The Associations of Maternal Hemoglobin Concentration in Different Time Points and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Birth Weight Outcomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Definition of Exposure
2.4. Definition of Outcome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. Maternal Hb Status in Different Time Points and Hb Changes during Pregnancy
3.3. Association of Maternal Hb Level and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Neonatal Birth Weight Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldenberg, R.L.; Culhane, J.F. Low birth weight in the United States. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 584s–590s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blencowe, H.; Krasevec, J.; de Onis, M.; Black, R.E.; An, X.; Stevens, G.A.; Borghi, E.; Hayashi, C.; Estevez, D.; Cegolon, L.; et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of low birthweight in 2015, with trends from 2000: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e849–e860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.C.; Katz, J.; Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Kozuki, N.; Vogel, J.P.; Adair, L.; Baqui, A.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; et al. National and regional estimates of term and preterm babies born small for gestational age in 138 low-income and middle-income countries in 2010. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e26–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.C.; Kozuki, N.; Cousens, S.; Stevens, G.A.; Blencowe, H.; Silveira, M.F.; Sania, A.; Rosen, H.E.; Schmiegelow, C.; Adair, L.S.; et al. Estimates of burden and consequences of infants born small for gestational age in low and middle income countries with INTERGROWTH-21(st) standard: Analysis of CHERG datasets. BMJ 2017, 358, j3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, D.J. The developmental origins of chronic adult disease. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkan, P.J.; Hsieh, C.C.; Johansson, A.L.; Dickman, P.W.; Cnattingius, S. Reasons for increasing trends in large for gestational age births. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 104, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Kong, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, L.; Zou, L.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Prevalence of macrosomia and its risk factors in china: A multicentre survey based on birth data involving 101,723 singleton term infants. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2014, 28, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Lee, J.E. Large for Gestational Age and Obesity-Related Comorbidities. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giapros, V.; Evagelidou, E.; Challa, A.; Kiortsis, D.; Drougia, A.; Andronikou, S. Serum adiponectin and leptin levels and insulin resistance in children born large for gestational age are affected by the degree of overweight. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 66, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boney, C.M.; Verma, A.; Tucker, R.; Vohr, B.R. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: Association with birth weight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e290–e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darnton-Hill, I. Global burden and significance of multiple micronutrient deficiencies in pregnancy. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2012, 70, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.G.; Sysyn, G.D. Abnormal fetal growth: Intrauterine growth retardation, small for gestational age, large for gestational age. Pediatric. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 51, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Means, R.T. Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia: Implications and Impact in Pregnancy, Fetal Development, and Early Childhood Parameters. Nutrients 2020, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crispin, P.J.; Sethna, F.; Andriolo, K. Red Cell and Reticulocyte Parameters for the Detection of Iron Deficiency in Pregnancy. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Guo, X.F.; Liu, S.; Long, J.H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Huang, M.C.; Qiu, X.Q. Impact and changes of maternal hemoglobin on birth weight in pregnant women of Zhuang Nationality, in Guangxi. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2017, 38, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, P.; Alam, M.A.; Wadsworth, J.; Welch, A. Relation between maternal haemoglobin concentration and birth weight in different ethnic groups. BMJ 1995, 310, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.M.; Abe, S.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Kanda, M.; Narita, S.; Bilano, V.; Ota, E.; Gilmour, S.; Shibuya, K. Maternal anemia and risk of adverse birth and health outcomes in low- and middle-income countries: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, J.C. A Summary of Pathways or Mechanisms Linking Preconception Maternal Nutrition with Birth Outcomes. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1437s–1444s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmati, S.; Delpishe, A.; Azami, M.; Hafezi Ahmadi, M.R.; Sayehmiri, K. Maternal Anemia during pregnancy and infant low birth weight: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2017, 15, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewey, K.G.; Oaks, B.M. U-shaped curve for risk associated with maternal hemoglobin, iron status, or iron supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1694s–1702s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scanlon, K.S.; Yip, R.; Schieve, L.A.; Cogswell, M.E. High and low hemoglobin levels during pregnancy: Differential risks for preterm birth and small for gestational age. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 96, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, G.F.; Steenland, K.; Tapia, V. Maternal hemoglobin level and fetal outcome at low and high altitudes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R1477–R1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Kang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zeng, L.; Chen, F.; Mi, B.; Qu, P.; Zhao, D.; et al. Maternal Hemoglobin Concentrations and Birth Weight, Low Birth Weight (LBW), and Small for Gestational Age (SGA): Findings from a Prospective Study in Northwest China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jwa, S.C.; Fujiwara, T.; Yamanobe, Y.; Kozuka, K.; Sago, H. Changes in maternal hemoglobin during pregnancy and birth outcomes. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randall, D.A.; Patterson, J.A.; Gallimore, F.; Morris, J.M.; McGee, T.M.; Ford, J.B. The association between haemoglobin levels in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakacak, M.; Avci, F.; Ercan, O.; Köstü, B.; Serin, S.; Kiran, G.; Bostanci, M.S.; Bakacak, Z. The effect of maternal hemoglobin concentration on fetal birth weight according to trimesters. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 28, 2106–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytten, F. Blood volume changes in normal pregnancy. Clin. Haematol. 1985, 14, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, C.P.; Brownbill, P.; Dilworth, M.; Glazier, J.D. Review: Adaptation in placental nutrient supply to meet fetal growth demand: Implications for programming. Placenta 2010, 31, S70–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandovici, I.; Hoelle, K.; Angiolini, E.; Constância, M. Placental adaptations to the maternal-fetal environment: Implications for fetal growth and developmental programming. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2012, 25, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.A.; Tikmani, S.S.; Saleem, S.; Patel, A.B.; Hibberd, P.L.; Goudar, S.S.; Dhaded, S.; Derman, R.J.; Moore, J.L.; McClure, E.M.; et al. Hemoglobin concentrations and adverse birth outcomes in South Asian pregnant women: Findings from a prospective Maternal and Neonatal Health Registry. Reprod. Health 2020, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; An, H.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Ye, R. Preconception Hemoglobin Concentration and Risk of Low Birth Weight and Small-for-Gestational-Age: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, N.; Graudal, N.; Nielsen, O.J.; Agger, A.O. Serum erythropoietin during normal pregnancy: Relationship to hemoglobin and iron status markers and impact of iron supplementation in a longitudinal, placebo-controlled study on 118 women. Int. J. Hematol. 1997, 66, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Buekens, P.; Fraser, W.D.; Guo, Z. Anemia during pregnancy in a Chinese population. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2003, 83, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perperoglou, A.; Sauerbrei, W.