Research on Environmental Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Participants
2.2. Geographical Division of Research Objects
2.3. Anthropometry and the Classification Criteria for Overweight and Obesity
2.4. Mathematical Processing
2.4.1. Socioeconomic Status
2.4.2. Gross Domestic Product
2.4.3. Engel Coefficient
2.4.4. Urbanization Level
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Situation
3.1.1. Distribution Characteristics of Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescents Aged 10–18
3.1.2. Distribution Characteristics of Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescents in Various Provinces
3.2. Research on Natural Environmental Factors Affecting Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescents
3.3. Research on Social Environmental Factors Affecting Nutritional Status of Children and Adolescents
3.4. Logistic Regression Analysis of Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents
3.4.1. Logistic Regression Analysis of Influencing Factors of Overweight in Children and Adolescents
3.4.2. Logistic Regression Analysis of Factors Affecting Obesity in Children and Adolescents
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Overweight and Obesity Status in Children and Adolescents in China
4.2. Analysis of the Relationship between Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents and Factors Affecting the Natural Environment
4.3. Analysis of the Relationship between Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents and Factors Affecting the Social Environment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
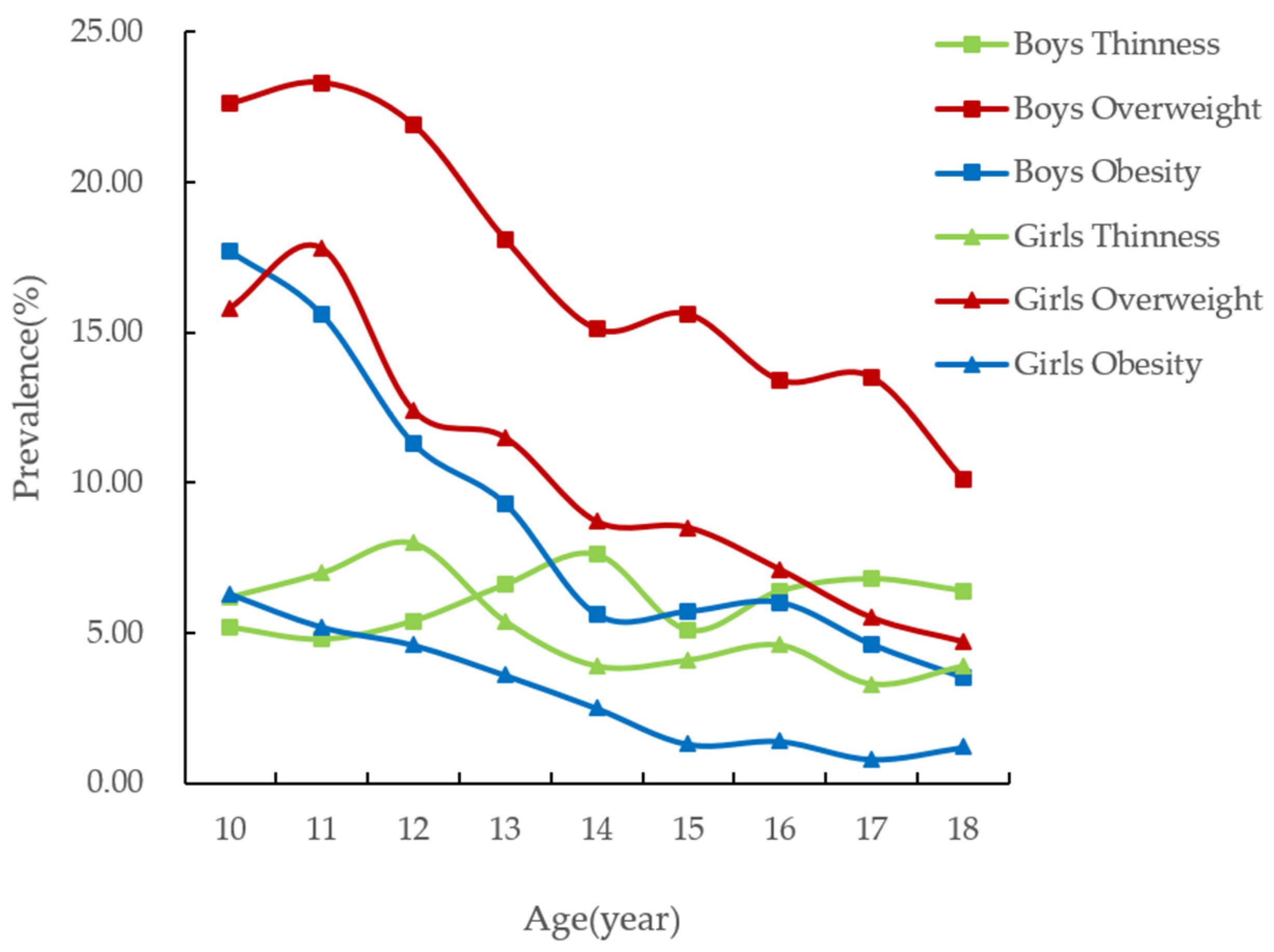
- Among children and adolescents aged 10 to 18, the prevalence of overweight and obesity generally decreases with age, and the overweight and obesity rates of boys are higher than those of girls. The highest was at the age of 10, but the overweight prevalence was highest at the age of 11.
