Effect of Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 on the Improvement of Bowel Movement in Loperamide-Treated SD Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
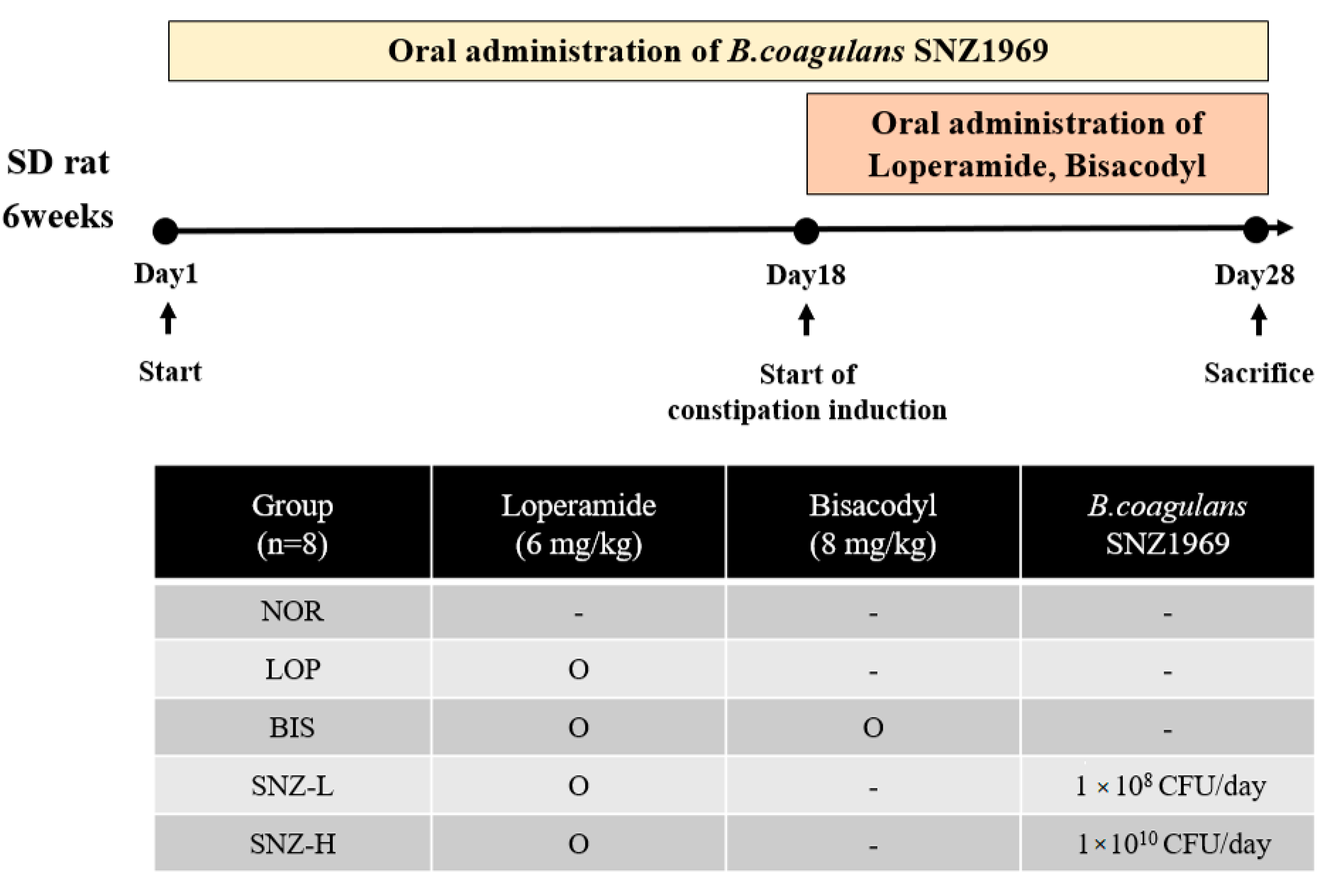
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Measurements of Body Weight, Food Intake, and Dietary Efficiency Ratio
2.3. Collection of Samples
2.4. Measurement of Fecal Pellet Weight and Water Content
2.5. Measurement of Gastrointestinal Transit Time
2.6. Measurement of Intestinal Motility
2.7. Measurement of Mucus Secretion in the Colon
2.8. Gastrointestinal Hormones
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight, Dietary Intake, and Food Efficiency Ratio (FER)
3.2. Various Organ Weights of Experimental Groups
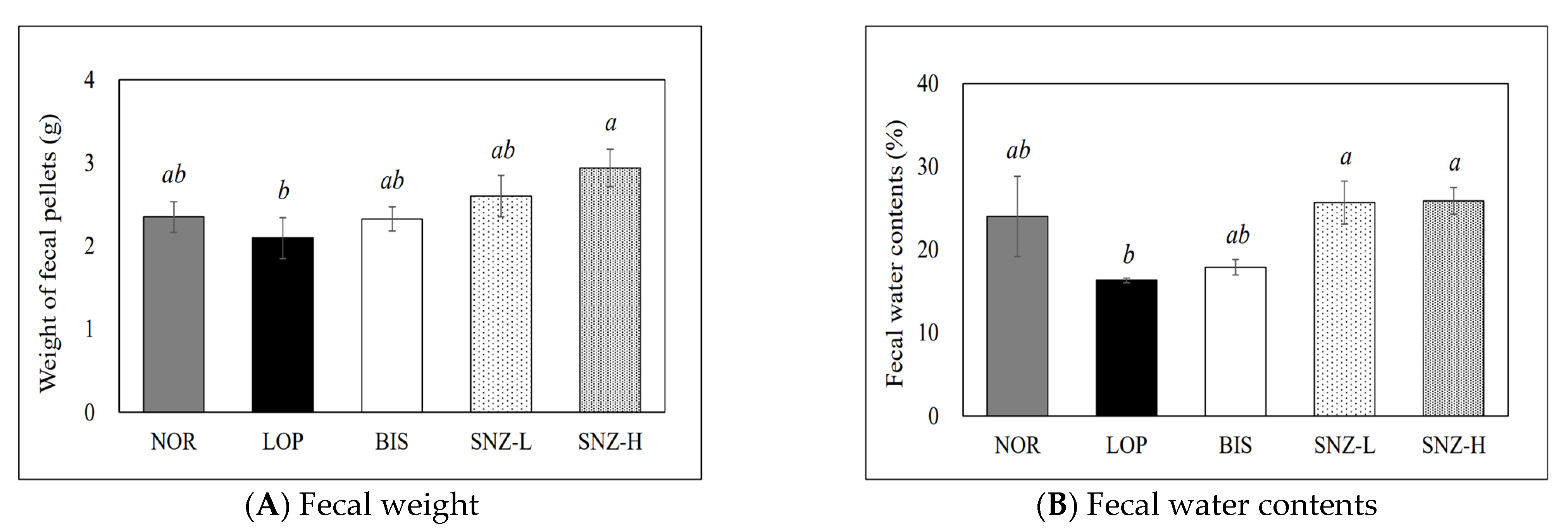
3.3. Fecal Pellet Weight and Fecal Water Content
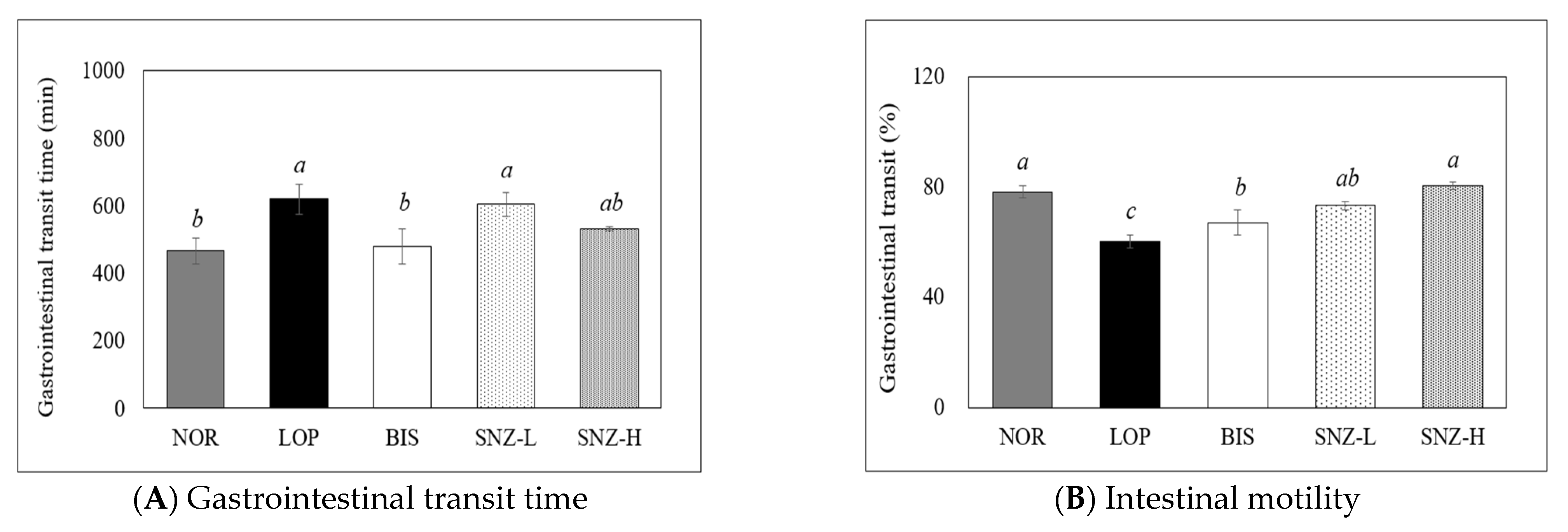
3.4. Gastrointestinal Transit Time and Intestinal Motility
3.4.1. Gastrointestinal Transit Time
3.4.2. Intestinal Motility
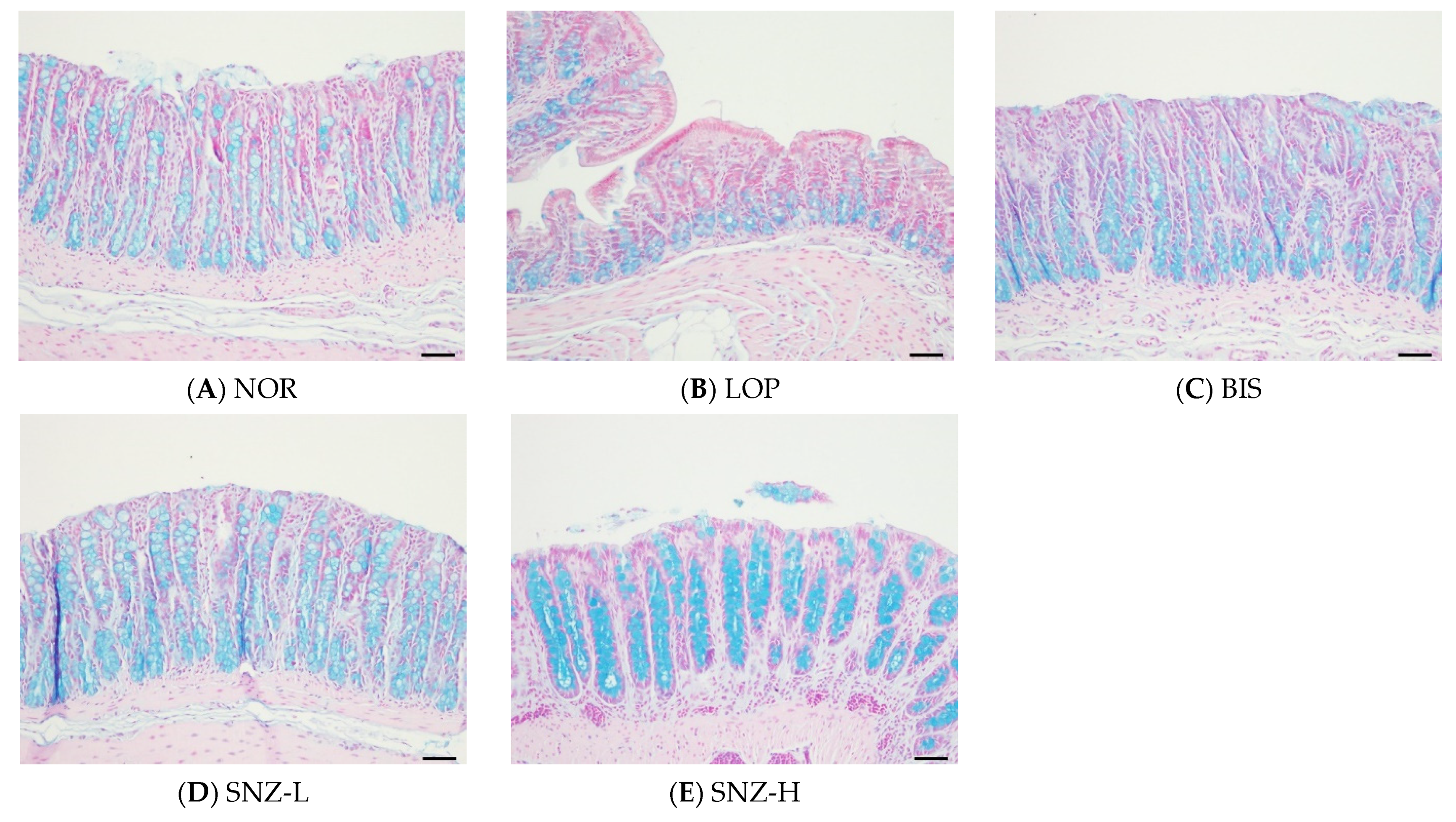
3.5. Secretion of Mucus in the Large Intestine
3.5.1. Histological Analysis
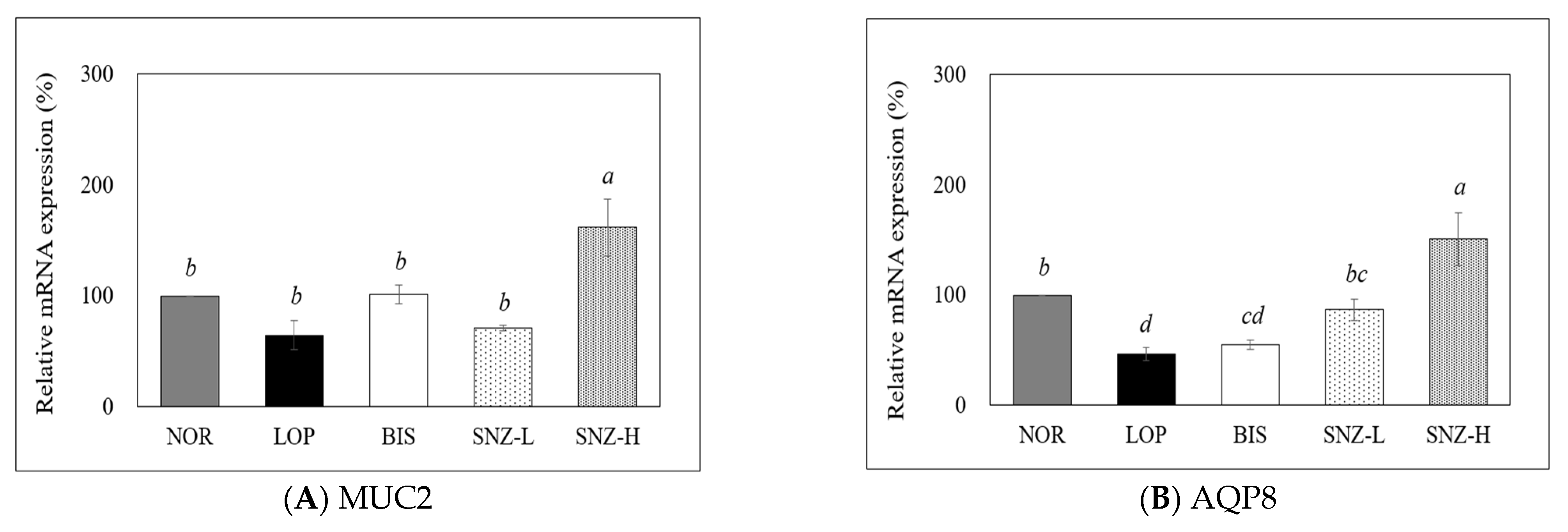
3.5.2. mRNA Expression of Mucin 2 and Aquaporin 8
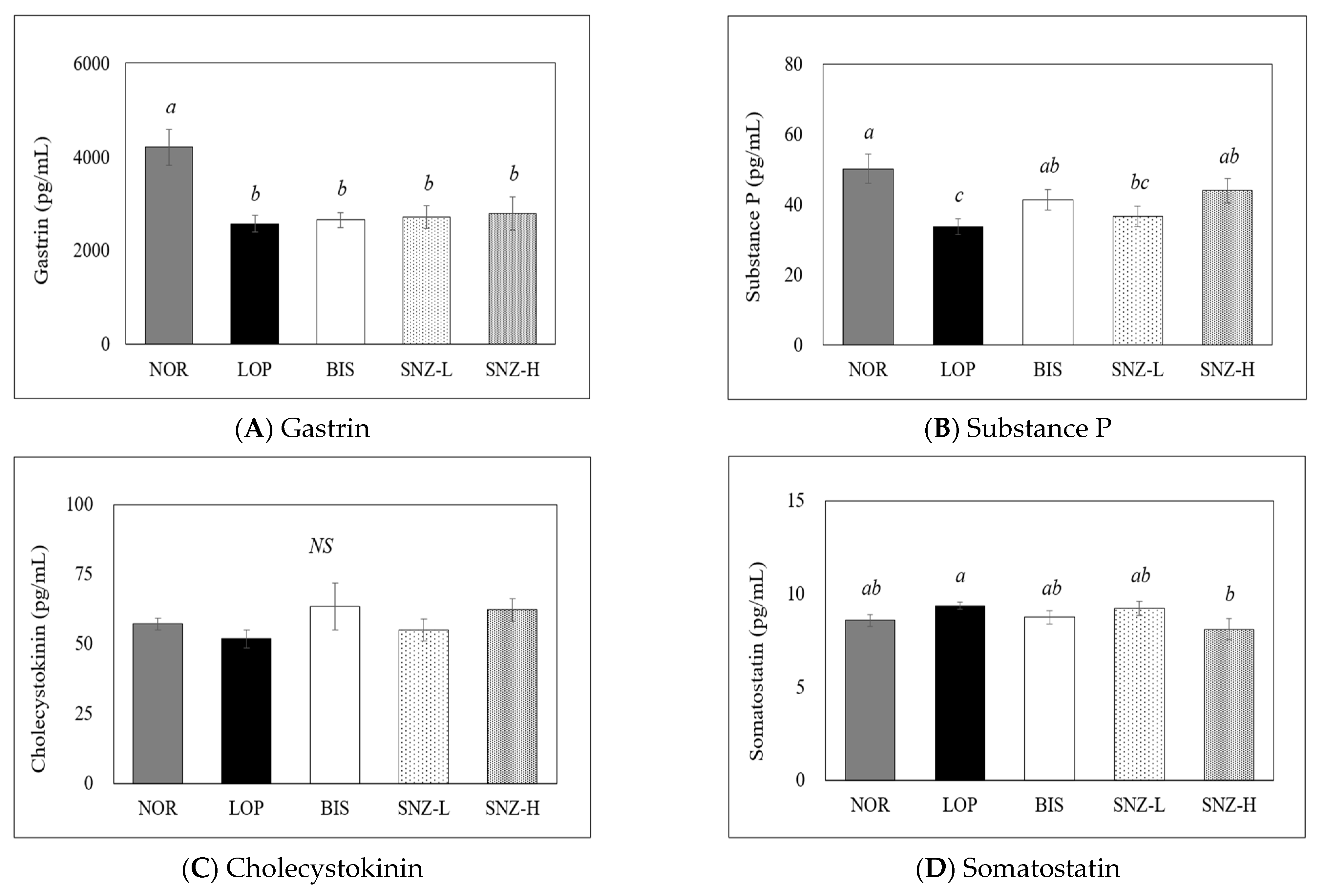
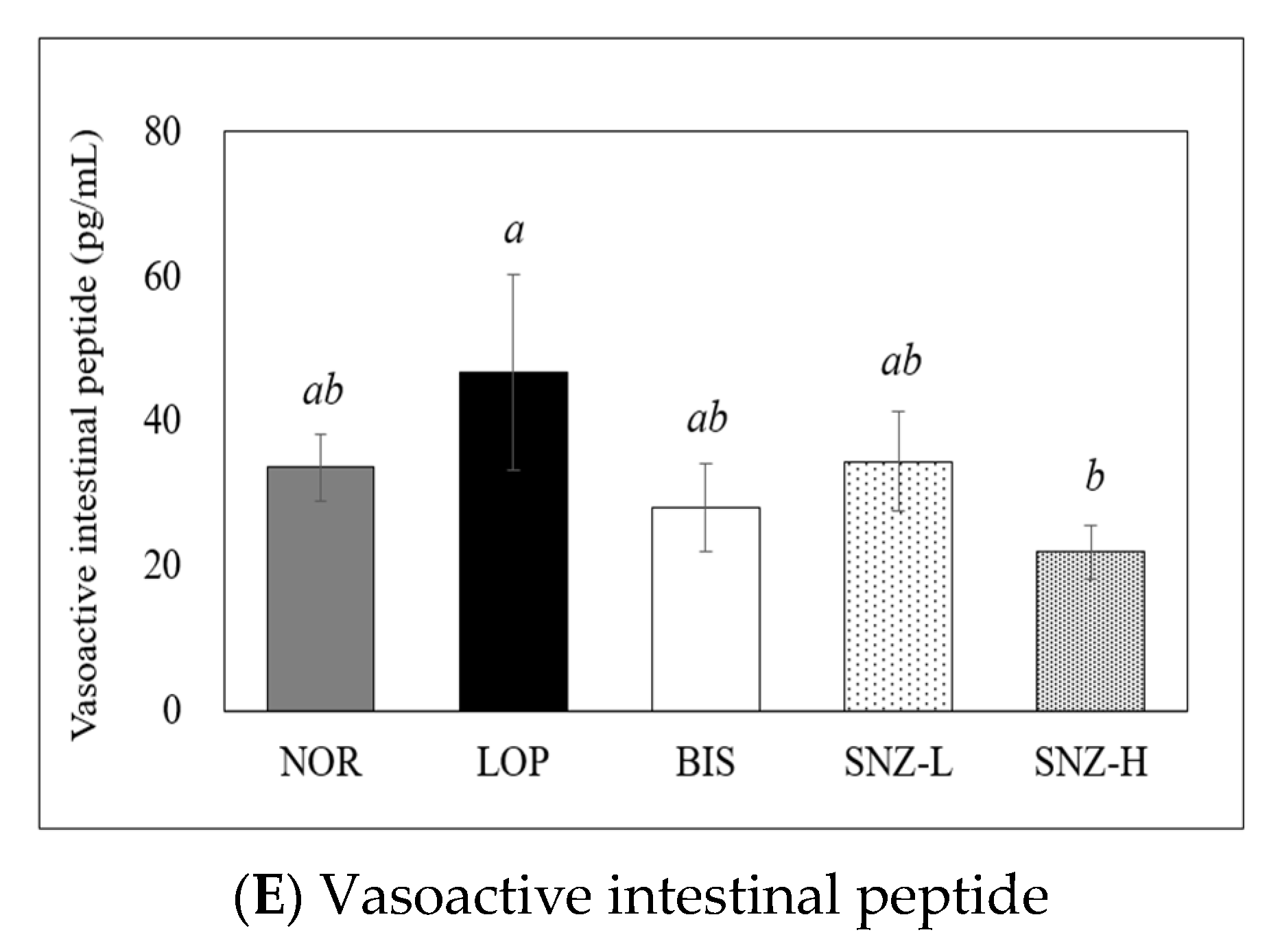
3.6. Measurement of Gastrointestinal Hormones
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aichbichler, B.W.; Wenzl, H.H.; Ana, C.A.S.; Porter, J.L.; Schiller, L.R.; Fordtran, J.S. A comparison of stool characteristics from normal and constipated people. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembo, A.; Camilleri, M. Chronic constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, B.L.; Christopher, S.A. Potential risk factors for constipation in the community. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2795–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheskin, L.J.; Kamal, N.; Crowell, M.D.; Schuster, M.M.; Whitehead, W.E. Mechanisms of constipation in older persons and effects of fiber compared with placebo. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.W. Chronic constipation: Current treatment options. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 22B–28B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, A.; Cavazzoni, V. Occurrence of selected bacterial groups in the feces of piglets fed with Bacillus coagulans as probiotic. J. Basic. Microbiol. 1999, 39, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Wilson, G. Probiotics genomics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuray, G.; Erginkaya, Z. Potential Use of Bacillus coagulans in the Food Industry. Foods 2018, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus As Potential Probiotics: Status, Concerns, and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.V.; Soman, J.L. Bacillus Coagulans Strain SNZ 1969 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene, Partial Sequence. 2013. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/KC146407 (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on The Maintenance of the List of QPS Biological Agents Intentionally Added to Food and Feed (2013 update). EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3449. [Google Scholar]
- Nithya, V.; Halami, P. Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics of Bacillus species isolated from different food sources. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetti, E.; Orrù, L.; Capozzi, V.; Martina, A.; Lamontanara, A.; Keller, D.; Cash, H.; Felis, G.E.; Cattivelli, L.; Torriani, S.; et al. Integrate genome-based assessment of safety for probiotic strains: Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 as a case study. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4595–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewska, A.; Szajewska, H. Systematic review of randomized controlled trials: Probiotics for functional constipation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haldar, L.; Gandhi, D.N. Effect of oral administration of Bacillus coagulans B37 and Bacillus pumilus B9 strains on fecal coliforms, Lactobacillus and Bacillus spp. in rat animal model. Vet. World 2016, 9, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.Y.; Hung, A.T.Y.; Lu, J.J. Effect of supplement with different level of Bacillus coagulans as probiotics on growth performance and intestinal microflora population of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazkour, S.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Basiri, S. The effects of supplementation of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus coagulans spores on the intestinal microflora and growth performance in rat. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Park, M.Y.; Brooks, I.