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Schmid, M. A review of spline function procedures in R. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, A.; Wang, J.; Ye, R.W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.M.; Li, Z. Low first-trimester hemoglobin and low birth weight, preterm birth and small for gestational age newborns. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2007, 98, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Swe, K.T.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.O.; Akter, S. Effects of hemoglobin levels during pregnancy on adverse maternal and infant outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.; Oian, P. First- and second-trimester hemoglobin levels. Relation to birth weight and gestational age. Acta Obstet. Et Gynecol. Scand. 1993, 72, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Buekens, P.; Alexander, S.; Demianczuk, N.; Wollast, E. Anemia during pregnancy and birth outcome: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, C.M.; Suchdev, P.S. Anemia epidemiology, pathophysiology, and etiology in low- and middle-income countries. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.H. Biological mechanisms that might underlie iron’s effects on fetal growth and preterm birth. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 581s–589s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steer, P.J. Maternal hemoglobin concentration and birth weight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1285s–1287s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z. Quantitative (stereological) study of placental structures in women with pregnancy iron-deficiency anemia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 97, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, P.G.; Macphail, S.; Lind, T. Serial hematologic changes and pregnancy outcome. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 88, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Y.; Özgü, E.; Unlu, S.B.; Salman, B.; Eyi, E.G. The relationship between third trimester maternal hemoglobin and birth weight/length; results from the tertiary center in Turkey. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, T.T.; Tam, K.F. Placental ratio and anemia in third-trimester pregnancy. J. Reprod. Med. 2000, 45, 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, S.; Bjelland, E.K.; Haavaldsen, C.; Eskild, A. Placental weight in pregnancies with high or low hemoglobin concentrations. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 206, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, R.M.; Billah, S.M.; Lyons, G.R.; Siraj, M.S.; Rahman, Q.S.; Thorsten, V.; McClure, E.M.; Haque, R.; Petri, W.A. U-Shaped Association between Maternal Hemoglobin and Low Birth Weight in Rural Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 106, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, L. Placental vascular dysfunction in diabetic pregnancies: Intimations of fetal cardiovascular disease? Microcirculation 2011, 18, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, S.P.; Rosso, P.; Espinoza, R.; Robert, J.A.; Valdés, G.; Donoso, E. Maternal plasma volume expansion and hormonal changes in women with idiopathic fetal growth retardation. Obstet. Gynecol. 