Breastfeeding Duration and High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study of Seven Provinces in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Measurement
2.3. BP Measurement and Outcome Variables
2.4. Assessment of Demographic Variables and Breastfeeding Duration
2.5. Measurement and Definition of Lifestyle Behaviors
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Association between Breastfeeding Duration and Blood Pressure
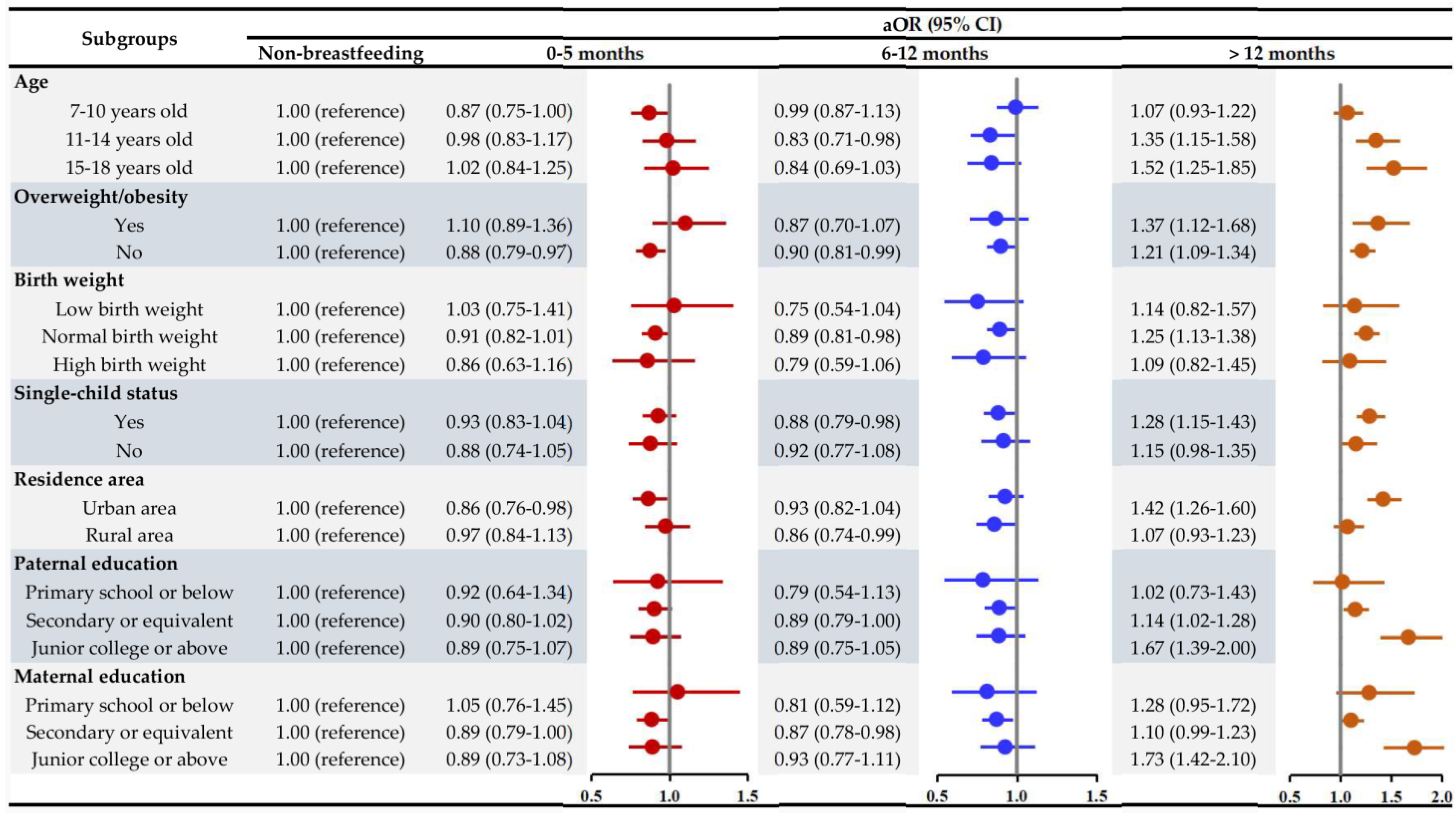
3.3. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zha, M.; Zhu, Y.; Rahimi, K.; Rudan, I. Global Prevalence of Hypertension in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Yi, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, M.; Yang, Q.; Xia, W.; Ye, Z.; Song, P. Trends in Prevalence of Hypertension and Hypertension Phenotypes Among Chinese Children and Adolescents Over Two Decades (1991-2015). Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 627741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B. Prevalence of Target Organ Damage in Chinese Hypertensive Children and Adolescents. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lande, M.; Carson, N.; Roy, J.; Meagher, C. Effects of childhood primary hypertension on carotid intima media thickness: A matched controlled study. Hypertension 2006, 48, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikonen, M.; Nuotio, J.; Magnussen, C.; Viikari, J.; Taittonen, L.; Laitinen, T.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Jokinen, E.; Jula, A.; Cheung, M.; et al. Repeated Blood Pressure Measurements in Childhood in Prediction of Hypertension in Adulthood. Hypertension 2016, 67, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobti, J.; Mathur, G.; Gupta, A.; WHO. WHO’s proposed global strategy for infant and young child feeding: A viewpoint. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 2002, 100, 502–504, 506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, M.; Asayama, K.; Staessen, J.; Ohkubo, T.; Hayashi, K.; Tatsuta, N.; Kurokawa, N.; Satoh, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Hirose, T.; et al. Breastfeeding leads to lower blood pressure in 7-year-old Japanese children: Tohoku Study of Child Development. Hypertens Res. 2013, 36, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miliku, K.; Moraes, T.; Becker, A.; Mandhane, P.; Sears, M.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Azad, M.B. Breastfeeding in the First Days of Life Is Associated with Lower Blood Pressure at 3 Years of Age. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Ness, A.; Gunnell, D.; Emmett, P.; Davey Smith, G. Does breast-feeding in infancy lower blood pressure in childhood? The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Circulation 2004, 109, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluymen, L.; Wijga, A.; Gehring, U.; Koppelman, G.; Smit, H.; van Rossem, L. Breastfeeding and cardiometabolic markers at age 12: A population-based birth cohort study. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, L.; Lessa, A. Influence of breastfeeding in the first months of life on blood pressure levels of preschool children. J. Pediatr. (Rio J.) 2016, 92, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.; Kramer, M.; Patel, R.; Rifas-Shiman, S.; Thompson, J.; Yang, S.; Vilchuck, K.; Bogdanovich, N.; Hameza, M.; Tilling, K.; et al. Effects of Promoting Long-term, Exclusive Breastfeeding on Adolescent Adiposity, Blood Pressure, and Growth Trajectories: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, e170698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, B.; Loret de Mola, C.; Victora, C. Long-term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.; França, G.