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, B.; Kim, J.W.; Kwon, O. Spore-forming Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 improved intestinal motility and constipation perception mediated by microbial alterations in healthy adults with mild intermittent constipation: A randomized controlled trial. Food. Res. Int. 2021, 146, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, K.; Meguro, S.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I.; Otsuji, K.; Kawai, S.; Ito, S.; Iino, H. Effect of spore-bearing lactic acid-forming bacteria (Bacillus coagulans SANK 70258) administration on the intestinal environment, defecation frequency, fecal characteristics and dermal characteristics in humans and rats. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2002, 14, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamida, K.; Nishimura, M.; Miwa, K.; Nishihira, J. Effects of dietary fiber with Bacillus coagulans lilac-01 on bowel movement and fecal properties of healthy volunteers with a tendency for constipation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Probiotic characteristics of Bacillus coagulans and associated implications for human health and diseases. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, W.K.; Ha, A.W. Effects of Phytochemicals on Blood Pressure and Neuroprotection Mediated Via Brain Renin-Angiotensin System. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Tao, F.; Tang, H.; Xu, P. Genome sequence of the thermophile Bacillus coagulans Hammer, the type strain of the species. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6294–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Endres, J.R.; Clewell, A.; Jade, K.A.; Farber, T.; Hauswirth, J.; Schauss, A.G. Safety assessment of a proprietary preparation of a novel Probiotic, Bacillus coagulans, as a food ingredient. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, J.R.; Qureshi, I.; Farber, T.; Hauswirth, J.; Hirka, G.; Pasics, I.; Schauss, A.G. One-year chronic oral toxicity with combined reproduction toxicity study of a novel probiotic, Bacillus coagulans, as a food ingredient. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohji, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Shimizu, M. Pharmacological studies of loperamide, an anti-diarrheal agent. II. Effects on peristalsis of the small intestine and colon in guinea pigs. Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1978, 74, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inatomi, T.; Honma, M. Effects of probiotics on loperamide-induced constipation in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, C.; Gupta, A.K.; Saroj, D.B.; Biyani, A.; Bagkar, P.; Kulkarni, J.; Dixit, Y. Impact of a Gastrointestinal Stable Probiotic Supplement Bacillus coagulans LBSC on Human Gut Microbiome Modulation. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 18, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Higgs, N.B.; Turnberg, L.A. Loperamide has antisecretory activity in the human jejunum in vivo. Gut 1984, 25, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimotoyodome, A.; Meguro, S.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I.; Sakata, T. Decreased colonic mucus in rats with loperamide-induced constipation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2000, 126, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Yin, H.; Wu, D.; Su, Q. Naringenin induces laxative effects by upregulating the expression levels of c-Kit and SCF, as well as those of aquaporin 3 in mice with loperamide-induced constipation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Sarosiek, I.; Wallner, G.; Edlavitch, S.A.; Sarosiek, J. Stimulation of mucin, mucus, and viscosity during lubiprostone in patients with chronic constipation may potentially lead to increase of lubrication. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2014, 5, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, B.G.; Srinivasan, S. Enteric nervous system in the small intestine: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, J.W.; Kang, M.J.; Choi, H.J.; Bae, S.J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, S.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Laxative effect of Spicatoside A by cholinergic regulation of enteric nerve in loperamide-induced constipation: ICR Mice Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhi, A. The potential of quercetin to protect against loperamide-induced constipation in rats. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3297–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hu, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, D.; Gao, M.; Xia, J.; Miao, M.; Shi, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Laxative Effect and Mechanism of Tiantian Capsule on loperamide-induced constipation in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Yin, B.; Fang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium adolescentis exerts