1993, 81, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Stephansson, O.; Dickman, P.W.; Johansson, A.; Cnattingius, S. Maternal hemoglobin concentration during pregnancy and risk of stillbirth. JAMA 2000, 284, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knottnerus, J.A.; Delgado, L.R.; Knipschild, P.G.; Essed, G.G.; Smits, F. Haematologic parameters and pregnancy outcome. A prospective cohort study in the third trimester. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1990, 43, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantz, K.L.; Kim, S.; Grobman, W.A.; Newman, R.; Owen, J.; Skupski, D.; Grewal, J.; Chien, E.K.; Wing, D.A.; Wapner, R.J.; et al. Fetal growth velocity: The NICHD fetal growth studies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 219, 285.E1–285.E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozuki, N.; Lee, A.C.; Katz, J. Moderate to severe, but not mild, maternal anemia is associated with increased risk of small-for-gestational-age outcomes. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sifakis, S.; Pharmakides, G. Anemia in pregnancy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 900, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
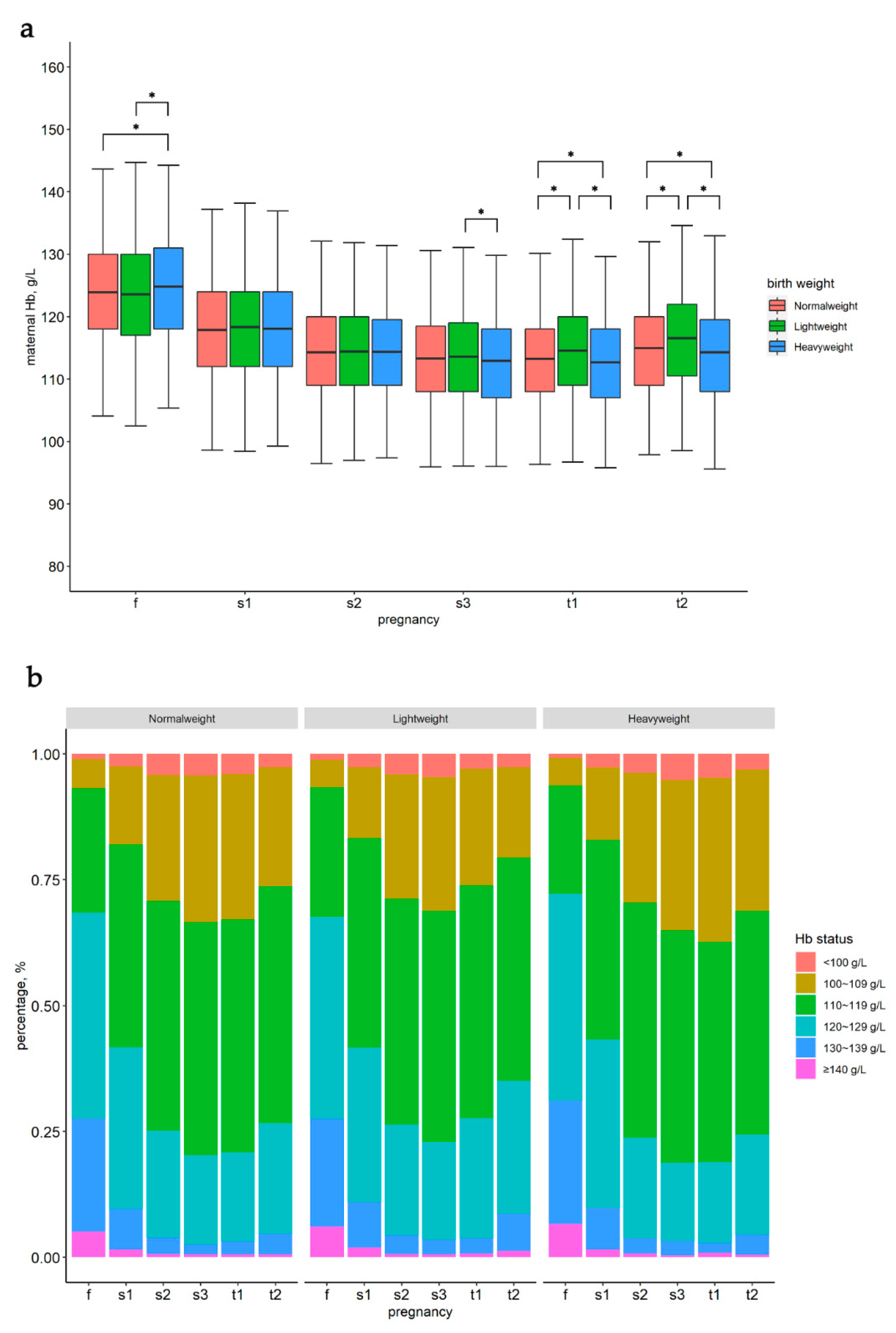
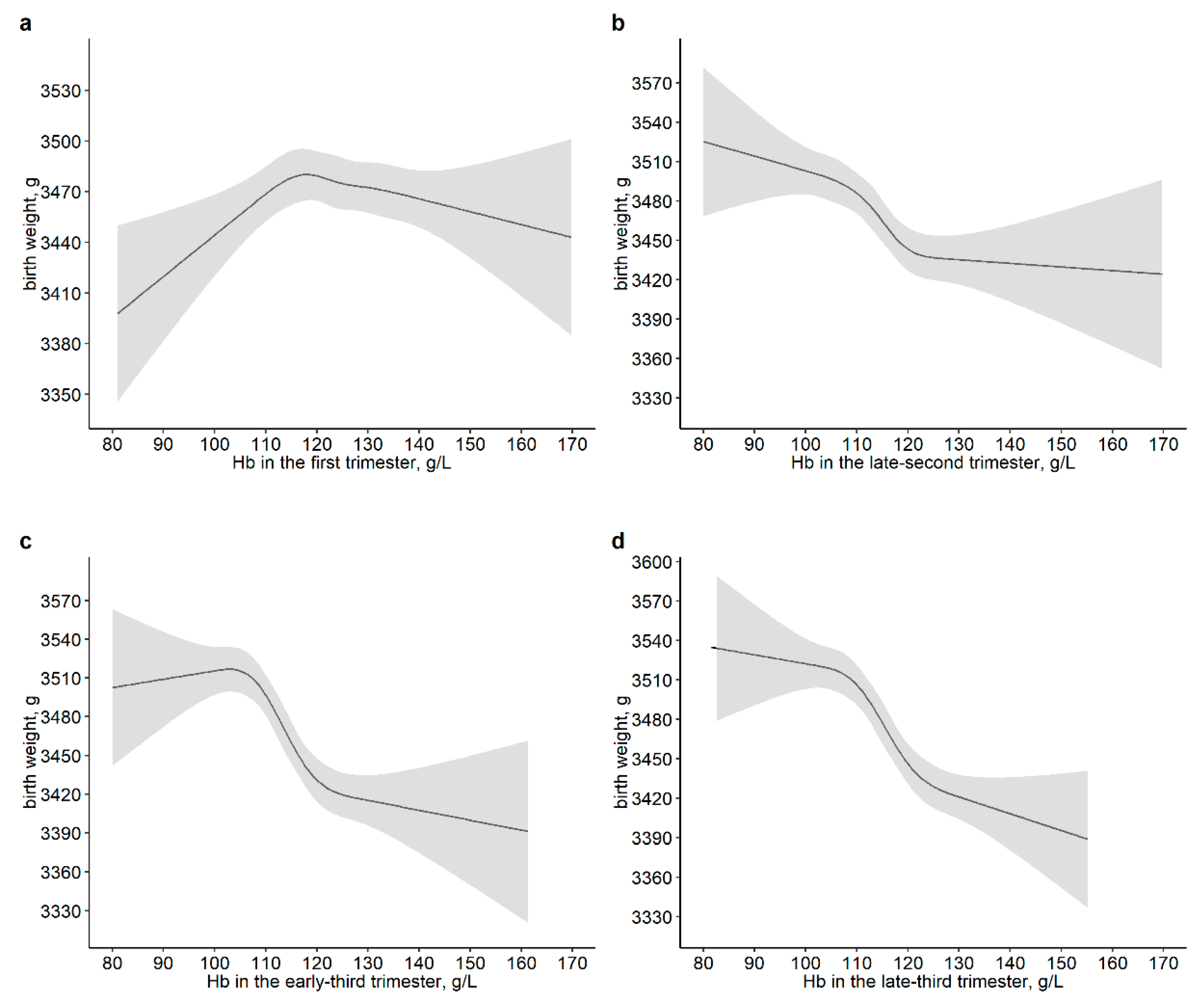
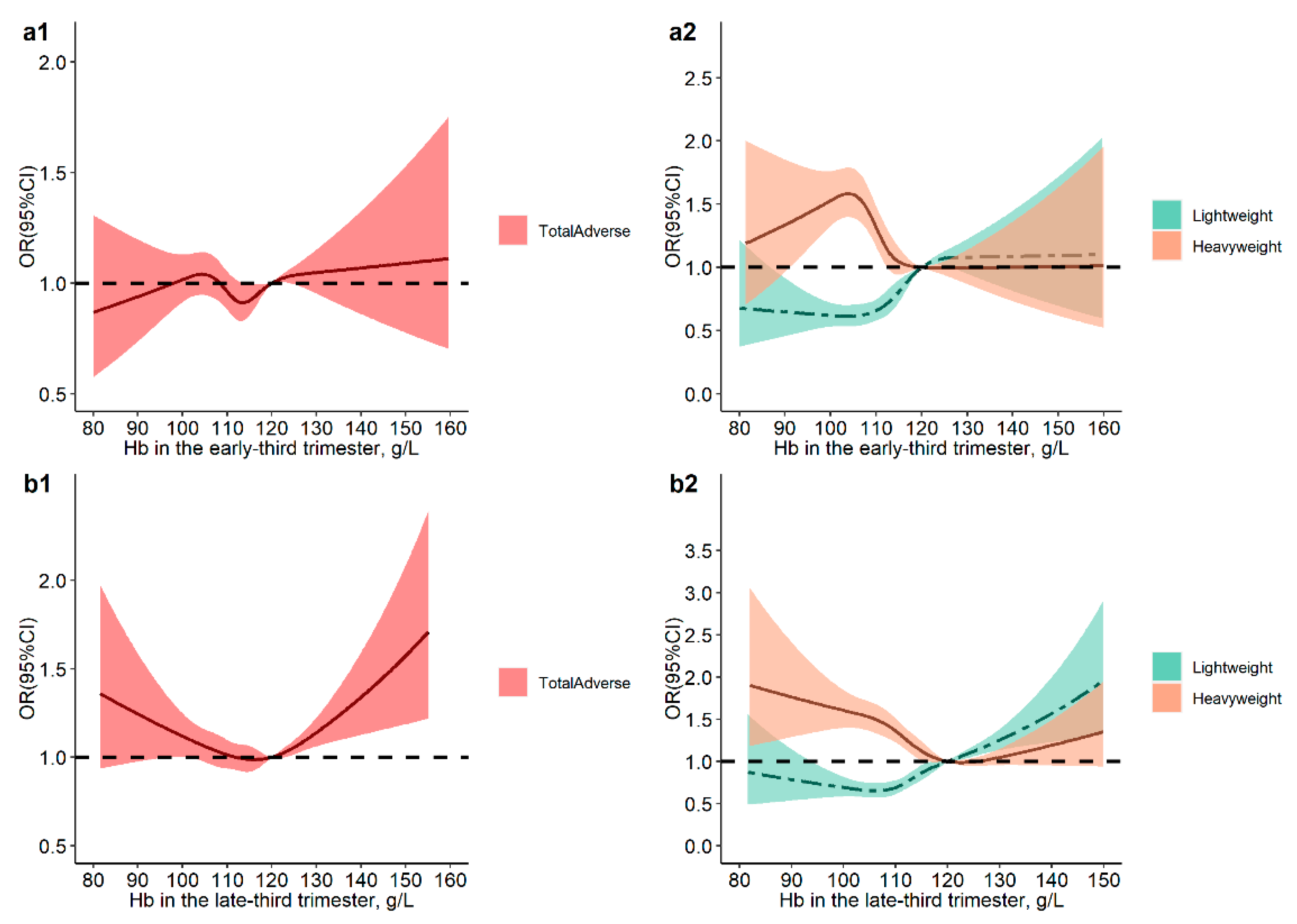
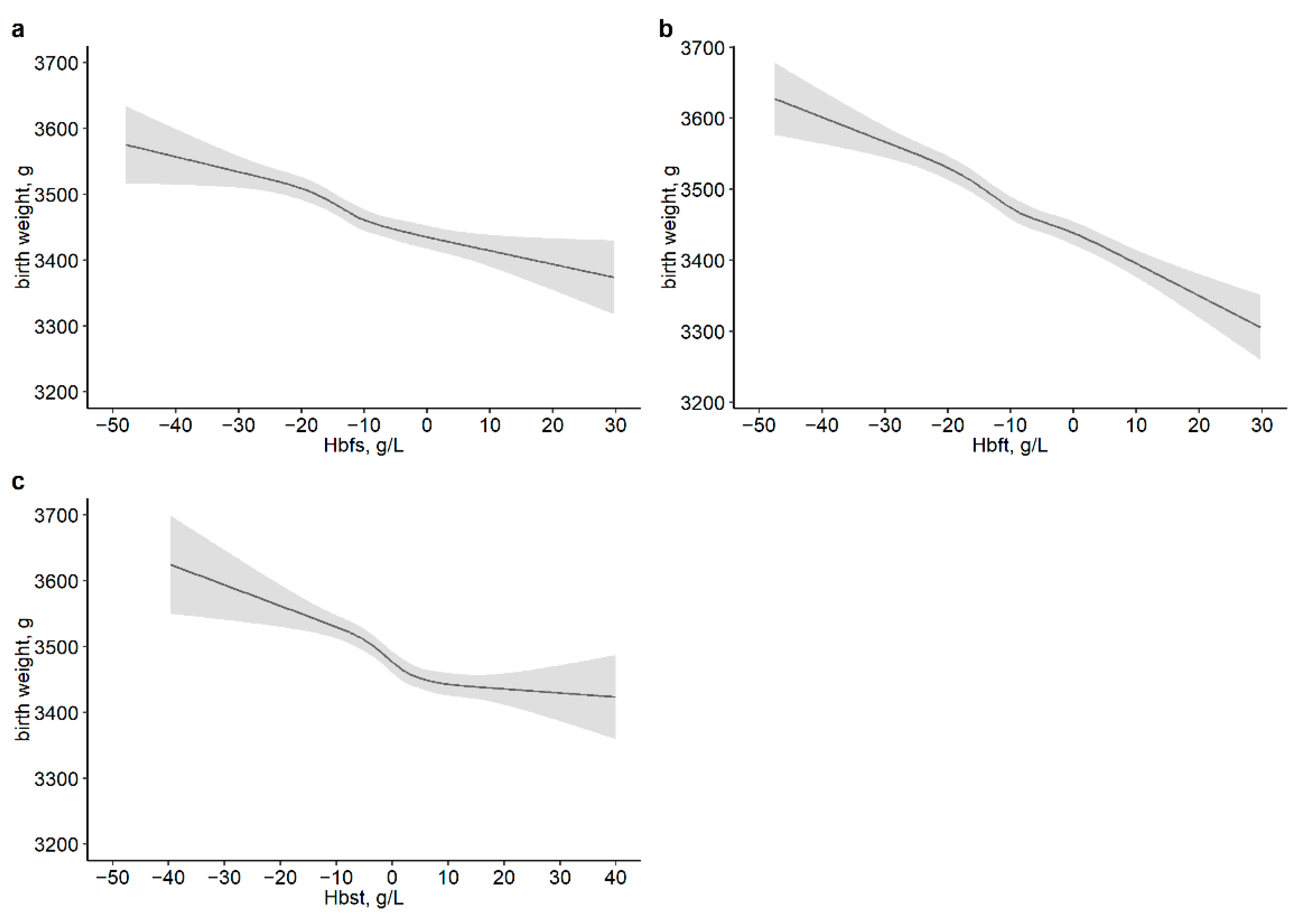
| Variables | Normalweight | Lightweight | Heavyweight | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 19,413 | N = 2055 | N = 2715 | ||
| Maternal Characteristics | ||||
| Maternal age, years, mean ± SD | 26.62 ± 3.70 | 26.49 ± 3.59 | 26.91 ± 3.94 | <0.001 |
| Education, N (%) | ||||
| Primary school or below | 335 (1.7) | 51 (2.5) | 55 (2.1) | 0.006 |
| Junior high school | 6603 (34.3) | 682 (33.4) | 985 (36.7) | |
| Senior high school | 4915 (25.6) | 488 (23.9) | 671 (25.0) | |
| College or above | 7383 (38.4) | 820 (40.2) | 971 (36.2) | |
| Primipara, N (%) | ||||
| Yes | 11,622 (59.9) | 1221 (59.4) | 1638 (60.3) | <0.001 |
| No | 1855 (9.6) | 138 (6.7) | 367 (13.5) | |
| Unknown | 5936 (30.6) | 696 (33.9) | 710 (26.2) | |
| BMI at 1st trimester, kg/m2, mean ± SD | 20.58 ± 2.53 | 19.95 ± 2.48 | 21.83 ± 2.85 | <0.001 |
| BMI categories, N (%) | ||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 13,820 (71.2) | 1295 (63.0) | 1928 (71.0) | <0.001 |
| Normalweight (18.5–23.9) | 3878 (20.0) | 616 (30.0) | 242 (8.9) | |
| Overweight (24.0–27.9) | 1458 (7.5) | 128 (6.2) | 462 (17.0) | |
| Obesity (≥28.0) | 257 (1.3) | 16 (0.8) | 83 (3.1) | |
| WG * during pregnancy, kg, mean ± SD | 13.88 ± 3.79 | 12.61 ± 3.95 | 15.41 ± 4.06 | <0.001 |
| Neonatal Characteristics | ||||
| Gender of newborn, N (%) | ||||
