α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Vimentin Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Treatment for TGF-β1-Induced EMT Analysis
2.4. Cell Invasion Assay
2.5. In Vitro Wound-Healing Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining Assay
2.7. Gelatin Zymography Analysis
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. ROS Detection Assay
2.10. In Vivo Xenograft Metastasis Experiments
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Blocked TGF-β1-Induced Invasion and Migration in NSCLC Cell Line A549
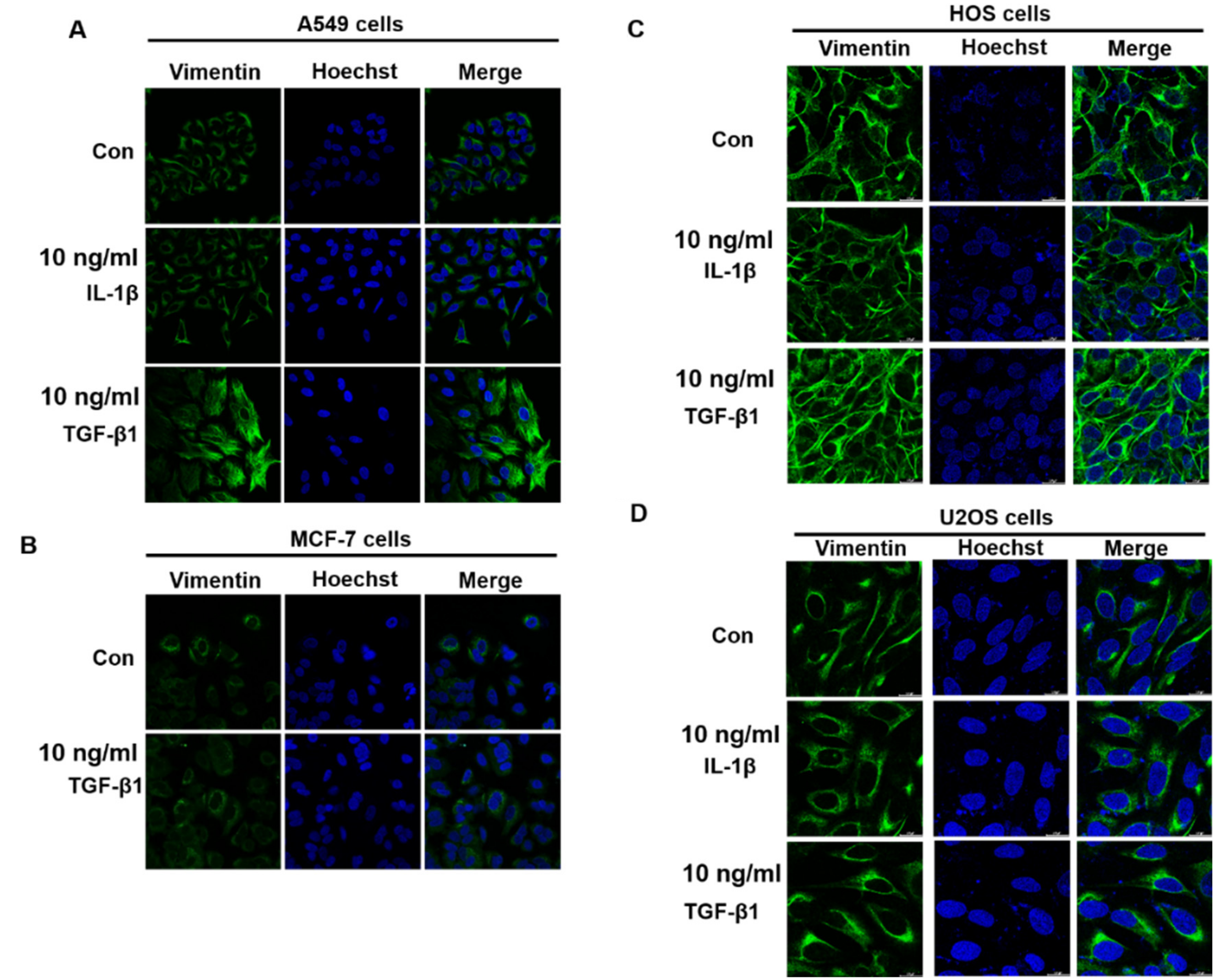
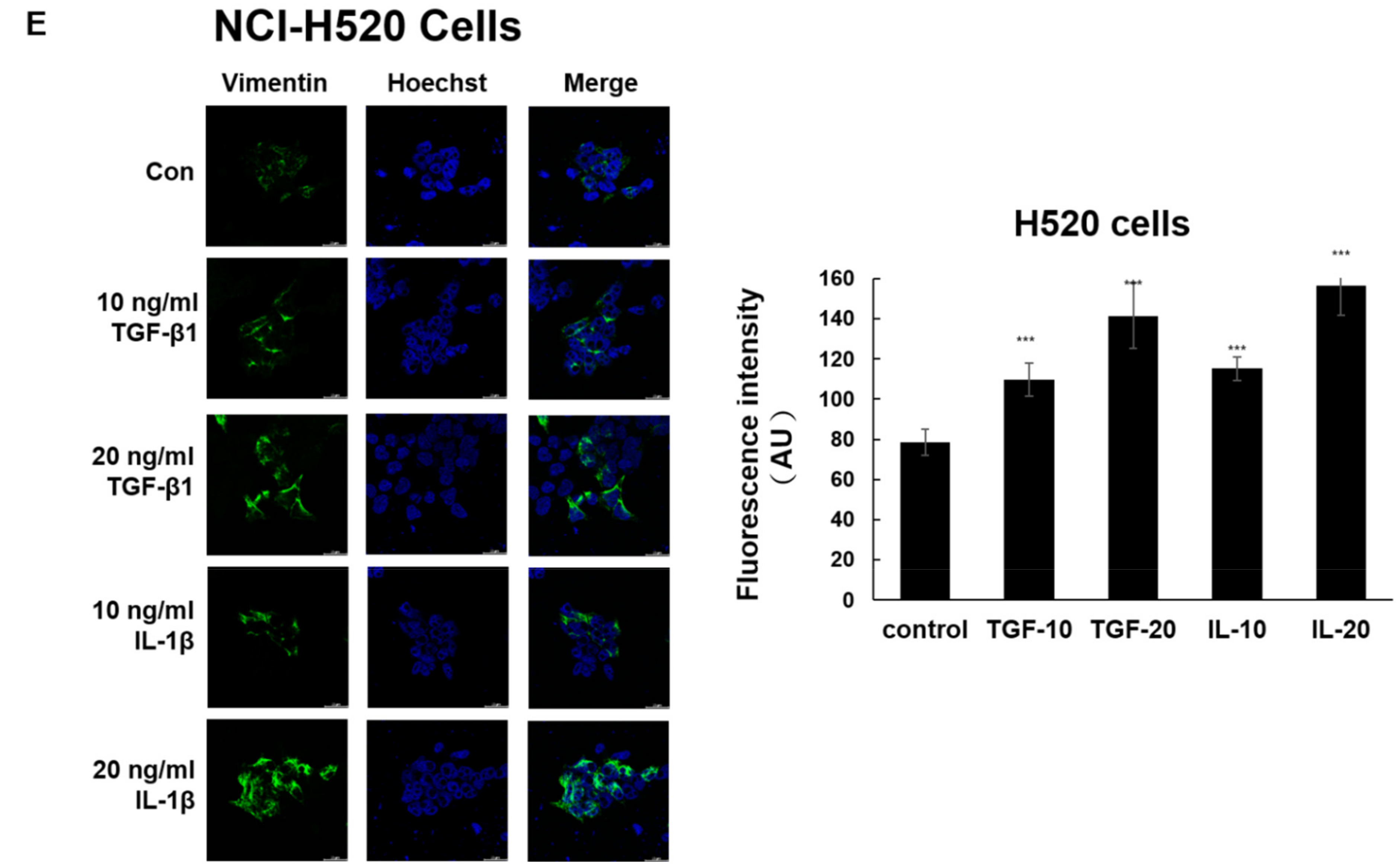
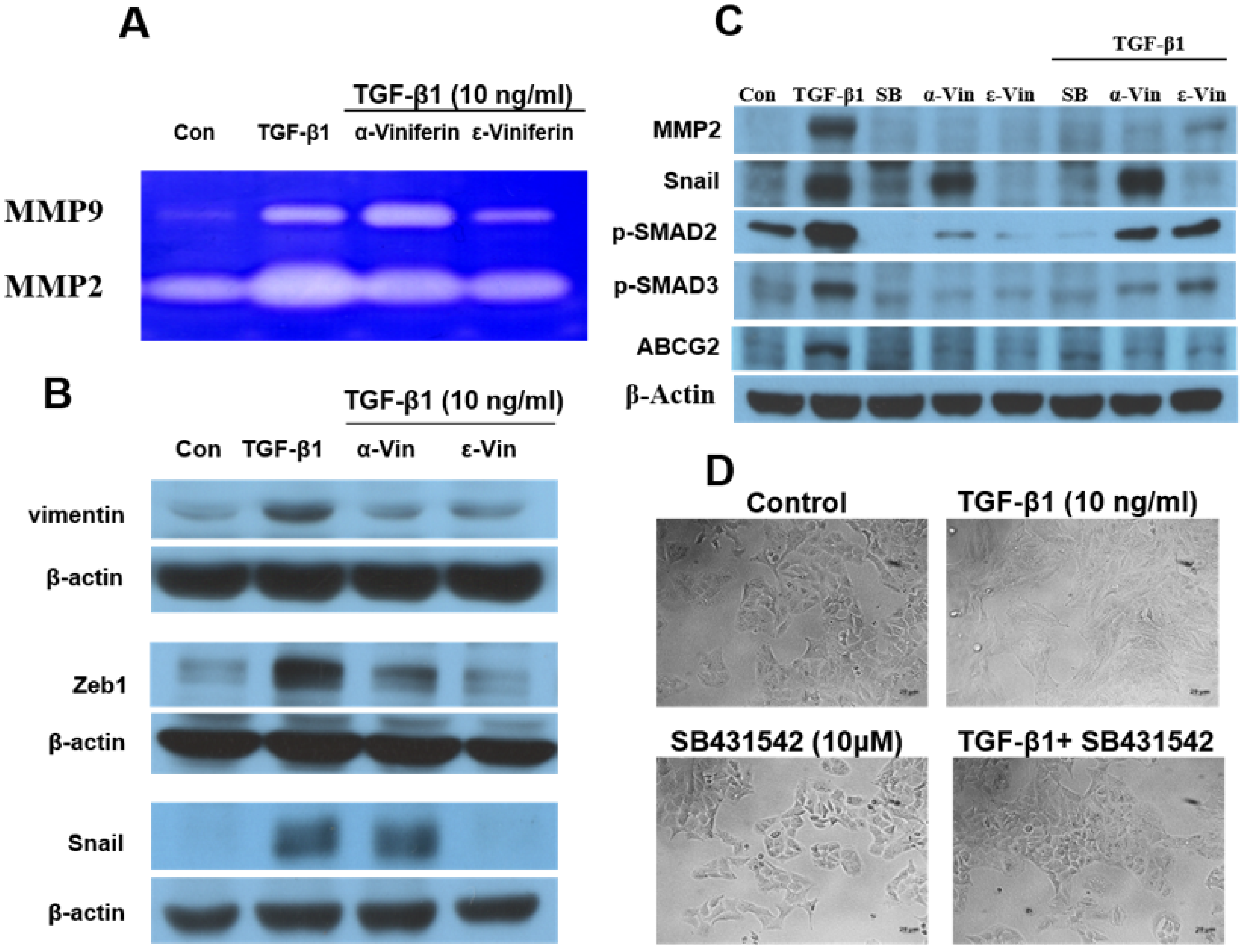
3.2. α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1- or IL-1β-Induced Vimentin Expression in NSCLC Cell Lines A549 and NCI-H460
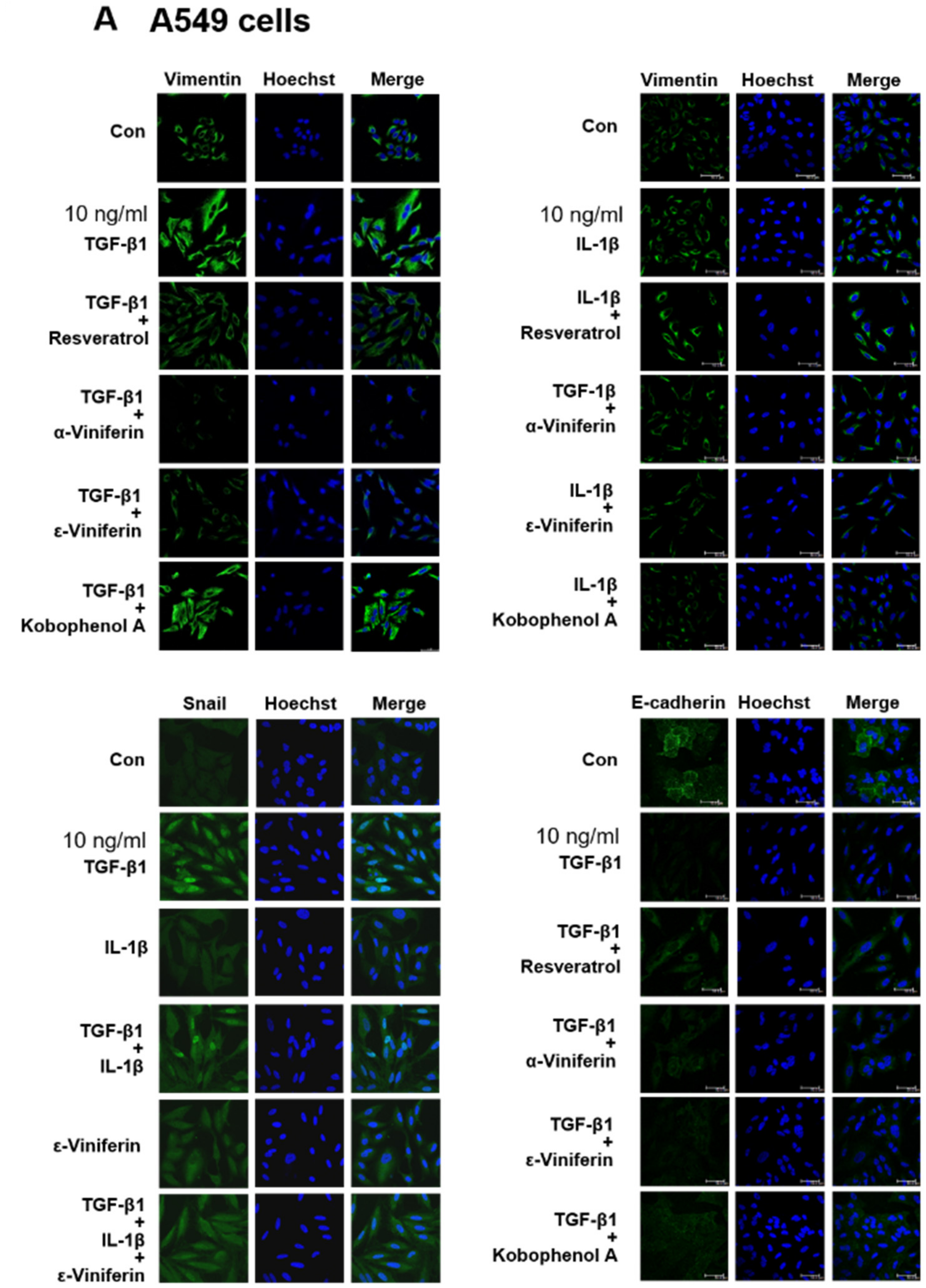
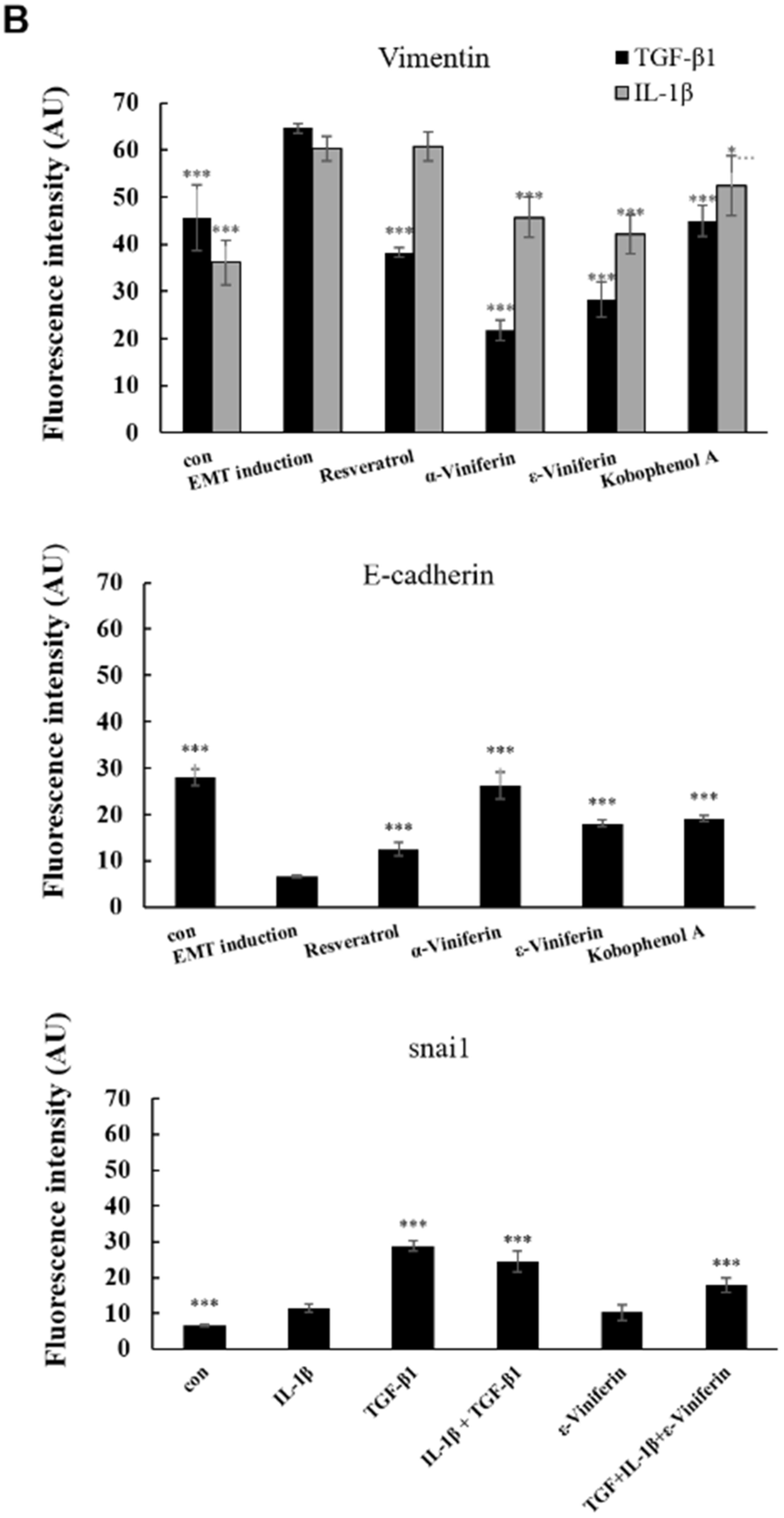
3.3. α-Viniferin, ε-Viniferin, and SB431542 Blocked TGF-β1-Induced Vimentin, Zeb1, Snail, MMP2, ABCG2, and SMAD2/SMAD3 Activation in NSCLC Cell Line A549
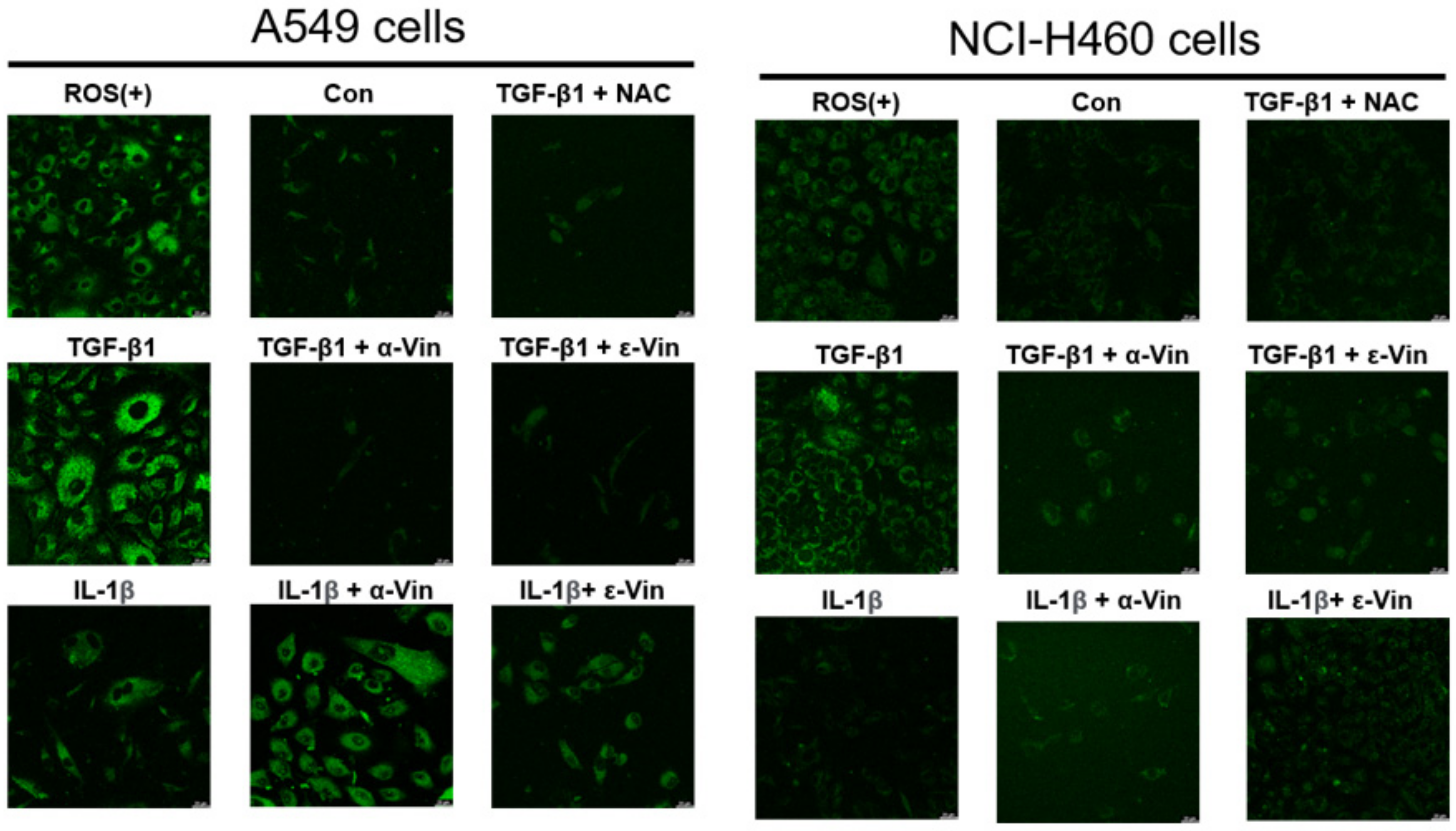
3.4. Induction of ROS Production in A549 and NCI-H460 Cells by TGF-β1 and Protective Effect of α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin against TGF-β1-Induced ROS Production
3.5. ε-Viniferin Inhibited A549 Cell Metastasis In Vivo
