A Composition of Phytonutrients for Glycemic and Weight Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Human Omental Preadipocytes
2.2. Treatment Conditions
2.3. Preparation of Total Cell Extracts
2.4. Capillary Isoelectric Focusing Immunoassays
2.5. Capillary Western Immunoassays
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Antibodies
2.8. Glucose Uptake Assays
2.9. Adipogenesis Assays
2.10. Diet-Induced Obesity Murine Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
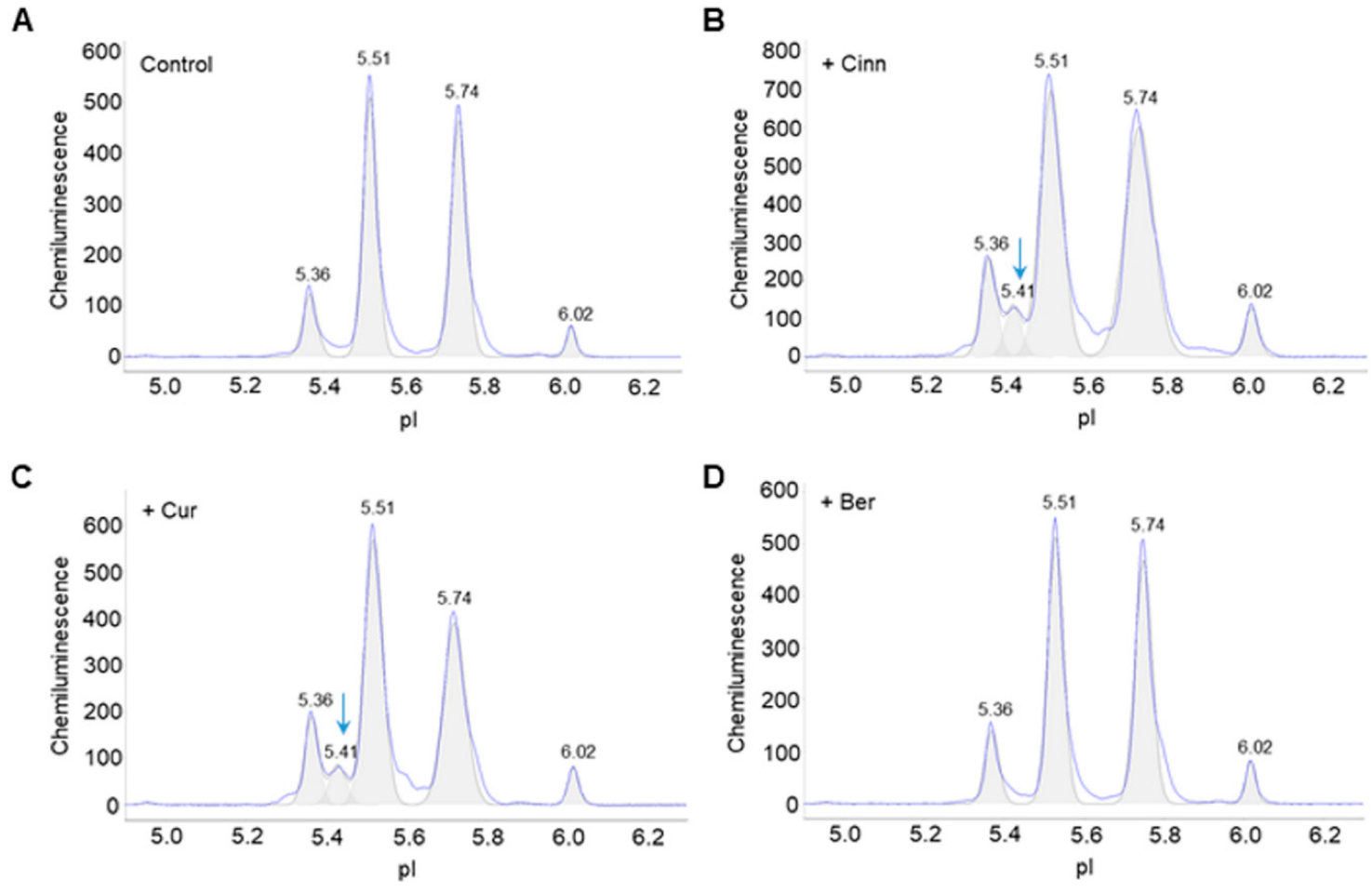
3.1. Cinnamaldehyde and Curcumin Induce Post-Translational Modifications of Akt2
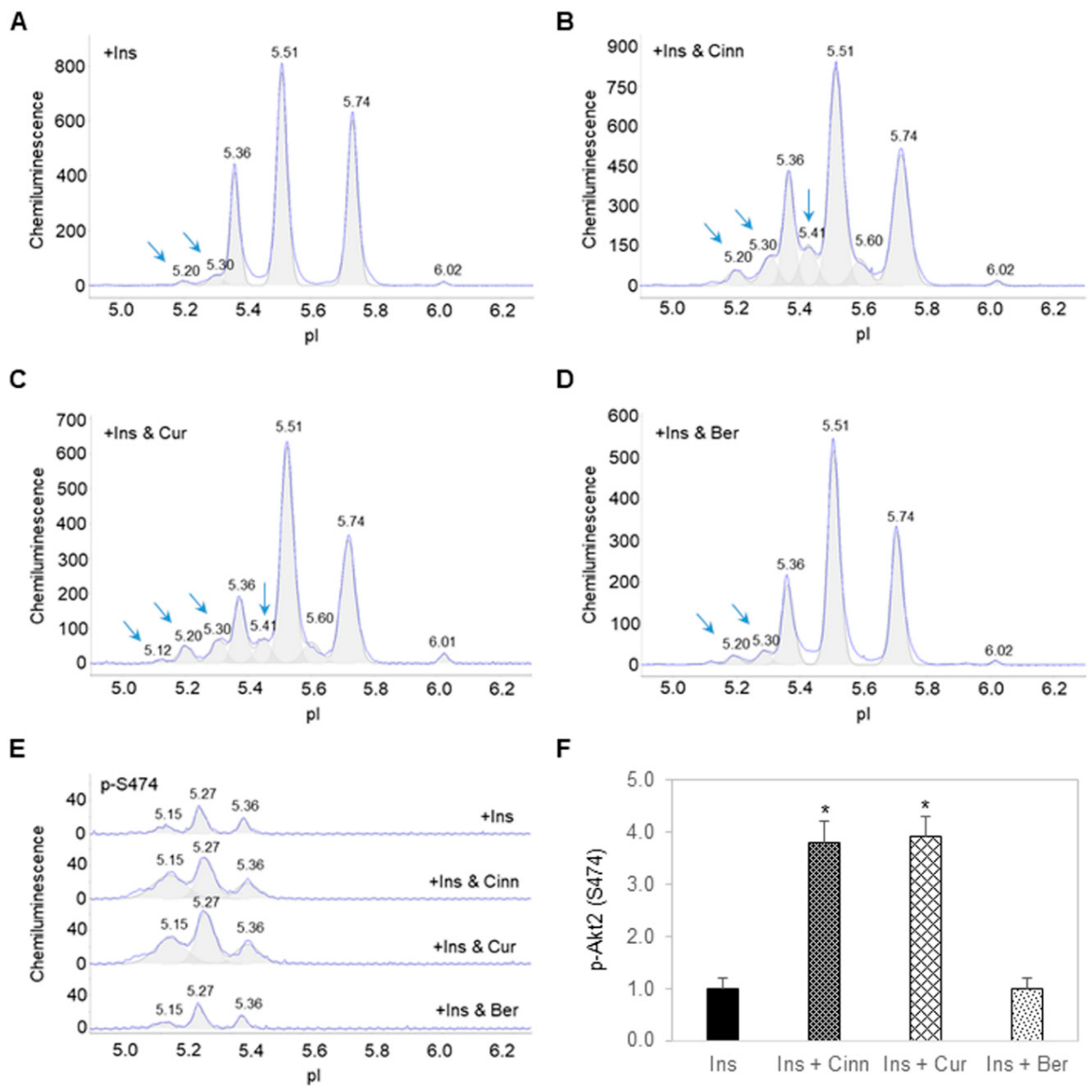
3.2. Cinnamaldehyde and Curcumin Enhance Insulin-Stimulated Activation of Akt2
3.3. Additive Effects of Cinnamaldehyde and Curcumin on Akt2 Activation and Glucose Transport
3.4. Berberine Inhibits Fat Cell Differentiation
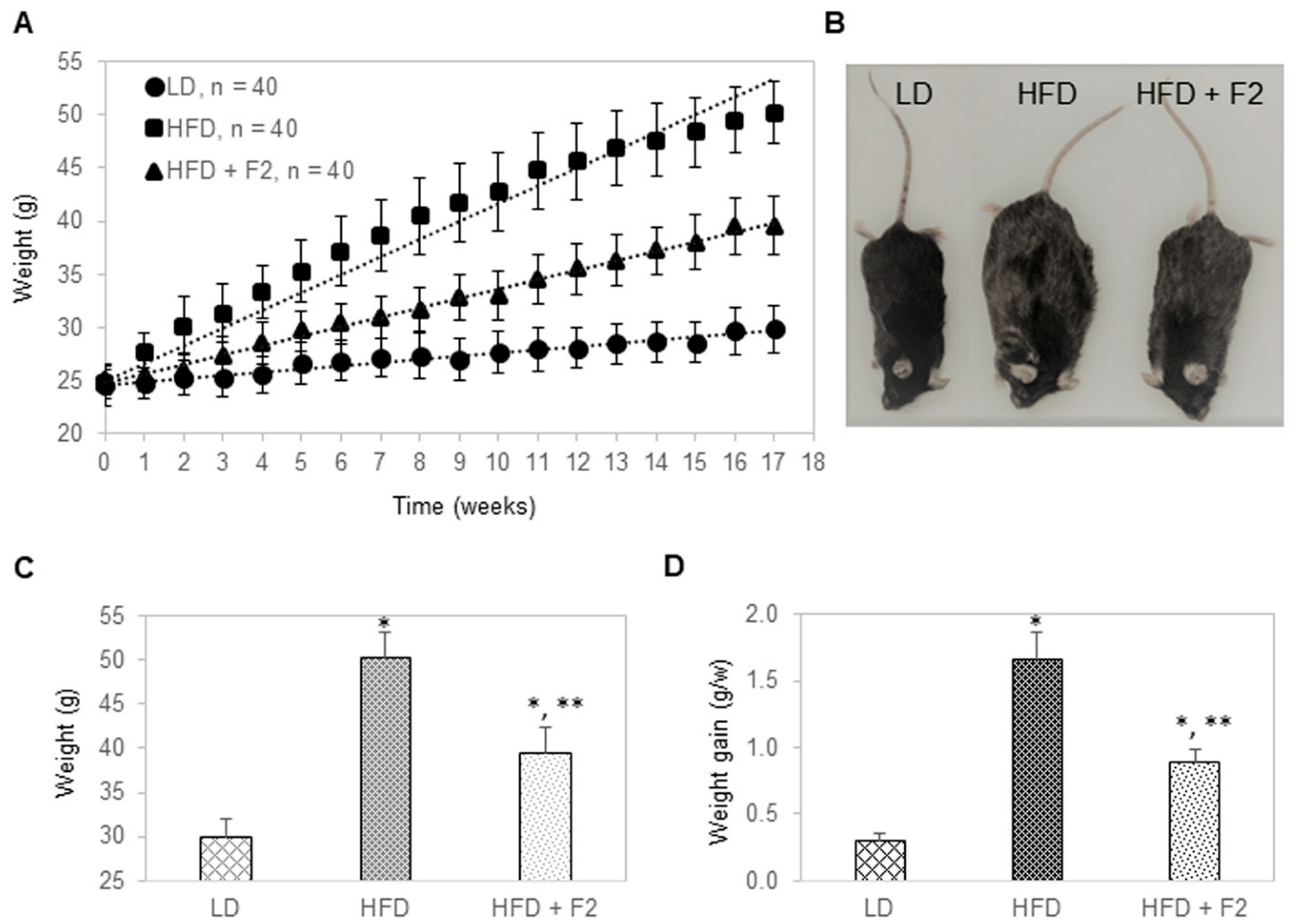
3.5. Dietary Supplement with F2 Composition Prevents Weight Gain
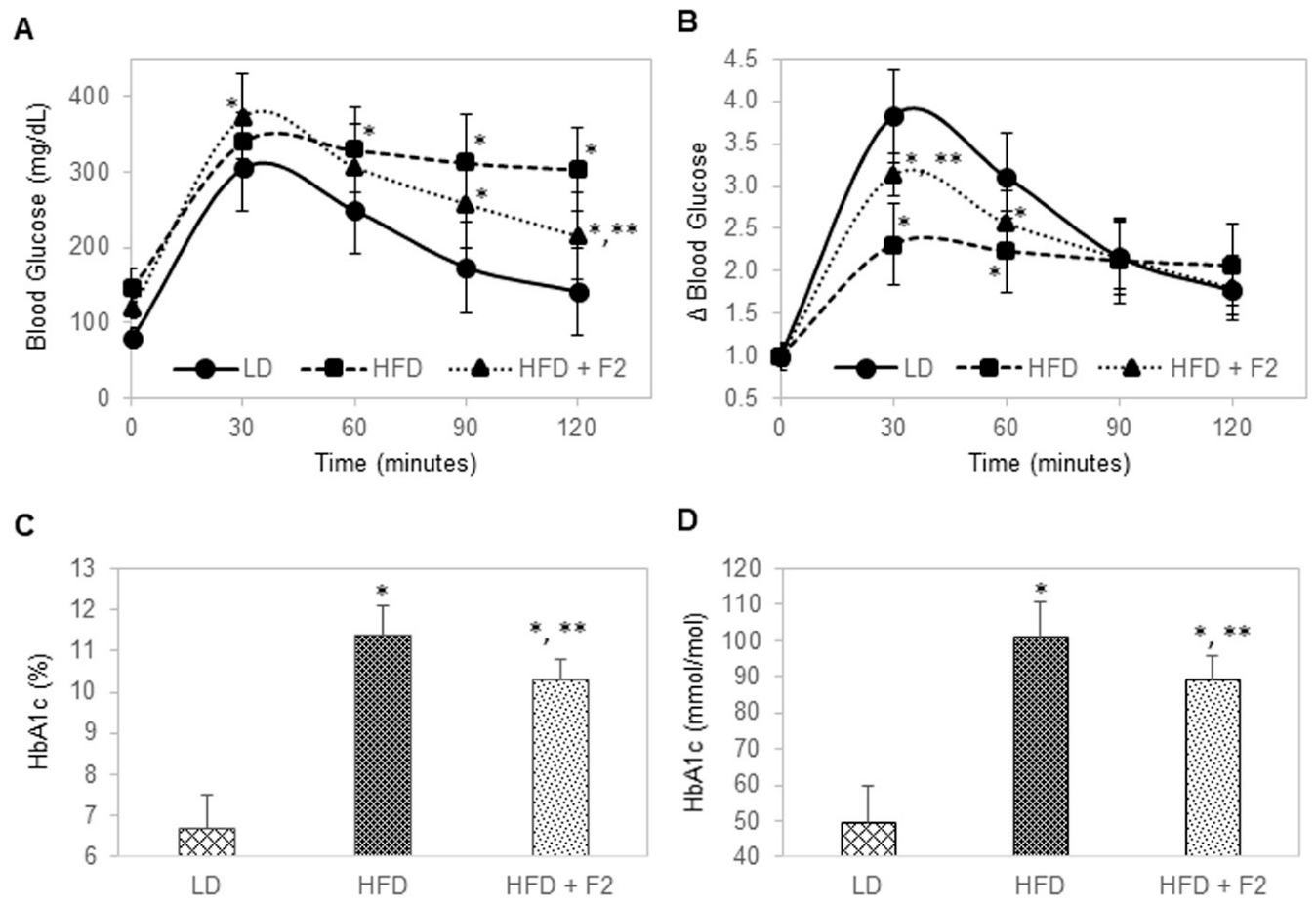
3.6. Dietary Supplement with F2 Composition Improves Glucose Tolerance and Reduces HbA1c
3.7. Dietary Supplement with F2 Composition Reduces Blood Lipids
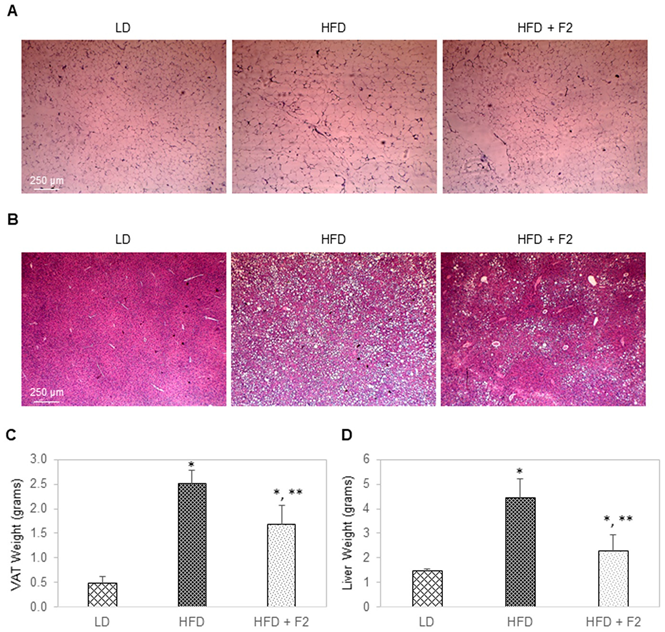
3.8. Dietary Supplement with F2 Composition Reduces Visceral Adiposity and Liver Steatosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report Website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Riddle, M.C.; Herman, W.H. The Cost of Diabetes Care-An Elephant in the Room. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjornsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gaal, L.; Scheen, A. Weight management in type 2 diabetes: Current and emerging approaches to treatment. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balducci, S.; Sacchetti, M.; Haxhi, J.; Orlando, G.; D’Errico, V.; Fallucca, S.; Menini, S.; Pugliese, G. Physical exercise as therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30 (Suppl. S1), 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Bickel, P.E.; Scherer, P.E. Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.; Ojcius, D.M.; Chang, C.J.; Lin, C.S.; Lu, C.C.; Ko, Y.F.; Tseng, S.F.; Lai, H.C.; Young, J.D. Anti-obesogenic and antidiabetic effects of plants and mushrooms. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xing, H.; Ye, J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2008, 57, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wei, J.; Abidi, P.; Lin, M.; Inaba, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Si, S.; Pan, H.; et al. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, R.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Niu, J.; Fu, M.; Zhang, D.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde in diabetes: A review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 122, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuengsamarn, S.; Rattanamongkolgul, S.; Luechapudiporn, R.; Phisalaphong, C.; Jirawatnotai, S. Curcumin extract for prevention of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tang, X.; Pan, L.; Gao, J.; Bi, R.; Lai, X. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacological Activities of Berberine in Diabetes Mellitus Treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9987097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivari, F.; Mingione, A.; Brasacchio, C.; Soldati, L. Curcumin and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, Y.; Le, T.T. Cinnamaldehyde and Curcumin Prime Akt2 for Insulin-Stimulated Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Lu, F. Berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 591654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, Z.; Perna, S.; Al-Thawadi, S.; Alalwan, T.A.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Gasparri, C.; Infantino, V.; Peroni, G.; Rondanelli, M. The effect of Berberine on weight loss in order to prevent obesity: A systematic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yin, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, M. Berberine improves insulin sensitivity by inhibiting fat store and adjusting adipokines profile in human preadipocytes and metabolic syndrome patients. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 363845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.C.; Deb-Basu, D.; Orban, M.W.; Gotlib, J.R.; Natkunam, Y.; O’Neill, R.; Padua, R.A.; Xu, L.; Taketa, D.; Shirer, A.E.; et al. Nanofluidic proteomic assay for serial analysis of oncoprotein activation in clinical specimens. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Wakefield, L.M.; Goldstein, D.J. Capillary nano-immunoassays: Advancing quantitative proteomics analysis, biomarker assessment, and molecular diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacovides, D.C.; Johnson, A.B.; Wang, N.; Boddapati, S.; Korkola, J.; Gray, J.W. Identification and quantification of AKT isoforms and phosphoforms in breast cancer using a novel nanofluidic immunoassay. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2013, 12, 3210–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urasaki, Y.; Fiscus, R.R.; Le, T.T. Molecular classification of fatty liver by high-throughput profiling of protein post-translational modifications. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urasaki, Y.; Fiscus, R.R.; Le, T.T. Detection of the Cell Cycle-Regulated Negative Feedback Phosphorylation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Breast Carcinoma using Nanofluidic Proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johlfs, M.G.; Gorjala, P.; Urasaki, Y.; Le, T.T.; Fiscus, R.R. Capillary Isoelectric Focusing Immunoassay for Fat Cell Differentiation Proteomics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urasaki, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.X.; Le, T.T. Quantitative Assessment of Liver Steatosis and Affected Pathways with Molecular Imaging and Proteomic