Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alter Small Intestinal Morphology and Its Global DNA Methylation in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats, Leading to Obesity Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
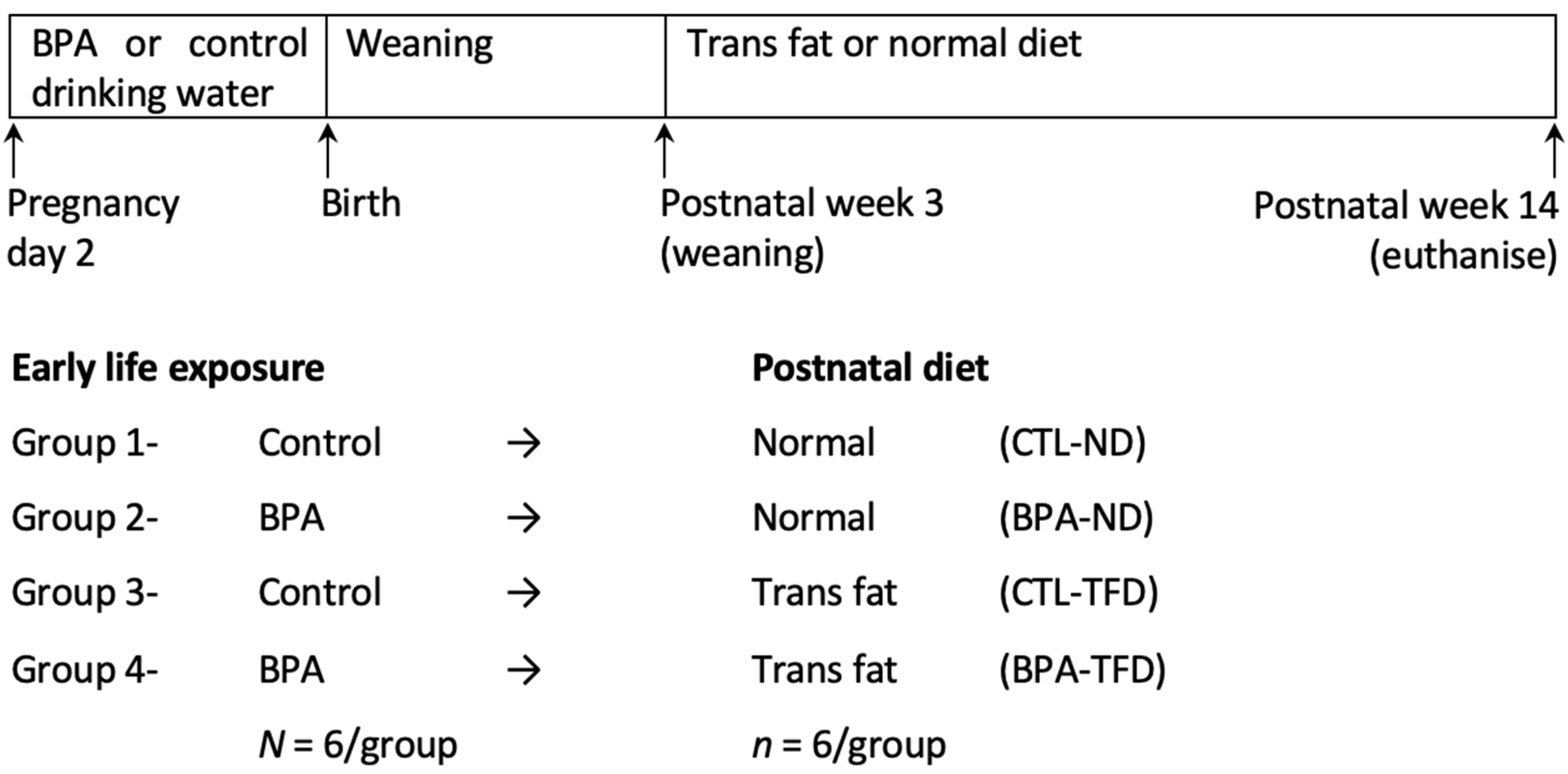
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Physiological Parameters for Obesity
2.4. Organ Tissue Collection
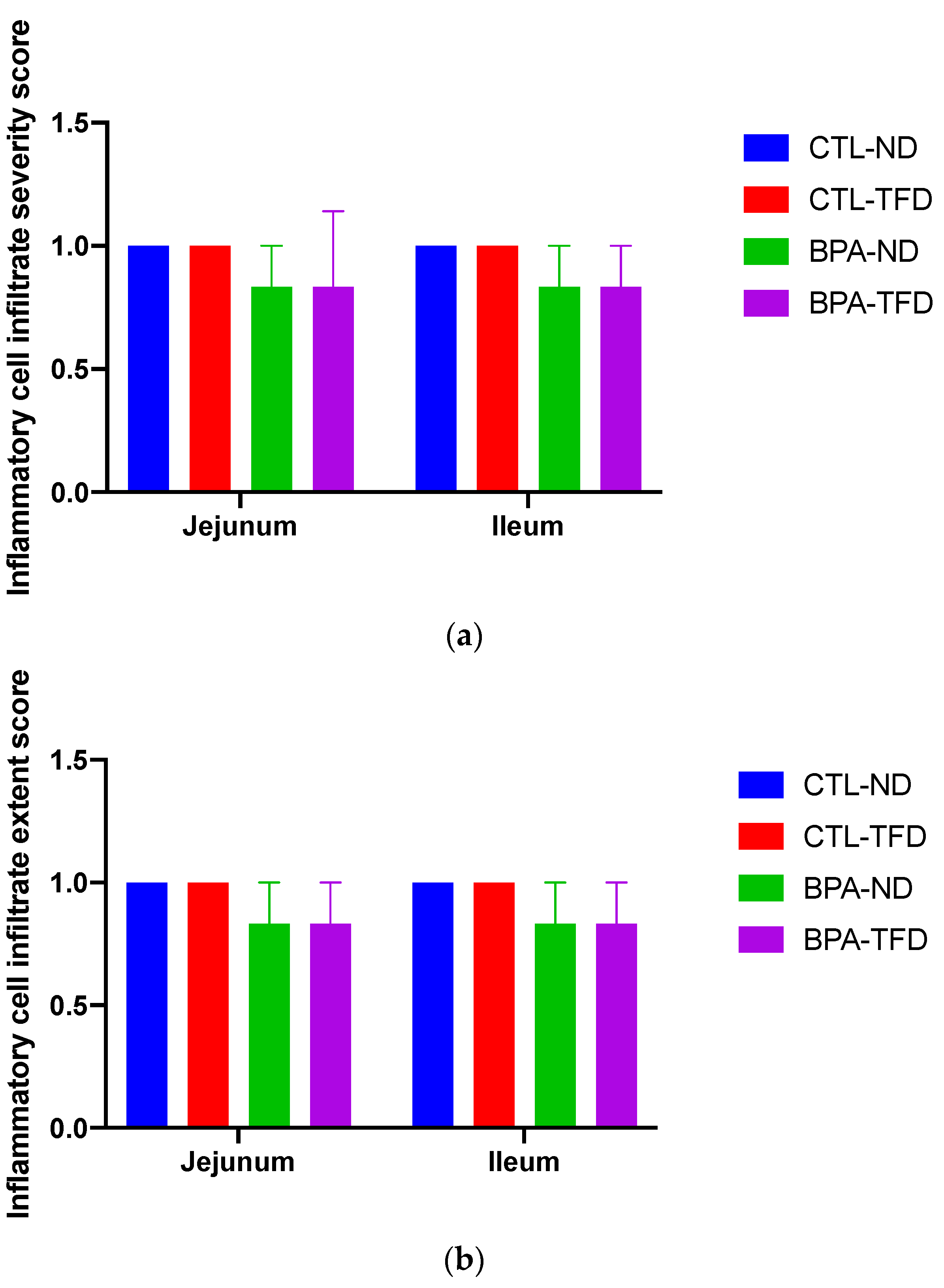
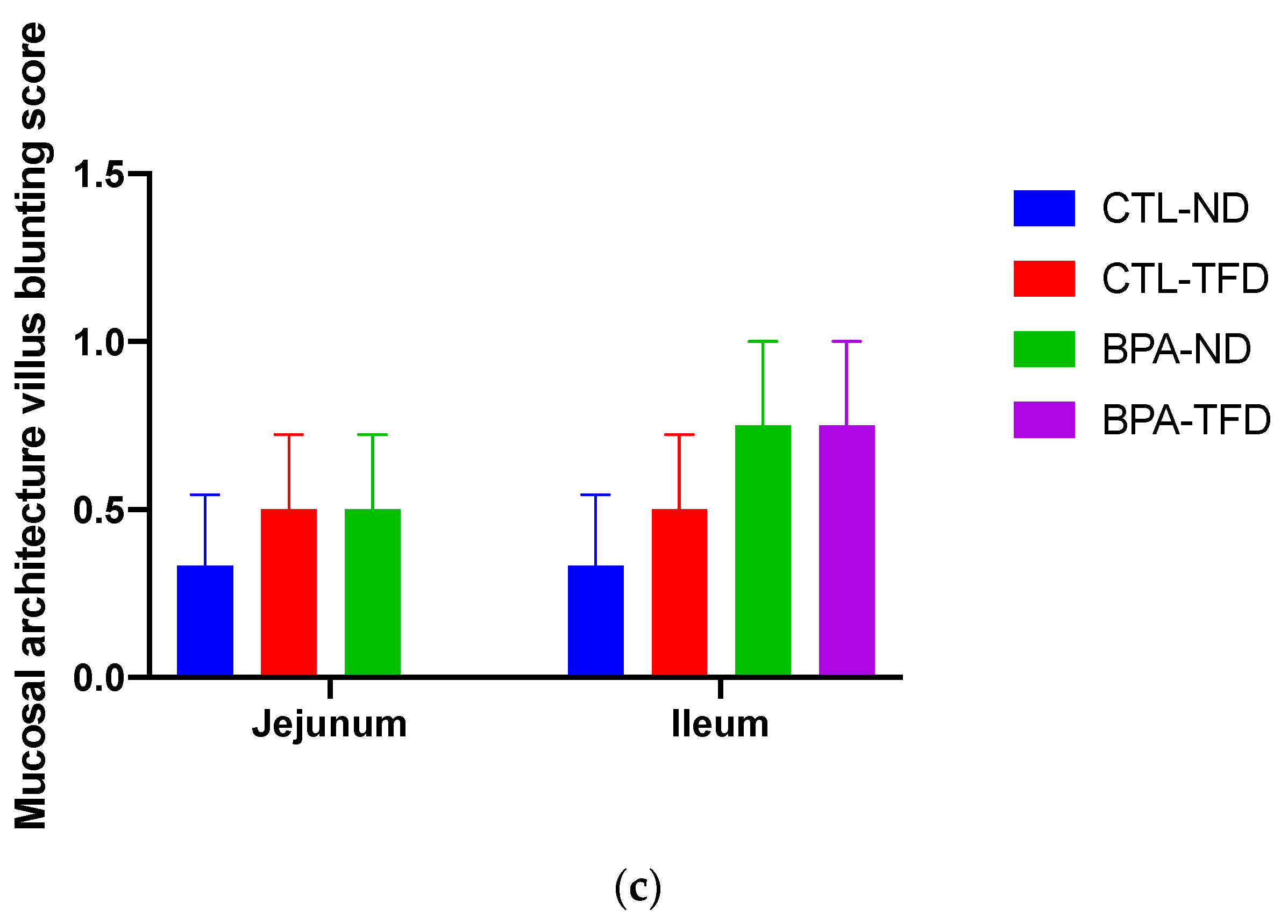
2.5. Histopathological Evaluation
2.6. DNA Isolation
2.7. Global Small Intestinal DNA Methylation
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Prenatal BPA Exposure and/or Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Affects the Physiological Parameters of Offspring
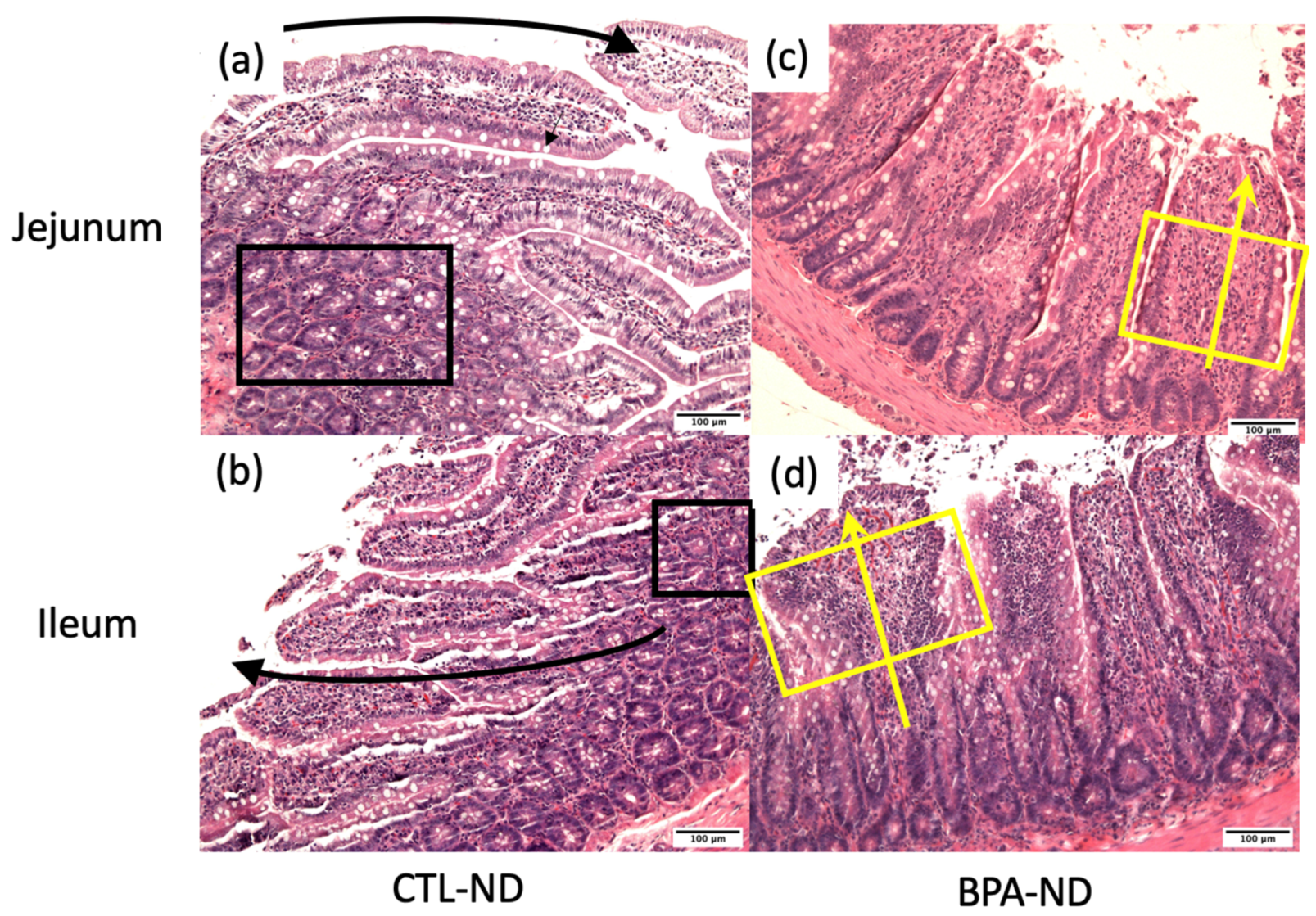
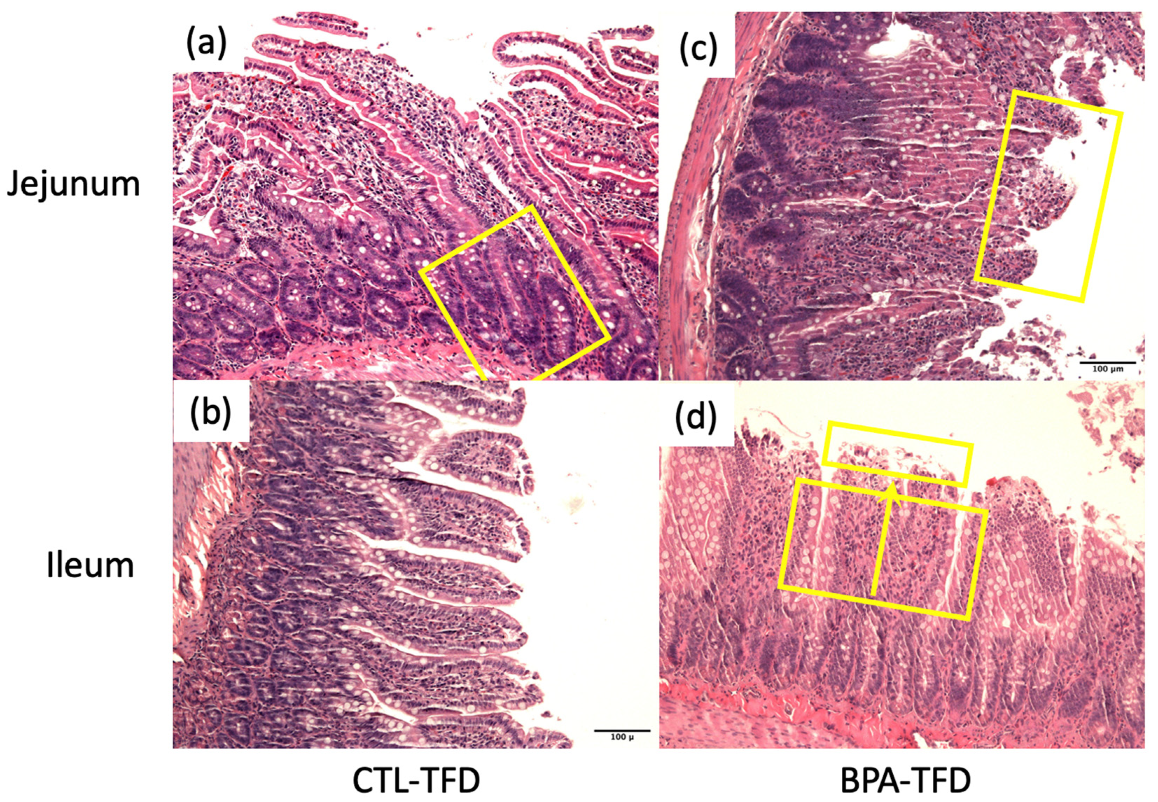
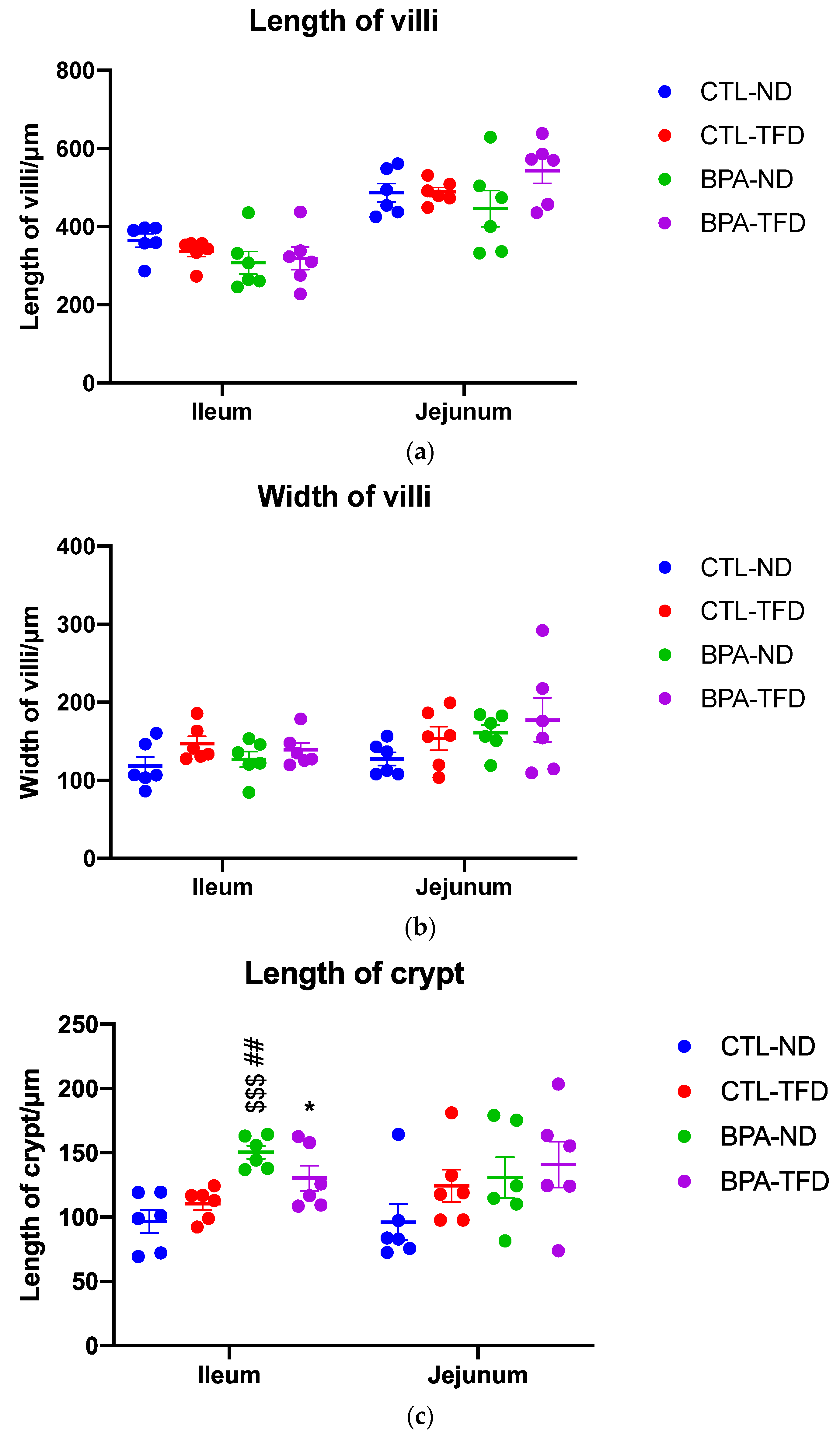
3.2. Prenatal BPA Exposure and/or Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alters Crypt Length of Offspring’s Small Intestine
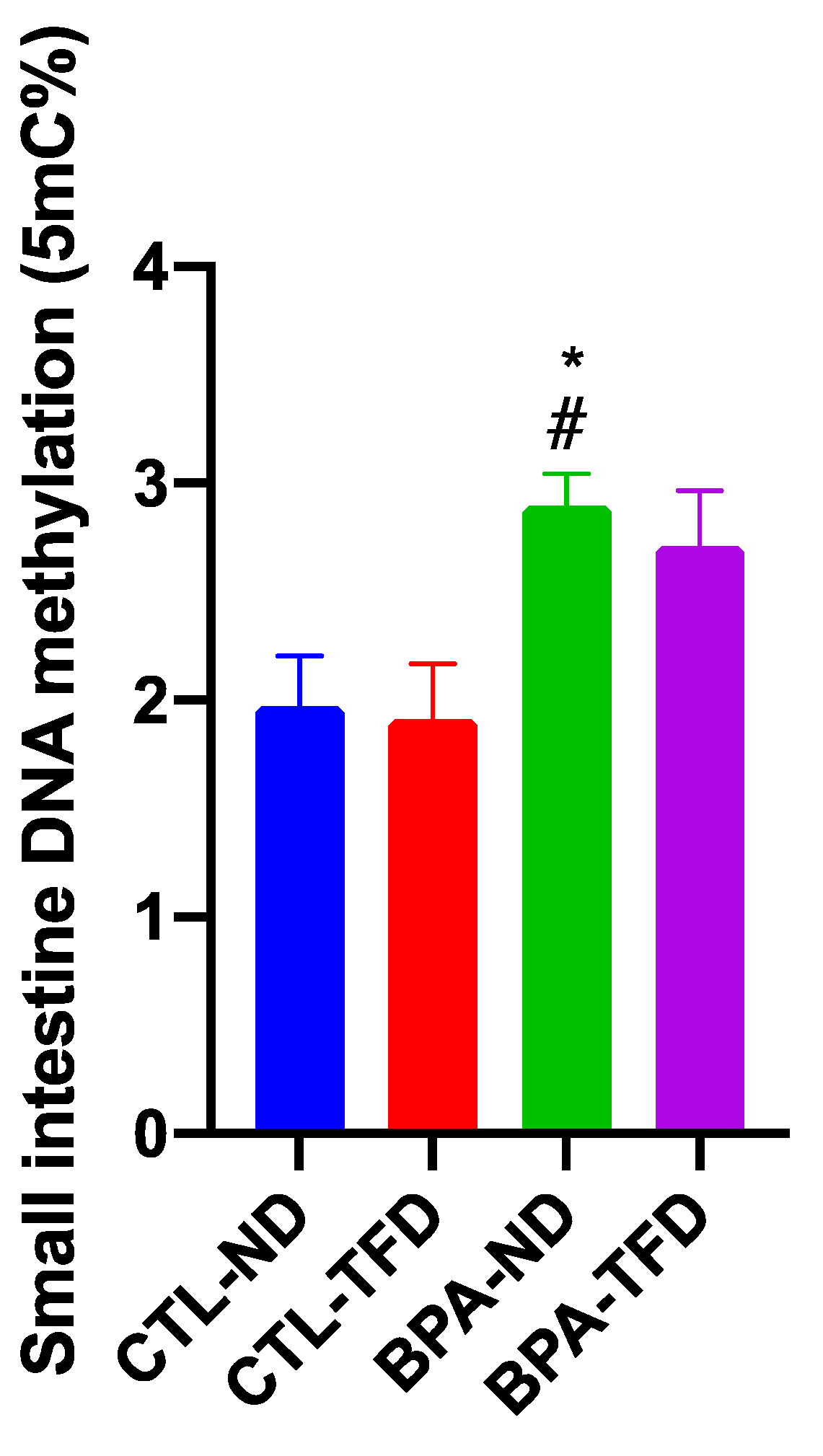
3.3. Prenatal BPA Exposure and/or Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Changes the Global DNA Methylation of Offspring’s Small Intestine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flint, S.; Markle, T.; Thompson, S.; Wallace, E. Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: A wildlife perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlstrom, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Jaghbir, M.; Salam, M.; Al-Kadamany, G.; Damsees, R.; Al-Rawashdeh, N. Testing baby bottles for the presence of residual and migrated bisphenol A. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 191, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, K.; Park, J.; Moon, H.B.; Choi, G.; Lee, J.J.; Suh, E.; Kim, H.J.; Eun, S.H.; Kim, G.H.; et al. Bisphenol A distribution in serum, urine, placenta, breast milk, and umbilical cord serum in a birth panel of mother-neonate pairs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, J.; Kristofco, L.A.; Steele, W.B.; Yates, B.S.; Breed, C.S.; Williams, E.S.; Brooks, B.W. Global Assessment of Bisphenol A in the Environment: Review and Analysis of Its Occurrence and Bioaccumulation. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815598308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, M.; Iwano, H.; Yanagisawa, R.; Koike, N.; Inoue, H.; Yokota, H. Placental transfer of conjugated bisphenol A and subsequent reactivation in the rat fetus. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Henare, K.; Thorstensen, E.B.; Ponnampalam, A.P.; Mitchell, M.D. Transfer of bisphenol A across the human placenta. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 393.e1–393.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, W.; Bai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, S.; Li, W. Urinary parabens, bisphenol A and triclosan in primiparas from Shenzhen, China: Implications for exposure and health risks. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, N.; Surendranath, A.R.; Pathak, J.L.; Yu, S.; Chung, C.Y. Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Forsen, T.; Osmond, C. Fetal origins of adult disease: Strength of effects and biological basis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 31, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.P.; Tsuprykov, O.; Hasan, A.A.; Reichetzeder, C.; Tian, M.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, G.Y.; Guo, J.; et al. Folate treatment of pregnant rat dams abolishes metabolic effects in female offspring induced by a paternal pre-conception unhealthy diet. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, D.L.; Pavanello, A.; Saavedra, L.P.; Pereira, T.S.; de Castro-Prado, M.A.A.; de Freitas Mathias, P.C. Environmental monitoring and the developmental origins of health and disease. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2019, 10, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, V.; Cardoso, R.C.; Puttabyatappa, M. Developmental Programming, a Pathway to Disease. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulkifli, S.; Rahman, A.A.; Kadir, S.; Nor, N.S.M. Bisphenol A and its effects on the systemic organs of children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 3111–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legeay, S.; Faure, S. Is bisphenol A an environmental obesogen? Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 31, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thaker, V.V. Genetic and Epigenetic Causes of Obesity. Adolesc. Med. State Art Rev. 2017, 28, 379–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Junge, K.M.; Leppert, B.; Jahreis, S.; Wissenbach, D.K.; Feltens, R.; Grutzmann, K.; Thurmann, L.; Bauer, T.; Ishaque, N.; Schick, M.; et al. MEST mediates the impact of prenatal bisphenol A exposure on long-term body weight development. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Shioda, K.; Mitsunaga, S.; Yawata, S.; Angle, B.M.; Nagel, S.C.; Vom Saal, F.S.; Shioda, T. Prenatal Exposure to Bisphenol A Disrupts Naturally Occurring Bimodal DNA Methylation at Proximal Promoter of fggy, an Obesity-Relevant Gene Encoding a Carbohydrate Kinase, in Gonadal White Adipose Tissues of CD-1 Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, M.J. Nutrient-induced intestinal adaption and its effect in obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 136, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddivari, L.; Veeramachaneni, D.N.R.; Walters, W.A.; Lozupone, C.; Palmer, J.; Hewage, M.K.K.; Bhatnagar, R.; Amir, A.; Kennett, M.J.; Knight, R.; et al. Perinatal Bisphenol A Exposure Induces Chronic Inflammation in Rabbit Offspring via Modulation of