- (2)
- The risk of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents increases with latitude; high altitude reduces the risk of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents.
- (3)
- The risk of overweight in children and adolescents increases with the increase in family SES and GDP; the higher the degree of urbanization, the greater the risk of obesity in children and adolescents.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Li, X.; Pan, J. Study on the prevalence of childhood overweight and underweight, and the association with family socio-economic status (SES). Wei Sheng Yan Jiu J. Hyg. Res. 2014, 43, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-J.; Fu, L.-G.; Ma, J.; Song, Y.; Hu, P.-J.; Zhang, B. Relationship between obesity, overweight and physical function in students of Han nationality aged 7–18 years in 2010. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 46, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradise, A.W.; Kernis, M.H. Self-esteem and Psychological Well-being: Implications of Fragile Self-esteem. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 2002, 21, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wild, T.C.; Kipp, W.; Kuhle, S.; Veugelers, P. The influence of childhood obesity on the development of self-esteem. Health Rep. 2009, 20, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; SongYan, L.Q. Meta-Analysis of Chinese Obese Adolescents Weight-losing Effect by Exercise. J. Shenyang Sport Univ. 2017, 36, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, A.; Barendregt, J.J.; Willekens, F.; MacKenbach, J.P.; Mamun, A.; Bonneux, L. Obesity in Adulthood and Its Consequences for Life Expectancy: A Life-Table Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.-Y.; Sun, J.-L.; Chen, T.-J. Dynamic analysis on the prevalence of obesity and overweight school-age children and adolescents in recent 15 years in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2004, 25, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. The current situation and countermeasures of childhood obesity. Chin. J. Med. 2005, 5, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Student Physique and Health Research Group. Report on the Physical Fitness and Health Surveillance of Chinese School Students; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2008; p. 521. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.Y. Childhood Simple Obesity; Henan Science and Technology Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2005; p. 350. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H. The prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents in China. Chin. J. Dis. Control. Prev. 2017, 21, 866–869. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.W.; Ge, M.; Cao, L.X.; Zhang, Y.P. Relationship between Reference Value of Chinese Adolescent Male Vital Capacity and Geographical Factors Based on Partial Least Squares Regression. J. Biomath. 2011, 26, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y. On the Regional Difference of Human Height and Its Causes. Hum. Geogr. 1993, 8, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.A.; Finch, B.K.; Bower, A.; Sastry, N. Collective efficacy and obesity: The potential influence of social factors on health. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikireddi, S.V.; Whitley, E.; Lewsey, J.; Gray, L.; Leyland, A.H. Socioeconomic status as an effect modifier of alcohol consumption and harm: Analysis of linked cohort data. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e267–e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Song, F.; Xu, W.; Pallard-Borg, S.; Qi, X. Relation of socioeconomic status to overweight and obesity: A large population-based study of Chinese adults. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2017, 44, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, R.E.; Fisher, J.O.; Taveras, E.M.; Geller, A.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Land, T.; Perkins, M.; Davison, K.K. Reasons Low-Income Parents Offer Snacks to Children: How Feeding Rationale Influences Snack Frequency and Adherence to Dietary Recommendations. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5982–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Information Management of Surveying and Mapping Site. Available online: http://www.nasg.gov.cn/ (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Baidu Map. Altitude Query Tool. Available online: https://www.chahaiba.com/ (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Tong, L.M. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Vegetation Change and Its Impact Factors in the Mid-Latitude Boundary Belt of East Asian Summer Monsoon in China. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2017; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, A.B.; Wang, S.G.; Shang, K.Z.; Su, J.L. Variation characteristics of different grades of precipitation in the mid-latitude zone of mainland China. J. Desert Res. 2017, 2, 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J. New Chinese Geography; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The Child Growth Standards. Available online: https://www.who.int/growthref/who2007_bmi_for_age_field/en/ (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Compiled by National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Programme for International Student Assessment. PISA 2003 Technical Report; OECD Publishing: Paris, French, 2003; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Ganzeboom, H.; Treiman, D.J. Internationally Comparable Measures of Occupational Status for the 1988 International Standard Classification of Occupations. Soc. Sci. Res. 1996, 25, 201–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Data Team. New Country Classifications by Income Level: 2017–2018. Available online: http://blogs.worldbank.org/zh-hans/opendata/new-country-classifications-income-level-2017-2018 (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/home/zh/ (accessed on 27 June 2019).
- Kelishadi, R.; Haghdoost, A.; Sadeghirad, B.; Khajehkazemi, R. Trend in the prevalence of obesity and overweight among Iranian children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition 2014, 30, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Wu, H.; Chai, X.; Yang, X. Trends in Overweight and Obesity among Children and Adolescents in China from 1991 to 2015: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, F.B.; Wu, L.J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. Child and Adolescent Health; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 420. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, S.K.; Luo, J.S.; Fan, X.; Feng, Y. Epidemiologic status and influencing factors of obesity in children and adolescents. Chin. J. Child Health Care 2011, 19, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Status of obesity and its influencing factors among pupils in Changning District, Shanghai. Chin. J. Sch. Dr. 2012, 26, 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.L.; Li, W.; Wang, W.Y. Study on Comprehensive Intervention for Obesity among Preschool Children. Chin. J. Soc. Med. 2014, 31, 204–206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Shan, C.D.