Profiling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, Y.; Le, T.T. Differentiation of Essential Oils Using Nanofluidic Protein Post-Translational Modification Profiling. Molecules 2019, 24, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, Y.; Beaumont, C.; Workman, M.; Talbot, J.N.; Hill, D.K.; Le, T.T. Potency Assessment of CBD Oils by Their Effects on Cell Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, Y.; Beaumont, C.; Talbot, J.N.; Hill, D.K.; Le, T.T. Akt3 Regulates the Tissue-Specific Response to Copaiba Essential Oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.A.; Bhamidipati, A.; Bi, X.; Deb-Basu, D.; Cahill, L.; Ferrante, J.; Gentalen, E.; Glazer, M.; Gossett, J.; Hacker, K.; et al. Isoelectric focusing technology quantifies protein signaling in 25 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16153–16158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Gao, M.; Lu, Y.; Liang, J.; Lorenzi, P.L.; Bai, S.; Hawke, D.H.; Li, J.; Dogruluk, T.; Scott, K.L.; et al. Coordinate phosphorylation of multiple residues on single AKT1 and AKT2 molecules. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall-O′Dea, M.; Pierce, A.; Pellicano, F.; Williamson, A.J.; Scott, M.T.; Walker, M.J.; Holyoake, T.L.; Whetton, A.D. Antibody-based detection of protein phosphorylation status to track the efficacy of novel therapies using nanogram protein quantities from stem cells and cell lines. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Molecular regulation of adipogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristancho, A.G.; Lazar, M.A. Forming functional fat: A growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yuan, H.D.; Kim, D.Y.; Quan, H.Y.; Chung, S.H. Cinnamaldehyde prevents adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis via regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3666–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Le, T.T.; Chen, C.; Cheng, J.X.; Kim, K.H. Curcumin inhibits adipocyte differentiation through modulation of mitotic clonal expansion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Deng, R.