| Male | 10,208 (52.6) | 878 (42.7) | 1769 (65.2) | <0.001 |
| Female | 9205 (47.4) | 1177 (57.3) | 946 (34.8) | |
| Mode of delivery, N (%) | ||||
| Vaginal | 7838 (40.4) | 956 (46.5) | 599 (22.1) | <0.001 |
| Cesarean | 10,515 (54.2) | 995 (48.4) | 1953 (71.9) | |
| Forceps | 205 (1.1) | 30 (1.5) | 25 (0.9) | |
| Others | 855 (4.4) | 74 (3.6) | 138 (5.1) | |
| GA * at delivery, weeks, mean ± SD | 39.15 ± 1.17 | 38.59 ± 2.07 | 39.34 ± 1.35 | <0.001 |
| Birth weight, g, mean ± SD | 3.38 ± 0.29 | 2.64 ± 0.31 | 4.14 ± 0.31 | <0.001 |
| Preterm, N (%) | ||||
| No | 19,048 (98.1) | 1760 (85.6) | 2637 (97.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 365 (1.9) | 295 (14.4) | 78 (2.9) | |
| Hemoglobin | Normalweight | Lightweight | Heavyweight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | Model 1 † | Model 2 ‡ | N (%) | Model 1 † | Model 2 ‡ | |
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | ||||
| First trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 189 (1.0) | 30 (1.5) | 1.51 (1.01, 2.25) | 1.45 (0.96, 2.18) | 17 (0.6) | 0.72 (0.44, 1.20) | 0.73 (0.43, 1.23) |
| 100~109 | 1136 (5.9) | 136 (6.6) | 1.15 (0.93, 1.40) | 1.11 (0.91, 1.37) | 139 (5.1) | 0.97 (0.79, 1.18) | 1.03 (0.84, 1.26) |
| 110~119 | 4830 (24.9) | 501 (24.4) | Ref. | Ref. | 613 (22.6) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 7911 (40.8) | 821 (40.0) | 1.00 (0.89, 1.12) | 1.03 (0.91, 1.16) | 1115 (41.1) | 1.10 (0.99, 1.23) | 1.02 (0.92, 1.14) |
| 130~139 | 4356 (22.4) | 447 (21.8) | 1.00 (0.87, 1.14) | 1.06 (0.92, 1.22) | 665 (24.5) | 1.17 (1.04, 1.32) | 1.05 (0.93, 1.19) |
| ≥140 | 991 (5.1) | 120 (5.8) | 1.17 (0.95, 1.46) | 1.26 (1.01, 1.57) | 166 (6.1) | 1.27 (1.05, 1.54) | 1.04 (0.86, 1.27) |
| Early-second trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 381 (2.4) | 43 (2.6) | 1.00 (0.72, 1.40) | 0.93 (0.67, 1.31) | 60 (2.7) | 1.20 (0.90, 1.60) | 1.34 (0.99, 1.80) |
| 100~109 | 2445 (15.3) | 230 (13.9) | 0.90 (0.76, 1.05) | 0.86 (0.73, 1.01) | 328 (14.7) | 1.01 (0.88, 1.15) | 1.12 (0.97, 1.29) |
| 110~119 | 6407 (40.2) | 672 (40.5) | Ref. | Ref. | 869 (39.0) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 5119 (32.1) | 533 (32.1) | 0.99 (0.88, 1.12) | 1.05 (0.93, 1.19) | 752 (33.7) | 1.06 (0.95, 1.18) | 0.96 (0.86, 1.07) |
| 130~139 | 1323 (8.3) | 147 (8.9) | 1.08 (0.89, 1.31) | 1.20 (0.99, 1.46) | 182 (8.2) | 0.97 (0.82, 1.16) | 0.80 (0.67, 0.96) |
| ≥140 | 266 (1.7) | 33 (2.0) | 1.13 (0.77, 1.65) | 1.25 (0.85, 1.83) | 38 (1.7) | 1.07 (0.75, 1.53) | 0.87 (0.60, 1.26) |
| Mediate-second trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 694 (4.0) | 73 (4.0) | 0.98 (0.76, 1.27) | 0.87 (0.67, 1.13) | 83 (3.4) | 0.86 (0.68, 1.10) | 1.04 (0.81, 1.33) |
| 100~109 | 4268 (24.8) | 450 (24.5) | 1.02 (0.90, 1.15) | 0.96 (0.85, 1.09) | 608 (25.1) | 1.00 (0.90, 1.12) | 1.12 (1.00, 1.25) |
| 110~119 | 7865 (45.6) | 815 (44.3) | Ref. | Ref. | 1130 (46.7) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 3720 (21.6) | 428 (23.3) | 1.10 (0.97, 1.25) | 1.17 (1.03, 1.33) | 500 (20.7) | 0.93 (0.83, 1.04) | 0.82 (0.73, 0.93) |
