sun R, Sugiyama M, Wang S, Kuno M, Sasaki T, Hirose T, Miyata T, Kobayashi T, Tsunekawa T, Onoue T, et al. Inflammation in VTA Caused by HFD Induces Activation of Dopaminergic Neurons Accompanied by Binge-like Eating. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183835
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Runan, Mariko Sugiyama, Sixian Wang, Mitsuhiro Kuno, Tomoyuki Sasaki, Tomonori Hirose, Takashi Miyata, Tomoko Kobayashi, Taku Tsunekawa, Takeshi Onoue, and et al. 2022. "Inflammation in VTA Caused by HFD Induces Activation of Dopaminergic Neurons Accompanied by Binge-like Eating" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183835
APA StyleSun, R., Sugiyama, M., Wang, S., Kuno, M., Sasaki, T., Hirose, T., Miyata, T., Kobayashi, T., Tsunekawa, T., Onoue, T., Yasuda, Y., Takagi, H., Hagiwara, D., Iwama, S., Suga, H., & Arima, H. (2022). Inflammation in VTA Caused by HFD Induces Activation of Dopaminergic Neurons Accompanied by Binge-like Eating. Nutrients, 14(18), 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183835





