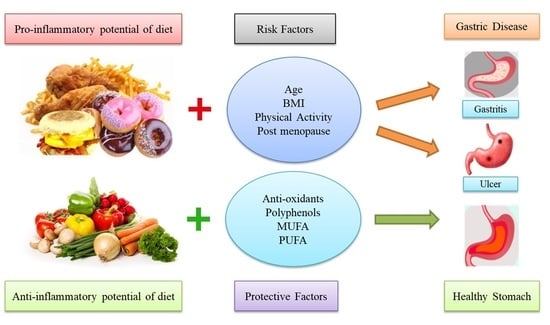
Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gastric Disease Risk: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Subjects
3.2. E-DII and Prevalent Gastric Diseases at Baseline
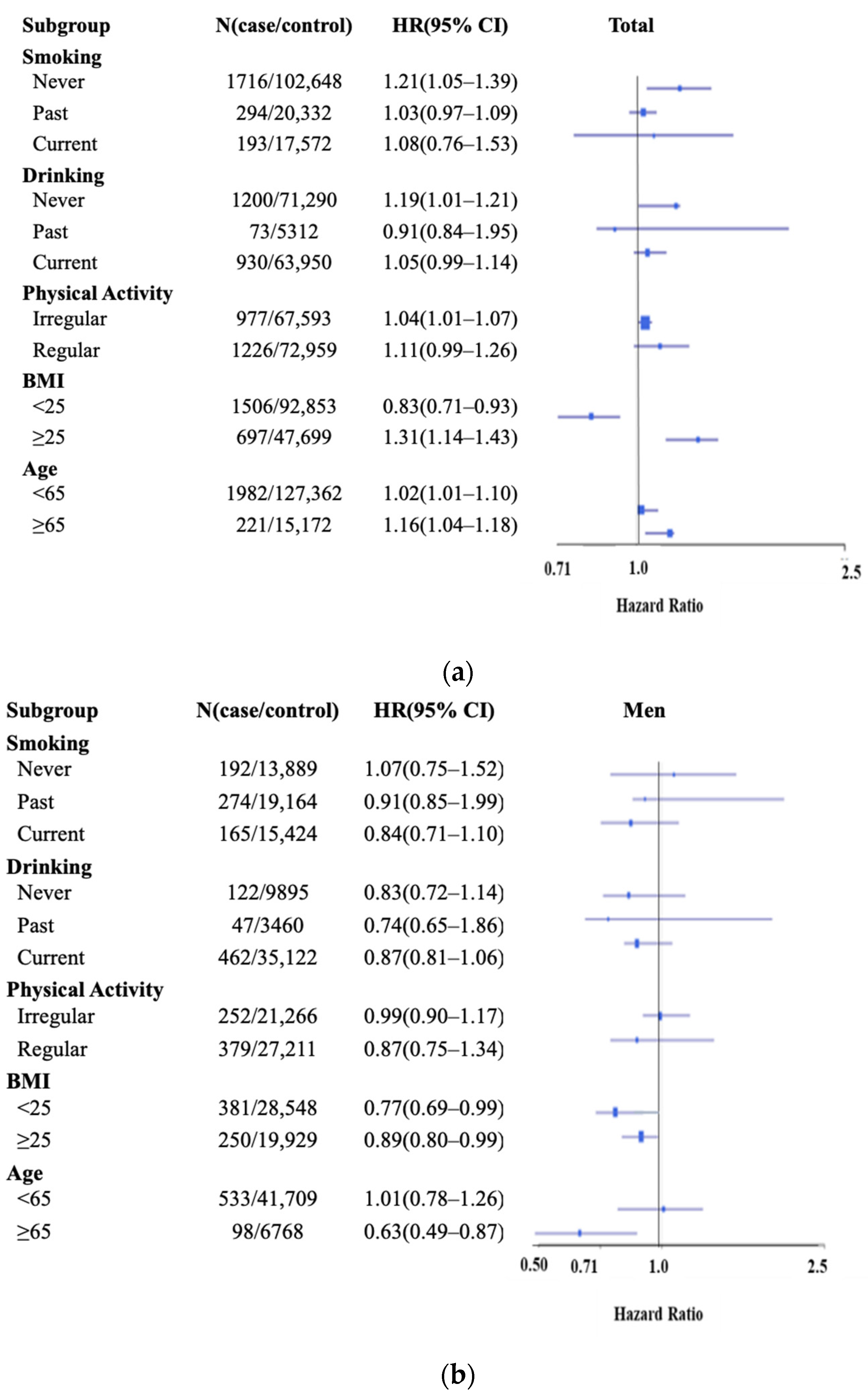
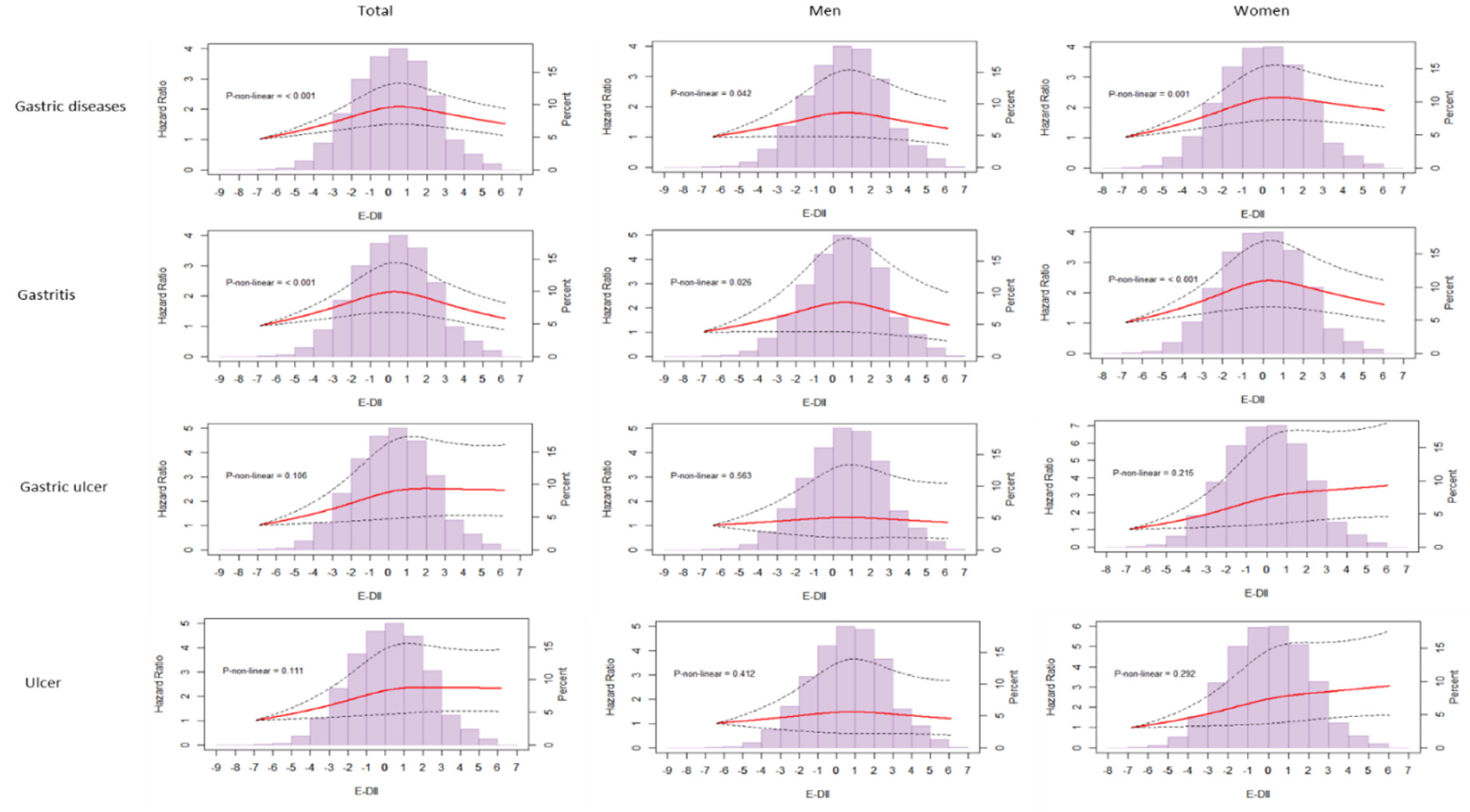
3.3. E-DII and Incident Gastric Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Cruz, M.; Gualillo, O. The physiology of inflammation—The final common pathway to disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schett, G.; Neurath, M.F. Resolution of chronic inflammatory disease: Universal and tissue-specific concepts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipponen, P.; Hyvärinen, H. Role of Helicobacter pylori in the pathogenesis of gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric cancer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 28, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipponen, P.; Maaroos, H.I. Chronic gastritis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muszyński, J.; Ziółkowski, B.; Kotarski, P.; Niegowski, A.; Górnicka, B.; Bogdańska, M.; Ehrmann-Josko, A.; Zemlak, M.; Bonikowska, B.M.; Sieminska, J. Gastritis–Facts and doubts. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2016, 11, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moss, S.F.; Blaser, M.J. Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammation and the origins of cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, V.; Shivani, A. An overview of history, pathogenesis and treatment of perforated peptic ulcer disease with evaluation of prognostic scoring in adults. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Multhoff, G.; Molls, M.; Radons, J. Chronic inflammation in cancer development. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straub, R.H.; Cutolo, M.; Pacifici, R. Evolutionary medicine and bone loss in chronic inflammatory diseases—A theory of inflammation-related osteopenia. Proc. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Flavell, R.A. Innate immune receptors: Key regulators of metabolic disease progression. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ando, T.; Goto, Y.; Maeda, O.; Watanabe, O.; Ishiguro, K.; Goto, H. Causal role of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodger, K.; Crabtree, J.E. Helicobacter pylori and gastric inflammation. Br. Med. Bull. 1998, 54, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ddine, L.C.; Ddine, C.C.; Rodrigues, C.C.R.; Kirsten, V.R.; Colpo, E. Factors associated with chronic gastritis in patients with presence and absence of Helicobacter pylori. ABCD Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2012, 25, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, T.E.S. Risk factors for atrophic chronic gastritis in a European population: Results of the Eurohepygast study. Gut 2002, 50, 779–785. [Google Scholar]
- Namiot, A.; Kemona, A.; Namiot, Z. Smoking habit and gastritis histology. Adv. Med. Sci. 2007, 52, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhu, L.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, F.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Nie, G. A new participant in the pathogenesis of alcoholic gastritis: Pyroptosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzeri, E.; Usai, P. Role of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on intestinal permeability and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3954–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, D.