Gut Bacteria and Their Metabolites. mSystems 2017, 2, e00093-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLuca, J.A.; Allred, K.F.; Menon, R.; Riordan, R.; Weeks, B.R.; Jayaraman, A.; Allred, C.D. Bisphenol-A alters microbiota metabolites derived from aromatic amino acids and worsens disease activity during colitis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braniste, V.; Jouault, A.; Gaultier, E.; Polizzi, A.; Buisson-Brenac, C.; Leveque, M.; Martin, P.G.; Theodorou, V.; Fioramonti, J.; Houdeau, E. Impact of oral bisphenol A at reference doses on intestinal barrier function and sex differences after perinatal exposure in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Qu, W.; Chen, Z. Bisphenol A increases intestinal permeability through disrupting intestinal barrier function in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoene, M.; Rytel, L.; Dzika, E.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Kruminis-Kaszkiel, E.; Konrad, P.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Bisphenol A Causes Liver Damage and Selectively Alters the Neurochemical Coding of Intrahepatic Parasympathetic Nerves in Juvenile Porcine Models under Physiological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneva, L.A.; Vyas, A.K.; McEachin, R.C.; Puttabyatappa, M.; Wang, H.S.; Sartor, M.A.; Padmanabhan, V. Developmental programming: Interaction between prenatal BPA and postnatal overfeeding on cardiac tissue gene expression in female sheep. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MohanKumar, S.M.; Rajendran, T.D.; Vyas, A.K.; Hoang, V.; Asirvatham-Jeyaraj, N.; Veiga-Lopez, A.; Olivier, N.B.; Padmanabhan, V.; MohanKumar, P.S. Effects of prenatal bisphenol-A exposure and postnatal overfeeding on cardiovascular function in female sheep. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veiga-Lopez, A.; Moeller, J.; Sreedharan, R.; Singer, K.; Lumeng, C.; Ye, W.; Pease, A.; Padmanabhan, V. Developmental programming: Interaction between prenatal BPA exposure and postnatal adiposity on metabolic variables in female sheep. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E238–E247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Han, S.; Wang, P.; Dong, Z.; Ma, X.; et al. Trans-Fatty Acids Aggravate Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis in C57BL/6 Mice, Possibly by Suppressing the IRS1 Dependent Pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oteng, A.B.; Loregger, A.; van Weeghel, M.; Zelcer, N.; Kersten, S. Industrial Trans Fatty Acids Stimulate SREBP2-Mediated Cholesterogenesis and Promote Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsen, M.U.; Gorst-Rasmussen, A.; Eriksen, H.H.; Stegger, J.; Joensen, A.M.; Tjonneland, A.; Dyerberg, J.; Schmidt, E.B.; Overvad, K. Trans fatty acids in adipose tissue and risk of myocardial infarction: A case-cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Nakanishi, N.