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.H.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, W.X.; Shen, B.; Dai, Y.M. Study on the relationship between dietary behaviors and overweight and obesity of primary and middle school students. Chin. J. Dis. Control. Prev. 2010, 14, 603–605. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.Y. A Comprehensive Survey of Health-Related Risk Behaviors among Adolescents in China 2005; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2007; p. 357. [Google Scholar]
- The National Task Force on Childhood Obesity and National Center for Women’s and Children’s Health. National epidemio-logical survey on childhood obesity, 2006. Chin. J. Pediatrics 2008, 46, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.G.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Xue, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Du, W.W.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.R.; Zhai, F.Y.; et al. Dietary patterns and their associations with childhood obesity in China. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W. The distribution of obese people in China decreases from north to south, and the proportion of obese people in Beijing and Shanghai exceeds 40%. China Food 2015, 22, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.L. Ecological Epidemiology Study on Food and Obesity Environment of Children and Adolescents Aged 7~17 in China (2000~2011); Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Hernández-Vásquez, A.; Bendezú-Quispe, G.; Díaz-Seijas, D.; Santero, M.; Minckas, N.; Azañedo, D.; Antiporta, D.A. Análisis espacial del sobrepeso y la obesidad infantil en el Perú, 2014. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2016, 33, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y. A Study on the Physical Development and Influencing Factors of Chinese Children and Adolescents. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 12 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.H.; He, L.; Chen, J.S. Research on the Changing Trend of Food Intake of Residents in North and South China. J. Hyg. Res. 2006, 35, 487–489. [Google Scholar]
- Pawson, I.G. Growth and development in high altitude populations: A review of Ethiopian, Peruvian, and Nepalese studies. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Series B. Biol. Sci. 1976, 194, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoh, W.E.; Israel-Aina, Y.T.; Sadoh, A.E.; Uduebor, J.E.; Shaibu, M.; Ogonor, E.; Enugwuna, F.C. Comparison of obesity, overweight and elevated blood pressure in children attending public and private primary schools in Benin City, Nigeria. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 20, 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Su, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Trend of dietary nutrient intake among adult females in 9 provinces in China, 2000–2011. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2015, 36, 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, X.L.; Tong, F.; Sun, S.L. The influence of parental obesity on childhood obesity. China Public Health 2002, 18, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Tao, X. Evolution and assessment on China’s urbanization 1960–2010: Under-urbanization or over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.J.; Jia, L.Q.; Gao, X.D.; Guo, Q. Comparative Study of Physical Fitness between Migrant Workers’ School Children and Those of the Shanghai Natives. J. Chengdu Sport Univ. 2011, 37, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wu, S.S.; Li, B.