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N. High-fat diet induces dysbiosis of gastric microbiota prior to gut microbiota in association with metabolic disorders in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsello, A.; Pugliese, D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Armuzzi, A. Diet and nutrients in gastrointestinal chronic diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Gerson, L.; Hershcovici, T.; Stave, C.; Fass, R. Systematic review: The effects of carbonated beverages on gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. 2010, 31, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Johnson, N.; Zhang, Q.; Du, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, C. Association of Symptoms with Eating Habits and Food Preferences in Chronic Gastritis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 5197201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Neto, M.; Pintalhao, M.; Ferreira, M.; Lunet, N. Salt intake and risk of gastric intestinal metaplasia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Heo, N.J.; Lim, J.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Chung, G.E.; Kim, J.S. High salt intake is associated with atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serafini, M.; Bellocco, R.; Wolk, A.; Ekström, A.M. Total antioxidant potential of fruit and vegetables and risk of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukos, D.H.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Agnantis, N.J.; Kappas, A.M. Fruits and vegetables: Do they protect from gastric cancer? Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-K.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, M.-H. Dietary intake assessment and biochemical characteristics of blood and urine in patients with chronic gastritis. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vomero, N.D.; Colpo, E. Nutritional care in peptic ulcer. ABCD Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2014, 27, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- James, R.H.; Shivappa, N. Chapter 2—History of Nutrition and Inflammation. In Diet, Inflammation, and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 39–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Han, B.-G.; KoGES, G. Cohort profile: The Korean genome and epidemiology study (KoGES) consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Examinees Study Group. The Health Examinees (HEXA) study: Rationale, study design and baseline characteristics. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanauchi, M.; Shibata, M.; Iwamura, M. A novel dietary inflammatory index reflecting for inflammatory ageing. Ann. Med. Surg. 2019, 47, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, J.A.; Steffen, L.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Jenny, N.S.; Jiang, R.; Herrington, D.M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Dietary patterns are associated with biochemical markers of inflammation and endothelial activation in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, B.K.S.; Oliveira, T.M.S.; Andrade, P.A.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Rosa, C.d.O.B.; Franceschini, S.d.C.C. Dietary pattern and macronutrients profile on the variation of inflammatory biomarkers: Scientific update. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 4762575. [Google Scholar]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Rashidkhani, B. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of esophageal squamous cell cancer in a case-control study from Iran. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Sandin, S.; Löf, M.; Hébert, J.R.; Adami, H.-O.; Weiderpass, E. Prospective study of dietary inflammatory index and risk of breast cancer in Swedish women. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.H.; Shin, A.; Kim, J. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of colorectal cancer: A case-control study in Korea. Nutrients 2016, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Bosetti, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of pancreatic cancer in an Italian case–control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sreeja, S.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kwon, M.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Kim, M.K. Dietary inflammatory index and its relationship with cervical carcinogenesis risk in Korean women: A case-control study. Cancers 2019, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Xu, X. Dietary inflammatory index and bladder cancer risk: A prospective study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. Dietary inflammatory index and the risk of prostate cancer: A dose-response meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, I.; Kwon, M.; Sohn, C.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Na, W.; Kim, M.K. The association between dietary inflammatory index (DII) and cancer risk in Korea: A prospective cohort study within the KoGES-HEXA study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariya, M.; Shahraki, H.R.; Farjam, M.; Ehrampoush, E.; Bahramali, E.; Homayounfar, R.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and metabolic syndrome in Iranian population (Fasa Persian Cohort Study). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto-Osorio, F.; Denova-Gutierrez, E.; Sánchez-Romero, L.M.; Salmerón, J.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T. Dietary inflammatory index and metabolic syndrome in Mexican adult population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, Z.; Yaghooti-Khorasani, M.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Sadabadi, F.; Mosa-Farkhany, E.; Darroudi, S.; Shabani, N.; Kamel-khodabandeh, A.; Bahrami, A.; Khorrami-Mohebbseraj, M.S.; et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and risk of cardiovascular disease in the Mashhad stroke and heart atherosclerotic disorder study population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 72, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Hong, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N. Dietary inflammatory index and cardiovascular risk and mortality: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Medicine 2020, 99, e20303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.E.; Xiang, J. The dietary inflammatory index is associated with diabetes severity. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2019, 32, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouali, N.; Mancini, F.R.; Hajji-Louati, M.; El Fatouhi, D.; Balkau, B.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Bonnet, F.; Fagherazzi, G. Dietary inflammatory index and type 2 diabetes risk in a prospective cohort of 70,991 women followed for 20 years: The mediating role of BMI. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, K.; Jing, Y.; He, J.; Sun, H.; Hu, X. Dietary inflammatory index and depression: A meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandari, S.; Mosalmanzadeh, N.; Moghadam, M.R.S.F.; Soleimani, D.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Jokar, M.; Karamati, M.; Abedi, S.S.; Malek, N.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and healthy eating index-2015 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 6007–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Shivappa, N.; Stubbs, B.; Smith, T.; Hébert, J.R.; Cooper, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Maggi, S. The relationship between the dietary inflammatory index and prevalence of radiographic symptomatic osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varkaneh, H.K.; Fatahi, S.; Tajik, S.; Rahmani, J.; Zarezadeh, M.