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fall, C.; Borja, J.; Osmond, C.; Richter, L.; Bhargava, S.; Martorell, R.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Infant-feeding patterns and cardiovascular risk factors in young adulthood: Data from five cohorts in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, M.; Leung, G.; Schooling, C. Breastfeeding and adolescent blood pressure: Evidence from Hong Kong’s "Children of 1997" Birth Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Mei, W.; Zhang, J. Association of breastfeeding duration, birth weight, and current weight status with the risk of elevated blood pressure in preschoolers. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xiao, L.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Childhood Hypertension in Urban-Rural Areas of China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, 2374231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Pan, D.; et al. A national school-based health lifestyles interventions among Chinese children and adolescents against obesity: Rationale, design and methodology of a randomized controlled trial in China. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Dong, B.; Dong, Y.; Ma, J.; Arnold, L. The Association between Breastfeeding Duration and Lipid Profile among Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Ma, T.; Ma, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Association between Fruit Consumption and Lipid Profile among Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Study in China. Nutrients 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. Association between Vegetable Consumption and Blood Pressure, Stratified by BMI, among Chinese Adolescents Aged 13-17 Years: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, L.; Sun, F.; Ma, Y.; Jing, J.; Chen, Y.J. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.; Wong, B.; Lo, W.; Mak, K.; Thomas, G.; Lam, T. Neighbourhood food environment and dietary intakes in adolescents: Sex and perceived family affluence as moderators. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010, 5, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, T.; Knowles, S.; Farouk, M. Global Provisioning of Red Meat for Flexitarian Diets. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary Guidelines for Chinese School-Age Children (2016); People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the international physical activity questionnaire short form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djalalinia, S.; Qorbani, M.; Heshmat, R.; Motlagh, M.; Ardalan, G.; Bazyar, N.; Taheri, M.; Asayesh, H.; Kelishadi, R. Association of Breast Feeding and Birth Weight with Anthropometric Measures and Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: The CASPIAN-IV Study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2015, 56, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Rossem, L.; Smit, H.; Armand, M.; Bernard, J.; Bisgaard, H.; Bønnelykke, K.; Bruun, S.; Heude, B.; Husby, S.; Kyhl, H.B.; et al. Breast milk n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and blood pressure: An individual participant meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, J.; Willatts, P.; Agostoni, C.; Bissenden, J.; Casaer, P.; Boehm, G. Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in infant formula and blood pressure in later childhood: Follow up of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003, 326, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azad, M.; Konya, T.; Persaud, R.; Guttman, D.; Chari, R.; Field, C.; Sears, M.R.; Mandhane, P.; Turvey, S.; Subbarao, P.; et al. Impact of maternal intrapartum antibiotics, method of birth and breastfeeding on gut microbiota during the first year of life: A prospective cohort study. BJOG 2016, 123, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komaroff, A. The Microbiome and Risk for Atherosclerosis. JAMA 2018, 319, 2381–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czosnykowska-Łukacka, M.; Królak-Olejnik, B.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. Breast Milk Macronutrient Components in Prolonged Lactation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fall, C.; Barker, D.; Osmond, C.; Winter, P.; Clark, P.; Hales, C. Relation of infant feeding to adult serum cholesterol concentration and death from ischaemic heart disease. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1992, 304, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO; UNICEF. Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huo, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Gong, W.; Wang, O. Prevalence of Complementary Feeding Indicators and Associated Factors Among 6- to 23-Month Breastfed Infants and Young Children in Poor Rural Areas of China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 691894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lai, J.; Yu, D.; Chang, S.; Pang, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Bi, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Exclusive Breastfeeding Rate and Complementary Feeding Indicators in China: A National Representative Survey in 2013. Nutrients 2018, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruun, S.; van Rossem, L.; Lauritzen, L.; Husby, S.; Neergaard Jacobsen, L.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Sandberg, M.B.; Stark, K.D.; Sørensen, J.; Zachariassen, G. Content of n-3 LC-PUFA in Breast Milk Four Months Postpartum is Associated with Infancy Blood Pressure in Boys and Infancy Blood Lipid Profile in Girls. Nutrients 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siziba, L.; Brenner, H.; Amitay, E.; Koenig, W.; Rothenbacher, D.; Genuneit, J. Potential sex differences in human milk leptin and their association with asthma and wheeze phenotypes: Results of the Ulm Birth Cohorts. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, K.; Barrett-Connor, E. The association between blood pressure, age, and dietary sodium and potassium: A population study. Circulation 1988, 77, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Steffen, L.M.; Ma, C.; Liang, Y.; Xi, B. Definition of pediatric hypertension: Are blood pressure measurements on three separate occasions necessary? Hypertens Res. 2017, 40, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Population | Non-Breastfeeding | 0–5 Months | 6–12 Months | >12 Months | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 57,201 | 7086 (12.39%) | 21,953 (38.38%) | 15,273 (26.70%) | 12,889 (22.53%) | |
| Baseline demographic factors | ||||||
| Age, year | 11.30 ± 3.12 | 10.81 ± 3.02 | 11.81 ± 3.25 | 10.88 ± 3.00 | 11.22 ± 2.95 | <0.001 |
| Boys, n (%) | 29,491 (51.56%) | 3652 (51.54%) | 11,735 (53.46%) | 7585 (49.66%) | 6519 (50.58%) | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 18.79 ± 3.76 | 18.66 ± 3.86 | 18.87 ± 3.69 | 18.49 ± 3.59 | 19.08 ± 3.98 | <0.001 |