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, S.W.; Zhang, B. Investigationon Physical Activity Among Children and Adolescents with Different Nutritional Statusin Five Cities in China. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2009, 30, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.-H.; Qian, Z.M.; Liu, M.-M.; Wang, D.; Ren, W.-H.; Flick, L.H.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Simckes, M.; et al. Ambient air pollution and the prevalence of obesity in chinese children: The seven northeastern cities study. Obesity 2012, 22, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-X.; Zhao, J.-S.; Chu, Z. Trends in overweight and obesity among rural children and adolescents from 1985 to 2014 in Shandong, China. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.S. On the relationship between urbanization rate and economic development level. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2014, 12, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
| Boy (n = 13,068) | Girl (n = 13,052) | Total (n = 26,120) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Ratio/% | N | Ratio/% | N | Ratio/% | |
| Latitude | ||||||
| Low | 4961 | 38 | 4966 | 38 | 9927 | 38 |
| Middle | 5576 | 42.7 | 5631 | 43.1 | 11,207 | 42.9 |
| High | 2531 | 19.4 | 2455 | 18.8 | 4986 | 19.1 |
| Altitude | ||||||
| Low | 9154 | 70 | 9201 | 70.5 | 18,355 | 70.3 |
| Medium | 2471 | 18.9 | 2330 | 17.9 | 4801 | 18.4 |
| High | 1443 | 11 | 1521 | 11.7 | 2964 | 11.3 |
| SES | ||||||
| Low | 1640 | 12.5 | 1862 | 14.3 | 3502 | 13.4 |
| Middle | 5682 | 43.5 | 5827 | 44.6 | 11,509 | 44.1 |
| High | 5746 | 44 | 5363 | 41.1 | 11,109 | 42.5 |
| Degree of urbanization | ||||||
| Worst | 1003 | 7.7 | 1229 | 9.4 | 2232 | 8.5 |
| Lower | 3003 | 23 | 3057 | 23.4 | 6060 | 23.2 |
| Middle and upper | 2511 | 19.2 | 2439 | 18.7 | 4950 | 19 |
| Best | 6551 | 50.1 | 6327 | 48.5 | 12,878 | 49.3 |
| GDP | ||||||
| Medium income | 788 | 6 | 766 | 5.9 | 1554 | 5.9 |
| Middle and upper | 8933 | 68.4 | 9043 | 69.3 | 17,976 | 68.8 |
| High income | 3347 | 25.6 | 3243 | 24.8 | 6590 | 25.2 |
| Engel coefficient | ||||||
| Well-off | 992 | 7.6 | 979 | 7.5 | 1971 | 7.5 |
| Rich | 6549 | 50.1 | 6525 | 50 | 13,074 | 50.1 |
| Richest | 5527 | 42.3 | 5548 | 42.5 | 11,075 | 42.4 |
| Age (Years) | N | Boys | N | Girls | Total | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | ||||
| 10 | 1437 | 5.2 | 54.5 | 22.6 | 17.7 | 1482 | 6.2 | 71.7 | 15.8 | 6.3 | 2919 | 5.7 | 63.2 | 19.2 | 11.9 |
| 11 | 1509 | 4.8 | 56.3 | 23.3 | 15.6 | 1476 | 7.0 | 70.0 | 17.8 | 5.2 | 2985 | 5.9 | 63.1 | 20.6 | 10.5 |
| 12 | 1473 | 5.4 | 61.4 | 21.9 | 11.3 | 1469 | 8.0 | 75.0 | 12.4 | 4.6 | 2942 | 6.7 | 68.2 | 17.1 | 7.9 |
| 13 | 1550 | 6.6 | 66.0 | 18.1 | 9.3 | 1510 | 5.4 | 79.5 | 11.5 | 3.6 | 3060 | 6.0 | 72.6 | 14.8 | 6.5 |
| 14 | 1544 | 7.6 | 71.7 | 15.1 | 5.6 | 1497 | 3.9 | 84.9 | 8.7 | 2.5 | 3041 | 5.8 | 78.2 | 11.9 | 4.0 |
| 15 | 1541 | 5.1 | 73.6 | 15.6 | 5.7 | 1500 | 4.1 | 86.1 | 8.5 | 1.3 | 3041 | 4.6 | 79.8 | 12.1 | 3.6 |
| 16 | 1473 | 6.4 | 74.1 | 13.4 | 6.0 | 1534 | 4.6 | 87.0 | 7.1 | 1.4 | 3007 | 5.5 | 80.7 | 10.2 | 3.6 |
| 17 | 1379 | 6.8 | 75.1 | 13.5 | 4.6 | 1382 | 3.3 | 90.4 | 5.5 | 0.8 | 2761 | 5.0 | 82.8 | 9.5 | 2.7 |
| 18 | 1162 | 6.4 | 80.0 | 10.1 | 3.5 | 1202 | 3.9 | 90.2 | 4.7 | 1.2 | 2364 | 5.1 | 85.2 | 7.4 | 2.3 |
| Tatal | 13,068 | 6.0 | 67.8 | 17.2 | 8.9 | 13,052 | 5.2 | 81.4 | 10.4 | 3.0 | 26,120 | 5.6 | 74.6 | 13.8 | 6.0 |
| Province | N | Boy | N | Girl | Total | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Normal Weight | Overweight | Obesity | ||||