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Takakuwa, H.; Hamaguchi, M.; et al. Trans Fatty Acid Intake Induces Intestinal Inflammation and Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkorn, S.; Kanlayaprasit, S.; Jindatip, D.; Tencomnao, T.; Hu, V.W.; Sarachana, T. Sex Differences in the Effects of Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure on Genes Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Silva, A.P.; de Moura, E.G.; Pinheiro, C.R.; Oliveira, E.; Lisboa, P.C. Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure During Breastfeeding on the Biochemical and Endocrine Profiles in Rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.; Ullah, H.; Ullah, W.; Jahan, S. Comparative effects of Bisphenol S and Bisphenol A on the development of female reproductive system in rats; a neonatal exposure study. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerge, D.R.; Twaddle, N.C.; Vanlandingham, M.; Fisher, J.W. Pharmacokinetics of bisphenol A in neonatal and adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 247, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, U.; Loddenkemper, C.; Doerfel, K.; Spieckermann, S.; Haller, D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B.; Kuhl, A.A. A guide to histomorphological evaluation of intestinal inflammation in mouse models. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4557–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Engin, A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar]
- Ranciere, F.; Lyons, J.G.; Loh, V.H.; Botton, J.; Galloway, T.; Wang, T.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J. Bisphenol A and the risk of cardiometabolic disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, Y. The Association between Bisphenol A Exposure and Obesity in Children-A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Arevalo, M.; Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Santos, J.R.D.; Quesada, I.; Carneiro, E.M.; Nadal, A. Exposure to Bisphenol-A during Pregnancy Partially Mimics the Effects of a High-Fat Diet Altering Glucose Homeostasis and Gene Expression in Adult Male Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Ying, C.; Chen, J.; Song, L.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, Z.; Xia, W.; Chen, X.; et al. Perinatal exposure to bisphenol A at reference dose predisposes offspring to metabolic syndrome in adult rats on a high-fat diet. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3049–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaise, Y.; Menard, S.; Cartier, C.; Gaultier, E.; Lasserre, F.; Lencina, C.; Harkat, C.; Geoffre, N.; Lakhal, L.; Castan, I.; et al. Gut dysbiosis and impairment of immune system homeostasis in perinatally-exposed mice to Bisphenol A precede obese phenotype development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfin-Slater, R.B. Carbohydrate-Lipid Effects on Cholesterol Metabolism. J. Dairy Sci. 1967, 50, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambreen, S.; Akhtar, T.; Hameed, N.; Ashfaq, I.; Sheikh, N. In Vivo Evaluation of Histopathological Alterations and Trace Metals Estimation of the Small Intestine in Bisphenol A-Intoxicated Rats. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 9292316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, F.G.; UzunhİSarcikli, M.; AslantÜRk, A.; Kalender, S. Bisfenol A’nın Sıçan İnce Bağırsak Dokusunda Oluşturduğu Histopatolojik Değişiklikler Üzerine Taurin ve Kurkumin’in Koruyucu Rolü. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Mou, D.; Che, L.; Fang, Z.; Feng, B.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Wu, D. Maternal Methyl Donor Supplementation during Gestation Counteracts the Bisphenol A-Induced Impairment of Intestinal Morphology, Disaccharidase Activity, and Nutrient Transporters Gene Expression in Newborn and Weaning Pigs. Nutrients 2017, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szymanska, K.; Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of High and Low Doses of Bisphenol A (BPA) on the Enteric Nervous System of the Porcine Ileum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, J.; Hu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, C.; Ding, Y.; Hou, N.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X. Overnutrition stimulates intestinal epithelium proliferation through beta-catenin signaling in obese mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3736–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Lund, P.K. Role of intestinal inflammation as an early event in obesity and insulin resistance. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Di Leo, V.; Buda, A.; Pinzani, M.; Palu, G.; Martines, D. Increased intestinal permeability in obese mice: New evidence in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G518–G525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eweda, S.M.; Newairy, A.S.A.; Abdou, H.M.; Gaber, A.S. Bisphenol A-induced oxidative damage in the hepatic and cardiac tissues of rats: The modulatory role of sesame lignans. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Mi, K.; Xue, W.; Wei, W.; Yang, H. Acute BPA exposure-induced oxidative stress, depressed immune genes expression and damage of hepatopancreas in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macczak, A.; Duchnowicz, P.; Sicinska, P.; Koter-Michalak, M.; Bukowska, B.; Michalowicz, J. The in vitro comparative study of the effect of BPA, BPS, BPF and BPAF on human erythrocyte membrane; perturbations in membrane fluidity, alterations in conformational state and damage to proteins, changes in ATP level and Na+/K+ ATPase and AChE activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, G.; Liand, M.; Mauduit, C.; Chehade, H.; Benahmed, M.; Simeoni, U.; Siddeek, B. Maternal Exposure to High-Fat Diet Induces Long-Term Derepressive Chromatin Marks in the Heart. Nutrients 2020, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.W.; Friso, S. Epigenetics: A New Bridge between Nutrition and Health. Adv. Nutr. 2010, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Yuan, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Seif, M.M. Bisphenol A-associated alterations in DNA and histone methylation affects semen quality in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 226, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Henafy, H.M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Abd El Aziz, S.A.; Gouda, E.M. Oxidative Stress and DNA methylation in male rat pups provoked by the transplacental and translactational exposure to bisphenol A. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.S.; Nahar, M.S.; Faulk, C.; Jones, T.R.; Liao, C.; Kannan, K.; Weinhouse, C.; Rozek, L.S.; Dolinoy, D.C. Epigenetic responses following maternal dietary exposure to physiologically relevant levels of bisphenol A. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2012, 53, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, Y.; Lima, R.P.A.; Luna, R.C.P.; Monteiro, M.; da Silva, C.S.O.; do Nascimento, R.A.F.; de Farias Lima, K.Q.; Andrade, E.S.A.H.; de Lima Ferreira, F.E.L.; de Toledo Vianna, R.P.; et al. Decrease of the DNA methylation levels of the ADRB3 gene in leukocytes is related with serum folate in eutrophic adults. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, B.G.; Berent, R.M.; Ha, S.E.; Horiguchi, K.; Sasse, K.C.; Becker, L.S.; Ro, S. DNA methylation, through DNMT1, has an essential role in the development of gastrointestinal smooth muscle cells and disease. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duty, S.M.; Mendonca, K.; Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Meeker, J.D.; Ackerman, R.; Cullinane, J.; Faller, J.; Ringer, S. Potential sources of bisphenol A in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hines, C.J.; Jackson, M.V.; Deddens, J.A.; Clark, J.C.; Ye, X.; Christianson, A.L.; Meadows, J.W.; Calafat, A.M. Urinary Bisphenol A (BPA) Concentrations among Workers in Industries that Manufacture and Use BPA in the USA. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2017, 61, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Ladeira, C.; Viegas, S. Occupational Exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA): A Reality That Still Needs to Be Unveiled. Toxics 2017, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huygh, J.; Clotman, K.; Malarvannan, G.; Covaci, A.; Schepens, T.; Verbrugghe, W.; Dirinck, E.; Van Gaal, L.; Jorens, P.G. Considerable exposure to the endocrine disrupting chemicals phthalates and bisphenol-A in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Countdown to 2023: WHO Report on Global Trans Fat Elimination 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.; Khee, S.G.S.; Shuid, A.N.; Muhammad, N.; Suhaimi, F.; Othman, F.; Babji, A.S.; Soelaiman, I.