| Overweight/obesity, n (%) | 5766 (10.08%) | 784 (11.06%) | 1998 (9.10%) | 1369 (8.96%) | 1615 (12.53%) | <0.001 |
| Birth weight, g | 3309.91 ± 509.47 | 3258.62 ± 532.07 | 3261.23 ± 522.58 | 3316.91 ± 493.18 | 3378.73 ± 493.64 | <0.001 |
| Birth weight group, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| Low birth weight | 12,672 (22.15%) | 724 (10.22%) | 9956 (45.35%) | 1177 (7.71%) | 815 (6.32%) | |
| Normal birth weight | 39,961 (69.86%) | 5772 (81.46%) | 10,874 (49.53%) | 12,631 (82.70%) | 10,684 (82.89%) | |
| High birth weight | 4568 (7.99%) | 590 (8.33%) | 1123 (5.12%) | 1465 (9.59%) | 1390 (10.78%) | |
| Single-child, n (%) | 40,633 (71.04%) | 5085 (71.76%) | 17,758 (80.89%) | 10,285 (67.34%) | 7505 (58.23%) | <0.001 |
| Urban area, n (%) | 37,739 (65.98%) | 4950 (69.86%) | 16,226 (73.91%) | 10,078 (65.99%) | 6485 (50.31%) | <0.001 |
| Parental or family factors | ||||||
| Maternal age at delivery, year | 27.47 ± 71.14 | 27.36 ± 5.36 | 27.49 ± 67.01 | 27.01 ± 54.82 | 28.06 ± 103.01 | 0.702 |
| Paternal educational attainment, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| Primary school or below | 3539 (6.19%) | 399 (5.63%) | 913 (4.16%) | 912 (5.97%) | 1315 (10.20%) | |
| Secondary or equivalent | 40,716 (71.18%) | 4331 (61.12%) | 17,281 (78.72%) | 9694 (63.47%) | 9410 (73.01%) | |
| Junior college or above | 12,946 (22.63%) | 2356 (33.25%) | 3759 (17.12%) | 4667 (30.56%) | 2164 (16.79%) | |
| Maternal educational attainment, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| Primary school or below | 4829 (8.44%) | 558 (7.87%) | 1247 (5.68%) | 1312 (8.59%) | 1712 (13.28%) | |
| Secondary or equivalent | 40,579 (70.94%) | 4323 (61.01%) | 17,251 (78.58%) | 9721 (63.65%) | 9284 (72.03%) | |
| Junior college or above | 11,793 (20.62%) | 2205 (31.12%) | 3455 (15.74%) | 4240 (27.76%) | 1893 (14.69%) | |
| Family history of diseases, n (%) | ||||||
| Hypertension | 3234 (5.65%) | 531 (7.49%) | 886 (4.04%) | 977 (6.40%) | 840 (6.52%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 1092 (1.91%) | 211 (2.98%) | 305 (1.39%) | 299 (1.96%) | 277 (2.15%) | <0.001 |
| Heart diseases | 1097 (1.92%) | 183 (2.58%) | 306 (1.39%) | 272 (1.78%) | 336 (2.61%) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | 513 (0.90%) | 77 (1.09%) | 133 (0.61%) | 156 (1.02%) | 147 (1.14%) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 4248 (7.43%) | 722 (10.19%) | 1009 (4.60%) | 1371 (8.98%) | 1146 (8.89%) | <0.001 |
| Monthly household income, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| <5000 CNY | 16,535 (28.91%) | 2160 (30.48%) | 3940 (17.95%) | 4586 (30.03%) | 5849 (45.38%) | |
| ≥5000 CNY | 8022 (14.02%) | 1211 (17.09%) | 2047 (9.32%) | 2712 (17.76%) | 2052 (15.92%) | |
| Refuse to answer | 32,644 (57.07%) | 3715 (52.43%) | 15,966 (72.73%) | 7975 (52.22%) | 4988 (38.70%) | |
| Dietary behaviors | ||||||
| Fruits of ≥1.5 servings/day, n (%) | 15,087 (26.38%) | 2109 (29.76%) | 4776 (21.76%) | 4248 (27.81%) | 3954 (30.68%) | <0.001 |
| Vegetables of ≥2 servings/day, n (%) | 23,682 (41.40%) | 3196 (45.10%) | 7637 (34.79%) | 6814 (44.61%) | 6035 (46.82%) | <0.001 |
| meat products of 2–3 servings/day, n (%) | 8078 (14.12%) | 1153 (16.27%) | 2776 (12.65%) | 2711 (17.75%) | 1438 (11.16%) | <0.001 |
| SSB of <1 serving/week | 34,298 (59.96%) | 4033 (56.92%) | 13,995 (63.75%) | 8888 (58.19%) | 7382 (57.27%) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity, hour/day | 0.40 ± 0.76 | 0.38 ± 0.73 | 0.42 ± 0.82 | 0.37 ± 0.69 | 0.42 ± 0.76 | <0.001 |