| Shanghai | 900 | 2.6 | 64.1 | 21.8 | 11.6 | 880 | 2.6 | 80.0 | 13.6 | 3.8 | 1780 | 2.6 | 72 | 17.8 | 7.7 |
| Heilongjiang | 842 | 7.1 | 58.3 | 20.7 | 13.9 | 779 | 5.4 | 75.7 | 13.9 | 5.0 | 1621 | 6.3 | 66.7 | 17.4 | 9.6 |
| Hebei | 724 | 7.0 | 65.1 | 18.2 | 9.7 | 865 | 4.9 | 80.8 | 11.4 | 2.9 | 1589 | 5.9 | 73.6 | 14.5 | 6 |
| Henan | 835 | 5.4 | 70.2 | 17.0 | 7.4 | 792 | 5.4 | 83.3 | 8.0 | 3.3 | 1627 | 5.4 | 76.6 | 12.6 | 5.4 |
| Shanxi | 819 | 4.6 | 66.2 | 19.0 | 10.1 | 768 | 3.8 | 80.5 | 11.7 | 4.0 | 1587 | 4.2 | 73.1 | 15.5 | 7.2 |
| Jiangsu | 778 | 3.5 | 72.8 | 17.6 | 6.2 | 767 | 3.3 | 85.5 | 8.6 | 2.6 | 1545 | 3.4 | 79.1 | 13.1 | 4.4 |
| Zhejiang | 900 | 6.6 | 69.4 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 900 | 6.0 | 80.9 | 10.2 | 2.9 | 1800 | 6.3 | 75.2 | 13.1 | 5.4 |
| Anhui | 738 | 6.9 | 69.5 | 15.7 | 7.9 | 733 | 9.1 | 79.8 | 8.3 | 2.7 | 1471 | 8 | 74.6 | 12 | 5.3 |
| Jiangxi | 880 | 9.0 | 75.6 | 10.6 | 4.9 | 900 | 9.8 | 84.0 | 4.2 | 2.0 | 1780 | 9.4 | 79.8 | 7.4 | 3.4 |
| Sichuan | 727 | 6.1 | 69.9 | 14.6 | 9.5 | 707 | 2.7 | 83.2 | 12.2 | 2.0 | 1434 | 4.4 | 76.4 | 13.4 | 5.8 |
| Guizhou | 724 | 6.2 | 74.3 | 13.0 | 6.5 | 807 | 5.0 | 86.9 | 6.7 | 1.5 | 1531 | 5.6 | 80.9 | 9.7 | 3.9 |
| Fujian | 791 | 4.7 | 61.6 | 23.5 | 10.2 | 775 | 3.6 | 81.5 | 11.1 | 3.7 | 1566 | 4.2 | 71.5 | 17.4 | 7 |
| Hainan | 900 | 8.7 | 70.8 | 13.3 | 7.2 | 900 | 5.8 | 83.1 | 8.3 | 2.8 | 1800 | 7.2 | 76.9 | 10.8 | 5 |
| Xinjiang | 788 | 3.8 | 65.1 | 20.2 | 10.9 | 775 | 4.1 | 80.5 | 13.2 | 2.2 | 1563 | 4 | 72.7 | 16.7 | 6.6 |
| Jilin | 900 | 9.3 | 59.8 | 19.0 | 11.9 | 900 | 7.3 | 75.2 | 13.1 | 4.3 | 1800 | 8.3 | 67.5 | 16.1 | 8.1 |
| Yunnan | 822 | 4.7 | 73.4 | 15.5 | 6.4 | 804 | 3.5 | 82.5 | 11.6 | 2.5 | 1626 | 4.1 | 77.9 | 13.5 | 4.5 |
| Items | Level | Boys | χ2 | p | Girls | χ2 | p | Total | χ2 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | ||||||||
| Latitude | 100.136 | 0.000 | 61.290 | 0.000 | 157.652 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Low | 6.6 | 15.5 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 2.6 | 6.2 | 12.1 | 4.9 | |||||||
| Middle | 5.2 | 17.6 | 8.8 | 4.4 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 4.8 | 14 | 5.9 | |||||||
| High | 6.9 | 19.9 | 12.2 | 5.7 | 13.4 | 3.9 | 6.3 | 16.7 | 8.1 | |||||||
| Altitude | 56.307 | 0.000 | 49.952 | 0.000 | 99.785 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Low | 6.4 | 17.4 | 8.9 | 5.7 | 10 | 3.2 | 6 | 13.7 | 6 | |||||||
| Medium | 5.1 | 18.7 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 13 | 3.1 | 4.4 | 15.9 | 7.1 | |||||||
| High | 5.7 | 13.8 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 8.7 | 1.8 | 5 | 11.2 | 3.8 | |||||||
| Items | Grade | Boys | χ2 | p | Girls | χ2 | p | Total | χ2 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | Thinness | Overweight | Obesity | ||||||||
| SES | 133.566 | 0.000 | 52.566 | 0.000 | 178.592 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Low | 8 | 11.2 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 1.9 | 6.5 | 9.1 | 3.7 | |||||||
| Middle | 6.5 | 16.4 | 8.5 | 4.8 | 9.8 | 3.4 | 5.6 | 13 | 5.9 | |||||||
| High | 5 | 19.8 | 10.3 | 5.6 | 12 | 3 | 5.3 | 16.1 | 6.8 | |||||||
| Degree of urbanization | 31.001 | 0.000 | 35.200 | 0.000 | 60.137 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Worst | 7.8 | 15.6 | 8 | 4.8 | 9 | 2.1 | 6.1 | 12 | 4.7 | |||||||
| Lower | 6.8 | 16.6 | 9.9 | 6.4 | 10.6 | 3.1 | 6.6 | 13.6 | 6.4 | |||||||
| Middle and upper | 6.9 | 16.8 | 8.4 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 3.4 | 6.5 | 13.4 | 6 | |||||||
| Best | 5.1 | 18 | 8.8 | 4.3 | 10.7 | 3 | 4.7 | 14.4 | 6 | |||||||