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary inflammatory index in relation to obesity and body mass index: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 48, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, C.L.; Dufour, A.B.; Shivappa, N.; Habtemariam, D.; Murabito, J.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Kiel, D.P.; Hannan, M.T.; Sahni, S.J.T.A.J.o.C.N. A pro-inflammatory diet is associated with increased odds of frailty after 12-year follow-up in a cohort of adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 115, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gao, T.; Sun, C.; Jia, M.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Ma, A. Association of dietary patterns and endoscopic gastric mucosal atrophy in an adult Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casas, R.; Estruch, R. Dietary patterns, foods, nutrients and chronic inflammatory disorders. Immunome Res. 2016, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, E.M.; Steffen, L.M.; Moran, A.; Basu, S.; Steinberger, J.; Ross, J.A.; Hong, C.-P.; Sinaiko, A.R. Fruit and vegetable consumption and its relation to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in adolescents. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feyisa, Z.T.; Woldeamanuel, B.T. Prevalence and associated risk factors of gastritis among patients visiting Saint Paul Hospital Millennium Medical College, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdous, J.; Hidayah, N.; Latif, N.; Muhamad, N.; Nurhidayah, N.; Syaz, D. A descriptive study on lifestyle factors influencing gastritis among university students of UniKL RCMP in Malaysia. Indian, J. Nat. Sci. 2016, 6, 10753–10756. [Google Scholar]
- Agbor, N.E.; Esemu, S.N.; Ndip, L.M.; Tanih, N.F.; Smith, S.I.; Ndip, R.N. Helicobacter pylori in patients with gastritis in West Cameroon: Prevalence and risk factors for infection. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, S.; Khedmat, H.; Ghamar-Chehred, M.E.; Hadi, R.; Aghaei, A. Female gender and Helicobacter pylori infection, the most important predisposition factors in a cohort of gastric cancer: A longitudinal study. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 7, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, M.C.; Goto, Y.; Zabaleta, J.; Morgan, D.R.; Correa, P.; Rabkin, C.S. Sex hormones, hormonal interventions, and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2012, 21, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuyama, S.; Ohkura, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Akagi, K.; Uchida, K.; Nakachi, K.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Hayashi, S.-I. Estrogen receptor β is expressed in human stomach adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Cinical Oncol. 2002, 128, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, N.D.; Chow, W.-H.; Gao, Y.-T.; Shu, X.-O.; Ji, B.-T.; Yang, G.; Lubin, J.H.; Li, H.-L.; Rothman, N.; Zheng, W. Menstrual and reproductive factors and gastric cancer risk in a large prospective study of women. Gut 2007, 56, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, K.Y.; Seok, H.E.; Chung, J.H. The analysis of risk for peptic ulcer disease using Korean national health and nutrition examination survey: A cross-sectional analysis of a national survey sample. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunn, J.; Buttriss, J. Carbohydrates and dietary fibre. Nutr. Bull. 2007, 32, 21–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaskar, R.S.; Ricardo, I.; Azliyati, A.; Laxminarayan, R.; Amol, B.; Santosh, W.; Boo, K. Assessment of risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection and peptic ulcer disease. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2013, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, L.B.; Holman, R.C.; Christensen, K.L.Y.; Steiner, C.A.; Swerdlow, D.L. Trends in hospitalizations for peptic ulcer disease, United States, 1998–2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, B.; Wen, G.; Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Dong, X.; Chow, J.Y.; Vallon, V. Estrogen regulation of duodenal bicarbonate secretion and sex-specific protection of human duodenum. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.; Contreras, C.; Ko, K.H.; Chow, J.; Dong, X.; Tuo, B.; Zhang, H.-h.; Chen, D.-b.; Dong, H. Gender-specific protection of estrogen against gastric acid-induced duodenal injury: Stimulation of duodenal mucosal bicarbonate secretion. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 4554–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogan, A.M.; Collins, D.; Baird, A.W.; Winter, D.C. Estrogen and its role in gastrointestinal health and disease. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2009, 24, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, I.; Tominaga, S.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Yoshii, Y.; Matsuura, A.; Kameya, A.; Kano, T. A comparative case-control analysis of stomach cancer and atrophic gastritis. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6559–6564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dorant, E.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Goldbohm, R.A.; Sturmans, F. Consumption of onions and a reduced risk of stomach carcinoma. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lira Mota, K.S.; Dias, G.E.N.; Pinto, M.E.F.; Luiz-Ferreira, Â.; Monteiro Souza-Brito, A.R.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Batista, L.M. Flavonoids with gastroprotective activity. Molecules 2009, 14, 979–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setiawan, V.W.; Zhang, Z.F.; Yu, G.P.; Lu, Q.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, M.L.; Wang, M.R.; Guo, C.H.; Yu, S.Z.; Kurtz, R.C. Protective effect of green tea on the risks of chronic gastritis and stomach cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Moriyama, M.; Fukushima, T.; Kaetsu, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Une, H. Green tea consumption and chronic atrophic gastritis: A cross-sectional study in a green tea production village. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydning, A.; Berstad, A. Dietary fibre and peptic ulcer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1987, 22, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Clemow, L.; Ockene, I.S.; Saperia, G.; Stanek, E.J., 3rd; Merriam, P.A.; Ockene, J.K. Gender differences in social desirability and social approval bias in dietary self-report. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 146, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Kwon, E.; Shim, J.E.; Park, M.K.; Joo, Y.; Kimm, K. Validation and reproducibility of food frequency questionnaire for Korean genome epidemiologic study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Institute. NRRD. Food Composition Table, 9th ed.; Rural Development Administration. National Rural Resources Department Institute: Suwon, Korea. Available online: http://koreanfoodrdagokr/eng/fctFoodSrchEng/engMain (accessed on 17 March 2021).