strain-specific effects on constipation induced by loperamide in BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riezzo, G.; Chimienti, G.; Clemente, C.; D’Attoma, B.; Orlando, A.; Mammone Rinaldi, C.; Russo, F. Colonic transit time and gut peptides in adult patients with slow and normal colonic transit constipation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3178263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene (1) | Primer | Sequence (2) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward primer | 5’-AGTGCCAGCCTCGTCTCATA-3’ |
| Reverse primer | 5’-ACCAGCTTCCCATTCTCAGC-3’ | |
| MUC2 | Forward primer | 5’-GGTGGCCTTCAAATCAGGTG-3’ |
| Reverse primer | 5’-AGGGTTTGAAGATGGAGAAGCTC-3’ | |
| AQP8 | Forward primer | 5’-CAGATATGTCTGGGGAGCAG-3’ |
| Reverse primer | 5’-GCCTAATGAGCAGTCCCACA-3’ |
| Group | Initial Weight (g) | Final Weight (g) | Weight Gain (g/28 days) | Diet Intake (g/28 days) | FER (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOR (2) | 195.6 ± 5.9 NS,(3) | 354.2 ± 5.0 (4),a,(5) | 158.6 ± 7.6 NS | 469.8 ± 11.3 NS | 0.34 ± 0.01 NS |
| LOP | 197.8 ± 4.9 | 342.8 ± 6.7 a,b | 145.1 ± 6.9 | 453.5 ± 13.4 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| BIS | 192.4 ± 11.4 | 329.1 ± 4.5 b | 136.7 ± 11.5 | 448.2 ± 10.1 | 0.30 ± 0.02 |
| SNZ-L | 198.4 ± 4.0 | 347.3 ± 5.0 a | 148.9 ± 5.5 | 465.3 ± 9.4 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| SNZ-H | 202.0 ± 3.9 | 348.7 ± 3.9 a | 146.7 ± 5.1 | 473.9 ± 11.0 | 0.31 ± 0.00 |
| Group | Liver | Kidney | Epididymal Fat Pad | Spleen | Thymus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOR (1) | 10.55 ± 0.33 (2),a,(3) | 2.66 ± 0.08 NS,(4) | 5.27 ± 0.287 a | 0.72 ± 0.02 NS | 1.61 ± 0.09 NS |