| GDP | 61.548 | 0.000 | 23.485 | 0.001 | 64.581 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Medium income | 9.6 | 11.2 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 2.7 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 4.1 | |||||||
| Middle and upper | 6 | 17 | 9.3 | 5.4 | 10.9 | 3.1 | 5.7 | 13.9 | 6.2 | |||||||
| High income | 5.3 | 19.2 | 8.7 | 4.7 | 9.9 | 2.9 | 5 | 14.6 | 5.8 | |||||||
| Engel coefficient | 68.703 | 0.000 | 36.859 | 0.000 | 78.199 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| Well-off | 9.3 | 11.1 | 5.5 | 4.8 | 6.5 | 2.5 | 7.1 | 8.8 | 4 | |||||||
| Rich | 5.4 | 17.4 | 9 | 5.7 | 10 | 2.7 | 5.6 | 13.7 | 5.9 | |||||||
| Richest | 6.2 | 18.1 | 9.4 | 4.7 | 11.4 | 3.5 | 5.4 | 14.8 | 6.4 | |||||||
| OR (95%CI) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Boys | 1.00 | ||
| Girls | 0.55 (0.52–0.60) | 0.000 | |
| Latitude | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 0.99 (0.87–1.12) | 0.837 | |
| High | 1.33 (1.15–1.54) | 0.000 | |
| Altitude | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 0.99 (0.88–1.12) | 0.853 | |
| High | 0.79 (0.66–0.95) | 0.012 | |
| SES | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 1.17 (1.03–1.34) | 0.020 | |
| High | 1.41 (1.24–1.61) | 0.000 | |
| Degree of urbanization | |||
| Worst | 1.00 | ||
| Lower | 0.98 (0.83–1.16) | 0.792 | |
| Middle and upper | 0.99 (0.83–1.18) | 0.879 | |
| Best | 1.12 (0.96–1.32) | 0.149 | |
| GDP | |||
| Medium income | 1.00 | ||
| Middle and upper | 1.50 (1.02–2.21) | 0.041 | |
| High income | 1.66 (1.11–2.47) | 0.013 | |
| Engel coefficient | |||
| Well-off | 1.00 | ||
| Rich | 0.91 (0.64–1.28) | 0.579 | |
| Richest | 1.00 (0.70–1.44) | 0.982 |
| OR (95%CI) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Boys | 1.00 | ||
| Girls | 0.31 (0.28–0.35) | 0.000 | |
| Latitude | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 0.98 (0.81–1.17) | 0.779 | |
| High | 1.52 (1.24–1.86) | 0.000 | |
| Altitude | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 0.85 (0.71–1.02) | 0.072 | |
| High | 0.60 (0.45–0.80) | 0.000 | |
| SES | |||
| Low | 1.00 | ||
| Middle | 1.13 (0.93–1.38) | 0.216 | |
| High | 1.18 (0.97–1.45) | 0.099 | |
| Degree of urbanization | |||
| Worst | 1.00 | ||
| Lower | 1.11 (0.86–1.43) | 0.425 | |
| Middle and upper | 1.01 (0.77–1.32) | 0.950 | |
| Best | 1.29 (1.01–1.65) | 0.038 | |
| GDP | |||
| Medium income | 1.00 | ||
| Middle and upper | 1.30 (0.71–2.37) | 0.392 | |
| High income | 1.30 (0.70–2.40) | 0.408 | |
| Engel coefficient | |||
| Well-off | 1.00 | ||
| Rich | 0.87 (0.50–1.50) | 0.614 | |
| Richest | 1.04 (0.59–1.82) | 0.906 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Pei, D.; Huang, T. Research on Environmental Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010035
Guo Y, Yin X, Sun Y, Zhang T, Li M, Zhang F, Liu Y, Xu J, Pei D, Huang T. Research on Environmental Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents in China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yaru, Xiaojian Yin, Yi Sun, Ting Zhang, Ming Li, Feng Zhang, Yuan Liu, Jianyi Xu, Dandan Pei, and Tianlong Huang. 2022. "Research on Environmental Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents in China" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010035
APA StyleGuo, Y., Yin, X., Sun, Y., Zhang, T., Li, M., Zhang, F., Liu, Y., Xu, J., Pei, D., & Huang, T. (2022). Research on Environmental Influencing Factors of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents in China. Nutrients, 14(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010035