| Characteristics | E-DII Quartiles a | p Value d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (n = 36,049) | Q2 (n = 36,049) | Q3 (n = 36,049) | Q4 (n = 36,049) | ||
| E-DII score | −8.20 to −1.22 | −1.22 to 0.23 | 0.23 to 1.61 | 1.61 to 6.36 | |
| Energy (kcal/day) b | 1805.0 ± 593.5 | 1802.0 ± 520.6 | 1751.1 ± 481.7 | 1644.5 ± 459.1 | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) b | 52.9 ± 8.0 | 52.6 ± 8.2 | 53.7 ± 8.5 | 54.1 ± 8.8 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) b | 24.3 ± 5.8 | 24.1 ± 5.1 | 23.9 ± 4.6 | 23.7 ± 5.2 | <0.0001 |
| <18.5 c | 584 (1.6) | 649 (1.8) | 687 (1.9) | 814 (2.3) | <0.0001 |
| 18.5–<23 | 13,286 (36.7) | 13,506 (37.5) | 13,215 (36.7) | 12,850 (35.6) | |
| 23–25 | 9934 (27.6) | 10,025 (27.8) | 9973 (27.7) | 9917 (27.5) | |
| >25 | 12,245 (34.1) | 11,869 (32.9) | 12,174 (33.8) | 12,468 (34.6) | |
| Sex c, Female | 26,634 (73.9) | 24,622 (68.3) | 22,785 (63.2) | 20,327 (56.4) | <0.0001 |
| Male | 9415 (26.1) | 11,427 (31.7) | 13,264 (36.8) | 15,722 (43.6) | |
| Marital status c, Married | 31,851 (88.4) | 31,933 (89.6) | 31,805 (88.2) | 31,010 (86.0) | <0.0001 |
| Single/divorced/widowed | 4198 (11.6) | 4116 (11.4) | 4244 (11.8) | 5039 (14.0) | |
| Education c, <Middle school | 5125 (14.2) | 5452 (15.1) | 6315 (17.5) | 7959 (22.1) | <0.0001 |
| Middle~high school | 20,494 (56.8) | 19,705 (54.7) | 19,564 (54.3) | 19,409 (53.8) | |
| ≥College | 10,430 (29.0) | 10,892 (30.2) | 10,170 (28.2) | 8681 (24.1) | |
| Smoking c, Never | 28,587 (79.3) | 26,987 (74.9) | 25,774 (71.5) | 23,496 (65.2) | <0.0001 |
| Past | 4174 (11.6) | 5028 (13.9) | 5565 (15.4) | 6339 (17.6) | |
| Current | 3288 (9.1) | 4034 (11.2) | 4710 (13.1) | 6214 (17.2) | |
| Drinking c, Never | 19,511 (54.1) | 18,395 (51.0) | 17,875 (49.6) | 17,189 (47.7) | <0.0001 |
| Past | 1386 (3.8) | 1330 (3.7) | 1478 (4.1) | 1672 (4.6) | |
| Current | 15,152 (42.1) | 16,324 (45.3) | 16,696 (46.3) | 17,188 (47.7) | |
| Physical activity e, Irregular | 14,401 (39.9) | 16,572 (46.0) | 18,143 (50.3) | 20,174 (56.0) | <0.0001 |
| Regular | 21,648 (60.1) | 19,477 (54.0) | 17,906 (49.7) | 15,875 (44.0) | |
| Menopausal status f, Post | 15,971 (60.1) | 14,200 (57.7) | 13,109 (57.5) | 12,564 (61.8) | <0.0001 |
| Pre | 10,663 (39.9) | 10,422 (42.3) | 9676 (42.5) | 7763 (38.2) | |
| Family history No | 31,396 (87.1) | 31,463 (87.3) | 30,521 (84.7) | 30,295 (84.0) | <0.0001 |
| of cancer Yes | 4673 (12.9) | 4586 (12.7) | 5528 (15.3) | 5754 (16.0) | |
| E-DII Quartiles a | Cross-Sectional (Logistic Regression) b | Prospective (Cox Proportional) c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases/Total | Total | Men | Women | Cases/Total | Total | Men | Women | |
| Multivariate OR | Multivariate OR | Multivariate OR | Multivariate HR | Multivariate HR | Multivariate HR | |||
| All Gastric Diseases | ||||||||