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L. Berberine Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation via Decreasing CREB Transcriptional Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrzewa, T.; Przychodzen, P.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M.; Kuban-Jankowska, A. Curcumin and Cinnamaldehyde as PTP1B Inhibitors With Antidiabetic and Anticancer Potential. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, B.; Beevers, C.S.; Odaka, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, T.; et al. Curcumin inhibits protein phosphatases 2A and 5, leading to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and death in tumor cells. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, T.T.; Matsunaga, K.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; et al. Berberine is an insulin secretagogue targeting the KCNH6 potassium channel. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Du, J. Phytonutrients: Sources, bioavailability, interaction with gut microbiota, and their impacts on human health. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 960309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rayess, Y.E.; Rizk, A.A.; Sadaka, C.; Zgheib, R.; Zam, W.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Neffe-Skocinska, K.; Zielinska, D.; et al. Turmeric and Its Major Compound Curcumin on Health: Bioactive Effects and Safety Profiles for Food, Pharmaceutical, Biotechnological and Medicinal Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 01021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Miao, Y.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lin, X.; Meng, L.K.; Tang, X. Bioavailability study of berberine and the enhancing effects of TPGS on intestinal absorption in rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Zheng, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Long, X.Y. Research progress on berberine with a special focus on its oral bioavailability. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Recent developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and metabolism of curcumin: The golden pigment from golden spice. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Chen, J.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; Chu, X. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cinnamaldehyde Microemulsion-Mucus interaction. J. Food Biochem. 2022, e14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.J.; Edwards, D.; Hamernig, I.; Jian, L.; James, A.P.; Johnson, S.K.; Tapsell, L.C. Vegetables containing phytochemicals with potential anti-obesity properties: A review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.N.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppeck II, J.E.; Gauss, C.-M.; Chamberlin, A.R. Inhibition of the Ser-Thr phosphatases PP1 and PP2A by naturally occurring toxins. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.S.; Liang, L.F.; Guo, Y.W. Natural products possessing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitory activity found in the last decades. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1217–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urasaki, Y.; Le, T.T. A Composition of Phytonutrients for Glycemic and Weight Management. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183784
Urasaki Y, Le TT. A Composition of Phytonutrients for Glycemic and Weight Management. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183784
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrasaki, Yasuyo, and Thuc T. Le. 2022. "A Composition of Phytonutrients for Glycemic and Weight Management" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183784
APA StyleUrasaki, Y., & Le, T. T. (2022). A Composition of Phytonutrients for Glycemic and Weight Management. Nutrients, 14(18), 3784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183784