| 130~139 | 588 (3.4) | 61 (3.3) | 1.04 (0.79, 1.38) | 1.11 (0.83, 1.46) | 81 (3.3) | 0.92 (0.72, 1.18) | 0.79 (0.61, 1.02) |
| ≥140 | 104 (0.6) | 11 (0.6) | 0.95 (0.50, 1.80) | 1.04 (0.54, 2.00) | 16 (0.7) | 1.10 (0.64, 1.89) | 0.95 (0.55, 1.66) |
| Late-second trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 714 (4.1) | 83 (4.6) | 1.11 (0.87, 1.42) | 0.99 (0.78, 1.27) | 111 (4.6) | 1.23 (0.99, 1.52) | 1.47 (1.18, 1.83) |
| 100~109 | 4885 (28.4) | 497 (27.3) | 0.99 (0.88, 1.12) | 0.93 (0.82, 1.05) | 733 (30.5) | 1.15 (1.03, 1.27) | 1.29 (1.16, 1.43) |
| 110~119 | 8036 (46.7) | 820 (45.0) | Ref. | Ref. | 1068 (44.5) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 3097 (18.0) | 351 (19.3) | 1.12 (0.98, 1.28) | 1.21 (1.06, 1.39) | 412 (17.2) | 0.98 (0.86, 1.11) | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) |
| 130~139 | 395 (2.3) | 60 (3.3) | 1.49 (1.11, 1.98) | 1.59 (1.19, 2.14) | 67 (2.8) | 1.30 (0.99, 1.71) | 1.08 (0.81, 1.43) |
| ≥140 | 83 (0.5) | 10 (0.5) | 1.05 (0.53, 2.07) | 1.19 (0.59, 2.37) | 10 (0.4) | 1.01 (0.52, 1.98) | 0.89 (0.45, 1.76) |
| Early-third trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 716 (4.2) | 58 (3.2) | 0.73 (0.55, 0.97) | 0.66 (0.49, 0.88) | 104 (4.4) | 1.12 (0.90, 1.40) | 1.30 (1.04, 1.63) |
| 100~109 | 4929 (29.2) | 442 (24.5) | 0.84 (0.74, 0.95) | 0.80 (0.70, 0.90) | 794 (33.3) | 1.24 (1.12, 1.37) | 1.34 (1.21, 1.49) |
| 110~119 | 7698 (45.5) | 806 (44.6) | Ref. | Ref. | 1012 (42.4) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 3007 (17.8) | 429 (23.8) | 1.33 (1.17, 1.51) | 1.40 (1.23, 1.59) | 396 (16.6) | 0.99 (0.87, 1.12) | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) |
| 130~139 | 458 (2.7) | 60 (3.3) | 1.19 (0.89, 1.58) | 1.28 (0.96, 1.70) | 61 (2.6) | 0.98 (0.74, 1.30) | 0.88 (0.66, 1.17) |
| ≥140 | 94 (0.6) | 11 (0.6) | 1.02 (0.53, 1.94) | 1.04 (0.54, 1.99) | 18 (0.8) | 1.53 (0.91, 2.56) | 1.33 (0.77, 2.30) |
| Late-third trimester | |||||||
| <100 | 529 (2.8) | 49 (2.6) | 0.98 (0.72, 1.33) | 0.92 (0.67, 1.25) | 91 (3.5) | 1.25 (0.98, 1.58) | 1.38 (1.09, 1.76) |
| 100~109 | 4541 (24.3) | 375 (19.8) | 0.86 (0.76, 0.98) | 0.83 (0.73, 0.94) | 741 (28.5) | 1.23 (1.11, 1.36) | 1.29 (1.16, 1.44) |
| 110~119 | 8534 (45.8) | 819 (43.3) | Ref. | Ref. | 1121 (43.2) | Ref. | Ref. |
| 120~129 | 4080 (21.9) | 496 (26.2) | 1.26 (1.12, 1.42) | 1.31 (1.16, 1.48) | 503 (19.4) | 0.94 (0.83, 1.05) | 0.85 (0.76, 0.96) |
| 130~139 | 849 (4.6) | 131 (6.9) | 1.58 (1.30, 1.94) | 1.78 (1.45, 2.19) | 119 (4.6) | 1.06 (0.86, 1.30) | 0.90 (0.73, 1.11) |
| ≥140 | 119 (0.6) | 22 (1.2) | 1.84 (1.14, 2.96) | 1.96 (1.20, 3.18) | 21 (0.8) | 1.35 (0.84, 2.17) | 1.16 (0.71, 1.91) |
| ΔHb | Normalweight | Lightweight | Heavyweight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | Model 1 † | Model 2 ‡ | N (%) | Model 1 † | Model 2 ‡ | |
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | ||||
| Hbfs | |||||||