| Q1 | 324/36,049 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 530/35,689 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 369/36,049 | 1.10 (0.97–1.25) | 1.01 (0.79–1.28) | 1.15 (0.99–1.33) | 598/35,689 | 1.19 (1.06–1.34) | 1.10 (0.86–1.42) | 1.22 (1.06–1.39) |
| Q3 | 392/36,049 | 1.22 (1.07–1.40) | 1.28 (1.00–1.65) | 1.20 (1.02–1.41) | 604/35,688 | 1.25 (1.11–1.41) | 1.22 (0.96–1.55) | 1.25 (1.09–1.44) |
| Q4 | 356/36,049 | 1.09 (0.94–1.26) | 1.01 (0.77–1.32) | 1.13 (0.95–1.34) | 541/35,689 | 1.22 (1.08–1.38) * | 1.15 (0.91–1.46) | 1.27 (1.08–1.45) * |
| p for trend d | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.01 | ||
| p for interaction e | 0.23 | 0.10 | ||||||
| Continuous | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.99 (0.95–1.05) | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | 1.02 (1.01–1.06) * | 0.99 (0.93–1.01) | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) * | ||
| Gastritis | ||||||||
| Q1 | 210/36,049 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 386/35,689 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 218/36,049 | 1.06 (0.93–1.22) | 0.99 (0.74–1.34) | 1.10 (0.93–1.31) | 415/35,689 | 1.14 (0.99–1.32) | 1.06 (0.78–1.45) | 1.14 (0.96–1.35) |
| Q3 | 244/36,049 | 1.17 (1.01–1.39) | 1.23 (0.91–1.69) | 1.15 (0.96–1.39) | 410/35,688 | 1.16 (1.01–1.34) | 1.12 (0.84–1.50) | 1.19 (1.02–1.39) |
| Q4 | 184/36,049 | 1.12 (0.94–1.27) | 1.10 (0.79–1.54) | 1.12 (0.91–1.36) | 360/35,689 | 1.19 (1.04–1.37) * | 1.17 (0.87–1.57) | 1.19 (1.02–1.40) * |
| p for trend d | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.03 | ||
| p for interaction e | 0.21 | 0.84 | ||||||
| Continuous | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | 1.00 (0.95–1.07) | 1.02 (0.98–1.07) | 1.02 (1.01–1.04) * | 0.94 (0.90–0.98) | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) * | ||
| Gastric Ulcer | ||||||||
| Q1 | 94/36,049 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 123/35,689 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 127/36,049 | 1.16 (0.90–1.49) | 0.88 (0.58–1.33) | 1.36 (0.99–1.87) | 158/35,689 | 1.39 (1.1–1.76) | 1.08 (0.71–1.63) | 1.48 (1.11–1.96) |
| Q3 | 123/36,049 | 1.31 (0.99–1.70) | 1.27 (0.83–1.94) | 1.35 (0.96–1.90) | 166/35,688 | 1.44 (1.13–1.83) | 1.18 (0.77–1.81) | 1.57 (1.18–2.09) |
| Q4 | 146/36,049 | 1.22 (0.92–1.61) | 0.98 (0.61–1.56) | 1.38 (0.97–1.97) | 153/35,689 | 1.47 (1.16–1.85) * | 1.23 (0.81–1.85) | 1.68 (1.25–2.25) * |
| p for trend d | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.01 | ||
| p for interaction e | 0.31 | 0.15 | ||||||
| Continuous | 1.03 (0.98–1.10) | 1.02 (0.93–1.11) | 1.05 (0.98–1.13) | 1.02 (1.01–1.05) * | 0.96 (0.93–1.01) | 1.04 (1.01–1.15) * | ||
| Duodenal Ulcer | ||||||||