-N. The Effects of Cosmos caudatus on Structural Bone Histomorphometry in Ovariectomized Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 817814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.M.; Goh, Y.M.; Mohtarrudin, N.; Loh, S.P. Germinated brown rice ameliorates obesity in high-fat diet induced obese rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
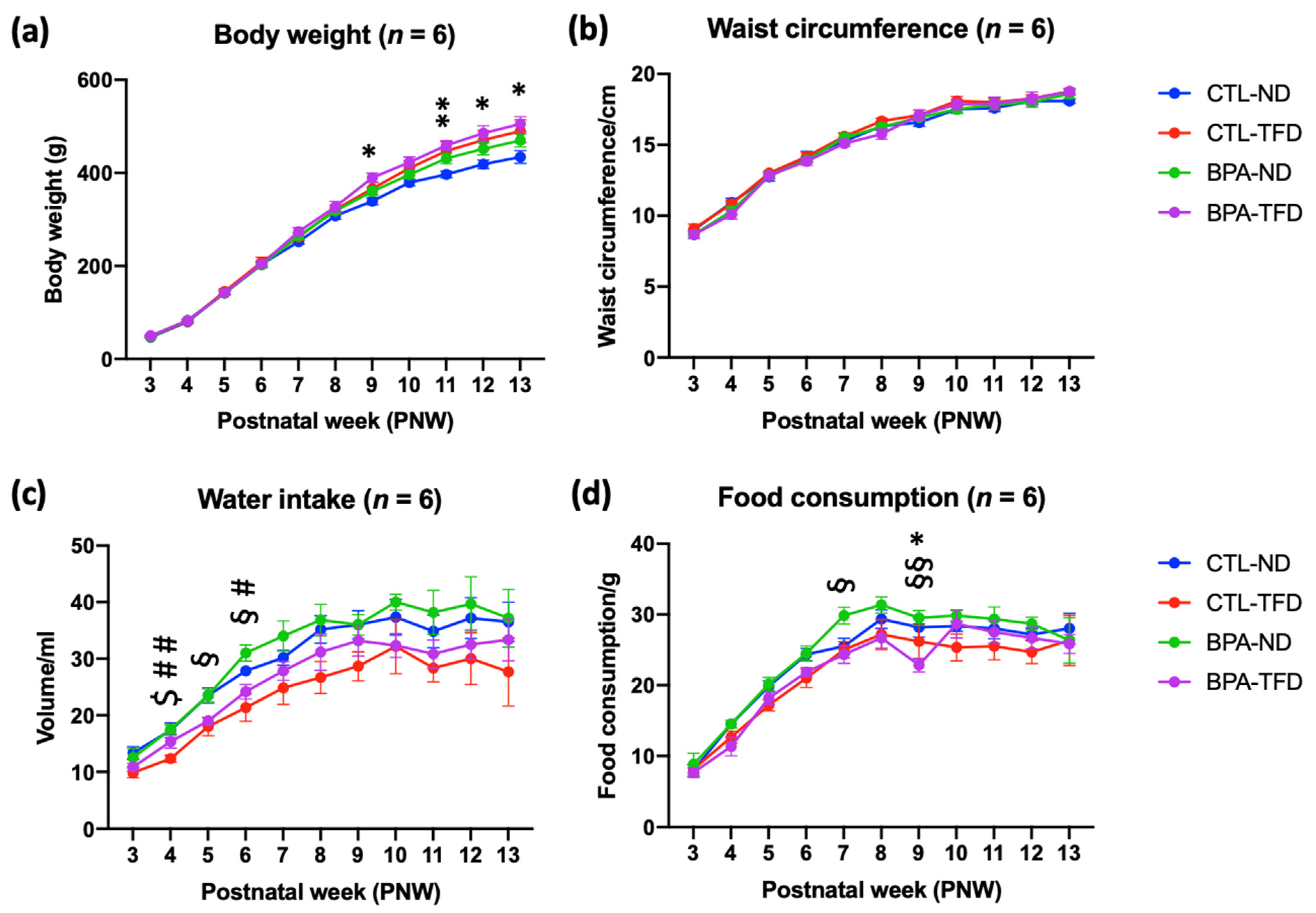
| Parameters | Postnatal Week (PNW) | Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL-ND | CTL-TFD | BPA-ND | BPA-TFD | ||
| Body weight (g) | 3 | 46.8 ± 0.8 | 48.3 ± 2.0 | 47.8 ± 2.2 | 50.0 ± 1.7 |
| 4 | 80.0 ± 2.2 | 81.2 ± 4.2 | 83.0 ± 2.9 | 82.7 ± 2.9 | |
| 5 | 143.0 ± 4.8 | 145.2 ± 0.8 | 141.3 ± 4.0 | 142.2 ± 3.0 | |
| 6 | 203.5 ± 7.2 | 208.3 ± 10.4 | 202.2 ± 5.3 | 204.2 ± 4.0 | |
| 7 | 252.2 ± 5.6 | 262.2 ± 7.3 | 264.7 ± 6.9 | 273.7 ± 8.4 | |
| 8 | 307.8 ± 7.7 | 321.3 ± 9.0 | 318.0 ± 6.2 | 327.3 ± 11.2 | |
| 9 | 339.0 ± 7.2 | 366.3 ± 13.4 | 360.3 ± 8.9 | 389.5 ± 10.0 * | |
| 10 | 379.3 ± 7.1 | 410.2 ± 16.3 | 396.0 ± 8.1 | 422.5 ± 11.8 | |
| 11 | 396.7 ± 7.0 | 447.2 ± 19.8 | 431.2 ± 11.1 | 459.2 ± 10.2 ** | |
| 12 | 418.5 ± 9.1 | 470.7 ± 20.7 | 451.7 ± 13.0 | 485.0 ± 16.2 * | |
| 13 | 434.2 ± 13.7 | 489.8 ± 24.4 | 469.8 ± 13.9 | 505.0 ± 15.6 * | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 3 | 9.0 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 0.3 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | 10.9 ± 0.3 | 10.8 ± 0.3 | 10.3 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.3 | |
| 5 | 12.8 ± 0.3 | 13.0 ± 0.1 | 12.8 ± 0.2 | 12.8 ± 0.2 | |
| 6 | 14.2 ± 0.4 | 14.2 ± 0.3 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | 13.8 ± 0.3 | |
| 7 | 15.3 ± 0.2 | 15.6 ± 0.3 | 15.5 ± 0.3 | 15.1 ± 0.2 | |
| 8 | 16.3 ± 0.3 | 16.7 ± 0.2 | 16.3 ± 0.1 | 15.8 ± 0.4 | |
| 9 | 16.6 ± 0.3 | 17.1 ± 0.8 | 16.9 ± 0.2 | 17.1 ± 0.4 | |
| 10 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 18.1 ± 0.3 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 17.8 ± 0.4 | |
| 11 | 17.6 ± 0.2 | 18.0 ± 0.3 | 17.8 ± 0.4 | 17.9 ± 0.4 | |
| 12 | 18.1 ± 0.2 | 18.3 ± 0.3 | 18.0 ± 0.4 | 18.3 ± 0.5 | |
| 13 | 18.1 ± 0.2 | 18.8 ± 0.2 | 18.6 ± 0.3 | 18.8 ± 0.2 | |
| Water intake (mL) | 3 | 13.3 ± 1.1 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | 12.5 ± 1.6 | 10.8 ± 0.7 |
| 4 | 17.3 ± 1.3 | 12.3 ± 0.6 $ | 17.5 ± 0.8 ## | 15.3 ± 1.1 | |
| 5 | 23.5 ± 1.3 | 18.0 ± 1.6 | 23.5 ± 1.1 | 19.0 ± 0.6 § | |
| 6 | 27.8 ± 0.9 | 21.3 ± 2.4 | 31.0 ± 1.4 # | 24.2 ± 1.3 § | |
| 7 | 30.2 ± 1.3 | 24.8 ± 2.9 | 34.0 ± 2.7 | 27.8 ± 1.6 | |
| 8 | 35.2 ± 2.5 | 26.7 ± 2.8 | 36.8 ± 2.8 | 31.2 ± 3.2 | |