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razzaghi, H.; Saraiya, M.; Thompson, T.D.; Henley, S.J.; Viens, L.; Wilson, R. Five-year relative survival for human papillomavirus-associated cancer sites. Cancer 2018, 124, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, H.; et al. Exosomes with low miR-34c-3p expression promote invasion and migration of non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating integrin alpha2beta1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, V.; Brabletz, T.; Ceppi, P. Targeting EMT in Cancer with Repurposed Metabolic Inhibitors. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Streel, G.; Lucas, S. Targeting immunosuppression by TGF-beta1 for cancer immunotherapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.L.; Blobe, G.C. Role of transforming growth factor Beta in human cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2078–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Baker, D.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koushki, M.; Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Ahmadi, N.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M. Resveratrol: A miraculous natural compound for diseases treatment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2473–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.M.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhao, M.; Su, S.B. Resveratrol Inhibits the Migration and Metastasis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer by Reversing TGF-beta1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Molecules 2019, 24, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Yan, L.; Jiang, H.; Ren, J.; Cai, J.; Li, Q. Resveratrol suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through TGF-beta1/Smads signaling pathway mediated Snail/E-cadherin expression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Alder, H.; Volinia, S.; Delmas, D.; Latruffe, N.; Croce, C.M. Resveratrol modulates the levels of microRNAs targeting genes encoding tumor-suppressors and effectors of TGFbeta signaling pathway in SW480 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Resveratrol inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer invasion and metastasis. Toxicology 2013, 303, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; He, C.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, P. Update on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Naturally Occurring Resveratrol Oligomers. Molecules 2017, 22, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Di, J.M.