| Q1 | 20/36,049 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 21/35,689 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 24/36,049 | 0.86 (0.45–1.65) | 0.90 (0.31–2.67) | 0.84 (0.37–1.91) | 25/35,689 | 1.21 (0.68–2.17) | 1.85 (0.59–5.73) | 1.05 (0.53–2.08) |
| Q3 | 25/36,049 | 1.54 (0.84–2.90) | 1.37 (0.50–4.06) | 1.63 (0.76–3.63) | 28/35,688 | 1.36 (0.77–2.40) | 1.88 (0.58–1.09) | 1.07 (0.54–2.15) |
| Q4 | 26/36,049 | 0.98 (0.50–1.98) | 0.92 (0.30–2.98) | 1.00 (0.42–2.44) | 28/35,689 | 1.38 (0.78–2.44) | 2.30 (0.75–2.06) | 1.31 (0.66–2.59) |
| p for trend d | 0.27 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.47 | ||
| p for interaction e | 0.24 | 0.07 | ||||||
| Continuous | 0.98 (0.86–1.12) | 0.99 (0.81–1.24) | 0.97 (0.82–1.15) | 0.94 (0.89–0.97) | 0.95 (0.81–1.09) | 0.97 (0.72–0.99) | ||
| Gastric and Duodenal Ulcer | ||||||||
| Q1 | 114/36,049 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 144/35,689 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 151/36,049 | 1.11 (0.88–1.40) | 0.88 (0.59–1.30) | 1.27 (0.94–1.70) | 183/35,689 | 1.35 (1.08–1.69) | 1.19 (0.79–1.78) | 1.42 (1.09–1.85) |
| Q3 | 148/36,049 | 1.33 (1.05–1.71) | 1.28 (0.87–1.91) | 1.38 (1.01–1.89) | 194/35,688 | 1.45 (1.16–1.81) | 1.32 (0.90–1.94) | 1.50 (1.15–1.96) |
| Q4 | 172/36,049 | 1.19 (0.92–1.54) | 0.98 (0.63–1.51) | 1.33 (0.96–1.85) | 181/35,689 | 1.46 (1.17–1.81) * | 1.14 (0.78–1.69) | 1.65 (1.26–2.17) * |
| p for trend d | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.01 | ||
| p for interaction e | 0.26 | 0.16 | ||||||
| Continuous | 1.03 (0.98–1.09) | 1.01 (0.93–1.10) | 1.04 (0.98–1.11) | 1.05 (1.01–1.06) * | 1.01 (0.91–1.08) | 1.06 (1.02–1.13) * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sreeja, S.R.; Le, T.-D.; Eom, B.W.; Oh, S.H.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Kim, M.K. Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gastric Disease Risk: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132662
Sreeja SR, Le T-D, Eom BW, Oh SH, Shivappa N, Hebert JR, Kim MK. Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gastric Disease Risk: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(13):2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132662
Chicago/Turabian StyleSreeja, Sundara Raj, Trong-Dat Le, Bang Wool Eom, Seung Hyun Oh, Nitin Shivappa, James R. Hebert, and Mi Kyung Kim. 2022. "Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gastric Disease Risk: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Cohort Study" Nutrients 14, no. 13: 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132662
APA StyleSreeja, S. R., Le, T.-D., Eom, B. W., Oh, S. H., Shivappa, N., Hebert, J. R., & Kim, M. K. (2022). Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gastric Disease Risk: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Cohort Study. Nutrients, 14(13), 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132662