| 9 | 36.0 ± 2.5 | 28.7 ± 2.6 | 36.0 ± 1.8 | 33.2 ± 2.7 | |
| 10 | 37.3 ± 3.1 | 32.2 ± 4.8 | 40.0 ± 1.4 | 32.3 ± 2.1 | |
| 11 | 34.8 ± 2.9 | 28.3 ± 2.4 | 38.2 ± 3.9 | 30.8 ± 2.5 | |
| 12 | 37.2 ± 3.6 | 30.0 ± 4.6 | 39.7 ± 4.8 | 32.5 ± 2.6 | |
| 13 | 36.5 ± 3.5 | 27.7 ± 6.0 | 37.2 ± 5.1 | 33.3 ± 3.7 | |
| Food intake (g) | 3 | 8.0 ± 0.8 | 8.2 ± 0.5 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 7.7 ± 0.7 |
| 4 | 14.5 ± 0.6 | 12.7 ± 0.8 | 14.5 ± 0.6 | 11.3 ± 1.3 | |
| 5 | 19.8 ± 0.8 | 17.2 ± 0.8 | 20.2 ± 0.9 | 18.2 ± 0.9 | |
| 6 | 24.3 ± 0.9 | 21.0 ± 1.3 | 24.5 ± 1.1 | 21.8 ± 0.7 | |
| 7 | 25.5 ± 1.1 | 25.0 ± 1.2 | 29.8 ± 1.2 | 24.3 ± 1.3 § | |
| 8 | 29.3 ± 1.3 | 27.2 ± 2.1 | 31.3 ± 1.1 | 26.7 ± 1.4 | |
| 9 | 28.2 ± 1.4 | 26.2 ± 2.5 | 29.5 ± 1.1 | 22.8 ± 0.9 *§§ | |
| 10 | 28.3 ± 0.7 | 25.3 ± 1.9 | 29.8 ± 0.7 | 28.7 ± 2.0 | |
| 11 | 28.0 ± 1.5 | 25.5 ± 1.9 | 29.3 ± 1.7 | 27.5 ± 1.6 | |
| 12 | 27.2 ± 0.8 | 24.7 ± 1.6 | 28.7 ± 1.0 | 26.7 ± 1.5 | |
| 13 | 28.0 ± 2.2 | 26.3 ± 3.6 | 26.3 ± 3.2 | 25.8 ± 1.3 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zulkifli, S.; Mohd Nor, N.S.; Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S.H.; Mohd Ranai, N.; Mohd Kornain, N.K.; Wan Mohd Zain, W.N.I.; Abdul Aziz, M. Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alter Small Intestinal Morphology and Its Global DNA Methylation in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats, Leading to Obesity Development. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122382
Zulkifli S, Mohd Nor NS, Sheikh Abdul Kadir SH, Mohd Ranai N, Mohd Kornain NK, Wan Mohd Zain WNI, Abdul Aziz M. Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alter Small Intestinal Morphology and Its Global DNA Methylation in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats, Leading to Obesity Development. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122382
Chicago/Turabian StyleZulkifli, Sarah, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir, Norashikin Mohd Ranai, Noor Kaslina Mohd Kornain, Wan Nor I’zzah Wan Mohd Zain, and Mardiana Abdul Aziz. 2022. "Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alter Small Intestinal Morphology and Its Global DNA Methylation in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats, Leading to Obesity Development" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122382
APA StyleZulkifli, S., Mohd Nor, N. S., Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S. H., Mohd Ranai, N., Mohd Kornain, N. K., Wan Mohd Zain, W. N. I., & Abdul Aziz, M. (2022). Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Postnatal Trans Fat Diet Alter Small Intestinal Morphology and Its Global DNA Methylation in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats, Leading to Obesity Development. Nutrients, 14(12), 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122382