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, K.J.; Wei, X.; Shi, Z. Resveratrol oligomers for the prevention and treatment of cancers. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 765832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazaki, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Sherpa, M.; Nakajima, M.; Matsuyama, M.; Kiwamoto, T.; Morishima, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Hizawa, N. ROS-Nrf2 pathway mediates the development of TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the activation of Notch signaling. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 100, 151181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk-Kasiuchnicz, A.; Ramlau, R.; Stencel, K. Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, D.; Savic Prince, S.; Rothschild, S.I. Targeted Therapy in Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. An Update on Treatment of the Most Important Actionable Oncogenic Driver Alterations. Cancers 2021, 13, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghonda, N.; Yoshida, S.; Araki, M.; Kusunoki, M.; Mliki, A.; Ghorbel, A.; Miyazaki, H. Greater effectiveness of epsilon-viniferin in red wine than its monomer resveratrol for inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Courtois, A.; Atgie, C.; Marchal, A.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Lapeze, C.; Faure, C.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. Tissular Distribution and Metabolism of trans-epsilon-Viniferin after Intraperitoneal Injection in Rat. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Min, J.S.; Kim, D.; Zheng, Y.F.; Mailar, K.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, C.; Bae, S.K. A simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for trans-epsilon-viniferin quantification in mouse plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Bhowmick, N.A. Role of EMT in Metastasis and Therapy Resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Tseng, J.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Tung, C.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Yeh, Y.C.; Chou, T.Y.; Yang, M.H.; et al. ABCG2 localizes to the nucleus and modulates CDH1 expression in lung cancer cells. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kali, A.; Ostapchuk, Y.O.; Belyaev, N.N. TNFalpha and TGFbeta-1 synergistically increase the cancer stem cell properties of MiaPaCa-2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, N.D.; Yang, K.; Shim, J.W.; Heo, K. Estradiol, TGF-beta1 and hypoxia promote breast cancer stemness and EMT-mediated breast cancer migration. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masola, V.; Carraro, A.; Granata, S.; Signorini, L.; Bellin, G.; Violi, P.; Lupo, A.; Tedeschi, U.; Onisto, M.; Gambaro, G.; et al. In vitro effects of interleukin (IL)-1 beta inhibition on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular and hepatic stellate cells. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jee, Y.S.; Jang, T.J.; Jung, K.H. Prostaglandin E(2) and interleukin-1beta reduce E-cadherin expression by enhancing snail expression in gastric cancer cells. J. Kor. Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Garduno, A.M.; Mendoza-Rodriguez, M.G.; Urrutia-Cabrera, D.; Dominguez-Robles, M.C.; Perez-Yepez, E.A.; Ayala-Sumuano, J.T.; Meza, I. IL-1beta induced methylation of the estrogen receptor ERalpha gene correlates with EMT and chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, L.A.; McIlroy, E.I.; Gorowiec, M.R.; Brodlie, M.; Johnson, G.E.; Ward, C.; Lordan, J.L.; Corris, P.A.; Kirby, J.A.; Fisher, A.J. Inflammation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung transplant recipients: Role in dysregulated epithelial wound repair. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ong, S.L.; Tran, L.M.; Jing, Z.; Liu, B.; Park, S.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Walser, T.C.; Heinrich, E.L.; Lee, G.; et al. Chronic IL-1beta-induced inflammation regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition memory phenotypes via epigenetic modifications in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X. Inflammatory cytokines augments TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells by up-regulating TbetaR-I. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2008, 65, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.; Qin, L.; Fang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yue, J.; Bai, W.; Wang, G.; Chen, Z.; Renz, H.; et al. IL-1beta augments TGF-beta inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial cells and associates with poor pulmonary function improvement in neutrophilic asthmatics. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancel, J.; Birembaut, P.; Dewolf, M.; Durlach, A.; Nawrocki-Raby, B.; Dalstein, V.; Delepine, G.; Blacher, S.; Deslee, G.; Gilles, C.; et al. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 and Vimentin: A Tandem Marker as Prognostic Factor in NSCLC. Cancers 2019, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satelli, A.; Li, S. Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3033–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rho, J.H.; Roehrl, M.H.; Wang, J.Y. Glycoproteomic analysis of human lung adenocarcinomas using glycoarrays and tandem mass spectrometry: Differential expression and glycosylation patterns of vimentin and fetuin A isoforms. Protein J. 2009, 28, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiou, W.-C.; Huang, C.; Lin, Z.-J.; Hong, L.-S.; Lai, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-C.; Huang, H.-C. α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Vimentin Expression. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112294
Chiou W-C, Huang C, Lin Z-J, Hong L-S, Lai Y-H, Chen J-C, Huang H-C. α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Vimentin Expression. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112294
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiou, Wei-Chung, Cheng Huang, Zi-Jun Lin, Lian-Sheng Hong, Yu-Heng Lai, Jui-Chieh Chen, and Hsiu-Chen Huang. 2022. "α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Vimentin Expression" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112294
APA StyleChiou, W.-C., Huang, C., Lin, Z.-J., Hong, L.-S., Lai, Y.-H., Chen, J.-C., & Huang, H.-C. (2022). α-Viniferin and ε-Viniferin Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Vimentin Expression. Nutrients, 14(11), 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112294