| Blood Pressure | Breastfeeding Duration | Categorical Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Breastfeeding | 0–5 Months | 6–12 Months | >12 Months | ||
| Total population | |||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 105.18 ± 12.01 | 104.07 ± 12.02 | 105.09 ± 12.07 | 103.66 ± 11.72 | 107.74 ± 11.81 |
| Unadjusted | 0.42 (0.40, 0.45) | 1 (Reference) | 1.02 (0.71, 1.34) | −0.40 (−0.74, −0.07) | 3.67 (3.32, 4.01) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.28 (0.26, 0.31) | 1 (Reference) | −0.35 (−0.97, 0.28) | −0.43 (−0.75, −0.11) | 1.97 (1.64, 2.31) |
| SBP Z-score | 0.00 ± 1.00 | −0.09 ± 1.00 | −0.01 ± 1.01 | −0.13 ± 0.98 | 0.21 ± 0.98 |
| Unadjusted | 0.04 (0.03, 0.04) | 1 (Reference) | 0.09 (0.06, 0.11) | −0.03 (−0.06, −0.01) | 0.31 (0.28, 0.33) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | −0.04 (−0.06, 0.01) | −0.04 (−0.06, −0.01) | 0.16 (0.14, 0.19) |
| DBP (mmHg) | 66.78 ± 8.70 | 66.02 ± 8.47 | 66.91 ± 8.90 | 65.70 ± 8.57 | 68.27 ± 8.41 |
| Unadjusted | 0.26 (0.24, 0.27) | 1 (Reference) | 0.89 (0.65, 1.12) | −0.32 (−0.57, −0.08) | 2.25 (2.00, 2.50) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.17 (0.15, 0.19) | 1 (Reference) | −0.38 (−0.64, −0.13) | −0.36 (−0.61, −0.12) | 1.18 (0.93, 1.43) |
| DBP Z-score | 0.00 ± 1.00 | −0.09 ± 0.97 | 0.01 ± 1.02 | −0.12 ± 0.98 | 0.17 ± 0.97 |
| Unadjusted | 0.03 (0.03, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | 0.10 (0.08, 0.13) | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | 0.26 (0.23, 0.29) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.02) | 1 (Reference) | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | 0.14 (0.11, 0.16) |
| Boys | |||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 106.66 ± 12.32 | 105.61 ± 12.27 | 106.73 ± 12.35 | 105.12 ± 12.11 | 108.89 ± 12.21 |
| Unadjusted | 0.39 (0.35, 0.42) | 1 (Reference) | 1.12 (0.66, 1.57) | −0.49 (−0.97, 0.00) | 3.28 (2.78, 3.78) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.27 (0.23, 0.30) | 1 (Reference) | −0.62 (−0.96, 0.03) | −0.56 (−1.02, −0.11) | 1.82 (1.35, 2.29) |
| SBP Z-score | 0.12 ± 1.03 | 0.04 ± 1.02 | 0.13 ± 1.03 | 0.00 ± 1.01 | 0.31 ± 1.02 |
| Unadjusted | 0.03 (0.03, 0.04) | 1 (Reference) | 0.09 (0.06, 0.13) | −0.04 (−0.08, 0.00) | 0.27 (0.23, 0.31) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | −0.05 (−0.09, 0.01) | −0.05 (−0.08, −0.01) | 0.15 (0.11, 0.19) |
| DBP (mmHg) | 67.34 ± 8.85 | 66.63 ± 8.57 | 67.57 ± 9.05 | 66.21 ± 8.71 | 68.64 ± 8.61 |
| Unadjusted | 0.23 (0.21, 0.26) | 1 (Reference) | 0.94 (0.62, 1.27) | −0.42 (−0.76, −0.07) | 2.01 (1.66, 2.37) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.16 (0.13, 0.18) | 1 (Reference) | −0.49 (−0.85, −0.13) | −0.54 (−0.88, −0.20) | 1.03 (0.67, 1.39) |
| DBP Z-score | 0.06 ± 1.02 | −0.02 ± 0.98 | 0.09 ± 1.04 | −0.07 ± 1.00 | 0.21 ± 0.99 |
| Unadjusted | 0.03 (0.02, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | 0.11 (0.07, 0.15) | −0.05 (−0.09, −0.01) | 0.23 (0.19, 0.27) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.02) | 1 (Reference) | −0.06 (−0.10, −0.02) | −0.06 (−0.10, −0.02) | 0.12 (0.08, 0.16) |
| Girls | |||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 103.61 ± 11.45 | 102.42 ± 11.52 | 103.21 ± 11.46 | 102.22 ± 11.13 | 106.55 ± 11.26 |
| Unadjusted | 0.46 (0.42, 0.49) | 1 (Reference) | 0.79 (0.35, 1.22) | −0.20 (−0.66, 0.25) | 4.13 (3.66, 4.60) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.29 (0.26, 0.33) | 1 (Reference) | −0.17 (−0.65, 0.30) | −0.24 (−0.69, 0.21) | 2.20 (1.73, 2.67) |
| SBP Z-score | −0.13 ± 0.95 | −0.23 ± 0.96 | −0.16 ± 0.95 | −0.25 ± 0.93 | 0.11 ± 0.94 |