| Q1 (−50~−17) | 4332 (25.2) | 444 (24.4) | Ref. | Ref. | 724 (30.2) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Q2 (−17~−11) | 4402 (25.6) | 429 (23.6) | 0.94 (0.82, 1.09) | 0.98 (0.85, 1.14) | 642 (26.8) | 0.90 (0.80, 1.02) | 0.83 (0.73, 0.94) |
| Q3 (−11~−5) | 4407 (25.7) | 476 (26.2) | 1.07 (0.93, 1.25) | 1.17 (1.00, 1.36) | 537 (22.4) | 0.75 (0.66, 0.86) | 0.65 (0.57, 0.75) |
| Q4 (−5~50) | 4034 (23.5) | 467 (25.7) | 1.16 (0.98, 1.38) | 1.32 (1.11, 1.57) | 495 (20.6) | 0.75 (0.65, 0.88) | 0.62 (0.53, 0.72) |
| Hbft | |||||||
| Q1 (−50~−16) | 4906 (26.3) | 391 (20.7) | Ref. | Ref. | 831 (32.1) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Q2 (−16~−9) | 4572 (24.6) | 438 (23.2) | 1.29 (1.11, 1.50) | 1.32 (1.14, 1.54) | 626 (24.2) | 0.82 (0.73, 0.93) | 0.78 (0.69, 0.89) |
| Q3 (−9~−2) | 4527 (24.3) | 477 (25.2) | 1.45 (1.24, 1.69) | 1.54 (1.32, 1.80) | 579 (22.3) | 0.78 (0.69, 0.89) | 0.71 (0.63, 0.82) |
| Q4 (−2~50) | 4617 (24.8) | 584 (30.9) | 1.81 (1.53, 2.14) | 1.97 (1.66, 2.33) | 555 (21.4) | 0.75 (0.65, 0.87) | 0.65 (0.56, 0.76) |
| Hbst * | |||||||
| Q1 (−50~−3.5) | 4362 (26.3) | 347 (20.7) | Ref. | Ref. | 678 (29.5) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Q2 (−3.5~2) | 4477 (27.0) | 431 (25.7) | 1.18 (1.01, 1.36) | 1.17 (1.01, 1.36) | 610 (26.6) | 0.91 (0.81, 1.03) | 0.93 (0.82, 1.05) |
| Q3 (2~7) | 3727 (22.5) | 405 (24.1) | 1.34 (1.15, 1.56) | 1.33 (1.14, 1.55) | 454 (19.8) | 0.82 (0.72, 0.93) | 0.82 (0.72, 1.01) |
| Q4 (7~50) | 4000 (24.1) | 497 (29.6) | 1.49 (1.29, 1.73) | 1.45 (1.25, 1.68) | 555 (24.2) | 0.96 (0.85, 1.09) | 1.00 (0.88, 1.14) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Z.; Si, S.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, H.; Chi, P.; Mo, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y. The Associations of Maternal Hemoglobin Concentration in Different Time Points and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Birth Weight Outcomes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122542
Peng Z, Si S, Cheng H, Zhou H, Chi P, Mo M, Zhuang Y, Liu H, Yu Y. The Associations of Maternal Hemoglobin Concentration in Different Time Points and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Birth Weight Outcomes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122542
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Zhicheng, Shuting Si, Haoyue Cheng, Haibo Zhou, Peihan Chi, Minjia Mo, Yan Zhuang, Hui Liu, and Yunxian Yu. 2022. "The Associations of Maternal Hemoglobin Concentration in Different Time Points and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Birth Weight Outcomes" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122542
APA StylePeng, Z., Si, S., Cheng, H., Zhou, H., Chi, P., Mo, M., Zhuang, Y., Liu, H., & Yu, Y. (2022). The Associations of Maternal Hemoglobin Concentration in Different Time Points and Its Changes during Pregnancy with Birth Weight Outcomes. Nutrients, 14(12), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122542