| LOP | 9.90 ± 0.27 a,b | 2.57 ± 0.08 | 5.29 ± 0.46 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 1.67 ± 0.10 |
| BIS | 9.28 ± 0.32 b | 2.51 ± 0.06 | 3.93 ± 0.26 b | 0.70 ± 0.03 | 1.59 ± 0.06 |
| SNZ-L | 9.33 ± 0.24 b | 2.58 ± 0.07 | 4.65 ± 0.29 a,b | 0.70 ± 0.04 | 1.70 ± 0.09 |
| SNZ-H | 9.31 ± 0.37 b | 2.45 ± 0.06 | 4.75 ± 0.51 a,b | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 1.76 ± 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.-M.; Ha, A.-W.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, W.-K. Effect of Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 on the Improvement of Bowel Movement in Loperamide-Treated SD Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183710
Jung S-M, Ha A-W, Choi S-J, Kim S-Y, Kim W-K. Effect of Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 on the Improvement of Bowel Movement in Loperamide-Treated SD Rats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183710
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Soo-Min, Ae-Wha Ha, Su-Jin Choi, Se-Young Kim, and Woo-Kyoung Kim. 2022. "Effect of Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 on the Improvement of Bowel Movement in Loperamide-Treated SD Rats" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183710
APA StyleJung, S.-M., Ha, A.-W., Choi, S.-J., Kim, S.-Y., & Kim, W.-K. (2022). Effect of Bacillus coagulans SNZ 1969 on the Improvement of Bowel Movement in Loperamide-Treated SD Rats. Nutrients, 14(18), 3710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183710