| Unadjusted | 0.04 (0.04, 0.04) | 1 (Reference) | 0.07 (0.03, 0.10) | −0.02 (−0.05, 0.02) | 0.34 (0.30, 0.38) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | −0.01 (−0.05, 0.03) | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.02) | 0.18 (0.14, 0.22) |
| DBP (mmHg) | 66.19 ± 8.50 | 65.38 ± 8.31 | 66.15 ± 8.67 | 65.19 ± 8.40 | 67.89 ± 8.19 |
| Unadjusted | 0.28 (0.25, 0.30) | 1 (Reference) | 0.77 (0.44, 1.10) | −0.19 (−0.53, 0.15) | 2.51 (2.16, 2.86) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.17 (0.15, 0.20) | 1 (Reference) | −0.25 (−0.61, 0.12) | −0.17 (−0.51, 0.17) | 1.36 (1.00, 1.71) |
| DBP Z-score | −0.07 ± 0.98 | −0.16 ± 0.95 | −0.07 ± 1.00 | −0.18 ± 0.97 | 0.13 ± 0.94 |
| Unadjusted | 0.03 (0.03, 0.03) | 1 (Reference) | 0.09 (0.05, 0.13) | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.02) | 0.29 (0.25, 0.33) |
| Fully adjusted | 0.02 (0.02, 0.02) | 1 (Reference) | −0.03 (−0.07, 0.01) | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.02) | 0.16 (0.11, 0.20) |
| Breastfeeding Duration | Population (%) | HBP Prevalence (%) | ORs (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Fully Adjusted | |||
| Total population | 57,201 | 8709 (15.23) | ||
| Non-breastfeeding | 7086 (12.39) | 986 (13.91) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 0–5 months | 21,953 (38.38) | 3359 (15.30) | 1.12 (1.04–1.21) | 0.94 (0.82–1.07) |
| 6–12 months | 15,273 (26.70) | 1900 (12.44) | 0.88 (0.81–0.96) | 0.87 (0.76–0.99) |
| >12 months | 12,889 (22.53) | 2464 (19.12) | 1.46 (1.35–1.59) | 1.21 (1.08–1.37) |
| Boys | 29,491 | 4660 (15.80) | ||
| Non-breastfeeding | 3652 (12.38) | 525 (14.38) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 0–5 months | 11,735 (39.79) | 1889 (16.10) | 1.14 (1.03–1.27) | 1.01 (0.84–1.21) |
| 6–12 months | 7585 (25.82) | 951 (12.54) | 0.85 (0.76–0.96) | 0.84 (0.70–1.01) |
| >12 months | 6519 (22.11) | 1295 (19.87) | 1.48 (1.32–1.65) | 1.33 (1.12–1.58) |
| Girls | 27,710 | 4049 (14.61) | ||
| Non-breastfeeding | 3434 (12.39) | 461 (13.42) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| 0–5 months | 10,218 (36.87) | 1470 (14.39) | 1.08 (0.97–1.21) | 0.88 (0.73–1.06) |
| 6–12 months | 7688 (27.74) | 949 (12.34) | 0.91 (0.81–1.02) | 0.90 (0.75–1.08) |
| >12 months | 6370 (22.99) | 1169 (18.35) | 1.45 (1.29–1.63) | 1.12 (0.94–1.33) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Breastfeeding Duration and High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study of Seven Provinces in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153152
Liu J, Gao D, Li Y, Chen M, Wang X, Ma Q, Ma T, Chen L, Ma Y, Zhang Y, et al. Breastfeeding Duration and High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study of Seven Provinces in China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153152
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jieyu, Di Gao, Yanhui Li, Manman Chen, Xinxin Wang, Qi Ma, Tao Ma, Li Chen, Ying Ma, Yi Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Breastfeeding Duration and High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study of Seven Provinces in China" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153152
APA StyleLiu, J., Gao, D., Li, Y., Chen, M., Wang, X., Ma, Q., Ma, T., Chen, L., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, J., & Dong, Y. (2022). Breastfeeding Duration and High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study of Seven Provinces in China. Nutrients, 14(15), 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153152







